How community health screenings get more people of color vaccinated
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
U.S. preventive health screening rates dropped drastically at the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. They have yet to go back to pre-pandemic levels, especially for Black and Latine communities.
Screenings, or routine medical checkups, are important ways to avoid and treat disease. They’re key to finding problems early on and can even help save people’s lives.
Community health workers say screenings are also a key to getting more people vaccinated. Screening fairs provide health workers the chance to build rapport and trust with the communities they serve, while giving their clients the chance to ask questions and get personalized recommendations according to their age, gender, and family history.
But systemic barriers to health care can often keep people from marginalized communities from accessing recommended screenings, exacerbating racial health disparities.
Public Good News spoke with Dr. Marie-Jose Francois, president and chief executive officer, and April Johnson, outreach coordinator, at the Center for Multicultural Wellness and Prevention (CMWP), in Central Florida, to learn how they promote the benefits of screening and leverage screenings for vaccination outreach among their diverse communities.
Here’s what they said.
[Editor’s note: This content has been edited for clarity and length.]
PGN: What is CMWP’s mission? How does vaccine outreach fit into the work you do in the communities you serve?
Dr. Marie-Jose Francois: Since 1995, our mission has been to enhance the health, wellness, and quality of life for diverse populations in Central Florida. At the beginning, our main focus was education, wellness, and screening for HIV/AIDS, and we continue to do case management for HIV screening and testing.
When the issue of COVID-19 came into the picture, we included COVID-19 information and education and stressed the importance of screening and receiving vaccinations during all of our outreach activities.
We try to meet the community where they are. Because there is so much misconception—and taboo—in regard to immunization.
April Johnson: So our job is to disperse accurate information. And how we do that is we go into rural communities. We build partnerships with local apartment complexes, hair salons, nail salons, laundromats, and provide a little community engagement, where people just hang out in different areas.
We build gatekeepers in those communities because you first have to get in there. You have to know that they trust you. Being in this field for about 30 years, I’ve [learned that] flexibility is key. Because sometimes you can’t get them from 9 to 5, or [from] Monday through Friday. So, you have to be very flexible in doing the outreach portion in order to get what you need.
I’ve built collaborations with senior citizen centers, community centers, schools, clinics, churches in Orlando and [in] different areas in Orange, Osceola, Seminole, and Lake counties. And we also partner with other community-based organizations to try to make it like a one-stop shop. So, partnership is a big thing.
PGN: How do you promote the importance of preventive screenings in the communities you serve?
M.F.: We try to make them view their health in a more comprehensive way, for them to understand the importance of screening. [That] self care is key, and for them to not be afraid.
We empower them to know what to ask when they go to the doctor. We ask them, ‘Do you know your status? Do you know your numbers?’
For example, if you go to the doctor, do you know your blood pressure? If you’re diabetic? Do you know your hemoglobin (A1C)? Do you know your cholesterol levels?
And now, [we also ask them]: ‘Have you received your flu shot for the year? Have you received all of your vaccine doses for COVID-19?’ We are even adding the mpox vaccine now, based on risk factors.
[We recommend they] ask their provider. For women, [we ask], ‘When do you need to have your mammogram?’ For the men, ‘You need to ask about your PSA and also about when and when to have your colonoscopy based on your age.’
We also try to explain to the community that the more they know their family history, the more they can engage in their own health. Because sometimes you have mom and dad who have a history of cancer. They have a history of diabetes or blood pressure—and they don’t talk to their children. So, we try to [recommend they] talk to their children. Your own family needs to know what’s going on so they can be proactive in their screenings.
PGN: What strategies or methods have you found most effective in getting people screened?
M.F.: Not everybody wants to be screened, not everybody wants to receive vaccines.
But with patience, just give them the facts. It goes right back to education, people have to be assured.
When you talk to them about COVID, or even HIV, you may hear them say, ‘Oh, I don’t see myself at risk for HIV.’ But we have to repeat to them that the more they get screened to make sure they’re OK, the better it is for them. ‘The more you use condoms, [the] safer it is for you.’
In Haitian culture, they listen to the radio. So we use the radio as a tool to educate and deliver information [to] get vaccinated, wash your hands. ‘If you’re coughing, cover your mouth. If you have a fever, wear your masks. Call your doctor.’
In our target population, we have people who have chronic conditions. We have people with HIV. So, we have to motivate them to receive the flu vaccine, to receive the COVID vaccine, to receive that RSV [vaccine], or to get the mpox vaccine. We have people with diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, depressed immune systems. We have people with lupus, we have people with sickle cell disease.
So, this is a way to [ensure that] whomever you’re talking to one-on-one understands the value of being safe.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Artichoke vs Asparagus – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing artichoke to asparagus, we picked the artichoke.
Why?
Both are great and it was close!
In terms of macros, artichoke has a little more protein and around 3x the carbs and fiber: the ratio there means that both vegetables have an identical glycemic index, so we’ll go with the “most food per food” reckoning of nutritional density, and call it for the artichoke.
When it comes to vitamins, artichoke has more of vitamins B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, and choline, while asparagus has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, E, and K. Both very respectable nutritional sets, but artichoke gets a marginal 6:5 win on strength of numbers.
In the category of minerals, artichoke has more calcium, copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium, while asparagus has more iron, selenium, and zinc. A clearer 6:3 win for artichoke this time.
Once again, both of these are great foods, so by all means enjoy either or both. But if you’re looking for the nutritionally densest option, it’s the artichoke!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Why do I poo in the morning? A gut expert explains
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
No, you’re not imagining it. People really are more likely to poo in the morning, shortly after breakfast. Researchers have actually studied this.
But why mornings? What if you tend to poo later in the day? And is it worth training yourself to be a morning pooper?
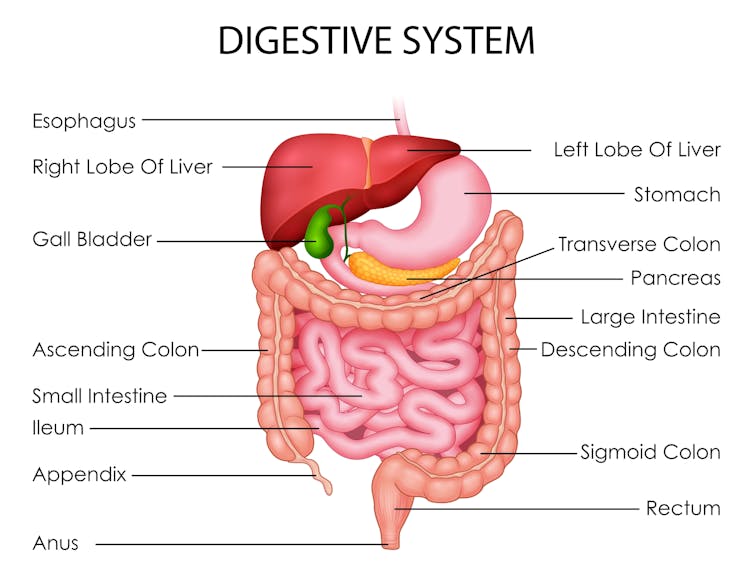
To understand what makes us poo when we do, we need to consider a range of factors including our body clock, gut muscles and what we have for breakfast.
Here’s what the science says.
H_Ko/Shutterstock So morning poos are real?
In a UK study from the early 1990s, researchers asked nearly 2,000 men and women in Bristol about their bowel habits.
The most common time to poo was in the early morning. The peak time was 7-8am for men and about an hour later for women. The researchers speculated that the earlier time for men was because they woke up earlier for work.
About a decade later, a Chinese study found a similar pattern. Some 77% of the almost 2,500 participants said they did a poo in the morning.
But why the morning?
There are a few reasons. The first involves our circadian rhythm – our 24-hour internal clock that helps regulate bodily processes, such as digestion.
For healthy people, our internal clock means the muscular contractions in our colon follow a distinct rhythm.
There’s minimal activity in the night. The deeper and more restful our sleep, the fewer of these muscle contractions we have. It’s one reason why we don’t tend to poo in our sleep.
Your lower gut is a muscular tube that contracts more strongly at certain times of day. Vectomart/Shutterstock But there’s increasing activity during the day. Contractions in our colon are most active in the morning after waking up and after any meal.
One particular type of colon contraction partly controlled by our internal clock are known as “mass movements”. These are powerful contractions that push poo down to the rectum to prepare for the poo to be expelled from the body, but don’t always result in a bowel movement. In healthy people, these contractions occur a few times a day. They are more frequent in the morning than in the evening, and after meals.
Breakfast is also a trigger for us to poo. When we eat and drink our stomach stretches, which triggers the “gastrocolic reflex”. This reflex stimulates the colon to forcefully contract and can lead you to push existing poo in the colon out of the body. We know the gastrocolic reflex is strongest in the morning. So that explains why breakfast can be such a powerful trigger for a bowel motion.
Then there’s our morning coffee. This is a very powerful stimulant of contractions in the sigmoid colon (the last part of the colon before the rectum) and of the rectum itself. This leads to a bowel motion.
How important are morning poos?
Large international surveys show the vast majority of people will poo between three times a day and three times a week.
This still leaves a lot of people who don’t have regular bowel habits, are regular but poo at different frequencies, or who don’t always poo in the morning.
So if you’re healthy, it’s much more important that your bowel habits are comfortable and regular for you. Bowel motions do not have to occur once a day in the morning.
Morning poos are also not a good thing for everyone. Some people with irritable bowel syndrome feel the urgent need to poo in the morning – often several times after getting up, during and after breakfast. This can be quite distressing. It appears this early-morning rush to poo is due to overstimulation of colon contractions in the morning.
Can you train yourself to be regular?
Yes, for example, to help treat constipation using the gastrocolic reflex. Children and elderly people with constipation can use the toilet immediately after eating breakfast to relieve symptoms. And for adults with constipation, drinking coffee regularly can help stimulate the gut, particularly in the morning.
A disturbed circadian rhythm can also lead to irregular bowel motions and people more likely to poo in the evenings. So better sleep habits can not only help people get a better night’s sleep, it can help them get into a more regular bowel routine.
A regular morning coffee can help relieve constipation. Caterina Trimarchi/Shutterstock Regular physical activity and avoiding sitting down a lot are also important in stimulating bowel movements, particularly in people with constipation.
We know stress can contribute to irregular bowel habits. So minimising stress and focusing on relaxation can help bowel habits become more regular.
Fibre from fruits and vegetables also helps make bowel motions more regular.
Finally, ensuring adequate hydration helps minimise the chance of developing constipation, and helps make bowel motions more regular.
Monitoring your bowel habits
Most of us consider pooing in the morning to be regular. But there’s a wide variation in normal so don’t be concerned if your poos don’t follow this pattern. It’s more important your poos are comfortable and regular for you.
If there’s a major change in the regularity of your bowel habits that’s concerning you, see your GP. The reason might be as simple as a change in diet or starting a new medication.
But sometimes this can signify an important change in the health of your gut. So your GP may need to arrange further investigations, which could include blood tests or imaging.
Vincent Ho, Associate Professor and clinical academic gastroenterologist, Western Sydney University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
The Best Exercise to Stop Your Legs From Giving Out
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Doug Weiss, seniors-specialist physio, has an exercise that stops your knees from being tricked into collapsing (which is very common) by a misfiring (also common) reflex.
Step up…
Setup to step up thus:
- Use a sturdy support like a countertop or chair.
- Have an aerobic step or similar firm surface to step onto.
When you’re ready:
- Stand facing away from the step.
- Place one hand on the support for stability.
- Step backwards up onto the step with your right leg, then your left leg, so both feet are on the step.
- Step forward to come back down.
Once you’re confident of the series of movements, do it without the support, and do it for a few minutes each day. Don’t worry about how easy it becomes; this is not, first and foremost, a strength-training exercise; you don’t have to start adding weights or anything (although of course you can if you want).
How it works: there’s a part of you called the Golgi tendon organ, and it can trigger a Golgi tendon reflex, which is one of the body’s equivalents of a steam valve. However, instead of letting off steam to avoid a boiler explosion, it collapses a joint to save it from overload. However, if not exercised regularly, it can get overly sensitive, causing it to mistake your mere bodyweight for an overload. So, it collapses, thinking it is saving you from snapping a tendon, but it’s not. By exercising in the way described, the Golgi tendon reflex will go back to only being triggered by an actual overload, not the mere act of stepping.
Writer’s note: this one’s interesting to me as I have a) a strong lower body b) hypermobile joints that thus occasionally just fold like laundry regardless. Could it be that this will fix that? I guess I’ll find out 🙂
Meanwhile, for more on all of the above plus a visual demonstration, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
What Nobody Teaches You About Strengthening Your Knees
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How Healers Heal – by Dr. Shilpi Pradhan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First note: the listed author here is in fact the compiler, with the authors being a collection of no fewer than 33 board-certified lifestyle medicine physicians. So, we’re not getting just a single person’s opinions/bias here!
But what is lifestyle medicine? This book holds the six pillars of lifestyle medicine to be:
- Nutrition
- Physical activity
- Stress management
- Restorative sleep
- Social connections
- Avoidance of risky substances
…and those things are what we read about throughout the book, both in highly educational mini-lecture form, and sometimes highly personal storytelling.
It’s not just a “do these things” book, though yes, there’s a large part of that. It also covers wide topics, from COVID to alopecia, burnout to grief, immune disorders to mysterious chest pains (and how such mysteries are unravelled, when taken seriously).
One of the greatest strengths of this book is that it’s very much “medicine, as it should be”, so that the reader knows how to recognize the difference.
Bottom line: this book doesn’t fit into a very neat category, but it’s a very worthwhile book to read, and one that could help inform a decision that changes the entire path of your life or that of a loved one.
Click here to check out How Healers Heal, and learn to recognize the healthcare you deserve!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Older adults need another COVID-19 vaccine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- The CDC recommends people 65 and older and immunocompromised people receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring—if at least four months have passed since they received a COVID-19 vaccine.
- Updated COVID-19 vaccines are effective at protecting against severe illness, hospitalization, death, and long COVID.
- The CDC also shortened the isolation period for people who are sick with COVID-19.
Last week, the CDC said people 65 and older should receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring. The recommendation also applies to immunocompromised people, who were already eligible for an additional dose.
Older adults made up two-thirds of COVID-19-related hospitalizations between October 2023 and January 2024, so enhancing protection for this group is critical.
The CDC also shortened the isolation period for people who are sick with COVID-19, although the contagiousness of COVID-19 has not changed.
Read on to learn more about the CDC’s updated vaccination and isolation recommendations.
Who is eligible for another COVID-19 vaccine this spring?
The CDC recommends that people ages 65 and older and immunocompromised people receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring—if at least four months have passed since they received a COVID-19 vaccine. It’s safe to receive an updated COVID-19 vaccine from Pfizer, Moderna, or Novavax, regardless of which COVID-19 vaccines you received in the past.
Updated COVID-19 vaccines are available at pharmacies, local clinics, or doctor’s offices. Visit Vaccines.gov to find an appointment near you.
Under- and uninsured adults can get the updated COVID-19 vaccine for free through the CDC’s Bridge Access Program. If you’re over 60 and unable to leave your home, call the Aging Network at 1-800-677-1116 to learn about free at-home vaccination options.
What are the benefits of staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines?
Staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines prevents severe illness, hospitalization, death, and long COVID.
Additionally, the CDC says staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines is a safer and more reliable way to build protection against COVID-19 than getting sick from COVID-19.
What are the new COVID-19 isolation guidelines?
According to the CDC’s general respiratory virus guidance, people who are sick with COVID-19 or another common respiratory illness, like the flu or RSV, should isolate until they’ve been fever-free for at least 24 hours without the use of fever-reducing medication and their symptoms improve.
After that, the CDC recommends taking additional precautions for the next five days: wearing a well-fitting mask, limiting close contact with others, and improving ventilation in your home if you live with others.
If you’re sick with COVID-19, you can infect others for five to 12 days, or longer. Moderately or severely immunocompromised patients may remain infectious beyond 20 days.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Foods For Managing Hypothyroidism (incl. Hashimoto’s)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Foods for Managing Hypothyroidism
For any unfamiliar, hypothyroidism is the condition of having an underactive thyroid gland. The thyroid gland lives at the base of the front of your neck, and, as the name suggests, it makes and stores thyroid hormones. Those are important for many systems in the body, and a shortage typically causes fatigue, weight gain, and other symptoms.
What causes it?
This makes a difference in some cases to how it can be treated/managed. Causes include:
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune condition
- Severe inflammation (end result is similar to the above, but more treatable)
- Dietary deficiencies, especially iodine deficiency
- Secondary endocrine issues, e.g. pituitary gland didn’t make enough TSH for the thyroid gland to do its thing
- Some medications (ask your pharmacist)
We can’t do a lot about those last two by leveraging diet alone, but we can make a big difference to the others.
What to eat (and what to avoid)
There is nuance here, which we’ll go into a bit, but let’s start by giving the
one-linetwo-line summary that tends to be the dietary advice for most things:- Eat a nutrient-dense whole-foods diet (shocking, we know)
- Avoid sugar, alcohol, flour, processed foods (ditto)
What’s the deal with meat and dairy?
- Meat: avoid red and processed meats; poultry and fish are fine or even good (unless fried; don’t do that)
- Dairy: limit/avoid milk; but unsweetened yogurt and cheese are fine or even good
What’s the deal with plants?
First, get plenty of fiber, because that’s important to ease almost any inflammation-related condition, and for general good health for most people (an exception is if you have Crohn’s Disease, for example).
If you have Hashimoto’s, then gluten (as found in wheat, barley, and rye) may be an issue, but the jury is still out, science-wise. Here’s an example study for “avoid gluten” and “don’t worry about gluten”, respectively:
- The Effect of Gluten-Free Diet on Thyroid Autoimmunity in Women with Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
- Doubtful Justification of the Gluten-Free Diet in the Course of Hashimoto’s Disease
So, you might want to skip it, to be on the safe side, but that’s up to you (and the advice of your nutritionist/doctor, as applicable).
A word on goitrogens…
Goitrogens are found in cruciferous vegetables and soy, both of which are very healthy foods for most people, but need some extra awareness in the case of hypothyroidism. This means there’s no need to abstain completely, but:
- Keep serving sizes small, for example a 100g serving only
- Cook goitrogenic foods before eating them, to greatly reduce goitrogenic activity
For more details, reading even just the abstract (intro summary) of this paper will help you get healthy cruciferous veg content without having a goitrogenic effect.
(as for soy, consider just skipping that if you suffer from hypothyroidism)
What nutrients to focus on getting?
- Top tier nutrients: iodine, selenium, zinc
- Also important: vitamin B12, vitamin D, magnesium, iron
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: