An unbroken night’s sleep is a myth. Here’s what good sleep looks like
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What do you imagine a good night’s sleep to be?
Often when people come into our sleep clinic seeking treatment, they share ideas about healthy sleep.
Many think when their head hits the pillow, they should fall into a deep and restorative sleep, and emerge after about eight hours feeling refreshed. They’re in good company – many Australians hold the same belief.
In reality, healthy sleep is cyclic across the night, as you move in and out of the different stages of sleep, often waking up several times. Some people remember one or more of these awakenings, others do not. Let’s consider what a healthy night’s sleep looks like.

Sleep cycles are a roller-coaster
As an adult, our sleep moves through different cycles and brief awakenings during the night. Sleep cycles last roughly 90 minutes each.
We typically start the night with lighter sleep, before moving into deeper sleep stages, and rising again into rapid eye movement (REM) sleep – the stage of sleep often linked to vivid dreaming.
If sleeping well, we get most of our deep sleep in the first half of the night, with REM sleep more common in the second half of the night.

Adults usually move through five or six sleep cycles in a night, and it is entirely normal to wake up briefly at the end of each one. That means we might be waking up five times during the night. This can increase with older age and still be healthy. If you’re not remembering these awakenings that’s OK – they can be quite brief.
What does getting a ‘good’ sleep actually mean?
You’ll often hear that adults need between seven and nine hours of sleep per night. But good sleep is about more than the number of hours – it’s also about the quality.
For most people, sleeping well means being able to fall asleep soon after getting into bed (within around 30 minutes), sleeping without waking up for long periods, and waking feeling rested and ready for the day.
You shouldn’t be feeling excessively sleepy during the day, especially if you’re regularly getting at least seven hours of refreshing sleep a night (this is a rough rule of thumb).
But are you noticing you’re feeling physically tired, needing to nap regularly and still not feeling refreshed? It may be worthwhile touching base with your general practitioner, as there a range of possible reasons.
Common issues
Sleep disorders are common. Up to 25% of adults have insomnia, a sleep disorder where it may be hard to fall or stay asleep, or you may wake earlier in the morning than you’d like.
Rates of common sleep disorders such as insomnia and sleep apnoea – where your breathing can partially or completely stop many times during the night – also increase with age, affecting 20% of early adults and 40% of people in middle age. There are effective treatments, so asking for help is important.
Beyond sleep disorders, our sleep can also be disrupted by chronic health conditions – such as pain – and by certain medications.
There can also be other reasons we’re not sleeping well. Some of us are woken by children, pets or traffic noise during the night. These “forced awakenings” mean we may find it harder to get up in the morning, take longer to leave bed and feel less satisfied with our sleep. For some people, night awakenings may have no clear cause.
A good way to tell if these awakenings are a problem for you is by thinking about how they affect you. When they cause feelings of frustration or worry, or are impacting how we feel and function during the day, it might be a sign to seek some help.

We also may struggle to get up in the morning. This could be for a range of reasons, including not sleeping long enough, going to bed or waking up at irregular times – or even your own internal clock, which can influence the time your body prefers to sleep.
If you’re regularly struggling to get up for work or family needs, it can be an indication you may need to seek help. Some of these factors can be explored with a sleep psychologist if they are causing concern.
Can my smart watch help?
It is important to remember sleep-tracking devices can vary in accuracy for looking at the different sleep stages. While they can give a rough estimate, they are not a perfect measure.
In-laboratory polysomnography, or PSG, is the best standard measure to examine your sleep stages. A PSG examines breathing, oxygen saturation, brain waves and heart rate during sleep.
Rather than closely examining nightly data (including sleep stages) from a sleep tracker, it may be more helpful to look at the patterns of your sleep (bed and wake times) over time.
Understanding your sleep patterns may help identify and adjust behaviours that negatively impact your sleep, such as your bedtime routine and sleeping environment.
And if you find viewing your sleep data is making you feel worried about your sleep, this may not be useful for you. Most importantly, if you are concerned it is important to discuss it with your GP who can refer you to the appropriate specialist sleep health provider.
Amy Reynolds, Associate Professor in Clinical Sleep Health, Flinders University; Claire Dunbar, Research Associate, Sleep Health, Flinders University; Gorica Micic, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Clinical Psychologist, Flinders University; Hannah Scott, Research Fellow in Sleep Health, Flinders University, and Nicole Lovato, Associate Professor, Adelaide Institute for Sleep Health, Flinders University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eat Move Sleep – by Tom Rath
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The subtitle of this book, “how small choices lead to big changes“, is very much the idea that a lot of what we do here at 10almonds is about.
And the title itself, “Eat Move Sleep”? Well, that’s 3/5 of The Usual Five Things™ that we promote here (the other two being: reduce or eliminate alcohol, and don’t smoke). So, naturally this book got our attention.
One of the key ideas that Rath presents is that every action we take leads to a net gain or loss in health. The question then is: what are the biggest point-swingers? In other words, what are the places in our life where the smallest changes can make the biggest difference?
Rath looks at what parts of diet make the biggest difference to our health, and the findings there alone probably make reading the book worthwhile.
When it comes to movement, he actually flips this! For Rath, it’s less about how much exercise you get, and more about minimizing how long we spend not moving… And especially, minimizing how long we spend sitting. So, lots of little tweaks for that.
In the category of sleep: a key idea is that quality is as important as quantity, and there’s an aspect of bringing together as a synergistic routine. To finish off a productive day with good rest, and power up ready for the next morning.
In short: tying these items together—and focusing on the smallest choices that lead to the biggest changes—makes for quite a manifesto that we could describe as “Atomic Habits, for health specifically”.
Share This Post
-
Swordfish vs Tuna – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing swordfish to tuna, we picked the tuna.
Why?
Today in “that which is more expensive is not necessarily the healthier”…
Considering the macros first, swordfish has more than 8x more total fat, about 9x more saturated fat, and yes, more cholesterol. On the other hand, tuna has more protein. An easy win for tuna.
In terms of vitamins, swordfish has more of vitamins A, B5, D, and E, while tuna has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, and B12. A marginal win for tuna, unless you want to weight the other vitamins more heavily, in which case, more likely a tie, or maybe even an argument for swordfish if you have a particular vitamin deficiency on that side.
When it comes to minerals, swordfish has more calcium and zinc, while tuna has more iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium. A clear win for tuna.
One other thing: they’re both very rich in mercury, and while tuna is bad for that, swordfish has nearly 3x as much.
In short, both have a good spread of vitamins and minerals, and both are quite tainted with mercury, but in relative terms, there’s a clear winner even before considering the very different macros, and the winner is tuna.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Farmed Fish vs Wild Caught: Important Differences
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Gut Health for Women – by Aurora Bloom
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First things first: though the title says “For Women”, almost all of it applies to men too—and the things that don’t apply, don’t cause a problem. So if you’re cooking for your family that contains one or more men, this is still great.
Bloom gives us a good, simple, practical introduction to gut health. Her overview also covers gut-related ailments beyond the obvious “tummy hurts”. On which note:
A very valuable section of this book covers dealing with any stomach-upsets that do occur… without harming your trillions of tiny friends (friendly gut microbiota). This alone can make a big difference!
The book does of course also cover the things you’d most expect: things to eat or avoid. But it goes beyond that, looking at optimizing and maintaining your gut health. It’s not just dietary advice here, because the gut affects—and is affected by—other lifestyle factors too. Ranges from mindful eating, to a synchronous sleep schedule, to what kinds of exercise are best to keep your gut ticking over nicely.
There’s also a two-week meal plan, and an extensive appendix of resources, not to mention a lengthy bibliography for sourcing health claims (and suggesting further reading).
In short, a fine and well-written guide to optimizing your gut health and enjoying the benefits.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Olive oil is healthy. Turns out olive leaf extract may be good for us too
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Olive oil is synonymous with the Mediterranean diet, and the health benefits of both are well documented.
Olive oil reduces the risk of heart disease, cancer, diabetes and premature death. Olives also contain numerous healthy nutrients.
Now evidence is mounting about the health benefits of olive leaves, including from studies in a recent review.
Here’s what’s in olive leaves and who might benefit from taking olive leaf extract.
mtphoto19/Shutterstock What’s in olive leaves?
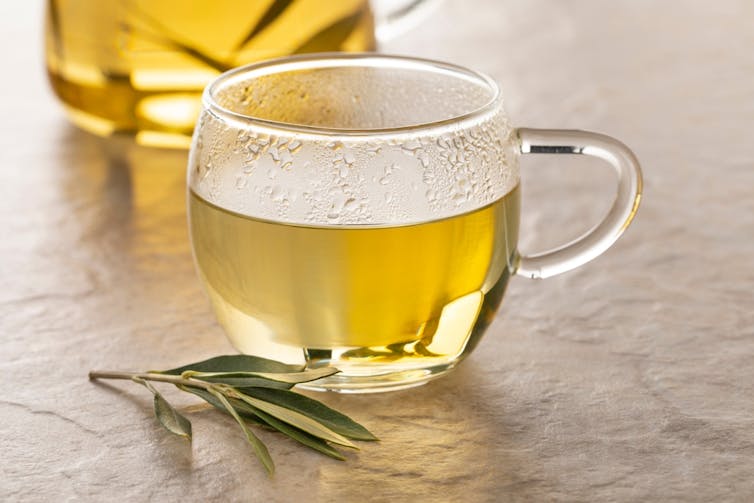
Olive leaves have traditionally been brewed as a tea in the Mediterranean and drunk to treat fever and malaria.
The leaves contain high levels of a type of antioxidant called oleuropein. Olives and olive oil contain this too, but at lower levels.
Generally, the greener the leaf (the less yellowish) the more oleuropein it contains. Leaves picked in spring also have higher levels compared to ones picked in autumn, indicating levels of oleuropein reduce as the leaves get older.
Olive leaves also contain other antioxidants such as hydroxytyrosol, luteolin, apigenin and verbascoside.
Antioxidants work by reducing the oxidative stress in the body. Oxidative stress causes damage to our DNA, cell membranes and tissues, which can lead to chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
Are olive leaves healthy?
One review and analysis combined data from 12 experimental studies with 819 participants in total. Overall, olive leaf extract improved risk factors for heart disease. This included healthier blood lipids (fats) and lowering blood pressure.
The effect was greater for people who already had high blood pressure.
Most studies in this review gave olive leaf extract as a capsule, with daily doses of 500 milligrams to 5 grams for six to 48 weeks.
Another review and analysis published late last year looked at data from 12 experimental studies, with a total of 703 people. Some of these studies involved people with high blood lipids, people with high blood pressure, people who were overweight or obese, and some involved healthy people.
Daily doses were 250-1,000mg taken as tablets or baked into bread.
Individual studies in the review showed significant benefits in improving blood glucose (sugar) control, blood lipid levels and reducing blood pressure. But when all the data was combined, there were no significant health effects. We’ll explain why this may be the case shortly.
Olive leaves can be brewed into tea. Picture Partners/Shutterstock Another review looked at people who took oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol (the antioxidants in olive leaves). This found significant improvement in body weight, blood lipid profiles, glucose metabolism and improvements in bones, joints and cognitive function.
The individual studies included tested either the two antioxidants or olive leaf incorporated into foods such as bread and cooking oils (but not olive oil). The doses were 6-500mg per day of olive leaf extract.
So what can we make of these studies overall? They show olive leaf extract may help reduce blood pressure, improve blood lipids and help our bodies handle glucose.
But these studies show inconsistent results. This is likely due to differences in the way people took olive leaf extract, how much they took and how long for. This type of inconsistency normally tells us we need some more research to clarify the health effects of olive leaves.
Can you eat olive leaves?
Olive leaves can be brewed into a tea, or the leaves added to salads. Others report grinding olive leaves into smoothies.
However the leaves are bitter, because of the antioxidants, which can make them hard to eat, or the tea unpalatable.
Olive leaf extract has also been added to bread and other baked goods. Researchers find this improves the level of antioxidants in these products and people say the foods tasted better.
Olive leaves can taste bitter, which can put people off. But you can bake the extract into bread. Repina Valeriya/Shutterstock Is olive leaf extract toxic?
No, there seem to be no reported toxic effects of eating or drinking olive leaf extract.
It appears safe up to 1g a day, according to studies that have used olive leaf extract. However, there are no official guidelines about how much is safe to consume.
There have been reports of potential toxicity if taken over 85mg/kg of body weight per day. For an 80kg adult, this would mean 6.8g a day, well above the dose used in the studies mentioned in this article.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women are recommended not to consume it as we don’t know if it’s safe for them.
What should I do?
If you have high blood pressure, diabetes or raised blood lipids you may see some benefit from taking olive leaf extract. But it is important you discuss this with your doctor first and not change any medications or start taking olive leaf extract until you have spoken to them.
But there are plenty of antioxidants in all plant foods, and you should try to eat a wide variety of different coloured plant foods. This will allow you to get a range of nutrients and antioxidants.
Olive leaf and its extract is not going to be a panacea for your health if you’re not eating a healthy diet and following other health advice.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can We Drink To Good Health?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Can we drink to good health?
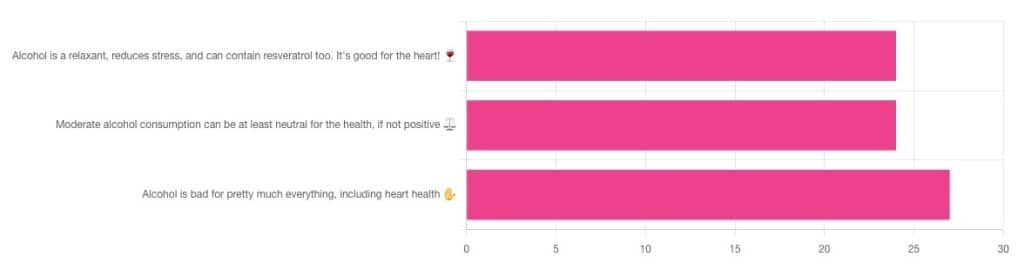
We asked you for your thoughts on alcohol and heart health, and we got quite an even spread of results!
If perchance that’s too tiny to read, the figures were:
- 32% voted for “Alcohol is a relaxant, reduces stress, and can contain resveratrol too. It’s good for the heart!”
- 32% voted for: “Moderate alcohol consumption can be at least neutral for the health, if not positive ⚖️”
- 36% voted for: “Alcohol is bad for pretty much everything, including heart health ✋”
One subscriber who voted for “Alcohol is a relaxant, reduces stress, and can contain resveratrol too. It’s good for the heart!” added the following thoughts:
❝While it isn’t necessary to consume alcohol, moderate amounts can be beneficial and contribute to well-being through social activity, celebrations, etc.❞
That’s an interesting point, and definitely many people do see alcohol that way! Of course, that does not mean that one will find no social activities, celebrations, etc, in parts of the world where alcohol consumption is uncommon. Indeed, in India, wedding parties where no alcohol is consumed can go on for days!
But, “we live in a society” and all that, and while we’re a health newsletter not a social issues newsletter, it’d be remiss of us to not acknowledge the importance of socialization for good mental health—and thus the rest of our health too.
So, if indeed all our friends and family drink alcohol, it can certainly make abstaining more of a challenge.
On that note, let’s take a moment to consider “The French Paradox” (an observation of a low prevalence of ischemic heart disease despite high intakes of saturated fat, a phenomenon accredited to the consumption of red wine).
As it happens, a comprehensive review in “Circulation”, a cardiovascular health journal, has suggested the French Paradox may not be so paradoxical after all.
Research suggests it has more to do with other lifestyle factors (and historic under-reporting of cardiovascular disease by French doctors), which would explain why Japan has lower rates of heart disease, despite drinking little wine, and more beer and spirits.
So, our subscriber’s note may not be completely without reason! It’s just about the party, not the alcohol.
One subscriber who voted for “Moderate alcohol consumption can be at least neutral for the health, if not positive ⚖️” wrote:
❝Keeping in mind, moderate means one glass of wine for women a day and two for men. Hard alcohol doesn’t have the same heart benefits as wine❞
That is indeed the guideline according to some health bodies!
In other places with different guiding advisory bodies, that’s been dropped down to one a day for everyone (the science may be universal, but how government institutions interpret that is not).
About that wine… Specifically, red wine, for its resveratrol content:
While there are polyphenols such as resveratrol in red wine that could boost heart health, there’s so little per glass that you may need 100–1000 glasses to get the dosage that provides benefits in mouse studies. If you’re not a mouse, you might even need more.
To this end, many people prefer resveratrol supplementation. ← link is to an example product, but there are plenty more so feel free to shop around
A subscriber who voted for “Alcohol is bad for pretty much everything, including heart health ✋” says:
❝New guidelines suggest 1 to 2 drinks a week are okay but the less the better.❞
If you haven’t heard these new guidelines, we’ll mention again: every government has its own official bodies and guidelines so perhaps your local guidelines differ, but for example here’s what that World Health Organization has to say (as of January this year):
WHO: No level of alcohol consumption is safe for our health
So, whom to believe? The governments who hopefully consider the welfare of their citizenry more important than the tax dollars from alcohol sales, or the World Health Organization?
It’s a tough one, but we’ll always err on the side of the science.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
Piperine, a compound found in Piper nigrum (black pepper, to its friends), has many health benefits. It’s included as a minor ingredient in some other supplements, because it boosts bioavailability. In its form as a kitchen spice, it’s definitely a superfood.
What does it do?
First, three things that generally go together:
These things often go together for the simple reason that oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer often go together. In each case, it’s a matter of cellular wear-and-tear, and what can mitigate that.
For what it’s worth, there’s generally a fourth pillar: anti-aging. This is again for the same reason. That said, black pepper hasn’t (so far as we could find) been studied specifically for its anti-aging properties, so we can’t cite that here as an evidence-based claim.
Nevertheless, it’s a reasonable inference that something that fights oxidation, inflammation, and cancer, will often also slow aging.
Special note on the anti-cancer properties
We noticed two very interesting things while researching piperine’s anti-cancer properties. It’s not just that it reduces cancer risk and slows tumor growth in extant cancers (as we might expect from the above-discussed properties). Let’s spotlight some studies:
It is selectively cytotoxic (that’s a good thing)
Piperine was found to be selectively cytotoxic to cancerous cells, while not being cytotoxic to non-cancerous cells. To this end, it’s a very promising cancer-sniper:
Piperine as a Potential Anti-cancer Agent: A Review on Preclinical Studies
It can reverse multi-drug resistance in cancer cells
P-glycoprotein, found in our body, is a drug-transporter that is known for “washing out” chemotherapeutic drugs from cancer cells. To date, no drug has been approved to inhibit P-glycoprotein, but piperine has been found to do the job:
Targeting P-glycoprotein: Investigation of piperine analogs for overcoming drug resistance in cancer
What’s this about piperine analogs, though? Basically the researchers found a way to “tweak” piperine to make it even more effective. They called this tweaked version “Pip1”, because calling it by its chemical name,
((2E,4E)-5-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-1-(6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1 H)-yl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one)
…got a bit unwieldy.
The upshot is: Pip1 is better, but piperine itself is also good.
Other benefits
Piperine does have other benefits too, but the above is what we were most excited to talk about today. Its other benefits include:
- Neuroprotective effects (against Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and more)
- Blood-sugar balancing / antidiabetic effect
- Good for gut microbiome diversity
- Heart health benefits, including cholesterol-balancing
- Boosts bioavailability of other nutrients/drugs
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: