Beat Osteoporosis with Exercise – by Dr. Karl Knopf
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are a lot of books about beating osteoporosis, and yet when it comes to osteoporosis exercises, it took us some work to find a good one. But, this one’s it!
A lot of books give general principles and a few sample exercises. This one, in contrast, gives:
- An overview of osteopenia and osteoporosis, first
- A brief overview of non-exercise osteoporosis considerations
- Principles for exercising a) to reduce one’s risk of osteoporosis b) if one has osteoporosis
- Clear explanations of about 150 exercises that fit both categories
This last item’s important, because a lot of popular advice is exercises that are only good for one or the other (given that a lot of things that strengthen a healthy person’s bones can break the bones of someone with osteoporosis), so having 150 exercises that are safe and effective in both cases, is a real boon.
That doesn’t mean you have to do all 150! If you want to, great. But even just picking and choosing and putting together a little program is good.
Bottom line: if you’d like a comprehensive guide to exercise to keep you strong in the face of osteoporosis, this is a great one.
Click here to check out Beat Osteoporosis With Exercise, and stay strong!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Eat To Beat Cancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Controlling What We Can, To Avoid Cancer
Every time a cell in our body is replaced, there’s a chance it will be cancerous. Exactly what that chance is depends on very many factors. Some of them we can’t control; others, we can.
Diet is a critical, modifiable factor
We can’t choose, for example, our genes. We can, for the most part, choose our diet. Why “for the most part”?
- Some people live in a food desert (the Arctic Circle is a good example where food choices are limited by supply)
- Some people have dietary restrictions (whether by health condition e.g. allergy, intolerance, etc or by personal-but-unwavering choice, e.g. vegetarian, vegan, kosher, halal, etc)
But for most of us, most of the time, we have a good control over our diet, and so that’s an area we can and should focus on.
Choose your animal protein wisely
If you are vegan, you can skip this section. If you are not, then the short version is:
- Fish: almost certainly fine
- Poultry: the jury is out; data is leaning towards fine, though
- Red meat: significantly increased cancer risk
- Processed meat: significantly increased cancer risk
For more details (and a run-down on the science behind the above super-summarized version):
- Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy? ← A mythbuster article that outlines many health properties (good and bad) of animal products
- The Whys and Hows of Cutting Meats Out Of Your Diet ← A life-hack article about acting on that information
Skip The Ultra-Processed Foods
Ok, so this one’s probably not a shocker in its simplest form:
❝Studies are showing us is that not only do the ultraprocessed foods increase the risk of cancer, but that after a cancer diagnosis such foods increase the risk of dying❞
Source: Is there a connection between ultraprocessed food and cancer?
There’s an unfortunate implication here! If you took the previous advice to heart and cut out [at least some] meat, and/but then replaced that with ultra-processed synthetic meat, then this was not a great improvement in cancer risk terms.
Ultra-processed meat is worse than unprocessed, regardless of whether it was from an animal or was synthetic.
In other words: if you buy textured soy pieces (a common synthetic meat), it pays to look at the ingredients, because there’s a difference between:
- INGREDIENTS: SOY
- INGREDIENTS: Rehydrated Textured SOY Protein (52%), Water, Rapeseed Oil, SOY Protein Concentrate, Seasoning (SULPHITES) (Dextrose, Flavourings, Salt, Onion Powder, Food Starch Modified, Yeast Extract, Colour: Red Iron Oxide), SOY Leghemoglobin, Fortified WHEAT Flour (WHEAT Flour, Calcium Carbonate, Iron, Niacin, Thiamin), Bamboo Fibre, Methylcellulose, Tomato Purée, Salt, Raising Agent: Ammonium Carbonates
Now, most of those original base ingredients are/were harmless per se (as are/were the grapes in wine—before processing into alcohol), but it has clearly been processed to Hell and back to do all that.
Choose the one that just says “soy”. Or eat soybeans. Or other beans. Or lentils. Really there are a lot of options.
About soy, by the way…
There is (mostly in the US, mostly funded by the animal agriculture industry) a lot of fearmongering about soy. Which is ironic, given the amount of soy that is fed to livestock to be fed to humans, but it does bear addressing:
❝Soy foods are safe for all cancer patients and are an excellent source of plant protein. Studies show soy may improve survival after breast cancer❞
Source: Food risks and cancer: What to avoid
(obviously, if you have a soy allergy then you should not consume soy—for most people, the above advice stands, though)
Advanced Glycation End-Products
These (which are Very Bad™ for very many things, including cancer) occur specifically as a result of processing animal proteins and fats.
Note: not even necessarily ultra-processing, just processing can do it. But ultra-processing is worse. What’s the difference, you wonder?
The difference between “ultra-processed” and just “processed”:
- Your average hotdog has been ultra-processed. It’s not only usually been changed with many artificial additives, it’s also been through a series of processes (physical and chemical) and ends up bearing little relation to the creature it came from.
- Your bacon (that you bought fresh from your local butcher, not a supermarket brand of unknown provenance, and definitely not the kind that might come on the top of frozen supermarket pizza) has been processed. It’s undergone a couple of simple processes on its journey “from farm to table”. Remember also that when you cook it, that too is one more process (and one that results in a lot of AGEs).
Read more: What’s so bad about AGEs?
Note if you really don’t want to cut out certain foods, changing the way you cook them (i.e., the last process your food undergoes before you eat it) can also reduce AGES:
Advanced Glycation End Products in Foods and a Practical Guide to Their Reduction in the Diet
Get More Fiber
❝The American Institute for Cancer Research shows that for every 10-gram increase in fiber in the diet, you improve survival after cancer diagnosis by 13%❞
Source: Plant-based diet is encouraged for patients with cancer
Yes, that’s post-diagnosis, but as a general rule of thumb, what is good/bad for cancer when you have it is good/bad for cancer beforehand, too.
If you’re thinking that increasing your fiber intake means having to add bran to everything, happily there are better ways:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Enjoy!
Share This Post

Heart Healthy Diet Plan – by Stephen William
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve covered heart-healthy cooking books before, but variety is good, and boredom is an enemy of health, so let’s shake it up with a fresh stack of recipes!
After a brief overview of the relevant science (which if you’re a regular 10almonds reader, probably won’t be new to you), the author takes the reader on a 28-day journey. Yes, we know the subtitle says 30 days, but unless they carefully hid the other two days somewhere we didn’t find, there are “only” 28 inside. Perhaps the publisher heard it was a month and took creative license. Or maybe there’s a different edition. Either way…
Rather than merely giving a diet plan (though yes, he also does that), he gives a wide range of “spotlight ingredients”, such that many of the recipes, while great in and of themselves, can also be jumping-off points for those of us who like to take recipes and immediately do our own things to them.
Each day gets a breakfast, lunch, dinner, and he also covers drinks, desserts, and such like.
Notwithstanding the cover art being a lot of plants, the recipes are not entirely plant-based; there are a selection of fish dishes (and other seafood, e.g. shrimp) and also some dairy products (e.g. Greek yoghurt). The recipes are certainly very “plant-forward” though and many are just plants. If you’re a strict vegan though, this probably isn’t the book for you.
Bottom line: if you’d like to cook heart-healthy but are often stuck wondering “aaah, what to cook again today?”, then this is the book to get you out of any culinary creative block!
Click here to check out the Heart Healthy Diet Plan, and widen your heart-healthy repertoire!
Share This Post

An Accessible New Development Against Alzheimer’s
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dopamine vs Alzheimer’s
One of the key hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease is the formation of hardened beta-amyloid plaques around neurons. The beta-amyloid peptides themselves are supposed to be in the brain, but the hardened pieces of them that form the plaques are not.
While the full nature of the relationship between those plaques and Alzheimer’s disease is not known for sure (there are likely other factors involved, and “the amyloid hypothesis” is at this stage nominally just that, a hypothesis), one thing that has been observed is that increasing or reducing the plaques increases or reduces (respectively) Alzheimer’s symptoms such as memory loss.
Neprilysin
There is an enzyme, neprilysin, that can break down those plaques.
Neprilysin is made naturally in the brain, and/but we cannot take it as a supplement or medication, because it’s too big to pass through the blood-brain barrier.
A team of researchers led by Dr. Takaomi Saido genetically manipulated mice to produce more neprilysin, and those mice resultantly experienced fewer beta-amyloid plaques and better memory in their old age.
However wonderful for the mice (and a great proof of principle) the above approach is not useful as a treatment for humans whose genomes weren’t modified at our conception in a lab.
Since (as mentioned before) we also can’t take it as a medication/supplement, that leaves one remaining option: find a way to make our already-existing brains produce more of it.
The team’s previous research allowed them to narrow this down to “there is probably a hormone made in the hypothalamus that modulates this”, so they began experimenting with making the mice produce more hormones there.
The DREADD switch
DREADDs, or Designer Receptors Exclusively Activated by Designer Drugs, were the next tool in the toolbox. The scientists attached these designer receptors to dopamine-producing neurons in the mice, so that they could be activated by the appropriate designer drugs—basically, allowing for a “make more dopamine” button, without having to literally wire up the brains with electrodes. The “button” gets triggered instead by a chemical trigger, the designer drug. You can read more about them here:
DREADDs for Neuroscientists: A Primer
The result was positive; when the mice made more dopamine, the result was that they also made more neprilysin. So far, the hypothesis is that the presence of dopamine upregulates the production of neprilysin. In other words, the increased neprilysin levels were caused by the increased dopamine levels (the alternatives would have been: they were both caused by the same thing—in this case that’d be the DREADD activation—or the increase was caused by something else entirely that hadn’t been controlled for).
As to how the causal relationship was determined…
“But I don’t have (or want) a DREADD switch in my head”
Happily for us (and probably happily for the mice too, because dopamine causes feelings of happiness), the experiments continued.
This time, instead of using the DREADD system, they tried simply supplementing the mouse food with l-dopa, a dopamine precursor. L-dopa is often used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, because the molecules are small enough to pass through the blood-brain barrier, and can be converted to full dopamine inside the brain itself. So, taking l-dopa normally raises dopamine levels.
The results? The mice who were given l-dopa enjoyed:
- higher dopamine levels
- higher neprilysin levels
- lower beta-amyloid plaque levels
- better memory in tests
The next step for the researchers is to investigate how exactly dopamine regulates neprilysin in the brain, but for now, the relationship between l-dopa consumption and the reduction of Alzheimer’s symptoms seems clear.
You can read about the study here:
The dopaminergic system promotes neprilysin-mediated degradation of amyloid-β in the brain
Is there a catch?
L-dopa has common side effects that are not pleasant; the list begins with nausea and vomiting, and continues with things that one might expect from having “too much of a good thing” when it comes to dopamine, such as dyskinesia (extra movements) and hallucinations.
You can read about it more here at the Parkinson’s Foundation:
Parkinson’s Foundation | Levodopa
However! All is not lost. Rather than reaching for the heavy guns by taking l-dopa unnecessarily, there are other dopamine precursors that don’t have those side effects (and are consequently less restricted, to the point they can be purchased as supplements, or indeed, enjoyed where they occur naturally in some foods).
Top of the list of such safe* and readily-available dopamine precursors is…
N-Acetyl L-Tyrosine (NALT): The Dopamine Precursor & More
If you’d like to try that, here’s an example product on Amazon… Or you could eat fish, white beans, tofu, natto, or pumpkin seeds 😉
*Quick note on safety: “safe” is a relative term and may vary from person to person. Please speak with your own doctor to be sure, check with your pharmacist in case of any meds interactions, and be especially careful taking anything that increases dopamine levels if you have bipolar disorder or are otherwise prone to psychosis of any kind. For most people, this shouldn’t be an issue as our brains have a built-in mechanism for scrubbing excess dopamine and ensuring we don’t end up with too much, but for some people whose dopamine regulation is not so good in that regard, it can cause problems. So again, speak with your doctor to be sure, because we are not doctors, let alone your doctor.
Lastly…
If you’d like an entirely drug-free approach, that’s skipping even the “nutraceuticals”, you might enjoy:
Short On Dopamine? Science Has The Answer
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts

Never Too Old?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Age Limits On Exercise?
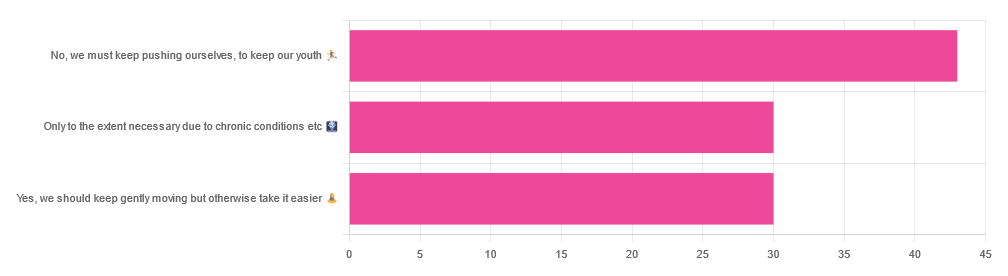
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your opinion on whether we should exercise less as we get older, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:

- About 42% said “No, we must keep pushing ourselves, to keep our youth“
- About 29% said “Only to the extent necessary due to chronic conditions etc”
- About 29% said “Yes, we should keep gently moving but otherwise take it easier”
One subscriber who voted for “No, we must keep pushing ourselves, to keep our youth“ wrote to add:
❝I’m 71 and I push myself. I’m not as fast or strong as I used to be but, I feel great when I push myself instead of going through the motions. I listen to my body!❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
One subscriber who voted for “Only to the extent necessary due to chronic conditions etc” wrote to add:
❝It’s never too late to get stronger. Important to keep your strength and balance. I am a Silver Sneakers instructor and I see first hand how helpful regular exercise is for seniors.❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
One subscriber who voted to say “Yes, we should keep gently moving but otherwise take it easier” wrote to add:
❝Keep moving but be considerate and respectful of your aging body. It’s a time to find balance in life and not put yourself into a positon to damage youself by competing with decades younger folks (unless you want to) – it will take much longer to bounce back.❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
These will be important, because we’ll come back to them at the end.
So what does the science say?
Endurance exercise is for young people only: True or False?
False! With proper training, age is no barrier to serious endurance exercise.
Here’s a study that looked at marathon-runners of various ages, and found that…
- the majority of middle-aged and elderly athletes have training histories of less than seven years of running
- there are virtually no relevant running time differences (p<0.01) per age in marathon finishers from 20 to 55 years
- after 55 years, running times did increase on average, but not consistently (i.e. there were still older runners with comparable times to the younger age bracket)
The researchers took this as evidence of aging being indeed a biological process that can be sped up or slowed down by various lifestyle factors.
See also:
Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
this covers the many aspects of biological aging (it’s not one number, but many!) and how our various different biological ages are often not in sync with each other, and how we can optimize each of them that can be optimized
Resistance training is for young people only: True or False?
False! In fact, it’s not only possible for older people, but is also associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality.
Specifically, those who reported strength-training at least once per week enjoyed longer lives than those who did not.
You may be thinking “is this just the horse-riding thing again, where correlation is not causation and it’s just that healthier people (for other reasons) were able to do strength-training more, rather than the other way around?“
…which is a good think to think of, so well-spotted if you were thinking that!
But in this case no; the benefits remained when other things were controlled for:
❝Adjusted for demographic variables, health behaviors and health conditions, a statistically significant effect on mortality remained.
Although the effects on cardiac and cancer mortality were no longer statistically significant, the data still pointed to a benefit.
Importantly, after the physical activity level was controlled for, people who reported strength exercises appeared to see a greater mortality benefit than those who reported physical activity alone.❞
See the study: Is strength training associated with mortality benefits? A 15 year cohort study of US older adults
And a pop-sci article about it: Strength training helps older adults live longer
Closing thoughts
As it happens… All three of the subscribers we quoted all had excellent points!
Because in this case it’s less a matter of “should”, and more a selection of options:
- We (most of us, at least) can gain/regain/maintain the kind of strength and fitness associated with much younger people, and we need not be afraid of exercising accordingly (assuming having worked up to such, not just going straight from couch to marathon, say).
- We must nevertheless be mindful of chronic conditions or even passing illnesses/injuries, but that goes for people of any age
- We also can’t argue against a “safety first” cautious approach to exercise. After all, sure, maybe we can run marathons at any age, but that doesn’t mean we have to. And sure, maybe we can train to lift heavy weights, but if we’re content to be able to carry the groceries or perhaps take our partner’s weight in the salsa hall (or the bedroom!), then (if we’re also at least maintaining our bones and muscles at a healthy level) that’s good enough already.
Which prompts the question, what do you want to be able to do, now and years from now? What’s important to you?
For inspiration, check out: Train For The Event Of Your Life!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

More Salt, Not Less?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I’m curious about the salt part – learning about LMNT and what they say about us needing more salt than what’s recommended by the government, would you mind looking into that? From a personal experience, I definitely noticed a massive positive difference during my 3-5 day water fasts when I added salt to my water compared to when I just drank water. So I’m curious what the actual range for salt intake is that we should be aiming for.❞
That’s a fascinating question, and we’ll have to tackle it in several parts:
When fasting
3–5 days is a long time to take only water; we’re sure you know most people fast from food for much less time than that. Nevertheless, when fasting, the body needs more water than usual—because of the increase in metabolism due to freeing up bodily resources for cellular maintenance. Water is necessary when replacing cells (most of which are mostly water, by mass), and for ferrying nutrients around the body—as well as escorting unwanted substances out of the body.
Normally, the body’s natural osmoregulatory process handles this, balancing water with salts of various kinds, to maintain homeostasis.
However, it can only do that if it has the requisite parts (e.g. water and salts), and if you’re fasting from food, you’re not replenishing lost salts unless you supplement.
Normally, monitoring our salt intake can be a bit of a guessing game, but when fasting for an entire day, it’s clear how much salt we consumed in our food that day: zero
So, taking the recommended amount of sodium, which varies but is usually in the 1200–1500mg range (low end if over aged 70+; high end if aged under 50), becomes sensible.
More detail: How Much Sodium You Need Per Day
See also, on a related note:
When To Take Electrolytes (And When We Shouldn’t!)
When not fasting
Our readers here are probably not “the average person” (since we have a very health-conscious subscriber-base), but the average person in N. America consumes about 9g of salt per day, which is several multiples of the maximum recommended safe amount.
The WHO recommends no more than 5g per day, and the AHA recommends no more than 2.3g per day, and that we should aim for 1.5g per day (this is, you’ll note, consistent with the previous “1200–1500mg range”).
Read more: Massive efforts needed to reduce salt intake and protect lives
Questionable claims
We can’t speak for LMNT (and indeed, had to look them up to discover they are an electrolytes supplement brand), but we can say that sometimes there are articles about such things as “The doctor who says we should eat more salt, not less”, and that’s usually about Dr. James DiNicolantonio, a doctor of pharmacy, who wrote a book that, because of this question today, we’ve now also reviewed:
Spoiler, our review was not favorable.
The body knows
Our kidneys (unless they are diseased or missing) do a full-time job of getting rid of excess things from our blood, and dumping them into one’s urine.
That includes excess sugar (which is how diabetes was originally diagnosed) and excess salt. In both cases, they can only process so much, but they do their best.
Dr. DiNicolantino recognizes this in his book, but chalks it up to “if we do take too much salt, we’ll just pass it in urine, so no big deal”.
Unfortunately, this assumes that our kidneys have infinite operating capacity, and they’re good, but they’re not that good. They can only filter so much per hour (it’s about 1 liter of fluids). Remember we have about 5 liters of blood, consume 2–3 liters of water per day, and depending on our diet, several more liters of water in food (easy to consume several more liters of water in food if one eats fruit, let alone soups and stews etc), and when things arrive in our body, the body gets to work on them right away, because it doesn’t know how much time it’s going to have to get it done, before the next intake comes.
It is reasonable to believe that if we needed 8–10g of salt per day, as Dr. DiNicolantonio claims, our kidneys would not start dumping once we hit much, much lower levels in our blood (lower even than the daily recommended intake, because not all of the salt in our body is in our blood, obviously).
See also: How Too Much Salt Can Lead To Organ Failure
Lastly, a note about high blood pressure
This is one where the “salt’s not the bad guy” crowd have at least something close to a point, because while salt is indeed still a bad guy (if taken above the recommended amounts, without good medical reason), when it comes to high blood pressure specifically, it’s not the worst bad guy, nor is it even in the top 5:
Hypertension: Factors Far More Relevant Than Salt
Thanks for writing in with such an interesting question!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Radiant Rebellion – by Karen Walrond
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In health terms, we are often about fighting aging here. But to be more specific, what we’re fighting in those cases is not truly aging itself, so much as age-related decline.
Karen Walrond makes a case that we’ve made from the very start of 10almonds (but she wrote a whole book about it), that there’s merit in looking at what we can and can’t control about aging, doing what we reasonably can, and embracing what we can’t.
And yes, embracing, not merely accepting. This is not a downer of a book; it’s a call to revolution. It asks us to be proud of our grey hairs, to see our smile-lines around our eyes as the sign of a lived-in body, and even to embrace some of the unavoidable “actual decline” things as part of the journey of life. Maybe we’re not as strong as we used to be and now need a grippety-doodah to open jars; not everyone gets to live long enough to experience that! How lucky we are.
Perhaps most importantly, she bids us be the change we want to see in the world, and inspire others with our choices and actions, and shake off ageist biases for good.
Bottom line: if you want to foster a better attitude to aging not only for yourself, but also those around you, then this is a top-tier book for that.
Click here to check out Radiant Rebellion, and reclaim aging!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: