Break the Cycle – by Dr. Mariel Buqué
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Intergenerational trauma comes in two main varieties: epigenetic, and behavioral.
This book covers both. There’s a lot more we can do about the behavioral side than the epigenetic, but that’s not to say that Dr. Buqué doesn’t have useful input in the latter kind too.
If you’ve read other books on epigenetic trauma, then there’s nothing new here—though the refresher is always welcome.
On the behavioral side, Dr. Buqué gives a strong focus on practical techniques, such as specific methods of journaling to isolate trauma-generated beliefs and resultant behaviors, with a view to creating one’s own trauma-informed care, cutting through the cycle, and stopping it there.
Which, of course, will not only be better for you, but also for anyone who will be affected by how you are (e.g. now/soon, hopefully better).
As a bonus, if you see the mistakes your parents made and are pretty sure you didn’t pass them on, this book can help you troubleshoot for things you missed, and also to improve your relationship with your own childhood.
Bottom line: if you lament how things were, and do wish/hope to do better in terms of mental health for yourself now and generations down the line, this book is a great starting point.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Less Common Oral Hygiene Options
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Less Common Alternatives For Oral Hygiene!
You almost certainly brush your teeth. You might use mouthwash. A lot of people floss for three weeks at a time, often in January.
There are a lot of options for oral hygiene; variations of the above, and many alternatives too. This is a big topic, so rather than try to squeeze it all in one, this will be a several-part series.
- The first part was: Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
- The second part was: Flossing, Better (And Easier!)
- The third (and for now at least, final) part will look at some less common alternatives.
Tooth soap
The idea here is simplicity, and brushing with as few ingredients as possible. Soap cleans your teeth the same way it cleans your (sometimes compositionally quite similar—enamel and all) dishes, without damaging them.
We’d love to link to some science here, but alas, it appears to have not yet been done—at least, we couldn’t find any!
You can make your own tooth soap if you are feeling confident, or you might prefer to buy one ready-made (here’s an example product on Amazon, with various flavor options)
Oil pulling
We are getting gradually more scientific now; there is science for this one… But the (scientific) reviews are mixed:
Wooley et al., 2020, conducted a review of extant studies, and concluded:
❝The limited evidence suggests that oil pulling with coconut oil may have a beneficial effect on improving oral health and dental hygiene❞
The “Science-Based Medicine” project was less positive in its assessment, and declared that all and any studies that found oil pulling to be effective were a matter of researcher/publication bias. We would note that SBM is a private project and is not without its own biases, but for balance, here is what they had to offer:
A more rounded view seems to be that it is a good method for cleaning your teeth if you don’t have better options available (whereby, “better options” is “almost any other method”).
One final consideration, which the above seemed not to consider, is:
If you have sensitive teeth/gums, oil-pulling is the gentlest way of cleaning them, and getting them back into sufficient order that you can comfortably use other methods.
Want to try it? You can use any food-grade oil (coconut oil or olive oil are common choices).
Chewing stick
Not just any stick—a twig of the Salvadora persica tree. This time, there’s lots of science for it, and it’s uncontroversially effective:
❝A number of scientific studies have demonstrated that the miswak (Salvadora persica) possesses antibacterial, anti-fungal, anti-viral, anti-cariogenic, and anti-plaque properties.
Several studies have also claimed that miswak has anti-oxidant, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory effects. The use of a miswak has an immediate effect on the composition of saliva.
Several clinical studies have confirmed that the mechanical and chemical cleansing efficacy of miswak chewing sticks are equal and at times greater than that of the toothbrush❞
Read in full: A review of the therapeutic effects of using miswak (Salvadora Persica) on oral health
And about the efficacy vs using a toothbrush, here’s an example:
Comparative effect of chewing sticks and toothbrushing on plaque removal and gingival health
Want to try the miswak stick? Here’s an example product on Amazon.
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Frozen/Thawed/Refrozen Meat: How Much Is Safety, And How Much Is Taste?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What You Can (And Can’t) Safely Do With Frozen Meat
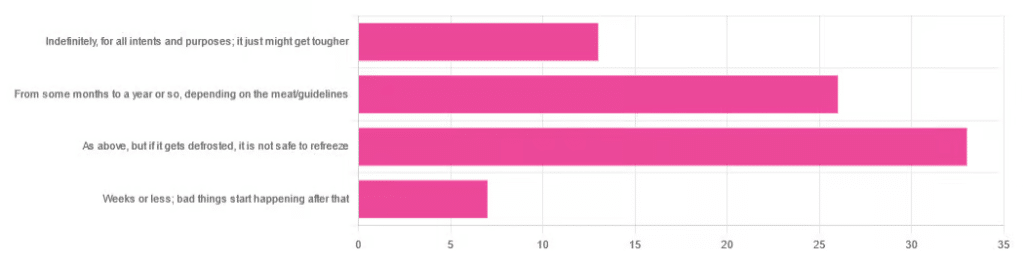
Yesterday, we asked you:
❝You have meat in the freezer. How long is it really safe to keep it?❞
…and got a range of answers, mostly indicating to a) follow the instructions (a very safe general policy) and b) do not refreeze if thawed because that would be unsafe. Fewer respondents indicated that meat could be kept for much longer than guidelines say, or conversely, that it should only be kept for weeks or less.
So, what does the science say?
Meat can be kept indefinitely (for all intents and purposes) in a freezer; it just might get tougher: True or False?
False, assuming we are talking about a normal household electrical freezer that bottoms out at about -18℃ / 0℉.
Fun fact: cryobiologists cryopreserve tissue samples (so basically, meat) at -196℃ / -320℉, and down at those temperatures, the tissues will last a lot longer than you will (and, for all practical purposes: indefinitely). There are other complications with doing so (such as getting the sample through the glass transition point without cracking it during the vitrification process) but those are beyond the scope of this article.
If you remember back to your physics or perhaps chemistry classes at school, you’ll know that molecules move more quickly at higher temperatures, and more slowly at lower ones, only approaching true stillness as they near absolute zero (-273℃ / -459℉ / 0K ← we’re not saying it’s ok, although it is; rather, that is zero kelvin; no degree sign is used with kelvins)
That means that when food is frozen, the internal processes aren’t truly paused; it’s just slowed to a point of near imperceptibility.
So, all the way up at the relatively warm temperatures of a household freezer, a lot of processes are still going on.
What this means in practical terms: those guidelines saying “keep in the freezer for up to 4 months”, “keep in the freezer for up to 9 months”, “keep in the freezer for up to 12 months” etc are being honest with you.
More or less, anyway! They’ll usually underestimate a little to be on the safe side—but so should you.
Bad things start happening within weeks at most: True or False?
False, for all practical purposes. Again, assuming a normal and properly-working household freezer as described above.
(True, technically but misleadingly: the bad things never stopped; they just slowed down to a near imperceptible pace—again, as described above)
By “bad” here we should clarify we mean “dangerous”. One subscriber wrote:
❝Meat starts losing color and flavor after being in the freezer for too long. I keep meat in the freezer for about 2 months at the most❞
…and as a matter of taste, that’s fair enough!
It is unsafe to refreeze meat that has been thawed: True or False?
False! Assuming it has otherwise been kept chilled, just the same as for fresh meat.
Food poisoning comes from bacteria, and there is nothing about the meat previously having been frozen that will make it now have more bacteria.
That means, for example…
- if it was thawed (but chilled) for a period of time, treat it like you would any other meat that has been chilled for that period of time (so probably: use it or freeze it, unless it’s been more than a few days)
- if it was thawed (and at room temperature) for a period of time, treat it like you would any other meat that has been at room temperature for that period of time (so probably: throw it out, unless the period of time is very small indeed)
The USDA gives for 2 hours max at room temperature before considering it unsalvageable, by the way.
However! Whenever you freeze meat (or almost anything with cells, really), ice crystals will form in and between cells. How much ice crystallization occurs depends on several variables, with how much water there is present in the food is usually the biggest factor (remember that animal cells are—just like us—mostly water).
Those ice crystals will damage the cell walls, causing the food to lose structural integrity. When you thaw it out, the ice crystals will disappear but the damage will be left behind (this is what “freezer burn” is).
So if your food seems a little “squishy” after having been frozen and thawed, that’s why. It’s not rotten; it’s just been stabbed countless times on a microscopic level.
The more times you freeze and thaw and refreeze food, the more this will happen. Your food will degrade in structural integrity each time, but the safety of it won’t have changed meaningfully.
Want to know more?
Further reading:
You can thaw and refreeze meat: five food safety myths busted
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Retrain Your Brain – by Dr. Seth Gillihan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
15-Minute Arabic”, “Sharpen Your Chess Tactics in 24 Hours”, “Change Your Life in 7 Days”, “Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in 7 weeks”—all real books from this reviewer’s shelves.
The thing with books with these sorts of time periods in the titles is that the time period in the title often bears little relation to how long it takes to get through the book. So what’s the case here?
You’ll probably get through it in more like 7 days, but the pacing is more important than the pace. By that we mean:
Dr. Gillihan starts by assuming the reader is at best “in a rut”, and needs to first pick a direction to head in (the first “week”) and then start getting one’s life on track (the second “week”).
He then gives us, one by one, an array of tools and power-ups to do increasingly better. These tools aren’t just CBT, though of course that features prominently. There’s also mindfulness exercises, and holistic / somatic therapy too, for a real “bringing it all together” feel.
And that’s where this book excels—at no point is the reader left adrift with potential stumbling-blocks left unexamined. It’s a “whole course”.
Bottom line: whether it takes you 7 hours or 7 months, “Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in 7 Weeks” is a CBT-and-more course for people who like courses to work through. It’ll get you where you’re going… Wherever you want that to be for you!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
15 Easy Japanese Habits That Will Transform Your Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The original title says “no-cost habits”, but in fairness, for most of us food is not usually free (alas). So, we will say “easy” instead, because they are indeed easy to build into your life:
15 Healthy Habits To Adopt
We’ll not keep them a mystery; they are:
- Intermittent fasting: naturally fasting for at least 12 hours overnight improves digestion and sleep quality.
- Fermented foods: regularly consuming fermented foods (like kimchi, or even just sauces like miso and shio koji) supports gut health.
- Rice & legumes over wheat: choosing wholegrain rice as a staple reduces bloating and benefits skin health (lentils are even better).
- Big breakfast, light dinner: eating a heavier breakfast and a lighter dinner gives energy in the morning and allows digestion to rest at night.
- Balancing indulgences: enjoying social meals without guilt and balancing food intake the next day.
- Daily gentle exercise: doing at least 15 minutes of yoga, Pilates, or light walking for long-term health.
- Daily baths: taking a warm bath boosts blood circulation and relaxation.
- Eating seasonal & diverse foods: including a variety of fresh, seasonal ingredients for balanced nutrition.
- Consistent morning routine: waking up at the same time, cleansing and moisturizing, and having a proper breakfast.
- Enjoying soup with meals: consuming nutrient-rich soups with vegetables and protein to prevent overeating.
- Chewing food thoroughly: eating slowly and chewing well aids digestion and enhances enjoyment.
- Light seasoning in food: avoiding overly salty or flavorful meals to appreciate natural tastes.
- Maintaining good posture: paying attention to posture during daily activities for better overall health.
- Prioritizing protein intake: eating protein-rich foods like tofu, beans, eggs, and fish, to maintain skin firmness as well as muscletone.
- Confidence in aging: focusing on internal well-being over external opinions and embracing health at every age.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What’s the difference between burnout and depression?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If your summer holiday already feels like a distant memory, you’re not alone. Burnout – a state of emotional, physical and mental exhaustion following prolonged stress – has been described in workplaces since a 5th century monastery in Egypt.
Burnout and depression can look similar and are relatively common conditions. It’s estimated that 30% of the Australian workforce is feeling some level of burnout, while almost 20% of Australians are diagnosed with depression at some point in their lives.
So what’s the difference between burnout and depression?
Burnout is marked by helplessness and depression by hopelessness. They can have different causes and should also be managed differently.
Yuri A/Shutterstock What is burnout?
The World Health Organization defines burnout as an “occupational phenomenon” resulting from excessively demanding workload pressures. While it is typically associated with the workplace, carers of children or elderly parents with demanding needs are also at risk.
Our research created a set of burnout symptoms we captured in the Sydney Burnout Measure to assist self-diagnosis and clinicians undertaking assessments. They include:
- exhaustion as the primary symptom
- brain fog (poor concentration and memory)
- difficulty finding pleasure in anything
- social withdrawal
- an unsettled mood (feeling anxious and irritable)
- impaired work performance (this may be result of other symptoms such as fatigue).
People can develop a “burning out” phase after intense work demands over only a week or two. A “burnout” stage usually follows years of unrelenting work pressure.
What is depression?
A depressive episode involves a drop in self-worth, increase in self-criticism and feelings of wanting to give up. Not everyone with these symptoms will have clinical depression, which requires a diagnosis and has an additional set of symptoms.
Clinically diagnosed depression can vary by mood, how long it lasts and whether it comes back. There are two types of clinical depression:
- melancholic depression has genetic causes, with episodes largely coming “out of the blue”
- non-melancholic depression is caused by environmental factors, often triggered by significant life events which cause a drop in self-worth.
When we created our burnout measure, we compared burnout symptoms with these two types of depression.
Burnout shares some features with melancholic depression, but they tend to be general symptoms, such as feeling a loss of pleasure, energy and concentration skills.
We found there were more similarities between burnout and non-melancholic (environmental) depression. This included a lack of motivation and difficulties sleeping or being cheered up, perhaps reflecting the fact both have environmental causes.
Looking for the root cause
The differences between burnout and depression become clearer when we look at why they happen.
Personality comes into play. Our work suggests a trait like perfectionism puts people at a much higher risk of burnout. But they may be less likely to become depressed as they tend to avoid stressful events and keep things under control.
Excessive workloads can contribute to burnout. tartanparty/Shutterstock Those with burnout generally feel overwhelmed by demands or deadlines they can’t meet, creating a sense of helplessness.
On the other hand, those with depression report lowered self-esteem. So rather than helpless they feel that they and their future is hopeless.
However it is not uncommon for someone to experience both burnout and depression at once. For example, a boss may place excessive work demands on an employee, putting them at risk of burnout. At the same time, the employer may also humiliate that employee and contribute to an episode of non-melancholic depression.
What can you do?
A principal strategy in managing burnout is identifying the contributing stressors. For many people, this is the workplace. Taking a break, even a short one, or scheduling some time off can help.
Australians now have the right to disconnect, meaning they don’t have to answer work phone calls or emails after hours. Setting boundaries can help separate home and work life.
Burnout can be also be caused by compromised work roles, work insecurity or inequity. More broadly, a dictatorial organisational structure can make employees feel devalued. In the workplace, environmental factors, such as excessive noise, can be a contributor. Addressing these factors can help prevent burnout.
As for managing symptoms, the monks had the right idea. Strenuous exercise, meditation and mindfulness are effective ways to deal with everyday stress.
Regular exercise can help manage symptoms of burnout. alexei_tm/Shutterstock Deeper contributing factors, including traits such as perfectionism, should be managed by a skilled clinical psychologist.
For melancholic depression, clinicians will often recommend antidepressant medication.
For non-melancholic depression, clinicians will help address and manage triggers that are the root cause. Others will benefit from antidepressants or formal psychotherapy.
While misdiagnosis between depression and burnout can occur, burnout can mimic other medical conditions such as anemia or hypothyroidism.
For the right diagnosis, it’s best to speak to your doctor or clinician who should seek to obtain a sense of “the whole picture”. Only then, once a burnout diagnosis has been affirmed and other possible causes ruled out, should effective support strategies be put in place.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14.
Correction: This article originally stated that depression is marked by helplessness and burnout by hopelessness, when in fact it is vice versa. This has been amended.
Gordon Parker, Scientia Professor of Psychiatry, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Radishes vs Carrots – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing radishes to carrots, we picked the carrots.
Why?
In terms of macros, carrots have more fiber and carbs; the two root vegetables both have comparable (low) glycemic indices, so we’re saying that the one with more fiber wins, and that’s carrots.
In the category of vitamins, radishes have more of vitamins B9 and C, while carrots have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, E, K, and choline. An easy win for carrots.
When it comes to minerals, radishes have more selenium, while carrots have more calcium, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium. Another clear win for carrots.
In terms of polyphenols, radishes do have some, but carrots have more, and thus win this category too.
All in all, enjoy either or both, but carrots deliver the most nutrients by far!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What Do The Different Kinds Of Fiber Do? 30 Foods That Rank Highest
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: