Should You Soak Your Nuts?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝hi. how many almonds should one eat per day? do they need to be soaked? thank you.❞
Within reason, however many you like! Given that protein is an appetite suppressant, you’ll probably find it’s not too many.
Dr. Michael Greger, of “How Not To Die” fame, suggests aiming for 30g of nuts per day. Since almonds typically weigh about 1g each, that means 30 if it’s all almonds.
And if you’re wondering about 10 almonds? The name’s a deliberate reference to an old internet hoax about 10 almonds being the equivalent of an aspirin for treating a headache. It’s a reminder to be open-mindedly skeptical about information circulating wildly, and look into the real, evidence-based, science of things.
- Sometimes, the science validates claims, and we’re excited to share that!
- Sometimes, the science just shoots claims down, and it’s important to acknowledge when that happens too.
On which note, about soaking…
Short version: soaking can improve the absorption of some nutrients, but not much more than simply chewing thoroughly. See:
- A review of the impact of processing on nutrient bioaccessibility and digestion of almonds
- Mastication of almonds: effects of lipid bioaccessibility, appetite, and hormone response
Soaking does reduce certain “antinutrients” (compounds that block absorption of other nutrients), such as phytic acid. However, even a 24-hour soak reduces them only by about 5%:
If you don’t want to take 24-hours to get a 5% benefit, there’s good news! A 12-hour soak can result in 4% less phytic acid in chopped (but not whole) almonds:
The Effect of Soaking Almonds and Hazelnuts on Phytate and Mineral Concentrations
Lest that potentially underwhelming benefit leave a bitter taste in your mouth, one good thing about soaking almonds (if you don’t like bitter tastes, anyway) is that it will reduce their bitterness:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hello Sleep – by Dr. Jade Wu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed other sleep books before, so what makes this one stand out?
Mostly, it’s because this one takes quite a different approach.
While still giving a nod to the sensible advice you’ve already read in many places (including here at 10almonds), Dr. Wu looks to help the reader avoid falling into the trap (or: help the reader get out of the trap, if already there) of focussing so much on getting better sleep that it becomes an all-consuming stressor that takes up much of the day thinking about it, and guess what, much of the night too, because you’re busy working out how sleep-deprived you’re going to be tomorrow.
Instead, Dr. Wu recommends to work with your body rather than against it, worry less, and ultimately sleep better. Of course, the “how” of this is what makes most of the book.
She does also give chapters on things that may be different for you, based on such things as hormones, age, or medical conditions.
The writing style is pop-science but with frequent references to scientific papers as appropriate, making good science very accessible.
Bottom line: if you’ve tried everything else and/but good sleep still eludes you, this book will help you to end the battle and make friends with your sleep (a metaphor the author uses throughout the book, by the way).
Click here to check out Hello Sleep, and indeed get better sleep!
Share This Post
-
The Cold Truth About Respiratory Infections
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Pathogens That Came In From The Cold
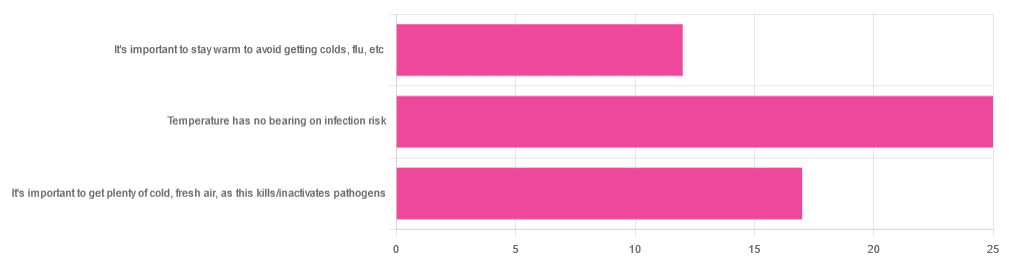
Yesterday, we asked you about your climate-themed policy for avoiding respiratory infections, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of answers:
- About 46% of respondents said “Temperature has no bearing on infection risk”
- About 31% of respondents said “It’s important to get plenty of cold, fresh air, as this kills/inactivates pathogens”
- About 22% of respondents said “It’s important to stay warm to avoid getting colds, flu, etc”
Some gave rationales, including…
For “stay warm”:
❝Childhood lessons❞
For “get cold, fresh air”:
❝I just feel that it’s healthy to get fresh air daily. Whether it kills germs, I don’t know❞
For “temperature has no bearing”:
❝If climate issue affected respiratory infections, would people in the tropics suffer more than those in colder climates? Pollutants may affect respiratory infections, but I doubt just temperature would do so.❞
So, what does the science say?
It’s important to stay warm to avoid getting colds, flu, etc: True or False?
False, simply. Cold weather does increase the infection risk, but for reasons that a hat and scarf won’t protect you from. More on this later, but for now, let’s lay to rest the idea that bodily chilling will promote infection by cold, flu, etc.
In a small-ish but statistically significant study (n=180), it was found that…
❝There was no evidence that chilling caused any acute change in symptom scores❞
Read more: Acute cooling of the feet and the onset of common cold symptoms
Note: they do mention in their conclusion that chilling the feet “causes the onset of cold symptoms in about 10% of subjects who are chilled”, but the data does not support that conclusion, and the only clear indicator is that people who are more prone to colds generally, were more prone to getting a cold after a cold water footbath.
In other words, people who were more prone to colds remained more prone to colds, just the same.
It’s important to get plenty of cold, fresh air, as this kills/inactivates pathogens: True or False?
Broadly False, though most pathogens do have an optimal operating temperature that (for obvious reasons) is around normal human body temperature.
However, given that they don’t generally have to survive outside of a host body for long to get passed on, the fact that the pathogens may be a little sluggish in the great outdoors will not change the fact that they will be delighted by the climate in your respiratory tract as soon as you get back into the warm.
With regard to the cold air not being a reliable killer/inactivator of pathogens, we call to the witness stand…
Polar Bear Dies From Bird Flu As H5N1 Spreads Across Globe
(it was found near Utqiagvik, one of the northernmost communities in Alaska)
Because pathogens like human body temperature, raising the body temperature is a way to kill/inactivate them: True or False?
True! Unfortunately, it’s also a way to kill us. Because we, too, cannot survive for long above our normal body temperature.
So, for example, bundling up warmly and cranking up the heating won’t necessarily help, because:
- if the temperature is comfortable for you, it’s comfortable for the pathogen
- if the temperature is dangerous to the pathogen, it’s dangerous to you too
This is why the fever response evolved, and/but why many people with fevers die anyway. It’s the body’s way of playing chicken with the pathogen, challenging “guess which of us can survive this for longer!”
Temperature has no bearing on infection risk: True or False?
True and/or False, circumstantially. This one’s a little complex, but let’s break it down to the essentials.
- Temperature has no direct effect, for the reasons we outlined above
- Temperature is often related to humidity, which does have an effect
- Temperature does tend to influence human behavior (more time spent in open spaces with good ventilation vs more time spent in closed quarters with poor ventilation and/or recycled air), which has an obvious effect on transmission rates
The first one we covered, and the third one is self-evident, so let’s look at the second one:
Temperature is often related to humidity, which does have an effect
When the environmental temperature is warmer, water droplets in the air will tend to be bigger, and thus drop to the ground much more quickly.
When the environmental temperature is colder, water droplets in the air will tend to be smaller, and thus stay in the air for longer (along with any pathogens those water droplets may be carrying).
Some papers on the impact of this:
- Cold temperature and low humidity are associated with increased occurrence of respiratory tract infections
- A Decrease in Temperature and Humidity Precedes Human Rhinovirus Infections in a Cold Climate
So whatever temperature you like to keep your environment, humidity is a protective factor against respiratory infections, and dry air is a risk factor.
So, for example:
- If the weather doesn’t suit having good ventilation, a humidifier is a good option
- Being in an airplane is one of the worst places to be for this, outside of a hospital
Don’t have a humidifier? Here’s an example product on Amazon, but by all means shop around.
A crock pot with hot water in and the lid off is also a very workable workaround too
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Best Form Of Sugar During Exercise
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝What is the best form of sugar for an energy kick during exercise? Both type of sugar eg glicoae fructose dextrose etc and medium, ie drink, gel, solids etc❞
Great question! Let’s be clear first that we’re going to answer this specifically for the context of during exercise.
Because, if you’re not actively exercising strenuously right at the time when you’re taking the various things we’re going to be talking about, the results will not be the same.
For scenarios that are anything less than “I am exercising right now and my muscles (not joints, or anything else) are feeling the burn”, then instead please see this:
Snacks & Hacks: Eating For Energy (In Ways That Actually Work)
Because, to answer your question, we’re going to be going 100% against the first piece of advice in that article, which was “Skip the quasi-injectables”, i.e., anything marketed as very quick release. Those things are useful for diabetics to have handy just in case of needing to urgently correct a hypo, but for most people most of the time, they’re not. See also:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
However…
When strenuously exercising in a way that is taxing our muscles, we do not have to worry about the usual problem of messing up our glucose metabolism by overloading our body with sugars faster than it can use it (thus: it has to hurriedly convert glucose and shove it anywhere it’ll fit to put it away, which is very bad for us), because right now, in the exercise scenario we’re describing, the body is already running its fastest metabolism and is grabbing glucose anywhere it can find it.
Which brings us to our first key: the best type of sugar for this purpose is glucose. Because:
- glucose: the body can use immediately and easily convert whatever’s spare to glycogen (a polysaccharide of glucose) for storage
- fructose: the body cannot use immediately and any conversion of fructose to glycogen has to happen in the liver, so if you take too much fructose (without anything to slow it down, such as the fiber in whole fruit), you’re not only not going to get usable energy (the sugar is just going to be there in your bloodstream, circulating, not getting used, because it doesn’t trigger insulin release and insulin is the gatekeeper that allows sugar to be used), but also, it’s going to tax the liver, which if done to excess, is how we get non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- sucrose: is just a disaccharide of glucose and fructose, so it first gets broken down into those, and then its constituent parts get processed as above. Other disaccharides you’ll see mentioned sometimes are maltose and lactose, but again, they’re just an extra step removed from useful metabolism, so to save space, we’ll leave it at that for those today.
- dextrose: is just glucose, but when the labeller is feeling fancy. It’s technically informational because it specifies what isomer of glucose it is, but basically all glucose found in food is d-glucose, i.e. dextrose. Other isomers of glucose can be synthesized (very expensively) in laboratories or potentially found in obscure places (the universe is vast and weird), but in short: unless someone’s going to extreme lengths to get something else, all glucose we encounter is dextrose, and all (absolutely all) dextrose is glucose.
We’d like to show scientific papers contesting these head-to-head for empirical proof, but since the above is basic chemistry and physiology, all we could find is papers taking this for granted and stating in their initial premise that sports drinks, gels, bars usually contain glucose as their main sugar, potentially with some fructose and sucrose. Like this one:
A Comprehensive Study on Sports and Energy Drinks
As for how to take it, again this is the complete opposite of our usual health advice of “don’t drink your calories”, because in this case, for once…
(and again, we must emphasize: only while actively doing strenuous exercise that is making specifically your muscles burn, not your joints or anything else; if your joints are burning you need to rest and definitely don’t spike your blood sugars because that will worsen inflammation)
…just this once, we do want those sugars to be zipping straight into the blood. Which means: liquid is best for this purpose.
And when we say liquid: gel is the same as a drink, so far as the body is concerned, provided the body in question is adequately hydrated (i.e., you are also drinking water).
Here are a pair of studies (by the same team, with the same general methodology), testing things head-to-head, with endurance cyclists on 6-hour stationary cycle rides:
CHO Oxidation from a CHO Gel Compared with a Drink during Exercise
Meanwhile, liquid beat solid, but only significantly so from the 90-minute mark onwards, and even that significant difference was modest (i.e. it’s clinically significant, it’s a statistically reliable result and improbable as random happenstance, but the actual size of the difference was not huge):
Oxidation of Solid versus Liquid CHO Sources during Exercise
We would hypothesize that the reason that liquids only barely outperformed solids for this task is precisely because the solids in question were also designed for the task. When a company makes a fast-release energy bar, they don’t load it with fiber to slow it down. Which differentiates this greatly from, say, getting one’s sugars from whole fruit.
If the study had compared apples to apple juice, we hypothesize the results would have been very different. But alas, if that study has been done, we couldn’t find it.
Today has been all about what’s best during exercise, so let’s quickly finish with a note on what’s best before and after:
Before: What To Eat, Take, And Do Before A Workout
After: Overdone It? How To Speed Up Recovery After Exercise
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Unlock Your Flexibility With These 4 New Stretches
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
People often stick to the same few stretches, which may limit flexibility progress, especially as the most common stretches often miss deeper, harder-to-reach areas.
So, here are some new (well, probably new to most people, at least) stretches that can get things moving in different directions:
Diversity Continues To Be Good!
The stretches are:
90/90 Hip stretch with a twist:
- Sit with your knees forming 90° angles; add an arm bar and twist your chest upward.
- Hold for 5 deep breaths and repeat.
- This one targets top glute muscles and quadratus lumborum in the lower back.
Shoulder mobility stretch using a wall:
- Kneel in front of a wall with your forearms placed shoulder-width apart, hands turned outward.
- Lift your hips, push your chest toward your legs, and use the wall and your body weight for deeper leverage.
- This one targets multiple shoulder and rotator cuff muscles through external rotation.
Quad stretch using body weight:
- Sit with your feet hip-width apart, lift your hips, step one foot back, and tuck in your tailbone.
- Focus on pointing your knee down and forward for a deep quad stretch.
- This one targets all four quad muscles, hip flexors, plantar fascia, and opens chest/shoulders.
Chicken wing stretch for upper back:
- Sit with bent knees, place the back of one hand on your waist (chicken wing position).
- Tuck the “wing” into the inner thigh, press your knee inward while resisting with the arm.
- This one broadens the shoulder blade and stretches rear shoulder/upper back muscles; it’s particularly effective for reaching difficult upper back areas not typically stretched.
For more on each of these plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Yoga Teacher: “If I wanted to get flexible in 2025, here’s what I’d do”
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Half Of Americans Over 50 Have Hemorrhoids, But They Can Be Prevented!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Hello. I was hoping you could give some useful tips about how to avoid a painful ailment that has affected Ernest Hemingway, Karl Marx, David Livingstone, Napoleon, Marilyn Monroe, King Alfred, and Martin Luther, and, I confess, me from time to time … namely, hemorrhoids. Help!❞
Firstly: that list could be a lot longer! We don’t have global stats, but in the US for example, half of adults over 50 have hemorrhoids.
So, you’re certainly not alone. People just don’t talk about it.
But, there are preventative things you can do:
Fiber, fiber, fiber. See also:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Hydrate, hydrate, hydrate.
This one’s simple enough. If you are dehydrated, constipation is more likely, and with it, hemorrhoids.
Watch your meds…
Some medications can cause constipation—painkillers containing codeine are a common culprit, for example.
When you go, go!
Not only can prolonged straining promote hemorrhoids, but also (if you’ll pardon the phrasing—there’s only so delicately we can say this) simply sitting with things partway “open” down there is not good for its health; things can quickly become irritated, and that can lead to hemorrhoids.
So: when you go, go. Leave your phone in another room!
Wash—but carefully.
Beyond your normal showering/bathing routine, a bidet is a great option for keeping things happy down there, if you have that option available to you.
However, if you have hemorrhoids, don’t use soap, as this can cause irritation and make it worse.
Warm water is fine, as is a salt bath, and pat dry and/or use gentle wet-wipes rather than rougher paper.
You can follow up with a hemorrhoid cream of your choice (or hydrocortisone, unless that’s contraindicated by another condition you have)
Know when to seek help
Hemorrhoids will usually go away by themselves if not exacerbated. But if it’s getting unduly difficult, and/or you’re bleeding down there, it’s time to see a doctor.
Note on bleeding: even if you’re 100% sure you have hemorrhoids, there are still other reasons you could be bleeding, and so it needs checking out.
Hemorrhoid treatment, if needed, will vary depending on severity. Beyond creams and lotions, there are other options that are less fun but sometimes necessary, including injections, electrotherapy, banding, or surgery.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Only walking for exercise? Here’s how to get the most out of it
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’re living longer than in previous generations, with one in eight elderly Australians now aged over 85. But the current gap between life expectancy (“lifespan”) and health-adjusted life expectancy (“healthspan”) is about ten years. This means many of us live with significant health problems in our later years.
To increase our healthspan, we need planned, structured and regular physical activity (or exercise). The World Health Organization recommends 150–300 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise – such as brisk walking, cycling and swimming – per week and muscle strengthening twice a week.
Yet few of us meet these recommendations. Only 10% meet the strength-training recommendations. Lack of time is one of the most common reasons.
Walking is cost-effective, doesn’t require any special equipment or training, and can be done with small pockets of time. Our preliminary research, published this week, shows there are ways to incorporate strength-training components into walking to improve your muscle strength and balance.
Why walking isn’t usually enough
Regular walking does not appear to work as muscle-strengthening exercise.
In contrast, exercises consisting of “eccentric” or muscle-lengthening contractions improve muscle strength, prevent muscle wasting and improve other functions such as balance and flexibility.
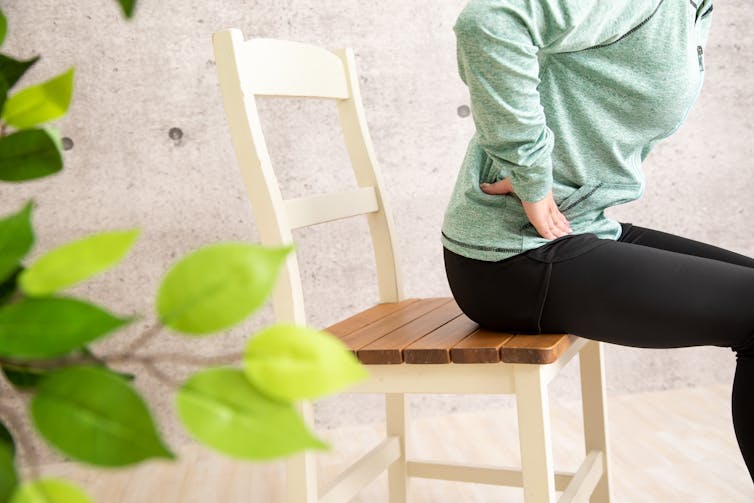
Typical eccentric contractions are seen, for example, when we sit on a chair slowly. The front thigh muscles lengthen with force generation.
When you sit down slowly on a chair, the front thigh muscles lengthen.
buritora/ShutterstockOur research
Our previous research found body-weight-based eccentric exercise training, such as sitting down on a chair slowly, improved lower limb muscle strength and balance in healthy older adults.
We also showed walking down stairs, with the front thigh muscles undergoing eccentric contractions, increased leg muscle strength and balance in older women more than walking up stairs. When climbing stairs, the front thigh muscles undergo “concentric” contractions, with the muscles shortening.
It can be difficult to find stairs or slopes suitable for eccentric exercises. But if they could be incorporated into daily walking, lower limb muscle strength and balance function could be improved.
This is where the idea of “eccentric walking” comes into play. This means inserting lunges in conventional walking, in addition to downstairs and downhill walking.
In our new research, published in the European Journal of Applied Physiology, we investigated the effects of eccentric walking on lower limb muscle strength and balance in 11 regular walkers aged 54 to 88 years.
The intervention period was 12 weeks. It consisted of four weeks of normal walking followed by eight weeks of eccentric walking.
The number of eccentric steps in the eccentric walking period gradually increased over eight weeks from 100 to 1,000 steps (including lunges, downhill and downstairs steps). Participants took a total of 3,900 eccentric steps over the eight-week eccentric walking period while the total number of steps was the same as the previous four weeks.
We measured the thickness of the participants’ front thigh muscles, muscle strength in their knee, their balance and endurance, including how many times they could go from a sitting position to standing in 30 seconds without using their arms. We took these measurements before the study started, at four weeks, after the conventional walking period, and at four and eight weeks into the eccentric walking period.
We also tested their cognitive function using a digit symbol-substitution test at the same time points of other tests. And we asked participants to complete a questionnaire relating to their activities of daily living, such as dressing and moving around at home.
Finally, we tested participants’ blood sugar, cholesterol levels and complement component 1q (C1q) concentrations, a potential marker of sarcopenia (muscle wasting with ageing).
Regular walking won’t contract your muscles in the same way as eccentric walking.
alexei_tm/ShutterstockWhat did we find?
We found no significant changes in any of the outcomes in the first four weeks when participants walked conventionally.
From week four to 12, we found significant improvements in muscle strength (19%), chair-stand ability (24%), balance (45%) and a cognitive function test (21%).
Serum C1q concentration decreased by 10% after the eccentric walking intervention, indicating participants’ muscles were effectively stimulated.
The sample size of the study was small, so we need larger and more comprehensive studies to verify our findings and investigate whether eccentric walking is effective for sedentary people, older people, how the different types of eccentric exercise compare and the potential cognitive and mental health benefits.
But, in the meantime, “eccentric walking” appears to be a beneficial exercise that will extend your healthspan. It may look a bit eccentric if we insert lunges while walking on the street, but the more people do it and benefit from it, the less eccentric it will become.
Ken Nosaka, Professor of Exercise and Sports Science, Edith Cowan University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: