Homeopathy: Evidence So Tiny That It’s Not there?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Homeopathy: Evidence So Tiny That It’s Not There?
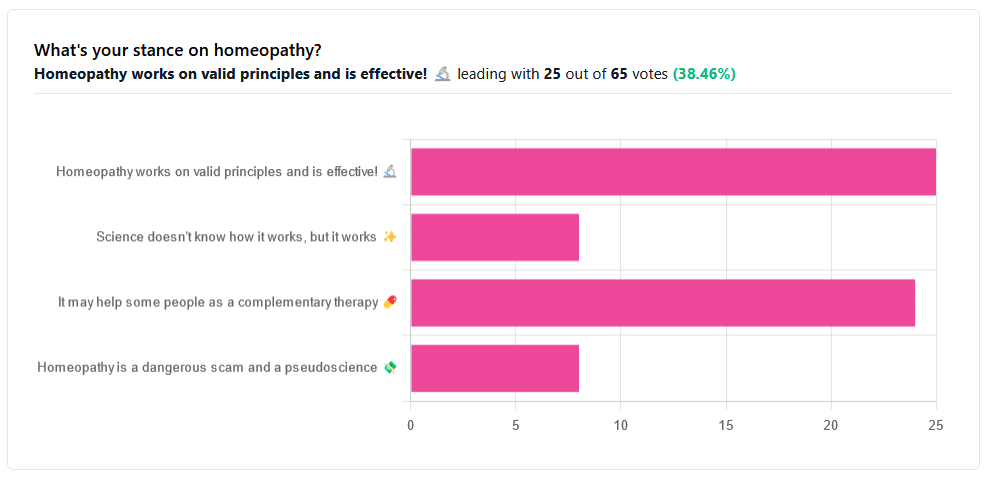
Yesterday, we asked you your opinions on homeopathy. The sample size of responses was a little lower than we usually get, but of those who did reply, there was a clear trend:
- A lot of enthusiasm for “Homeopathy works on valid principles and is effective”
- Near equal support for “It may help some people as a complementary therapy”
- Very few people voted for “Science doesn’t know how it works, but it works”; this is probably because people who considered voting for this, voted for the more flexible “It may help some people as a complementary therapy” instead.
- Very few people considered it a dangerous scam and a pseudoscience.
So, what does the science say?
Well, let us start our investigation by checking out the position of the UK’s National Health Service, an organization with a strong focus on providing the least expensive treatments that are effective.
Since homeopathy is very inexpensive to arrange, they will surely want to put it atop their list of treatments, right?
❝Homeopathy is a “treatment” based on the use of highly diluted substances, which practitioners claim can cause the body to heal itself.
There’s been extensive investigation of the effectiveness of homeopathy. There’s no good-quality evidence that homeopathy is effective as a treatment for any health condition.❞
The NHS actually has a lot more to say about that, and you can read their full statement here.
But that’s just one institution. Here’s what Australia’s National Health and Medical Research Council had to say:
❝There was no reliable evidence from research in humans that homeopathy was effective for treating the range of health conditions considered: no good-quality, well-designed studies with enough participants for a meaningful result reported either that homeopathy caused greater health improvements than placebo, or caused health improvements equal to those of another treatment❞
You can read their full statement here.
The American FDA, meanwhile, have a stronger statement:
❝Homeopathic drug products are made from a wide range of substances, including ingredients derived from plants, healthy or diseased animal or human sources, minerals and chemicals, including known poisons. These products have the potential to cause significant and even permanent harm if they are poorly manufactured, since that could lead to contaminated products or products that have potentially toxic ingredients at higher levels than are labeled and/or safe, or if they are marketed as substitute treatments for serious or life-threatening diseases and conditions, or to vulnerable populations.❞
You can read their full statement here.
Homeopathy is a dangerous scam and a pseudoscience: True or False?
False and True, respectively, mostly.
That may be a confusing answer, so let’s elaborate:
- Is it dangerous? Mostly not; it’s mostly just water. However, two possibilities for harm exist:
- Careless preparation could result in a harmful ingredient still being present in the water—and because of the “like cures like” principle, many of the ingredients used in homeopathy are harmful, ranging from heavy metals to plant-based neurotoxins. However, the process of “ultra-dilution” usually removes these so thoroughly that they are absent or otherwise scientifically undetectable.
- Placebo treatment has its place, but could result in “real” treatment going undelivered. This can cause harm if the “real” treatment was critically needed, especially if it was needed on a short timescale.
- Is it a scam? Probably mostly not; to be a scam requires malintent. Most practitioners probably believe in what they are practising.
- Is it a pseudoscience? With the exception that placebo effect has been highly studied and is a very valid complementary therapy… Yes, aside from that it is a pseudoscience. There is no scientific evidence to support homeopathy’s “like cures like” principle, and there is no scientific evidence to support homeopathy’s “water memory” idea. On the contrary, they go against the commonly understood physics of our world.
It may help some people as a complementary therapy: True or False?
True! Not only is placebo effect very well-studied, but best of all, it can still work as a placebo even if you know that you’re taking a placebo… Provided you also believe that!
Science doesn’t know how it works, but it works: True or False?
False, simply. At best, it performs as a placebo.
Placebo is most effective when it’s a remedy against subjective symptoms, like pain.
However, psychosomatic effect (the effect that our brain has on the rest of our body, to which it is very well-connected) can mean that placebo can also help against objective symptoms, like inflammation.
After all, our body, directed primarily by the brain, can “decide” what immunological defenses to deploy or hold back, for example. This is why placebo can help with conditions as diverse as arthritis (an inflammatory condition) or diabetes (an autoimmune condition, and/or a metabolic condition, depending on type).
Here’s how homeopathy measures up, for those conditions:
(the short answer is “no better than placebo”)
Homeopathy works on valid principles and is effective: True or False?
False, except insofar as placebo is a valid principle and can be effective.
The stated principles of homeopathy—”like cures like” and “water memory”—have no scientific basis.
We’d love to show the science for this, but we cannot prove a negative.
However, the ideas were conceived in 1796, and are tantamount to alchemy. A good scientific attitude means being open-minded to new ideas and testing them. In homeopathy’s case, this has been done, extensively, and more than 200 years of testing later, homeopathy has consistently performed equal to placebo.
In summary…
- If you’re enjoying homeopathic treatment and that’s working for you, great, keep at it.
- If you’re open-minded to enjoying a placebo treatment that may benefit you, be careful, but don’t let us stop you.
- If your condition is serious, please do not delay seeking evidence-based medical treatment.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What to Know About Stillbirths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Series: Stillbirths:When Babies Die Before Taking Their First Breath
The U.S. has not prioritized stillbirth prevention, and American parents are losing babies even as other countries make larger strides to reduce deaths late in pregnancy.
Every year, more than 20,000 pregnancies in the U.S. end in a stillbirth, the death of an expected child at 20 weeks or more of pregnancy. Research shows as many as 1 in 4 stillbirths may be preventable. We interviewed dozens of parents of stillborn children who said their health care providers did not tell them about risk factors or explain what to watch for while pregnant. They said they felt blindsided by what followed. They did not have the information needed to make critical decisions about what happened with their baby’s body, about what additional testing could have been done to help determine what caused the stillbirth, or about how to navigate the process of requesting important stillbirth documents.
This guide is meant to help fill the void of information on stillbirths. It’s based on more than 150 conversations with parents, health care providers, researchers and other medical experts.
Whether you’re trying to better prepare for a pregnancy or grieving a loss, we hope this will help you and your family. This guide does not provide medical advice. We encourage you to seek out other reliable resources and consult with providers you trust.
We welcome your thoughts and questions at mailto:[email protected]. You can share your experience with stillbirth with us. If you are a health care provider interested in distributing this guide, let us know if we can help.
Table of contents:
- What Is Stillbirth?
- Are Stillbirths Preventable?
- What to Expect After a Stillbirth.
- Grieving After a Stillbirth.
- What You Might Say and Do After a Loved One Experiences a Stillbirth.
What Is Stillbirth?
Many people told us that the first time they heard the term stillbirth was after they delivered their stillborn baby. In many cases, the lack of information and awareness beforehand contributed to their heartache and guilt afterward.
Stillbirth is defined in the U.S. as the death of a baby in the womb at 20 weeks or more of pregnancy. Depending on when it happens, stillbirth is considered:
- Early: 20-27 weeks of pregnancy.
- Late: 28-36 weeks of pregnancy.
- Term: 37 or more weeks of pregnancy.
About half of all stillbirths in the U.S. occur at 28 weeks or later.
What is the difference between a stillbirth and a miscarriage?
Both terms describe pregnancy loss. The distinction is when the loss occurs. A miscarriage is typically defined as a loss before the 20th week of pregnancy, while stillbirth is after that point.
How common is stillbirth?
Each year, about 1 in 175 deliveries in the U.S. are stillbirths — that’s about 60 stillborn babies every day — making it one of the most common adverse pregnancy outcomes, but it is rarely discussed.
If you are surprised by that fact, you are not alone. Many people we spoke to did not know how common stillbirths are. Leandria Lee of Texas said she spent her 2021 pregnancy unaware that her daughter, Zuri Armoni, could die in the last phase of her pregnancy.
“If I was prepared to know that something could happen, I don’t think it would have been as bad. But to not know and then it happens, it affects you,” she said of her stillbirth at 35 weeks.
Some doctors have told us they don’t introduce the possibility of a stillbirth because they don’t want to create additional anxiety for patients.
Other doctors say withholding information leaves patients unprepared.
“We have this idea that we can’t scare the patient, which to me is very paternalistic,” said Dr. Heather Florescue, an OB-GYN near Rochester, New York, who works to inform doctors and patients about stillbirth prevention.
What causes stillbirths?
There is a lot we don’t know about stillbirths because there hasn’t been enough research. The cause of the stillbirth is unknown in about 1 in 3 cases.
What we do know is that a number of factors may cause or increase the risk of a stillbirth, including:
- The baby not growing as expected.
- Placental abnormalities or problems with the umbilical cord.
- Genetic or structural disorders that cause developmental issues.
- High blood pressure before pregnancy or preeclampsia, a potentially fatal complication that usually appears late in pregnancy and causes high blood pressure.
- Diabetes before or during pregnancy.
- An infection in the fetus, the placenta or the pregnant person.
- Smoking.
- Being 35 or older.
- Obesity.
- Being pregnant with more than one baby.
But not all doctors, hospitals or health departments perform tests to identify the potential cause of a stillbirth or determine if it could have been prevented. Even when a cause is identified, fetal death records are rarely updated. This means data is sometimes inaccurate. Researchers strongly encourage doctors to perform a stillbirth evaluation, which includes an examination of the placenta and umbilical cord, a fetal autopsy and genetic testing.
If your hospital or doctor does not proactively offer one or more of these exams, you can ask them to conduct the tests. Research shows that placental exams may help establish a cause of death or exclude a suspected one in about 65% of stillbirths, while autopsies were similarly useful in more than 40% of cases.
Are Stillbirths Preventable?
Not all stillbirths are preventable, but some are. For pregnancies that last 37 weeks or more, one study found that nearly half of stillbirths are potentially preventable.
Dr. Joanne Stone, who last year was president of the Society of Maternal-Fetal Medicine, leads the country’s first Rainbow Clinic at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York. The clinic is modeled on similar facilities in the United Kingdom that care for people who want to conceive again after a stillbirth. She said many doctors used to think there was nothing they could do to prevent stillbirth.
“People just looked at it like, ‘Oh, it was an accident, couldn’t have been prevented,’” said Stone, who also is the system chair of the obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive science department at the Icahn School of Medicine. “But we know now there are things that we can do to try to prevent that from happening.”
She said doctors can:
- More closely monitor patients with certain risk factors, like high blood pressure, diabetes or obesity.
- Ask about prior infant loss or other obstetrical trauma.
- Carefully assess whether a baby’s growth is normal.
- Work to diagnose genetic anomalies.
- Teach patients how to track their baby’s movements and encourage them to speak up if they notice activity has slowed or stopped.
- Deliver at or before 39 weeks if there are concerns.
What are the risks of stillbirth over the course of a pregnancy?
The risk of a stillbirth increases significantly toward the end of pregnancy, especially after 39 weeks. The risk is higher for people who get pregnant at 35 or older. The risk begins to climb even earlier, around 36 weeks, for people pregnant with twins.
What you and your doctor can do to reduce the risk of stillbirth.
While federal agencies in the U.S. have yet to come up with a checklist that may help reduce the risk of stillbirth, the Stillbirth Centre of Research Excellence in Australia has adopted a Safer Baby Bundle that lists five recommendations:
- Stop smoking.
- Regularly monitor growth to reduce the risk of fetal growth restriction, when the fetus is not growing as expected.
- Understand the importance of acting quickly if fetal movement decreases.
- Sleep on your side after 28 weeks.
- Talk to your doctor about when to deliver. Depending on your situation, it may be before your due date.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has compiled a list of tests and techniques doctors can use to try to reduce the risk of a stillbirth. They include:
- A risk assessment to identify prenatal needs.
- A nonstresstest, which checks the fetus’s heart rate and how it changes as the fetus moves.
- A biophysical profile, which is done with an ultrasound to measure body movement, muscle tone and breathing, along with amniotic fluid volume.
The group stressed that there is no test that can guarantee a stillbirth won’t happen and that individual circumstances should determine what tests are run.
Are some people at higher risk for stillbirth?
Black women are more than twice as likely to have a stillbirth as white women. There are a number of possible explanations for that disparity, including institutional bias and structural racism, and a patient’s pre-pregnancy health, socioeconomic status and access to health care. In addition, research shows that Black women are more likely than white women to experience multiple stressful life events while pregnant and have their concerns ignored by their health care provider. Similar racial disparities drive the country’s high rate of maternal mortality.
How to find a provider you trust.
Finding a doctor to care for you during your pregnancy can be a daunting process. Medical experts and parents suggest interviewing prospective providers before you decide on the right one.
Here is a short list of questions you might want to ask a potential OB-GYN:
- What is the best way to contact you if I have questions or concerns?
- How do you manage inquiries after hours and on weekends? Do you see walk-ins?
- How do you manage prenatal risk assessments?
- What should I know about the risks of a miscarriage or stillbirth?
- How do you decide when a patient should be induced?
If a provider doesn’t answer your questions to your satisfaction, don’t be reluctant to move on. Dr. Ashanda Saint Jean, chair of the obstetrics and gynecology department at HealthAlliance Hospitals of the Hudson Valley in New York, said she encourages her patients to find the provider that meets their needs.
“Seek out someone that is like-minded,” said Saint Jean “It doesn’t have to be that they’re the same ethnicity or the same race, but like-minded in terms of the goals of what that patient desires for their own health and prosperity.”
What to know in the last trimester.
The last trimester can be an uncomfortable and challenging time as the fetus grows and you get increasingly tired. During this critical time, your provider should talk to you about the following topics:
- Whether you need a nonstress test to determine if the fetus is getting enough oxygen.
- The best way to track fetal movements.
- What to do if your baby stops moving.
- Whether you are at risk for preeclampsia or gestational diabetes.
Rachel Foran’s child, Eoin Francis, was stillborn at 41 weeks and two days. Foran, who lives in New York, said she believes that if her doctor had tracked her placenta, and if she had understood the importance of fetal movement, she and her husband might have decided to deliver sooner.
She remembers that her son was “very active” until the day before he was stillborn.
“I would have gone in earlier if someone had told me, ‘You’re doing this because the baby could die,’” she said of tracking fetal movement. “That would have been really helpful to know.”
Researchers are looking at the best way to measure the health, blood flow and size of the placenta, but studies are still in their early stages.
“If someone had been doing that with my son’s,” Foran said, “my son would be alive.”
A placental exam and an autopsy showed that a small placenta contributed to Foran’s stillbirth.
How often should you feel movement?
Every baby and each pregnancy are different, so it is important to get to know what levels of activity are normal for you. You might feel movement around 20 weeks. You’re more likely to feel movement when you’re sitting or lying down. Paying attention to movement during the third trimester is particularly important because research shows that changes, including decreased movement or bursts of excessive activity, are associated with an increased risk of stillbirth. Most of the time, it’s nothing. But sometimes it can be a sign that your baby is in distress. If you’re worried, don’t rely on a home fetal doppler to reassure you. Reach out to your doctor.
Saint Jean offers a tip to track movement: “I still tell patients each day to lay on their left side after dinner and record how many times their baby moves, because then that will give you an idea of what’s normal for your baby,” she said.
Other groups recommend using the Count the Kicks app as a way of tracking fetal movements and establishing what is normal for that pregnancy. Although there is no scientific consensus that counting kicks can prevent stillbirths, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and other groups recommend that patients be aware of fetal movement patterns.
Dr. Karen Gibbins is a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Oregon Health & Science University who in 2018 had stillborn son named Sebastian. She said the idea that babies don’t move as much at the end of pregnancy is a dangerous myth.
“You might hear that babies slow down at the end,” she said. “They don’t slow down. They just have a little less space. So their movements are a little different, but they should be as strong and as frequent.”
What to Expect After a Stillbirth
What might happen at the hospital?
Parents are often asked to make several important decisions while they are still reeling from the shock and devastation of their loss. It’s completely understandable if you need to take some time to consider them.
Some other things you can ask for (if medical personnel don’t offer them) are:
- Blood work, a placental exam, an autopsy and genetic testing.
- A social worker or counselor, bereavement resources and religious or chaplain support.
- The option to be isolated from the labor rooms.
- Someone to take photos of you and your baby, typically either a nurse or an outside group.
- A small cooling cot that allows parents to spend more time with their babies after a stillbirth. If one is not available, you can ask for ice packs to put in the swaddle or the bassinet.
- A mold of your baby’s hands and feet.
- Information about burial or cremation services.
- Guidance on what to do if your milk comes in.
Getting an autopsy after a stillbirth.
Whether to have an autopsy is a personal decision. It may not reveal a cause of death, but it might provide important information about your stillbirth and contribute to broader stillbirth research. Autopsies can be useful if you are considering another pregnancy in the future. Families also told us that an autopsy can help parents feel they did everything they could to try to understand why their baby died.
But several families told us their health care providers didn’t provide them with the right information to help with that decision. Some aren’t trained in the advantages of conducting an autopsy after a stillbirth, or in when and how to sensitively communicate with parents about it. Some, for example, don’t explain that patients can still have an open-casket funeral or other service after an autopsy because the incisions can easily be covered by clothing. Others may not encourage an autopsy because they think they already know what caused the stillbirth or don’t believe anything could have been done to prevent it. In addition, not all hospitals have the capacity to do an autopsy, but there may be private autopsy providers that can perform one at an additional cost.
You can read more about autopsies in our reporting.
Paying for an autopsy after a stillbirth.
If you decide you want an autopsy, you may wonder whether you need to pay out-of-pocket for it. Several families told us their providers gave them incomplete or incorrect information. Many larger or academic hospitals offer autopsies at no cost to patients. Some insurance companies also cover the cost of an autopsy after a stillbirth.
When hospitals don’t provide an autopsy, they may give you names of private providers. That was the case for Rachel Foran. The hospital gave her and her husband a list of numbers to call if they wanted to pay for an autopsy themselves. The process, she said, shocked her.
“I had just delivered and we had to figure out what to do with his body,” Foran said. “It felt totally insane that that was what we had to do and that we had to figure it out on our own.”
An independent autopsy, records show, cost them $5,000.
What is a certificate of stillbirth and how do I get one?
A fetal death certificate is the official legal document that records the death. This is the document used to gather data on and track the number of stillbirths in the country. Many states also issue a certificate of stillbirth or a certificate of birth resulting in stillbirth, which acknowledge the baby’s birth. Families told us they appreciated having that document, since typical birth certificates are not issued for stillbirths. You can usually request a certificate from the vital records office.
Grieving After a Stillbirth
What are the effects of stillbirths on parents and families?
Over and over, families told us the effects of losing a baby can reverberate for a lifetime.
Bereavement support groups may help provide a space to share experiences and resources. Hospitals and birth centers may suggest a local grief group.
We talked with Anna Calix, a maternal health expert who became active in perinatal loss prevention after her son Liam was stillborn on his due date in 2016. Calix leads grief support groups for people of color in English and Spanish.
She suggested rededicating the time you would have spent taking care of a new baby to the grief process.
“You can do that by addressing your own thoughts and feelings and really experiencing those feelings,” Calix said. “We like to push those feelings away or try to do something to distract and avoid, but no matter what we do, the feelings are there.”
It’s important, she said, to give yourself permission to grow your connection with your child and work through thoughts of guilt or blame.
What You Might Say and Do After a Loved One Experiences a Stillbirth
Finding the right words can be difficult. The following are a few suggestions from parents who went through a stillbirth.
Helpful:
- Acknowledge the loss and offer condolences.
- Ask if the baby was named and use the name.
- Allow space for the family to talk about their baby.
Unhelpful:
- Avoid talking about the baby.
- Minimize the loss or compare experiences.
- Start statements with “at least.”
Suggested phrases to avoid:
- “You’re young. You can have more kids.”
- “At least you have other children.”
- “These things just happen.”
- “Your baby is in a better place now.”
Share This Post
-
Tiramisu Crunch Bites
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s coffee, it’s creamy, it’s nutty, it’s chocolatey, what’s not to love? It has all the well-loved flavors of tiramisu, but this recipe is a simple one, and it’s essentially stuffed dates in a way you’ve never had them before. They’re delectable, decadent, and decidedly good for your health. These things are little nutrient-bombs that’ll keep you reaching for more.
You will need
- Coffee (we will discuss this)
- 150g (5.5oz) mascarpone (if vegan or lactose-intolerant, can be substituted with vegan varieties, or at a pinch, pressed silken tofu)
- 500g (1lb) dates (Medjool are ideal)
- Twice as many almonds as you have dates
- 50g (2oz) dark chocolate (the darkest, bitterest, you can find)
- Edible flower petals if you can source them (some shops sell dried rose petals for this purpose)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Take the mascarpone and whisk (or blend) it with the coffee. What kind of coffee, you ask? Many will use instant coffee (1tbsp granules mixed with enough boiling water to dissolve it), and that is actually healthiest (counterintuitive but true) but if you care for flavor over health, and have the means to make espresso, make it ristretto (so, stop it halfway through filling up an espresso cup), let it cool, and use that. Absolute bonus for flavor (not for health): if you have the means to make Turkish coffee, use an equivalent amount of that (again, cooled).
You will now have coffee-flavoured mascarpone. It’s great for your gut and full of antioxidant polyphenols. Set it aside for the moment.
2) Take the dark chocolate and melt it. Please don’t microwave it or try to do it in a pan directly over the hob; instead, you will need to use a Bain-Marie. If you don’t have one made-for-purpose, you can place a metal or heatproof glass bowl in a saucepan, with something to stop it from touching the floor of the pan. Then boil water in the pan (without letting the water get into the bowl), and melt the chocolate in the bowl—this will allow you to melt it evenly without burning the chocolate.
You will now have melted dark chocolate. It has its own set of polyphenols, and is great for everything from the brain to the gut microbiome.
3) Cut the dates lengthways on one side and remove the stone. Stuff them carefully with the coffee-flavored mascarpone (you can use a teaspoon, or use a piping kit if you have one). Add a couple of almonds to each one. Place them all on a big plate, and drizzle the melted chocolate over them. Add the petals if you have them.
The dates and almonds deliver extra vitamins and minerals in abundance (not to mention, lots of fiber), and also are an amazing combination even just by themselves. With the mascarpone and chocolate added, this winning on new levels. We’re not done yet, though…
4) Chill them in the fridge for about 30 minutes.
Serve!
Learn more
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Make The Heart-Healthiest Coffee ← this is about cafestol content and why instant is heart-healthiest (alas)
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (Or Is It) ← this is about the health benefits (and some risks, but mostly benefits) of coffee
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts ← almonds are a top-tier choice, but other nuts are good too! This recipe could work well with hazelnuts, for example (we wouldn’t call it “tiramisu crunch bites” in that case, though, since the flavor profile would change)
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same? ← for any worrying “aren’t dates sugary, though?”
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
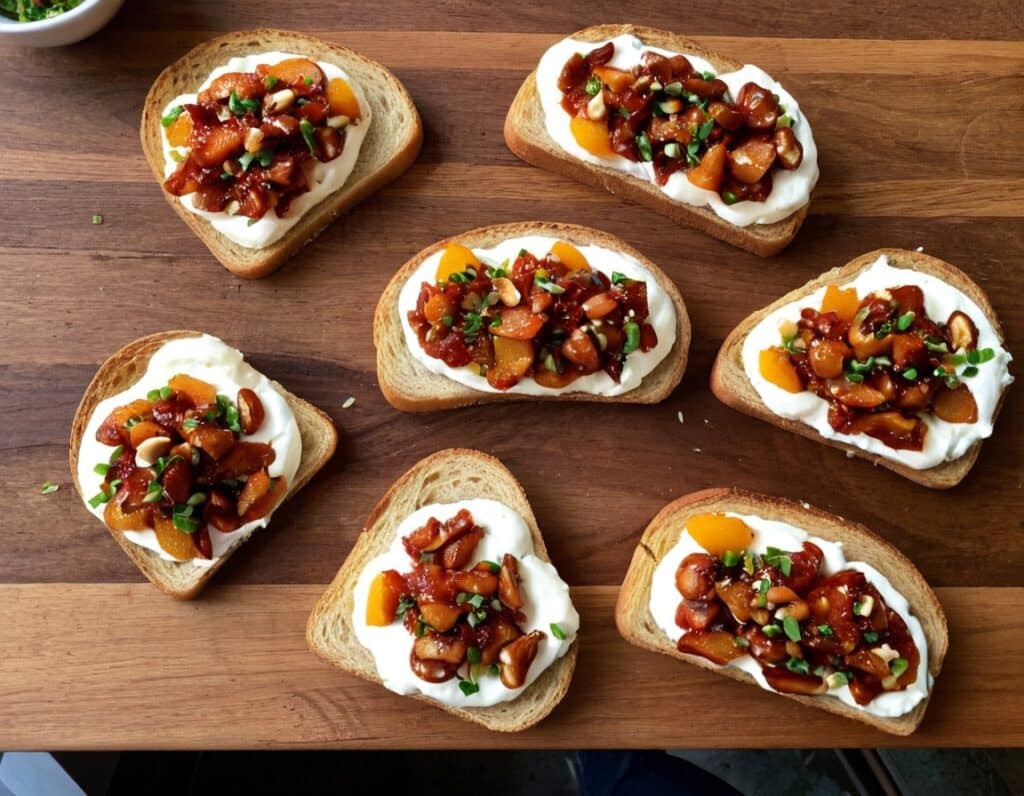
Chili Chestnut, Sweet Apricot, & Whipped Feta Toasts
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a delightful breakfast or light lunch option, full of gut-healthy ingredients and a fair list of healthy polyphenols too.
You will need
- ½ baguette, sliced into ½” slices; if making your own, feel free to use our Delicious Quinoa Avocado Bread recipe. If buying shop-bought, a sourdough baguette will likely be the healthiest option, and tasty too.
- 4 oz feta cheese; if you are vegan, a plant-based version will work in culinary terms, but will have a different (less gut-healthy) nutritional profile, as plant-based cheeses generally use a lot of coconut oil and potato starch, and are not actually fermented.
- 1 tbsp yogurt; your preference what kind; live-cultured with minimal additives is of course best—and this time, plant-based is also just as good, healthwise, since they are fermented and contain more or less the same beneficial bacteria, and have a good macro profile too.
- 4 oz precooked chestnuts, finely chopped
- 6 dried apricots, finely chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic, grated
- 2 tsp harissa paste
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil, for frying
- Optional garnish: finely chopped chives
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the feta and yogurt in a small, high-speed blender and process into a smooth purée. If it isn’t working, add 1 tbsp kettle-hot water and try again.
2) Heat the oil in a skillet over a medium heat; add the garlic and when it starts to turn golden, add the chestnuts and harissa, as well as the black pepper and MSG/salt. Stir for about 2 minutes, and then stir in the apricots and take it off the heat.
3) Toast the baguette slices under the grill. If you’re feeling bold about the multitasking, you can start this while still doing the previous step, for optimal timing. If not, simply doing it in the order presented is fine.
4) Assemble: spread the whipped feta over the toast; add the apricot-chestnut mixture, followed by the finely chopped chives if using, and serve immediately:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Apricots vs Peaches – Which is Healthier?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Some women’s breasts can’t make enough milk, and the effects can be devastating
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many new mothers worry about their milk supply. For some, support from a breastfeeding counsellor or lactation consultant helps.
Others cannot make enough milk no matter how hard they try. These are women whose breasts are not physically capable of producing enough milk.
Our recently published research gives us clues about breast features that might make it difficult for some women to produce enough milk. Another of our studies shows the devastating consequences for women who dream of breastfeeding but find they cannot.
Some breasts just don’t develop
Unlike other organs, breasts are not fully developed at birth. There are key developmental stages as an embryo, then again during puberty and pregnancy.
At birth, the breast consists of a simple network of ducts. Usually during puberty, the glandular (milk-making) tissue part of the breast begins to develop and the ductal network expands. Then typically, further growth of the ductal network and glandular tissue during pregnancy prepares the breast for lactation.
But our online survey of women who report low milk supply gives us clues to anomalies in how some women’s breasts develop.
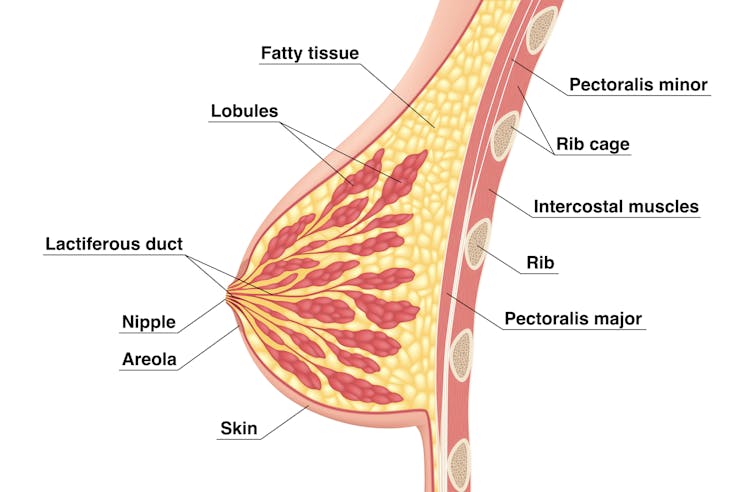
We’re not talking about women with small breasts, but women whose glandular tissue (shown in this diagram as “lobules”) is underdeveloped and have a condition called breast hypoplasia.
Sometimes not enough glandular tissue, shown here as lobules, develop.
Tsuyna/ShutterstockWe don’t know how common this is. But it has been linked with lower rates of exclusive breastfeeding.
We also don’t know what causes it, with much of the research conducted in animals and not humans.
However, certain health conditions have been associated with it, including polycystic ovary syndrome and other endocrine (hormonal) conditions. A high body-mass index around the time of puberty may be another indicator.
Could I have breast hypoplasia?
Our survey and other research give clues about who may have breast hypoplasia.
But it’s important to note these characteristics are indicators and do not mean women exhibiting them will definitely be unable to exclusively breastfeed.
Indicators include:
- a wider than usual gap between the breasts
- tubular-shaped (rather than round) breasts
- asymmetric breasts (where the breasts are different sizes or shapes)
- lack of breast growth in pregnancy
- a delay in or absence of breast fullness in the days after giving birth
In our survey, 72% of women with low milk supply had breasts that did not change appearance during pregnancy, and about 70% reported at least one irregular-shaped breast.
The effects
Mothers with low milk supply – whether or not they have breast hyoplasia or some other condition that limits their ability to produce enough milk – report a range of emotions.
Research, including our own, shows this ranges from frustration, confusion and surprise to intense or profound feelings of failure, guilt, grief and despair.
Some mothers describe “breastfeeding grief” – a prolonged sense of loss or failure, due to being unable to connect with and nourish their baby through breastfeeding in the way they had hoped.
These feelings of failure, guilt, grief and despair can trigger symptoms of anxiety and depression for some women.
Feelings of failure, guilt, grief and despair were common.
Bricolage/ShutterstockOne woman told us:
[I became] so angry and upset with my body for not being able to produce enough milk.
Many women’s emotions intensified when they discovered that despite all their hard work, they were still unable to breastfeed their babies as planned. A few women described reaching their “breaking point”, and their experience felt “like death”, “the worst day of [my] life” or “hell”.
One participant told us:
I finally learned that ‘all women make enough milk’ was a lie. No amount of education or determination would make my breasts work. I felt deceived and let down by all my medical providers. How dare they have no answers for me when I desperately just wanted to feed my child naturally.
Others told us how they learned to accept their situation. Some women said they were relieved their infant was “finally satisfied” when they began supplementing with formula. One resolved to:
prioritise time with [my] baby over pumping for such little amounts.
Where to go for help
If you are struggling with low milk supply, it can help to see a lactation consultant for support and to determine the possible cause.
This will involve helping you try different strategies, such as optimising positioning and attachment during breastfeeding, or breastfeeding/expressing more frequently. You may need to consider taking a medication, such as domperidone, to see if your supply increases.
If these strategies do not help, there may be an underlying reason why you can’t make enough milk, such as insufficient glandular tissue (a confirmed inability to make a full supply due to breast hypoplasia).
Even if you have breast hypoplasia, you can still breastfeed by giving your baby extra milk (donor milk or formula) via a bottle or using a supplementer (which involves delivering milk at the breast via a tube linked to a bottle).
More resources
The following websites offer further information and support:
- Australian Breastfeeding Association
- Lactation Consultants of Australia and New Zealand
- Royal Women’s Hospital, Melbourne
- Supply Line Breastfeeders Support Group of Australia Facebook support group
- IGT And Low Milk Supply Support Group Facebook support group
- Breastfeeding Medicine Network Australia/New Zealand
- Supporting breastfeeding grief (a collection of resources).
Shannon Bennetts, a research fellow at La Trobe University, contributed to this article.
Renee Kam, PhD candidate and research officer, La Trobe University and Lisa Amir, Professor in Breastfeeding Research, La Trobe University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Avoiding Razor Burn, Ingrown Hairs & Other Shaving Irritation
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How Does The Video Help?
Dr. Simi Adedeji’s incredibly friendly persona makes this video (below) on avoiding skin irritation, ingrown hairs, and razor burn after shaving a pleasure to watch.
To keep things simple, she breaks down her guide into 10 simple tips.
What Are The 10 Simple Tips?
Tip 1: Prioritize Hydration. Shaving dry hair can lead to increased skin irritation, so Dr. Simi recommends moistening the hair by showering or using a warm, wet towel for 2-4 minutes before getting the razor out.
Tip 2: Avoid Dry Shaving. Dry shaving not only removes hair but can also remove the protective upper layer of skin, which contributes to razor burn. To prevent this, simply use some shaving gel or cream.
Tip 3: Keep Blades New and Sharp. This one’s simple: dull blades can cause skin irritation, whilst a sharp blade ensures a smoother and more comfortable shaving experience.
Tip 4: Avoid Shaving the Same Area Repeatedly. Multiple passes over the same area can remove skin layers, leading to cuts and irritation. Aim to shave each area only once for safer results.
Tip 5: Consider Hair Growth Direction. Shaving in the direction of hair growth results in less irritation, although it may not provide the closest shave.
Tip 6: Apply Gentle Pressure While Shaving. Excessive pressure can lead to cuts and nicks. Use a gentle touch to reduce these risks.
Tip 7: Incorporate Exfoliation into Your Routine. Exfoliating helps release trapped hairs and reduces the risk of ingrown hairs. For those with sensitive skin, it’s recommended to exfoliate either two days before or after shaving.
Tip 8: Avoid Excessive Skin Stretching. Over-stretching the skin during shaving can cause hairs to become ingrown.
Tip 9: Moisturize After Shaving. Shaving can compromise the skin barrier, leading to dryness. Using a moisturizer can be a simple fix.
Tip 10: Regularly Rinse Your Blade. Make sure that, during the shaving process, you are rinsing your blade frequently to remove hair and skin debris. This keeps it sharp during your shave.
If this summary doesn’t do it for you, then you can watch the full video here:
How did you find that video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Yes, you do need to clean your tongue. Here’s how and why
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Has your doctor asked you to stick out your tongue and say “aaah”? While the GP assesses your throat, they’re also checking out your tongue, which can reveal a lot about your health.
The doctor will look for any changes in the tongue’s surface or how it moves. This can indicate issues in the mouth itself, as well as the state of your overall health and immunity.
But there’s no need to wait for a trip to the doctor. Cleaning your tongue twice a day can help you check how your tongue looks and feels – and improve your breath.
luisrsphoto/Shutterstock What does a healthy tongue look like?
Our tongue plays a crucial role in eating, talking and other vital functions. It is not a single muscle but rather a muscular organ, made up of eight muscle pairs that help it move.
The surface of the tongue is covered by tiny bumps that can be seen and felt, called papillae, giving it a rough surface.
These are sometimes mistaken for taste buds – they’re not. Of your 200,000-300,000 papillae, only a small fraction contain taste buds. Adults have up to 10,000 taste buds and they are invisible to the naked eye, concentrated mainly on the tip, sides and back of the tongue. https://www.youtube.com/embed/uYvpUl7li9Y?wmode=transparent&start=0
A healthy tongue is pink although the shade may vary from person to person, ranging from dark to light pink.
A small amount of white coating can be normal. But significant changes or discolouration may indicate a disease or other issues.
How should I clean my tongue?
Cleaning your tongue only takes around 10-15 seconds, but it’s is a good way to check in with your health and can easily be incorporated into your teeth brushing routine.
Build-up can occur if you stop brushing or scraping your tongue even for a few days. Anthony Shkraba/Pexels You can clean your tongue by gently scrubbing it with a regular toothbrush. This dislodges any food debris and helps prevent microbes building up on its rough textured surface.
Or you can use a special tongue scraper. These curved instruments are made of metal or plastic, and can be used alone or accompanied by scrubbing with your toothbrush.
Your co-workers will thank you as well – cleaning your tongue can help combat stinky breath. Tongue scrapers are particularly effective at removing the bacteria that commonly causes bad breath, hidden in the tongue’s surface.
What’s that stuff on my tongue?
So, you’re checking your tongue during your twice-daily clean, and you notice something different. Noting these signs is the first step. If you observe any changes and they worry you, you should talk to your GP.
Here’s what your tongue might be telling you.
White coating
Developing a white coating on the tongue’s surface is one of the most common changes in healthy people. This can happen if you stop brushing or scraping the tongue, even for a few days.
In this case, food debris and microbes have accumulated and caused plaque. Gentle scrubbing or scraping will remove this coating. Removing microbes reduces the risk of chronic infections, which can be transferred to other organs and cause serious illnesses.
Scrubbing or scraping your tongue only takes around ten seconds and can be done while brushing your teeth. Ketut Subiyanto/Pexels Yellow coating
This may indicate oral thrush, a fungal infection that leaves a raw surface when scrubbed.
Oral thrush is common in elderly people who take multiple medications or have diabetes. It can also affect children and young adults after an illness, due to the temporary suppression of the immune system or antibiotic use.
If you have oral thrush, a doctor will usually prescribe a course of anti-fungal medication for at least a month.
Black coating
Smoking or consuming a lot of strong-coloured food and drink – such as tea and coffee, or dishes with tumeric – can cause a furry appearance. This is known as a black hairy tongue. It’s not hair, but an overgrowth of bacteria which may indicate poor oral hygiene.
Smoking can add to poor oral hygiene and make the tongue look black. Sophon Nawit/Shutterstock Pink patches
Pink patches surrounded by a white border can make your tongue look like a map – this is called “geographic tongue”. It’s not known what causes this condition, which usually doesn’t require treatment.
Pain and inflammation
A red, sore tongue can indicate a range of issues, including:
- nutritional deficiencies such as folic acid or vitamin B12
- diseases including pernicious anaemia, Kawasaki disease and scarlet fever
- inflammation known as glossitis
- injury from hot beverages or food
- ulcers, including cold sores and canker sores
- burning mouth syndrome.
Dryness
Many medications can cause dry mouth, also called xerostomia. These include antidepressants, anti-psychotics, muscle relaxants, pain killers, antihistamines and diuretics. If your mouth is very dry, it may hurt.
What about cancer?
White or red patches on the tongue that can’t be scraped off, are long-standing or growing need to checked out by a dental professional as soon as possible, as do painless ulcers. These are at a higher risk of turning into cancer, compared to other parts of the mouth.
Oral cancers have low survival rates due to delayed detection – and they are on the rise. So checking your tongue for changes in colour, texture, sore spots or ulcers is critical.
Dileep Sharma, Professor and Head of Discipline – Oral Health, University of Newcastle
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: