The Exercises That Can Fix Sinus Problems (And More)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Who nose what benefits you will gain today?
This is James Nestor, a science journalist and author. He’s written for many publications, including Scientific American, and written a number of books, most notably Breath: The New Science Of A Lost Art.
Today we’ll be looking at what he has to share about what has gone wrong with our breathing, what problems this causes, and how to fix it.
What has gone wrong?
When it comes to breathing, we humans are the pugs of the primate world. In a way, we have the opposite problem to the squashed-faced dogs, though. But, how and why?
When our ancestors learned first tenderize food, and later to cook it, this had two big effects:
- We could now get much more nutrition for much less hunting/gathering
- We now did not need to chew our food nearly so much
Getting much more nutrition for much less hunting/gathering is what allowed us to grow our brains so large—as a species, we have a singularly large brain-to-body size ratio.
Not needing to chew our food nearly so much, meanwhile, had even more effects… And these effects have become only more pronounced in recent decades with the rise of processed food making our food softer and softer.
It changed the shape of our jaw and cheekbones, just as the size of our brains taking up more space in our skull moved our breathing apparatus around. As a result, our nasal cavities are anatomically ridiculous, our sinuses are a crime against nature (not least of all because they drain backwards and get easily clogged), and our windpipes are very easily blocked and damaged due to the unique placement of our larynx; we’re the only species that has it there. It allowed us to develop speech, but at the cost of choking much more easily.
What problems does this cause?
Our (normal, to us) species-wide breathing problems have resulted in behavioral adaptations such as partial (or in some people’s cases, total or near-total) mouth-breathing. This in turn exacerbates the problems with our jaws and cheekbones, which in turn exacerbates the problems with our sinuses and nasal cavities in general.
Results include such very human-centric conditions as sleep apnea, as well as a tendency towards asthma, allergies, and autoimmune diseases. Improper breathing also brings about a rather sluggish metabolism for how many calories we consume.
How are we supposed to fix all that?!
First, close your mouth if you haven’t already, and breathe through your nose.
In and out.
Both are important, and unless you are engaging in peak exercise, both should be through your nose. If you’re not used to this, it may feel odd at first, but practice, and build up your breathing ability.
Six seconds in and six seconds out is a very good pace.
If you’re sitting doing a breathing exercise, also good is four seconds in, four seconds hold, four seconds out, four seconds hold, repeat.
But those frequent holds aren’t practical in general life, so: six seconds in, six seconds out.
Through your nose only.
This has benefits immediately, but there are other more long-term benefits from doing not just that, but also what has been called (by Nestor, amongst many others), “Mewing”, per the orthodontist, Dr. John Mew, who pioneered it.
How (and why) to “mew”:
Place your tongue against the roof of your mouth. It should be flat against the palate; you’re not touching it with the tip here; you’re creating a flat seal.
Note: if you were mouth-breathing, you will now be unable to breathe. So, important to make sure you can breathe adequately through your nose first.
This does two things:
- It obliges nose-breathing rather than mouth-breathing
- It creates a change in how the muscles of your face interact with the bones of your face
In a battle between muscle and bone, muscle will always win.
Aim to keep your tongue there as much as possible; make it your new best habit. If you’re not eating, talking, or otherwise using your tongue to do something, it should be flat against the roof of your mouth.
You don’t have to exert pressure; this isn’t an exercise regime. Think of it more as a postural exercise, just, inside your mouth.
Quick note: read the above line again, because it’s important. Doing it too hard could cause the opposite problems, and you don’t want that. You cannot rush this by doing it harder; it takes time and gentleness.
Why would we want to do that?
The result, over time, will tend to be much healthier breathing, better sinus health, freer airways, reduced or eliminated sleep apnea, and, as a bonus, what is generally considered a more attractive face in terms of bone structure. We’re talking more defined cheekbones, straighter teeth, and a better mouth position.
Want to learn more?
This is the “Mewing” technique that Nestor encourages us to try:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
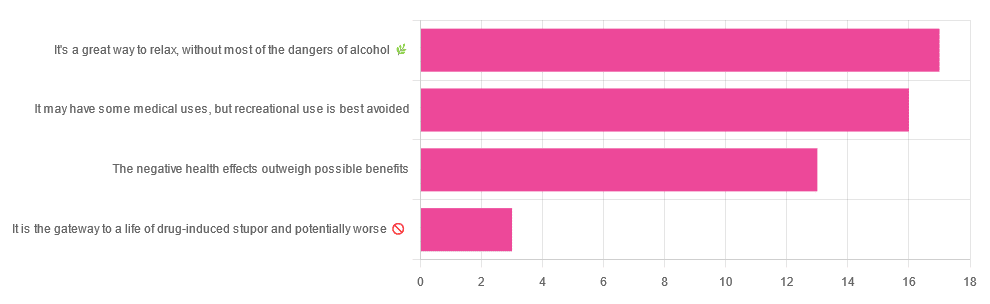
We asked you for your (health-related) opinion on cannabis use—specifically, the kind with psychoactive THC, not just CBD. We got the above-pictured, below-described, spread of responses:
- A little over a third of you voted for “It’s a great way to relax, without most of the dangers of alcohol”.
- A little under a third of you voted for “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”.
- About a quarter of you voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits”
- Three of you voted for “It is the gateway to a life of drug-induced stupor and potentially worse”
So, what does the science say?
A quick legal note first: we’re a health science publication, and are writing from that perspective. We do not know your location, much less your local laws and regulations, and so cannot comment on such. Please check your own local laws and regulations in that regard.
Cannabis use can cause serious health problems: True or False?
True. Whether the risks outweigh the benefits is a personal and subjective matter (for example, a person using it to mitigate the pain of late stage cancer is probably unconcerned with many other potential risks), but what’s objectively true is that it can cause serious health problems.
One subscriber who voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits” wrote:
❝At a bare minimum, you are ingesting SMOKE into your lungs!! Everyone SEEMS TO BE against smoking cigarettes, but cannabis smoking is OK?? Lung cancer comes in many forms.❞
Of course, that is assuming smoking cannabis, and not consuming it as an edible. But, what does the science say on smoking it, and lung cancer?
There’s a lot less research about this when it comes to cannabis, compared to tobacco. But, there is some:
❝Results from our pooled analyses provide little evidence for an increased risk of lung cancer among habitual or long-term cannabis smokers, although the possibility of potential adverse effect for heavy consumption cannot be excluded.❞
Read: Cannabis smoking and lung cancer risk: Pooled analysis in the International Lung Cancer Consortium
Another study agreed there appears to be no association with lung cancer, but that there are other lung diseases to consider, such as bronchitis and COPD:
❝Smoking cannabis is associated with symptoms of chronic bronchitis, and there may be a modest association with the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Current evidence does not suggest an association with lung cancer.❞
Read: Cannabis Use, Lung Cancer, and Related Issues
Cannabis edibles are much safer than smoking cannabis: True or False?
Broadly True, with an important caveat.
One subscriber who selected “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”, wrote:
❝I’ve been taking cannabis gummies for fibromyalgia. I don’t know if they’re helping but they’re not doing any harm. You cannot overdose you don’t become addicted.❞
Firstly, of course consuming edibles (rather than inhaling cannabis) eliminates the smoke-related risk factors we discussed above. However, other risks remain, including the much greater ease of accidentally overdosing.
❝Visits attributable to inhaled cannabis are more frequent than those attributable to edible cannabis, although the latter is associated with more acute psychiatric visits and more ED visits than expected.❞
Note: that “more frequent” for inhaled cannabis, is because more people inhale it than eat it. If we adjust the numbers to control for how much less often people eat it, suddenly we see that the numbers of hospital admissions are disproportionately high for edibles, compared to inhaled cannabis.
Or, as the study author put it:
❝There are more adverse drug events associated on a milligram per milligram basis of THC when it comes in form of edibles versus an inhaled cannabis. If 1,000 people smoked pot and 1,000 people at the same dose in an edible, then more people would have more adverse drug events from edible cannabis.❞
See the numbers: Acute Illness Associated With Cannabis Use, by Route of Exposure
Why does this happen?
- It’s often because edibles take longer to take effect, so someone thinks “this isn’t very strong” and has more.
- It’s also sometimes because someone errantly eats someone else’s edibles, not realising what they are.
- It’s sometimes a combination of the above problems: a person who is now high, may simply forget and/or make a bad decision when it comes to eating more.
On the other hand, that doesn’t mean inhaling it is necessarily safer. As well as the pulmonary issues we discussed previously, inhaling cannabis has a higher risk of cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (and the resultant cyclic vomiting that’s difficult to treat).
You can read about this fascinating condition that’s sometimes informally called “scromiting”, a portmanteau of screaming and vomiting:
Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome
You can’t get addicted to cannabis: True or False?
False. However, it is fair to say that the likelihood of developing a substance abuse disorder is lower than for alcohol, and much lower than for nicotine.
See: Prevalence of Marijuana Use Disorders in the United States Between 2001–2002 and 2012–2013
If you prefer just the stats without the science, here’s the CDC’s rendering of that:
Addiction (Marijuana or Cannabis Use Disorder)
However, there is an interesting complicating factor, which is age. One is 4–7 times more likely to develop a substance abuse disorder, if one starts use as an adolescent, rather than later in life:
Cannabis is the gateway to use of more dangerous drugs: True or False?
False, generally speaking. Of course, for any population there will be some outliers, but there appears to be no meaningful causal relation between cannabis use and other substance use:
Interestingly, the strongest association (where any existed at all) was between cannabis use and opioid use. However, rather than this being a matter of cannabis use being a gateway to opioid use, it seems more likely that this is a matter of people looking to both for the same purpose: pain relief.
As a result, growing accessibility of cannabis may actually reduce opioid problems:
- Cannabis as a Gateway Drug for Opioid Use Disorder
- Association between medical cannabis laws and opioid overdose mortality has reversed over time
Some final words…
Cannabis is a complex drug with complex mechanisms and complex health considerations, and research is mostly quite young, due to its historic illegality seriously cramping science by reducing sample sizes to negligible. Simply put, there’s a lot we still don’t know.
Also, we covered some important topics today, but there were others we didn’t have time to cover, such as the other potential psychological benefits—and risks. Likely we’ll revisit those another day.
Lastly, while we’ve covered a bunch of risks today, those of you who said it has fewer and lesser risks than alcohol are quite right—the only reason we couldn’t focus on that more, is because to talk about all the risks of alcohol would make this feature many times longer!
Meanwhile, whether you partake or not, stay safe and stay well.
Share This Post
-
Yoga for Better Sleep – by Mark Stephens
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The book has, as you might expect:
- postural exercises
- breathing exercises
- meditation exercises
Instructions given in all of the above categories are clear and easy to follow, and there are photographic illustrations too where appropriate.
What sets it apart from many books of this kind is that it also has chapters dedicated to various specific circumstances; the many actual reasons people seriously struggle to sleep; not just “screentime too late”, but for example deprepression, sleep apnea, hyperarousal, or even just aging.
As well as the comprehensive exercises, there are also many tips, tricks, hacks, and workarounds—it’s a practical guidebook with practical advice.
While the book is about yogic practices, the author also does tackle this holistically, acknowledging that there are many factors going on, and that yogic practices should be one more string to our sleep-improving bow—as we continue with other general good advice for good sleep too, have medical tests if it seems appropriate, that kind of thing. Basically, to have one’s assorted approaches work together with synergistic effect.
Bottom line: this book will quite possibly put you to sleep! But only in the best possible way.
Click here to check out Yoga for Better Sleep, and get those valuable Zs in, healthily!
Share This Post
-
Glucose Revolution – by Jessie Inchauspé
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
While we all know that keeping balanced blood sugars is important for all us (be we diabetic, pre-diabetic, or not at all), it can be a mystifying topic!
Beyond a generic “sugar is bad”…
- What does it all mean and how does it all work?
- Should we go low-carb?
- What’s the deal with fruit?
- Carbs or protein for breakfast?
- Is “quick energy” ever a good thing?
- How do starches weigh in again?
It’s all so confusing!
Happily, Jessie Inchauspé has the incredible trifecta of qualifications to help us: she’s a biochemist, a keen cook, and a great educator. What we mean by this latter is:
Instead of dry textbook explanations, or “trust me” hand-waives, she explains biochemistry in a clear, simple, digestible (if you’ll pardon the pun) way with very helpful diagrams what things cause (or flatten) blood sugar spikes and how and why. If you read this book, you will understand, without guesswork or gaps, exactly what is happening on a physical level, and why and how her “10 hacks” work.
Her “10 hacks” are explained so thoroughly that each gets a chapter of its own, but we’ll not keep them a mystery from you meanwhile, they are:
- Eat foods in the right order
- Add a green starter to your meals
- Stop counting calories
- Flatten your breakfast curve
- Have any type of sugar you like—they’re all the same
- Pick dessert over a sweet snack
- Reach for the vinegar before you eat
- After you eat, move
- If you have to snack, go savoury
- Put some clothes on your carbs
She then finishes up with a collection of handy cheat-sheets and some of her own recipes.
Bottom line: this isn’t just a “how-to” book. It gives the how-to, yes, but it also gives such good explanations that you’ll never be confused again by what’s going on in your glucose-related health.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Aging with Grace – by Dr. David Snowdon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this book is not: a book about Christianity. Don’t worry, we didn’t suddenly change the theme of 10almonds.
Rather, what this book is: a book about a famous large (n=678) study into the biology of aging, that took a population sample of women who had many factors already controlled-for, e.g. they ate the same food, had the same schedule, did the same activities, etc—for many years on end. In other words, a convent of nuns.
This allowed for a lot more to be learned about other factors that influence aging, such as:
- Heredity / genetics in general
- Speaking more than one language
- Supplementing with vitamins or not
- Key adverse events (e.g. stroke)
- Key chronic conditions (e.g. depression)
The book does also cover (as one might expect) the role that community and faith can play in healthy longevity, but since the subjects were 678 communally-dwelling people of faith (thus: no control group of faithless loners), this aspect is discussed only in anecdote, or in reference to other studies.
The author of this book, by the way, was the lead researcher of the study, and he is a well-recognised expert in the field of Alzheimer’s in particular (and Alzheimer’s does feature quite a bit throughout).
The writing style is largely narrative, and/but with a lot of clinical detail and specific data; this is by no means a wishy-washy book.
Bottom line: if you’d like to know what nuns were doing in the 1980s to disproportionally live into three-figure ages, then this book will answer those questions.
Click here to check out Aging with Grace, and indeed age with grace!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Delicious Daily Daal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You’re not obliged to eat this every day, but you might want to. The reason we called this one this, is because it’s a super simple recipe (don’t be put off by the long ingredients list; it’s mostly spices making it look long) which, after you’ve done it a couple of times, you could practically do it in your sleep quickly and easily.
The name “lentil daal” is a bit like “naan bread”—a redundant tautology repeated more than once unnecessarily, but it helps for international clarity. The dish is usually served with naan, by the way, and rice. We don’t have room for those today, maybe we’ll do them another day; for now, you can just cook rice how you normally do, and buy naan if necessary.
Writer’s note: I love strong flavors; many people don’t. For this reason I’m going to give a “basic” version. Please feel free to multiply the spices if you feel so inclined. Where I give “one teaspoon” of a spice below, I’d use a tablespoon at home. Chili peppers can vary in heat a lot even within the same type, so what I do for any given batch is taste one (raw), judge the heat, and use an appropriate number of peppers accordingly. If you don’t want to do that, I suggest just guessing low (as per the instructions below) and if you find at the end you want more heat, you can always stir in a little hot sauce. I know that sounds heretical, but at the end of the day, the primary goal of cooking is to have the meal you want at the end of it.
You will need
- 1 1/2 cups red lentils
- 1 large onion, chopped
- 1 large bulb garlic, minced
- 1 oz ginger, grated
- 2 hot peppers (e.g. serrano), chopped
- 1 tsp ground cumin
- 1 tsp ground coriander
- 1 tsp ground turmeric
- 1 tsp garam masala (this is also ground, but it doesn’t come any other way)
- 1 tsp chili flakes (omit if you’re not a fan of heat)
- 2 tsp cracked black pepper
- 1 tsp salt ← I wouldn’t recommend multiplying this one unless later, to taste. In fact, instead of 1 tsp salt I use 2 tsp MSG, which has less sodium than 1 tsp salt. But “1 tsp salt” is the “easy to find in the store” version.
- 2 large or 3 small tomatoes, chopped (or 1 can chopped tomatoes)
- 2 shallots, thinly sliced
- 1 tsp cumin seeds
- 1 tsp mustard seeds
- 1 tsp coriander seeds
- 1 tsp black peppercorns
- 1 lime
- 1/2 cup fresh cilantro, or if you have the “that tastes like soap” gene, parsley, chopped
- Coconut oil for cooking (if you don’t like coconut, consider springing for avocado oil—if you use olive oil, it’ll add an olivey taste which changes the dish a lot; not inherently bad, but it feels a lot less like traditional daal; seed oils are less healthy and we don’t recommend them; ghee is a traditional option and not bad in moderation, but not as healthy as the oils we mentioned first)
- Water for cooking the lentils
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) In a saucepan, boil water and add the lentils; let them simmer while doing the next things.
2) Sauté the onions until translucent. This should only take a few minutes.
3) Add the garlic, ginger, and hot peppers, and keep stirring for another couple of minutes.
4) Add the ground spices (cumin, coriander, turmeric, garam masala) chili flakes, and cracked black pepper, as well as the salt or MSG if using (not both), and stir them in quickly but thoroughly.
For the next step, you may need to transfer to larger pan if your sauté pan isn’t big enough to take the volume; if so, that’s fine, the sauté has done its job and can have a rest now. If your sauté pan is big enough, just carry on in the same pan; this is perfect.
5) Add the lentils with the water you cooked them in (there might not be much water left now, as the lentils will have absorbed a lot of it; this is fine) as well as the chopped tomatoes.
6) Simmer until it has the consistency of a very thick sauce (you can add a splash more water here and there if it seems to need more). In the West it’s common to serve lentils “al dente”, but in the East it’s usual to (for dishes like this) cook them until they start to
7) Add the juice of at least 1/2 of your lime, or the whole lime if you feel so inclined.
8) In a pre-heated skillet, flash-fry the sliced shallots and the seeds (cumin, coriander, mustard, black peppercorns) at the hottest temperature you can muster. Don’t worry if the oil smokes; we’re only going to be at this tadka-making stage for a moment and nothing will stick provided you keep it moving. When the seeds start popping, it’s ready. Add it all to the big pan and stir in.
9) Add the cilantro-or-parsley garnish once you’re ready to serve.
Enjoy!
Learn more
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- How Much Spice Is Right?
- Tasty Polyphenols
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What happens to your vagina as you age?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The vagina is an internal organ with a complex ecosystem, influenced by circulating hormone levels which change during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, breastfeeding and menopause.
Around and after menopause, there are normal changes in the growth and function of vaginal cells, as well as the vagina’s microbiome (groups of bacteria living in the vagina). Many women won’t notice these changes. They don’t usually cause symptoms or concern, but if they do, symptoms can usually be managed.
Here’s what happens to your vagina as you age, whether you notice or not.
Let’s clear up the terminology
We’re focusing on the vagina, the muscular tube that goes from the external genitalia (the vulva), past the cervix, to the womb (uterus). Sometimes the word “vagina” is used to include the external genitalia. However, these are different organs and play different roles in women’s health.
What happens to the vagina as you age?
Like many other organs in the body, the vagina is sensitive to female sex steroid hormones (hormones) that change around puberty, pregnancy and menopause.
Menopause is associated with a drop in circulating oestrogen concentrations and the hormone progesterone is no longer produced. The changes in hormones affect the vagina and its ecosystem. Effects may include:
- less vaginal secretions, potentially leading to dryness
- less growth of vagina surface cells resulting in a thinned lining
- alteration to the support structure (connective tissue) around the vagina leading to less elasticity and more narrowing
- fewer blood vessels around the vagina, which may explain less blood flow after menopause
- a shift in the type and balance of bacteria, which can change vaginal acidity, from more acidic to more alkaline.
What symptoms can I expect?
Many women do not notice any bothersome vaginal changes as they age. There’s also little evidence many of these changes cause vaginal symptoms. For example, there is no direct evidence these changes cause vaginal infection or bleeding in menopausal women.
Some women notice vaginal dryness after menopause, which may be linked to less vaginal secretions. This may lead to pain and discomfort during sex. But it’s not clear how much of this dryness is due to menopause, as younger women also commonly report it. In one study, 47% of sexually active postmenopausal women reported vaginal dryness, as did around 20% of premenopausal women.
Other organs close to the vagina, such as the bladder and urethra, are also affected by the change in hormone levels after menopause. Some women experience recurrent urinary tract infections, which may cause pain (including pain to the side of the body) and irritation. So their symptoms are in fact not coming from the vagina itself but relate to changes in the urinary tract.
Not everyone has the same experience
Women vary in whether they notice vaginal changes and whether they are bothered by these to the same extent. For example, women with vaginal dryness who are not sexually active may not notice the change in vaginal secretions after menopause. However, some women notice severe dryness that affects their daily function and activities.
In fact, researchers globally are taking more notice of women’s experiences of menopause to inform future research. This includes prioritising symptoms that matter to women the most, such as vaginal dryness, discomfort, irritation and pain during sex.
If symptoms bother you
Symptoms such as dryness, irritation, or pain during sex can usually be effectively managed. Lubricants may reduce pain during sex. Vaginal moisturisers may reduce dryness. Both are available over-the-counter at your local pharmacy.
While there are many small clinical trials of individual products, these studies lack the power to demonstrate if they are really effective in improving vaginal symptoms.
In contrast, there is robust evidence that vaginal oestrogen is effective in treating vaginal dryness and reducing pain during sex. It also reduces your chance of recurrent urinary tract infections. You can talk to your doctor about a prescription.
Vaginal oestrogen is usually inserted using an applicator, two to three times a week. Very little is absorbed into the blood stream, it is generally safe but longer-term trials are required to confirm safety in long-term use beyond a year.
Women with a history of breast cancer should see their oncologist to discuss using oestrogen as it may not be suitable for them.
Are there other treatments?
New treatments for vaginal dryness are under investigation. One avenue relates to our growing understanding of how the vaginal microbiome adapts and modifies around changes in circulating and local concentrations of hormones.
For example, a small number of reports show that combining vaginal probiotics with low-dose vaginal oestrogen can improve vaginal symptoms. But more evidence is needed before this is recommended.
Where to from here?
The normal ageing process, as well as menopause, both affect the vagina as we age.
Most women do not have troublesome vaginal symptoms during and after menopause, but for some, these may cause discomfort or distress.
While hormonal treatments such as vaginal oestrogen are available, there is a pressing need for more non-hormonal treatments.
Dr Sianan Healy, from Women’s Health Victoria, contributed to this article.
Louie Ye, Clinical Fellow, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The University of Melbourne and Martha Hickey, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: