Algorithms to Live By – by Brian Christian and Tom Griffiths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As humans, we subconsciously use heuristics a lot to make many complex decisions based on “fuzzy logic”. For example:
Do we buy the cheap shoes that may last us a season, or the much more expensive ones that will last us for years? We’ll—without necessarily giving it much conscious thought—quickly weigh up:
- How much do we like each prospective pair of shoes?
- What else might we need to spend money on now/soon?
- How much money do we have right now?
- How much money do we expect to have in the future?
- Considering our lifestyle, how important is it to have good quality shoes?
How well we perform this rapid calculation may vary wildly, depending on many factors ranging from the quality of the advertising to how long ago we last ate.
And if we make the wrong decision, later we may have buyer’s (or non-buyer’s!) remorse. So, how can we do better?
Authors Brain Christian and Tom Griffiths have a manual for us!
This book covers many “kinds” of decision we often have to make in life, and how to optimize those decisions with the power of mathematics and computer science.
The problems (and solutions) run the gamut of…
- Optimal stopping (when to say “alright, that’s good enough”)
- Overcoming cognitive biases
- Scheduling quandaries
- Bayes’ Theorem
- Game Theory
- And when it’s more efficient to just leave things to chance!
…and many more (12 main areas of decision-making are covered).
For all it draws heavily from mathematics and computer science, the writing style is very easy-reading. It’s a “curl up in the armchair and read for pleasure” book, no matter how weighty and practical its content.
Bottom line: if you improve your ability to make the right decisions even marginally, this book will have been worth your while in the long run!
Order your copy of “Algorithms To Live By” from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The 5 Love Languages Gone Wrong
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Levelling up the 5 love languages
The saying “happy wife; happy life” certainly goes regardless of gender, and if we’re partnered, it’s difficult to thrive in our individual lives if we’re not thriving as a couple. So, with the usual note that mental health is also just health, let’s take a look at getting beyond the basics of a well-known, often clumsily-applied model:
The 5 love languages
You’re probably familiar with “the 5 love languages”, as developed by Dr. Gary Chapman. If not, they are:
- Acts of Service
- Gift-Giving
- Physical Touch
- Quality Time
- Words of Affirmation
The idea is that we each weight these differently, and problems can arise when a couple are “speaking a different language”.
So, is this a basic compatibility test?
It doesn’t have to be!
We can, if we’re aware of each other’s primary love languages, make an effort to do a thing we wouldn’t necessarily do automatically, to ensure they’re loved the way they need to be.
But…
What a lot of people overlook is that we can also have different primary love languages for giving and for receiving. And, missing that can mean that even taking each other’s primarily love languages into account, efforts to make a partner feel loved, or to feel loved oneself, can miss 50% of the time.
For example, I (your writer here today, hi) could be asked my primary love language and respond without hesitation “Acts of Service!” because that’s my go-to for expressing love.
I’m the person who’ll run around bringing drinks, do all the housework, and without being indelicate, will tend towards giving in the bedroom. But…
A partner trying to act on that information to make me feel loved by giving Acts of Service would be doomed to catastrophic failure, because my knee-jerk reaction would be “No, here, let me do that for you!”
So it’s important for partners to ask each other…
- Not: “what’s your primary love language?” ❌
- But: “what’s your primary way of expressing love?” ✅
- And: “which love language makes you feel most loved?” ✅
For what it’s worth, I thrive on Words of Affirmation, so thanks again to everyone who leaves kind feedback on our articles! It lets me know I provided a good Act of Service
So far, so simple, right? You and your partner (or: other person! Because as we’ve just seen, these go for all kinds of dynamics, not just romantic partnerships) need to be aware of each other’s preferred love languages for giving and receiving.
But…
There’s another pitfall that many fall into, and that’s assuming that the other person has the same idea about what a given love language means, when there’s more to clarify.
For example:
- Acts of Service: is it more important that the service be useful, or that it took effort?
- Gift-Giving: is it better that a gift be more expensive, or more thoughtful and personal?
- Physical Touch: what counts here? If we’re shoulder-to-shoulder on the couch, is that physical touch or is something more active needed?
- Quality Time: does it count if we’re both doing our own thing but together in the same room, comfortable in silence together? Or does it need to be a more active and involved activity together? And is it quality time if we’re at a social event together, or does it need to be just us?
- Words of Affirmation: what, exactly, do we need to hear? For romantic partners, “I love you” can often be important, but is there something else we need to hear? Perhaps a “because…”, or perhaps a “so much that…”, or perhaps something else entirely? Does it no longer count if we have to put the words in our partner’s mouth, or is that just good two-way communication?
Bottom line:
There’s a lot more to this than a “What’s your love language?” click-through quiz, but with a little application and good communication, this model can really resolve a lot of would-be problems that can grow from feeling unappreciated or such. And, the same principles go just the same for friends and others as they do for romantic partners.
In short, it’s one of the keys to good interpersonal relationships in general—something critical for our overall well-being!
Share This Post
-
How to Prepare for Your First Therapy Session
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Everyone (who ever has therapy, anyway) has a first therapy session. So, how to make best use of that, and get things going most effectively? Dr. Tori Olds has advice:
Things to prepare
Questions that you should consider, and prepare answers to beforehand, include:
- Why are you here? Not in any deep philosophical sense, but, what brought you to therapy?
- What would you like to focus on? Chances are, you are paying a hefty hourly rate—so having considered this will allow you to get your money’s worth.
- How will you know when you’ve met your goal? Note that this is really two questions in one, because first you need to identify your goal, and then you need to expand on it. If you woke up tomorrow and all your psychological problems were solved, how would you know? What would be different? What does it look like?
If you have a little time between now and your first session, journaling can help a lot.
Remember also that a first therapy session can also be like a mutual interview, to decide whether it’s a good match. Not every therapist is good at their job, and not every therapist will be good for you specifically. Sometimes, a therapist may be a mismatch through no fault of their own. Considering what those reasons might be can also be a good thing to think about in advance, to help find the best therapist for you in fewer tries!
For most on these ideas, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Homeopathy: Evidence So Tiny That It’s Not there?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Homeopathy: Evidence So Tiny That It’s Not There?
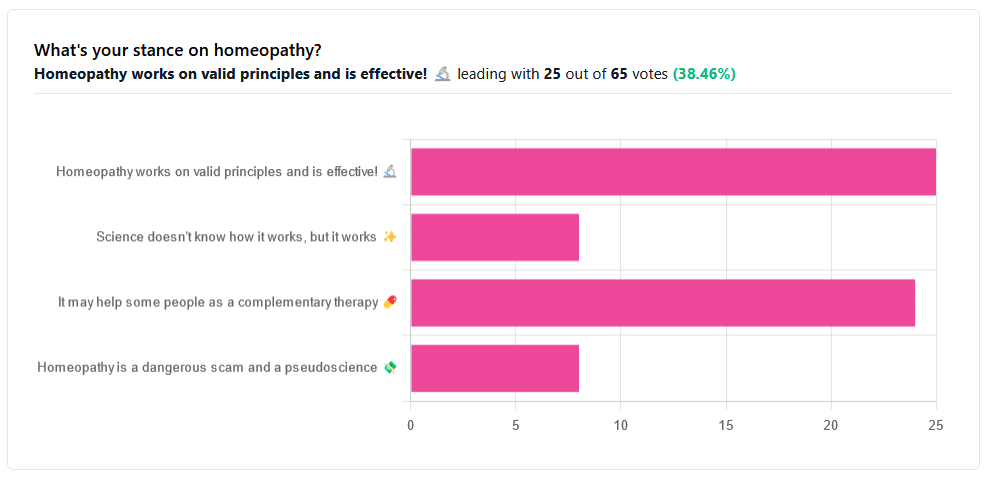
Yesterday, we asked you your opinions on homeopathy. The sample size of responses was a little lower than we usually get, but of those who did reply, there was a clear trend:
- A lot of enthusiasm for “Homeopathy works on valid principles and is effective”
- Near equal support for “It may help some people as a complementary therapy”
- Very few people voted for “Science doesn’t know how it works, but it works”; this is probably because people who considered voting for this, voted for the more flexible “It may help some people as a complementary therapy” instead.
- Very few people considered it a dangerous scam and a pseudoscience.
So, what does the science say?
Well, let us start our investigation by checking out the position of the UK’s National Health Service, an organization with a strong focus on providing the least expensive treatments that are effective.
Since homeopathy is very inexpensive to arrange, they will surely want to put it atop their list of treatments, right?
❝Homeopathy is a “treatment” based on the use of highly diluted substances, which practitioners claim can cause the body to heal itself.
There’s been extensive investigation of the effectiveness of homeopathy. There’s no good-quality evidence that homeopathy is effective as a treatment for any health condition.❞
The NHS actually has a lot more to say about that, and you can read their full statement here.
But that’s just one institution. Here’s what Australia’s National Health and Medical Research Council had to say:
❝There was no reliable evidence from research in humans that homeopathy was effective for treating the range of health conditions considered: no good-quality, well-designed studies with enough participants for a meaningful result reported either that homeopathy caused greater health improvements than placebo, or caused health improvements equal to those of another treatment❞
You can read their full statement here.
The American FDA, meanwhile, have a stronger statement:
❝Homeopathic drug products are made from a wide range of substances, including ingredients derived from plants, healthy or diseased animal or human sources, minerals and chemicals, including known poisons. These products have the potential to cause significant and even permanent harm if they are poorly manufactured, since that could lead to contaminated products or products that have potentially toxic ingredients at higher levels than are labeled and/or safe, or if they are marketed as substitute treatments for serious or life-threatening diseases and conditions, or to vulnerable populations.❞
You can read their full statement here.
Homeopathy is a dangerous scam and a pseudoscience: True or False?
False and True, respectively, mostly.
That may be a confusing answer, so let’s elaborate:
- Is it dangerous? Mostly not; it’s mostly just water. However, two possibilities for harm exist:
- Careless preparation could result in a harmful ingredient still being present in the water—and because of the “like cures like” principle, many of the ingredients used in homeopathy are harmful, ranging from heavy metals to plant-based neurotoxins. However, the process of “ultra-dilution” usually removes these so thoroughly that they are absent or otherwise scientifically undetectable.
- Placebo treatment has its place, but could result in “real” treatment going undelivered. This can cause harm if the “real” treatment was critically needed, especially if it was needed on a short timescale.
- Is it a scam? Probably mostly not; to be a scam requires malintent. Most practitioners probably believe in what they are practising.
- Is it a pseudoscience? With the exception that placebo effect has been highly studied and is a very valid complementary therapy… Yes, aside from that it is a pseudoscience. There is no scientific evidence to support homeopathy’s “like cures like” principle, and there is no scientific evidence to support homeopathy’s “water memory” idea. On the contrary, they go against the commonly understood physics of our world.
It may help some people as a complementary therapy: True or False?
True! Not only is placebo effect very well-studied, but best of all, it can still work as a placebo even if you know that you’re taking a placebo… Provided you also believe that!
Science doesn’t know how it works, but it works: True or False?
False, simply. At best, it performs as a placebo.
Placebo is most effective when it’s a remedy against subjective symptoms, like pain.
However, psychosomatic effect (the effect that our brain has on the rest of our body, to which it is very well-connected) can mean that placebo can also help against objective symptoms, like inflammation.
After all, our body, directed primarily by the brain, can “decide” what immunological defenses to deploy or hold back, for example. This is why placebo can help with conditions as diverse as arthritis (an inflammatory condition) or diabetes (an autoimmune condition, and/or a metabolic condition, depending on type).
Here’s how homeopathy measures up, for those conditions:
(the short answer is “no better than placebo”)
Homeopathy works on valid principles and is effective: True or False?
False, except insofar as placebo is a valid principle and can be effective.
The stated principles of homeopathy—”like cures like” and “water memory”—have no scientific basis.
We’d love to show the science for this, but we cannot prove a negative.
However, the ideas were conceived in 1796, and are tantamount to alchemy. A good scientific attitude means being open-minded to new ideas and testing them. In homeopathy’s case, this has been done, extensively, and more than 200 years of testing later, homeopathy has consistently performed equal to placebo.
In summary…
- If you’re enjoying homeopathic treatment and that’s working for you, great, keep at it.
- If you’re open-minded to enjoying a placebo treatment that may benefit you, be careful, but don’t let us stop you.
- If your condition is serious, please do not delay seeking evidence-based medical treatment.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Most adults will gain half a kilo this year – and every year. Here’s how to stop ‘weight creep’
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As we enter a new year armed with resolutions to improve our lives, there’s a good chance we’ll also be carrying something less helpful: extra kilos. At least half a kilogram, to be precise.
“Weight creep” doesn’t have to be inevitable. Here’s what’s behind this sneaky annual occurrence and some practical steps to prevent it.
Allgo/Unsplash Small gains add up
Adults tend to gain weight progressively as they age and typically gain an average of 0.5 to 1kg every year.
While this doesn’t seem like much each year, it amounts to 5kg over a decade. The slow-but-steady nature of weight creep is why many of us won’t notice the extra weight gained until we’re in our fifties.
Why do we gain weight?
Subtle, gradual lifestyle shifts as we progress through life and age-related biological changes cause us to gain weight. Our:
- activity levels decline. Longer work hours and family commitments can see us become more sedentary and have less time for exercise, which means we burn fewer calories
- diets worsen. With frenetic work and family schedules, we sometimes turn to pre-packaged and fast foods. These processed and discretionary foods are loaded with hidden sugars, salts and unhealthy fats. A better financial position later in life can also result in more dining out, which is associated with a higher total energy intake
- sleep decreases. Busy lives and screen use can mean we don’t get enough sleep. This disturbs our body’s energy balance, increasing our feelings of hunger, triggering cravings and decreasing our energy
Insufficient sleep can increase our appetite. Craig Adderley/Pexels - stress increases. Financial, relationship and work-related stress increases our body’s production of cortisol, triggering food cravings and promoting fat storage
- metabolism slows. Around the age of 40, our muscle mass naturally declines, and our body fat starts increasing. Muscle mass helps determine our metabolic rate, so when our muscle mass decreases, our bodies start to burn fewer calories at rest.
We also tend to gain a small amount of weight during festive periods – times filled with calorie-rich foods and drinks, when exercise and sleep are often overlooked. One study of Australian adults found participants gained 0.5 kilograms on average over the Christmas/New Year period and an average of 0.25 kilograms around Easter.
Why we need to prevent weight creep
It’s important to prevent weight creep for two key reasons:
1. Weight creep resets our body’s set point
Set-point theory suggests we each have a predetermined weight or set point. Our body works to keep our weight around this set point, adjusting our biological systems to regulate how much we eat, how we store fat and expend energy.
When we gain weight, our set point resets to the new, higher weight. Our body adapts to protect this new weight, making it challenging to lose the weight we’ve gained.
But it’s also possible to lower your set point if you lose weight gradually and with an interval weight loss approach. Specifically, losing weight in small manageable chunks you can sustain – periods of weight loss, followed by periods of weight maintenance, and so on, until you achieve your goal weight.
Holidays can also come with weight gain. Zan Lazarevic/Unsplash 2. Weight creep can lead to obesity and health issues
Undetected and unmanaged weight creep can result in obesity which can increase our risk of heart disease, strokes, type 2 diabetes, osteoporosis and several types of cancers (including breast, colorectal, oesophageal, kidney, gallbladder, uterine, pancreatic and liver).
A large study examined the link between weight gain from early to middle adulthood and health outcomes later in life, following people for around 15 years. It found those who gained 2.5 to 10kg over this period had an increased incidence of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, strokes, obesity-related cancer and death compared to participants who had maintained a stable weight.
Fortunately, there are steps we can take to build lasting habits that will make weight creep a thing of the past.
7 practical steps to prevent weight creep
1. Eat from big to small
Aim to consume most of your food earlier in the day and taper your meal sizes to ensure dinner is the smallest meal you eat.
A low-calorie or small breakfast leads to increased feelings of hunger, specifically appetite for sweets, across the course of the day.
We burn the calories from a meal 2.5 times more efficiently in the morning than in the evening. So emphasising breakfast over dinner is also good for weight management.
Aim to consume bigger breakfasts and smaller dinners. Michael Burrows/Pexels 2. Use chopsticks, a teaspoon or an oyster fork
Sit at the table for dinner and use different utensils to encourage eating more slowly.
This gives your brain time to recognise and adapt to signals from your stomach telling you you’re full.
3. Eat the full rainbow
Fill your plate with vegetables and fruits of different colours first to support eating a high-fibre, nutrient-dense diet that will keep you feeling full and satisfied.
Meals also need to be balanced and include a source of protein, wholegrain carbohydrates and healthy fat to meet our dietary needs – for example, eggs on wholegrain toast with avocado.
4. Reach for nature first
Retrain your brain to rely on nature’s treats – fresh vegetables, fruit, honey, nuts and seeds. In their natural state, these foods release the same pleasure response in the brain as ultra-processed and fast foods, helping you avoid unnecessary calories, sugar, salt and unhealthy fats.
5. Choose to move
Look for ways to incorporate incidental activity into your daily routine – such as taking the stairs instead of the lift – and boost your exercise by challenging yourself to try a new activity.
Just be sure to include variety, as doing the same activities every day often results in boredom and avoidance.
Try new activities or sports to keep your interest up. Cottonbro Studio/Pexels 6. Prioritise sleep
Set yourself a goal of getting a minimum of seven hours of uninterrupted sleep each night, and help yourself achieve it by avoiding screens for an hour or two before bed.
7. Weigh yourself regularly
Getting into the habit of weighing yourself weekly is a guaranteed way to help avoid the kilos creeping up on us. Aim to weigh yourself on the same day, at the same time and in the same environment each week and use the best quality scales you can afford.
At the Boden Group, Charles Perkins Centre, we are studying the science of obesity and running clinical trials for weight loss. You can register here to express your interest.
Nick Fuller, Clinical Trials Director, Department of Endocrinology, RPA Hospital, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
STI rates are increasing among midlife and older adults. We need to talk about it
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Globally, the rates of common sexually transmissible infections (STIs) are increasing among people aged over 50. In some cases, rates are rising faster than among younger people.
Recent data from the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention shows that, among people aged 55 and older, rates of gonorrhoea and chlamydia, two of the most common STIs, more than doubled between 2012 and 2022.
Australian STI surveillance data has reflected similar trends. Between 2013 and 2022, there was a steady increase in diagnoses of chlamydia, gonorrhoea and syphilis among people aged 40 and older. For example, there were 5,883 notifications of chlamydia in Australians 40 plus in 2013, compared with 10,263 in 2022.
A 2020 study of Australian women also showed that, between 2000 and 2018, there was a sharper increase in STI diagnoses among women aged 55–74 than among younger women.
While the overall rate of common STIs is highest among young adults, the significant increase in STI diagnoses among midlife and older adults suggests we need to pay more attention to sexual health across the life course.
Fit Ztudio/Shutterstock Why are STI rates rising among older adults?
STI rates are increasing globally for all age groups, and an increase among midlife and older people is in line with this trend.
However, increases of STIs among older people are likely due to a combination of changing sex and relationship practices and hidden sexual health needs among this group.
The “boomer” generation came of age in the 60s and 70s. They are the generation of free love and their attitude to sex, even as they age, is quite different to that of generations before them.
Given the median age of divorce in Australia is now over 43, and the internet has ushered in new opportunities for post-separation dating, it’s not surprising that midlife and older adults are exploring new sexual practices or finding multiple sexual partners.
People may start new relationships later in life. Tint Media/Shutterstock It’s also possible midlife and older people have not had exposure to sexual health education in school or do not relate to current safe sex messages, which tend to be directed toward young people. Condoms may therefore seem unnecessary for people who aren’t trying to avoid pregnancy. Older people may also lack confidence negotiating safe sex or accessing STI screening.
Hidden sexual health needs
In contemporary life, the sex lives of older adults are largely invisible. Ageing and older bodies are often associated with loss of power and desirability, reflected in the stereotype of older people as asexual and in derogatory jokes about older people having sex.
With some exceptions, we see few positive representations of older sexual bodies in film or television.
Older people’s sexuality is also largely invisible in public policy. In a review of Australian policy relating to sexual and reproductive health, researchers found midlife and older adults were rarely mentioned.
Sexual health policy generally targets groups with the highest STI rates, which excludes most older people. As midlife and older adults are beyond childbearing years, they also do not feature in reproductive health policy. This means there is a general absence of any policy related to sex or sexual health among midlife or older adults.
Added to this, sexual health policy tends to be focused on risk rather than sexual wellbeing. Sexual wellbeing, including freedom and capacity to pursue pleasurable sexual experiences, is strongly associated with overall health and quality of life for adults of all ages. Including sexual wellbeing as a policy priority would enable a focus on safe and respectful sex and relationships across the adult life course.
Without this priority, we have limited knowledge about what supports sexual wellbeing as people age and limited funding for initiatives to engage with midlife or older adults on these issues.
Midlife and older adults may have limited knowledge about STIs. Southworks/Shutterstock How can we support sexual health and wellbeing for older adults?
Most STIs are easily treatable. Serious complications can occur, however, when STIs are undiagnosed and untreated over a long period. Untreated STIs can also be passed on to others.
Late diagnosis is not uncommon as some STIs can have no symptoms and many people don’t routinely screen for STIs. Older, heterosexual adults are, in general, less likely than other groups to seek regular STI screening.
For midlife or older adults, STIs may also be diagnosed late because some doctors do not initiate testing due to concerns they will cause offence or because they assume STI risk among older people is negligible.
Many doctors are reluctant to discuss sexual health with their older patients unless the patient explicitly raises the topic. However, older people can be embarrassed or feel awkward raising matters of sex.
Resources for health-care providers and patients to facilitate conversations about sexual health and STI screening with older patients would be a good first step.
To address rising rates of STIs among midlife and older adults, we also need to ensure sexual health promotion is targeted toward these age groups and improve accessibility of clinical services.
More broadly, it’s important to consider ways to ensure sexual wellbeing is prioritised in policy and practice related to midlife and older adulthood.
A comprehensive approach to older people’s sexual health, that explicitly places value on the significance of sex and intimacy in people’s lives, will enhance our ability to more effectively respond to sexual health and STI prevention across the life course.
Jennifer Power, Associate Professor and Principal Research Fellow, Australian Research Centre in Sex, Health and Society, La Trobe University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The How Not to Die Cookbook – by Dr. Michael Greger
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Dr. Greger’s “How Not To Die”, which is excellent and/but very science-dense.
This book is different, in that the science is referenced and explained throughout, but the focus is the recipes, and how to prepare delicious healthy food in accordance with the principles laid out in How Not To Die.
It also follows “Dr Greger’s Daily Dozen“, that is to say, the 12 specific things he advises we make sure to have every day, and thus helps us to include them in an easy, no-fuss fashion.
The recipes themselves are by Robin Robertson, and/but with plenty of notes by Dr Greger; they clearly collaborated closely in creating them.
The ingredients are all things one can find in any well-stocked supermarket, so unless you live in a food desert, you can make these things easily.
And yes, the foods are delicious too.
Bottom line: if you’re interested in cooking according to perhaps the most science-based dietary system out there, then this book is a top-tier choice.
Click here to check out The How Not To Die Cookbook, and live well!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: