Acid Reflux After Meals? Here’s How To Stop It Naturally
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Harvard-trained gastroenterologist Dr. Saurabh Sethi advises:
Calming it down
First of all, what it actually is and how it happens: acid reflux occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) doesn’t close properly, allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. Chronic acid reflux is known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Symptoms can include heartburn, an acid taste in the mouth, belching, bloating, sore throat, and a persistent cough—but most people do not get all of the symptoms, usually just some.
Things that help it acutely (as in, you can do them today and they will help today): consider skipping certain foods/substances like peppermint, tomatoes, chocolate, alcohol, and caffeine, which can worsen acid reflux. Eating smaller, more frequent meals instead of large ones and leaving a gap of 3–4 hours before lying down after meals can also help manage symptoms.
Things that can help it chronically (as in, you do them in an ongoing fashion and they will help in an ongoing fashion): lifestyle changes like quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, and wearing loose clothing can strengthen the LES. Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding large meals, especially close to bedtime, can also reduce symptoms. Elevating the upper body while sleeping (using a wedge pillow or raising the bed by 10–20°) can make a big difference.
Medications to avoid, if possible, include: aspirin, ibuprofen, and calcium channel blockers.
Some drinks you can enjoy that will help: drinking water can quickly dilute stomach acid and provide relief. Herbal teas like basil tea, fennel tea, and ginger tea are also effective. But notably: not peppermint tea! Since, as mentioned earlier, peppermint is a known trigger for acid reflux (despite peppermint’s usual digestion-improving properties).
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Coughing/Wheezing After Dinner? Here’s How To Fix It ← this is about acid reflux and more
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can you get sunburnt or UV skin damage through car or home windows?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When you’re in a car, train or bus, do you choose a seat to avoid being in the sun or do you like the sunny side?
You can definitely feel the sun’s heat through a window. But can you get sunburn or skin damage when in your car or inside with the windows closed?
Let’s look at how much UV (ultraviolet) radiation passes through different types of glass, how tinting can help block UV, and whether we need sunscreen when driving or indoors.
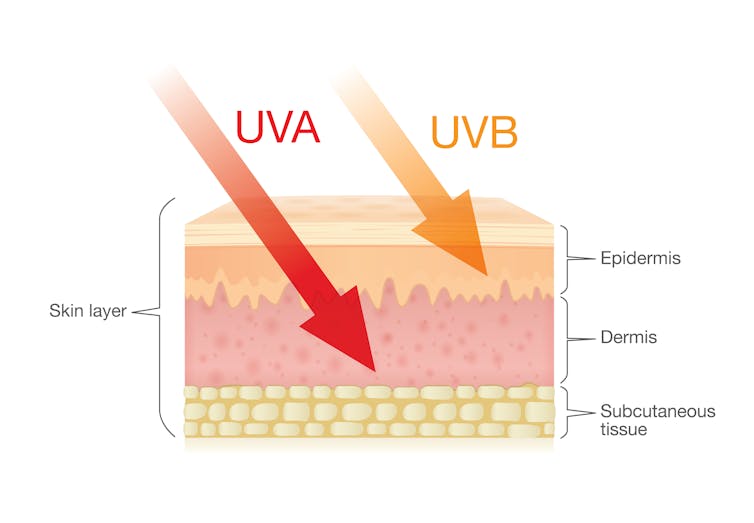
Zac Harris/Unsplash What’s the difference between UVA and UVB?
Of the total UV radiation that reaches Earth, about 95% is UVA and 5% is UVB.
UVB only reaches the upper layers of our skin but is the major cause of sunburn, cataracts and skin cancer.
UVA penetrates deeper into our skin and causes cell damage that leads to skin cancer.
UVA penetrates deeper than UVB. Shutterstock/solar22 Glass blocks UVA and UVB radiation differently
All glass used in house, office and car windows completely blocks UVB from passing through.
But only laminated glass can completely block UVA. UVA can pass through other glass used in car, house and office windows and cause skin damage, increasing the risk of cancer.
Car windscreens block UVA, but the side and rear windows don’t
A car’s front windscreen lets in lots of sunshine and light. Luckily it blocks 98% of UVA radiation because it is made of two layers of laminated glass.
But the side and rear car windows are made of tempered glass, which doesn’t completely block UVA. A study of 29 cars found a range from 4% to almost 56% of UVA passed through the side and rear windows.
The UVA protection was not related to the car’s age or cost, but to the type of glass, its colour and whether it has been tinted or coated in a protective film. Grey or bronze coloured glass, and window tinting, all increase UVA protection. Window tinting blocks around 95% of UVA radiation.
In a separate study from Saudi Arabia, researchers fitted drivers with a wearable radiation monitor. They found drivers were exposed to UV index ratings up to 3.5. (In Australia, sun protection is generally recommended when the UV index is 3 or above – at this level it takes pale skin about 20 minutes to burn.)
So if you have your windows tinted, you should not have to wear sunscreen in the car. But without tinted windows, you can accumulate skin damage.
UV exposure while driving increases skin cancer risk
Many people spend a lot of time in the car – for work, commuting, holiday travel and general transport. Repeated UVA radiation exposure through car side windows might go unnoticed, but it can affect our skin.
Indeed, skin cancer is more common on the driver’s side of the body. A study in the United States (where drivers sit on the left side) found more skin cancers on the left than the right side for the face, scalp, arm and leg, including 20 times more for the arm.
Another US study found this effect was higher in men. For melanoma in situ, an early form of melanoma, 74% of these cancers were on the on the left versus 26% on the right.
Earlier Australian studies reported more skin damage and more skin cancer on the right side.
Cataracts and other eye damage are also more common on the driver’s side of the body.
What about UV exposure through home or office windows?
We see UV damage from sunlight through our home windows in faded materials, furniture or plastics.
Most glass used in residential windows lets a lot of UVA pass through, between 45 and 75%.
Residential windows can let varied amounts of UVA through. Sherman Trotz/Pexels Single-pane glass lets through the most UVA, while thicker, tinted or coated glass blocks more UVA.
The best options are laminated glass, or double-glazed, tinted windows that allow less than 1% of UVA through.
Skylights are made from laminated glass, which completely stops UVA from passing through.
Most office and commercial window glass has better UVA protection than residential windows, allowing less than 25% of UVA transmission. These windows are usually double-glazed and tinted, with reflective properties or UV-absorbent chemicals.
Some smart windows that reduce heat using chemical treatments to darken the glass can also block UVA.
So when should you wear sunscreen and sunglasses?
The biggest risk with skin damage while driving is having the windows down or your arm out the window in direct sun. Even untinted windows will reduce UVA exposure to some extent, so it’s better to have the car window up.
For home windows, window films or tint can increase UVA protection of single pane glass. UVA blocking by glass is similar to protection by sunscreen.
When you need to use sunscreen depends on your skin type, latitude and time of the year. In a car without tinted windows, you could burn after one hour in the middle of the day in summer, and two hours in the middle of a winter’s day.
But in the middle of the day next to a home window that allows more UVA to pass through, it could take only 30 minutes to burn in summer and one hour in winter.
When the UV index is above three, it is recommended you wear protective sunglasses while driving or next to a sunny window to avoid eye damage.
Theresa Larkin, Associate Professor of Medical Sciences, University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Hit A Weight Loss Plateau? Here’s What To Do
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Around this time of year (early April, at time of writing) it’s especially common for people to hit a plateau in our progress towards various goals.
When it comes to weight loss specifically, a large (n=24,035) study of mostly women (19.972/24,035 = 83.09%) aged 31–70 (with more than half being in the 51–70 range) has good news about this:
Most people who sustainably lose weight weight over the course of a year, have a plateau at some point, usually at least one three-month plateau.
The top three weight loss patterns were:
- 15% lost weight for 6 months, then maintained their weight for a further 6 months, resulting in an average 11kg weight loss after a year (12% of their starting body weight)
- 11% lost weight in the first 3 months, then maintained for 9 months, losing 5kg after a year (nearly 6% of their starting body weight)
- 9% lost weight for 9 months, followed by 3 months of maintenance, resulting in an average 16kg loss (17% of their starting body weight)
You can read the full paper here: Weight Loss Patterns and Outcomes Over 12 Months on a Commercial Weight Management Program (CSIRO Total Wellbeing Diet Online): Large-Community Cohort Evaluation Study
Did you notice the reframe there? What may be seen (and not welcomed) by the individual is a plateau, but what it also is objectively, is weight loss maintenance. In other words, not regaining weight, as we all know can be all too easy for many.
You may be thinking: “but I want to continue losing weight!”
And that’s fine. The trick is to use the maintenance phase (or plateau, if you want to call it that) as an opportunity to assess what’s working for you and what’s not, and where you want to go from here.
The chances are good that your metabolism has simply adapted to whatever diet/exercises changes you made to your lifestyle… And that’s good!
Three months ago, you wanted your body to have this new “set point”, and now you have it. Congratulations on the improved metabolism!
Now, imagine yourself starting again, but this time you’re starting with a better metabolism than last time you started. What will you do next to up the ante?
Whatever you do, we recommend making sure to do it healthily, for example: How To Lose Weight (Healthily!)
You might even want to coast for a little in a maintenance phase, and use the opportunity to improve related areas of your health, before diving back into your next weight loss phase.
For example, you might want to: Stop Trying To Lose Weight (And Do This Instead) ← this is about metabolic health in a more general fashion, and is very important
Alternatively, you might want to take the opportunity to build a little muscle (which in turn will improve your metabolic health, because muscle “costs” calories to maintain, while fat cues your body to dial down the metabolism to survive the famine for which it thinks you were preparing).
If you want to do that, then check out: Can You Gain Muscle & Lose Fat At The Same Time?
And if at any point your weight loss journey (or perhaps a plateau somewhere along such) is getting you down, then… You know the saying “have fun and be yourself”? The trick here is to have fun and be your best self. Seriously! Mindset is actually really important, not just for your mental health, but also for your physical health, and yes, also for weight loss specifically, if that’s your goal.
See: 8 Pillars of Weight Loss Explained ← Surprise, diet is #6 and exercise is #7, while emotional freedom and resilience is #1 😎
Want to know more?
Check out this trio of articles that’ll keep you on the right path:
- How To Plan For The Unplannable & Always Follow Through
- How To Avoid Slipping Into (Bad) Old Habits
- How To Keep On Keeping On… Long Term!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Wildfires ignite infection risks, by weakening the body’s immune defences and spreading bugs in smoke
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Over the past several days, the world has watched on in shock as wildfires have devastated large parts of Los Angeles.
Beyond the obvious destruction – to landscapes, homes, businesses and more – fires at this scale have far-reaching effects on communities. A number of these concern human health.
We know fire can harm directly, causing injuries and death. Tragically, the death toll in LA is now at least 24.
But wildfires, or bushfires, can also have indirect consequences for human health. In particular, they can promote the incidence and spread of a range of infections.
Effects on the immune system
Most people appreciate that fires can cause burns and smoke inhalation, both of which can be life-threatening in their own right.
What’s perhaps less well known is that both burns and smoke inhalation can cause acute and chronic changes in the immune system. This can leave those affected vulnerable to infections at the time of the injury, and for years to come.
Burns induce profound changes in the immune system. Some parts go into overdrive, becoming too reactive and leading to hyper-inflammation. In the immediate aftermath of serious burns, this can contribute to sepsis and organ failure.
Other parts of the immune system appear to be suppressed. Our ability to recognise and fight off bugs can be compromised after sustaining burns. Research shows people who have experienced serious burns have an increased risk of influenza, pneumonia and other types of respiratory infections for at least the first five years after injury compared to people who haven’t experienced burns.
Wildfire smoke is a complex mixture containing particulate matter, volatile organic compounds, ozone, toxic gases, and microbes. When people inhale smoke during wildfires, each of these elements can play a role in increasing inflammation in the airways, which can lead to increased susceptibility to respiratory infections and asthma.
Research published after Australia’s Black Summer of 2019–20 found a higher risk of COVID infections in areas of New South Wales where bushfires had occurred weeks earlier.
We need more research to understand the magnitude of these increased risks, how long they persist after exposure, and the mechanisms. But these effects are thought to be due to sustained changes to the immune response.
Microbes travel in smoky air
Another opportunity for infection arises from the fire-induced movement of microbes from niches they usually occupy in soils and plants in natural areas, into densely populated urban areas.
Recent evidence from forest fires in Utah shows microbes, such as bacteria and fungal spores, can be transported in smoke. These microbes are associated with particles from the source, such as burned vegetation and soil.
There are thousands of different species of microbes in smoke, many of which are not common in background, non-smoky air.
Only a small number of studies on this have been published so far, but researchers have shown the majority of microbes in smoke are still alive and remain alive in smoke long enough to colonise the places where they eventually land.
How far specific microbes can be transported remains an open question, but fungi associated with smoke particles have been detected hundreds of miles downwind from wildfires, even weeks after the fire.
So does this cause human infections?
A subset of these airborne microbes are known to cause infections in humans.
Scientists are probing records of human fungal infections in relation to wildfire smoke exposure. In particular, they’re looking at soil-borne infectious agents such as the fungi Coccidioides immitis and Coccidioides posadasii which thrive in dry soils that can be picked up in dust and smoke plumes.
These fungi cause valley fever, a lung infection with symptoms that can resemble the flu, across arid western parts of the United States.
A study of wildland firefighters in California showed high rates of valley fever infections, which spurred occupational health warnings including recommended use of respirators when in endemic regions.
A California-based study of the wider population showed a 20% increase in hospital admissions for valley fever following any amount of exposure to wildfire smoke.
However, another found only limited evidence of excess cases after smoke exposure in wildfire-adjacent populations in California’s San Joaquin Valley.
These contrasting results show more research is needed to evaluate the infectious potential of wildfire smoke from this and other fungal and bacterial causes.
Staying safe
Much remains to be learned about the links between wildfires and infections, and the multiple pathways by which wildfires can increase the risk of certain infections.
There’s also a risk people gathering together after a disaster like this, such as in potentially overcrowded shelters, can increase the transmission of infections. We’ve seen this happen after previous natural disasters.
Despite the gaps in our knowledge, public health responses to wildfires should encompass infection prevention (such as through the provision of effective masks) and surveillance to enable early detection and effective management of any outbreaks.
Christine Carson, Senior Research Fellow, School of Medicine, The University of Western Australia and Leda Kobziar, Professor of Wildland Fire Science, University of Idaho
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Knee Cracking & Popping: Should You Be Worried?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Tom Walters (Doctor of Physical Therapy) explains about what’s going on behind our musical knees, and whether or not this synovial symphony is cause for concern.
When to worry (and when not to)
If the clicking/cracking/popping/etc does not come with pain, then it is probably being caused by the harmless movement of fluid within the joints, in this case specifically the patellofemoral joint, just behind the kneecap.
As Dr. Walters says:
❝It is extremely important that people understand that noises from the knee are usually not associated with pathology and may actually be a sign of a healthy, well-lubricated joint. let’s be careful not to make people feel bad about their knee noise as it can negatively influence how they view their body!❞
On the other hand, there is also such a thing as patellofemoral joint pain syndrome (PFPS), which is very common, and involves pain behind the kneecap, especially upon over-stressing the knee(s).
In such cases, it is good to get that checked out by a doctor/physiotherapist.
Dr. Walters advises us to gradually build up strength, and not try for too much too quickly. He also advises us to take care to strengthen our glutes in particular, so our knees have adequate support. Gentle stretching of the quadriceps and soft tissue mobilization with a foam roller, are also recommended, to reduce tension on the kneecap.
For more on these things and especially about the exercises, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
How To Really Take Care Of Your Joints
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Do You Know These 10 Common Ovarian Cancer Symptoms?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s better to know in advance:
Things you may need to know
The symptoms listed in the video are:
- Abdominal bloating: persistent bloating due to fluid buildup, often mistaken for overeating or weight gain.
- Pelvic or abdominal pain: continuous pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis, unrelated to menstruation.
- Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly: loss of appetite or feeling full after eating only a small amount.
- Urgent or frequent urination: increased need to urinate due to tumor pressure on the bladder.
- Unexplained weight loss: sudden weight loss without changes in diet or exercise (this goes for cancer in general, of course).
- Fatigue: extreme tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest, possibly linked to anemia.
- Back pain: persistent lower back pain due to tumor pressure or fluid buildup.
- Changes in bowel habits: unexplained constipation, diarrhea, or a feeling of incomplete bowel movements.
- Menstrual changes: irregular, heavier, lighter, or missed periods in premenopausal women.
- Pain during intercourse: discomfort or deep pelvic pain during or after vaginal sex—often overlooked!
Of course, some of those things can be caused by many things, but it’s worth getting it checked out, especially if you have a cluster of them together. Even if it’s not ovarian cancer (and hopefully it won’t be), having multiple things from this list certainly means that “something wrong is not right” in any case.
For those who remember better from videos than what you read, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Delicious Quinoa Avocado Bread
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
They’re gluten-free, full of protein and healthy fats, generous with the fiber, easy to make, and tasty too! What’s not to love? Keep this recipe (and its ingredients) handy for next time you want healthy burger buns or similar:
You will need
- 2½ cups quinoa flour
- 2 cups almond flour (if allergic, just substitute more quinoa flour)
- 1 avocado, peeled, pitted, and mashed
- zest and juice of 1 lime
- 2 tbsp ground flaxseed
- 1 tsp baking powder
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Optional: seeds, oats, or similar for topping the buns
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 350℉/175℃.
2) Mix the flaxseed with ⅓ cup warm water and set aside.
3) Mix, in a large bowl, the quinoa flour and almond flour with the baking powder and the MSG or salt.
4) Mix, in a separate smaller bowl, the avocado and lime.
5) Add the wet ingredients to the dry, slowly, adding an extra ½ cup water as you do, and knead into a dough.
6) Divide the dough into 4 equal portions, each shaped into a ball and then slightly flattened, to create a burger bun shape. If you’re going to add any seeds or similar as a topping, add those now.
7) Bake them in the oven (on a baking sheet lined with baking paper) for 20–25 minutes. You can check whether they’re done the same way you would a cake, by piercing them to the center with a toothpick and seeing whether it comes out clean.
8) Serve when sufficiently cooled.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Gluten: What’s The Truth?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: