Wasting Your Vitamins?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are you flushing away your vitamins?
Most likely…but you don’t have to.
We all know what a wasteful expense supplements can sometimes be, but you can optimise your intake to get more bang for your buck!
Top Tips for Getting Your Money’s Worth:
- Liquids are better than tablets—the body can’t absorb nutrients from tablets anywhere as easily as it can from liquids, with some saying as low as a 50% absorption rate for tablets, so if your supplement can come in drinkable form, take it that way!
- Capsules are better than tablets—capsules, depending on the kind, contain either a powder (true capsules) or a liquid (softgels). Once the capsule/softgel is broken down in the stomach, it releases its contents, which will now be absorbed as though you took it as a drink.
- Stay hydrated—on that note, your body can only make use of nutrients that it can easily transport, and if you’re dehydrated, the process is sluggish! Having a big glass of water with your supplements will go a long way to helping your body get them where they’re needed.
- Take with black pepper—studies disagree on exactly how much black pepper improves absorption of nutrients. Some say it improves it by 50%, others say as much as 7x better. The truth is probably that it varies from one nutrient to the next, but what is (almost) universally accepted is that black pepper helps you absorb many nutrients you take orally.
- Take with a meal—bonus if you seasoned it with black pepper! But also: many nutrients are best absorbed alongside food, and many are specifically fat-soluble (so you want to take a little fat around the same time for maximum absorption)
- Consider split doses—a lot of nutrients are best absorbed when spread out a bit. Why? Your body can often only absorb so much at once, and what it couldn’t absorb can, depending on the nutrient, pass right through you. So better to space out the doses—breakfast and dinner make for great times to take them.
- Consider cycling—no, not the two-wheeled kind, though feel free to do that too! What cycling means when it comes to supplements is to understand that your body can build a tolerance to some supplements, so you’ll get gradually less effect for the same dose. Combat this by scheduling a break—five days on, two days off is a common schedule—allowing your body to optimise itself in the process!
- Check Medications—and, as is always safe, make sure you check whether any medications you take can interrupt your supplement absorption!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Manage Your Mood With Food (8 Ways)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It is hard to be mentally healthy for long without good diet. Food can not only affect our mood directly, but also indirectly because of how our brain works (or doesn’t, if we don’t have the right nutrients, or it is being sabotaged in some other dietary fashion).
Selecting the food for setting the mood
Mind, the mental health charity, have these advices to share (with some bonus notes of our own):
- Eat regularly: blood sugar peaks and troughs can heighten feelings of tiredness, irritability, or depression. Instead, enjoy foods that are high in energy but low in glycemic index, such as nuts, seeds, and oats—that way you’ll have plenty of energy, that lasts longer.
- Choose the right fats: omega-3 fatty acids are essential for the brain. So are omega-6 fatty acids, but it is rare to have a deficiency in omega-6, and indeed, many people have the ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 far too imbalanced in omega-6’s favor. So, focussing on getting more omega-3 fatty acids is important. Nuts and seeds are again great, as are avocados, eggs, and oily fish.
- Get a healthy amount of protein: and importantly, with a good mix of amino acids—so a variety of sources of protein is best. In particular, if you are vegan, paying attention to ensure you get a full spread of amino acids is critical, as not many plants have all the ones we need (soy does, though). The reason this is important for mood is because many of those amino acids double up as the building blocks of neurotransmitters, so they’re not entirely interchangeable.
- Stay hydrated: our bodies are famously made of mostly water, and our brain will not work well if it’s dehydrated. The human body can squeeze water out of almost anything that has water in it, but water from food (such as fruit, or soups) is best. If enjoying actual drinks, then herbal teas are excellent for hydration.
- Eat a rainbow of fruits and vegetables: these have many nutrients that are important for brain health, and the point of the colors is that most of those pigments are themselves nutrients. Additionally, the fiber content of fruits and vegetables is of topmost important for your heart, and as you’ll remember (we say it often, because it’s true): what’s good for your heart is good for your brain.
- Limit caffeine intake: for many people, excess caffeine can lead to feelings of anxiety, disrupt your sleep, and for everyone who has developed an addiction to it, it will cause withdrawal symptoms if stopped abruptly. Cutting back on caffeine, or even eliminating it, may improve your mood and sleep quality. Note, however, that if you have ADHD, then your brain’s physiological relationship with caffeine is a little different, and stimulants will be more beneficial (and less deleterious) for you than for most people. If unsure, speak with your doctor about this one.
- Support your gut health: because of the gut-brain axis (via the vagal nerve), and also because nearly all of our endogenous serotonin is made in the gut (along with other neurotransmitters/hormones), getting plenty of fiber is important, and probiotics can help too.
- Consider food intolerances: if you know you have one, then keep that in mind and tailor your diet accordingly. If you suspect you have one, seek a nutritionist’s help to find out for sure. These can affect many aspects of health, including mood, so should not be dismissed as a triviality.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The 6 Pillars Of Nutritional Psychiatry
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Move over, COVID and Flu! We Have “Hybrid Viruses” To Contend With Now
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Move over, COVID and Flu! We have “hybrid viruses” to contend with now
COVID and influenza viruses can be serious, of course, so let’s be clear up front that we’re not being dismissive of those. But, most people are hearing a lot about them, whereas respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) has flown under a lot of radars.
Simply put, until recently it hasn’t been considered much of a threat except to the young, the old, or people with other respiratory illnesses. Only these days, the prevalence of “other respiratory illnesses” is a lot higher than it used to be!
It’s not just a comorbidity
It’s easy to think “well of course if you have more than one illness at once, especially similar ones, that’s going to suck” but it’s a bit more than that; it produces newer, more interesting, hybrid viruses. Here’s a research paper from last year’s “flu season”:
Coinfection by influenza A virus and respiratory syncytial virus produces hybrid virus particles
Best to be aware of this if you’re in the “older” age-range
It’s not just that the older we are, the more likely we are to get it. Critically, the older we are, the more likely we are to be hospitalized by it.
And..the older we are, the less likely we are to come back from hospital if hospitalized by it.
Some years back, the intensive care and mortality rates for people over the age of 65 were 8% and 7%, respectively:
Respiratory syncytial virus infection in elderly and high-risk adults
…but a new study this year has found the rates like to be 2.2x that, i.e. 15% intensive care rate and 18% mortality, respectively:
Want to know more?
Here are some hot-off-the-press news articles on the topic:
- Better awareness of RSV in older adults is needed to reduce hospitalizations
- Is there also a connection between RSV and asthma?
- Respiratory syncytial virus coinfections conspire to worsen disease
And as for what to do…
Same general advice as for COVID and Flu, just, ever-more important:
- Try to keep to well-ventilated places as much as possible
- Get any worrying symptoms checked out quickly
- Mask up when appropriate
- Get your shots as appropriate
See also:
Harvard Health Review | Fall shots: Who’s most vulnerable to RSV, COVID, and the flu, and which shots are the right choice for you to help protect against serious illness and hospitalization?
Stay safe!
Share This Post
-
Our ‘food environments’ affect what we eat. Here’s how you can change yours to support healthier eating
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In January, many people are setting new year’s resolutions around healthy eating. Achieving these is often challenging – it can be difficult to change our eating habits. But healthy diets can enhance physical and mental health, so improving what we eat is a worthwhile goal.
One reason it’s difficult to change our eating habits relates to our “food environments”. This term describes:
The collective physical, economic, policy and sociocultural surroundings, opportunities and conditions that influence people’s food and beverage choices and nutritional status.
Our current food environments are designed in ways that often make it easier to choose unhealthy foods than healthy ones. But it’s possible to change certain aspects of our personal food environments, making eating healthier a little easier.
Unhealthy food environments
It’s not difficult to find fast-food restaurants in Australian cities. Meanwhile, there are junk foods at supermarket checkouts, service stations and sporting venues. Takeaway and packaged foods and drinks routinely come in large portion sizes and are often considered tastier than healthy options.
Our food environments also provide us with various prompts to eat unhealthy foods via the media and advertising, alongside health and nutrition claims and appealing marketing images on food packaging.
At the supermarket, unhealthy foods are often promoted through prominent displays and price discounts.
We’re also exposed to various situations in our everyday lives that can make healthy eating challenging. For example, social occasions or work functions might see large amounts of unhealthy food on offer.
Not everyone is affected in the same way
People differ in the degree to which their food consumption is influenced by their food environments.
This can be due to biological factors (for example, genetics and hormones), psychological characteristics (such as decision making processes or personality traits) and prior experiences with food (for example, learned associations between foods and particular situations or emotions).
People who are more susceptible will likely eat more and eat more unhealthy foods than those who are more immune to the effects of food environments and situations.
Those who are more susceptible may pay greater attention to food cues such as advertisements and cooking smells, and feel a stronger desire to eat when exposed to these cues. Meanwhile, they may pay less attention to internal cues signalling hunger and fullness. These differences are due to a combination of biological and psychological characteristics.
These people might also be more likely to experience physiological reactions to food cues including changes in heart rate and increased salivation.
It’s common to eat junk food in front of the TV.
PR Image Factory/ShutterstockOther situational cues can also prompt eating for some people, depending on what they’ve learned about eating. Some of us tend to eat when we’re tired or in a bad mood, having learned over time eating provides comfort in these situations.
Other people will tend to eat in situations such as in the car during the commute home from work (possibly passing multiple fast-food outlets along the way), or at certain times of day such as after dinner, or when others around them are eating, having learned associations between these situations and eating.
Being in front of a TV or other screen can also prompt people to eat, eat unhealthy foods, or eat more than intended.
Making changes
While it’s not possible to change wider food environments or individual characteristics that affect susceptibility to food cues, you can try to tune into how and when you’re affected by food cues. Then you can restructure some aspects of your personal food environments, which can help if you’re working towards healthier eating goals.
Although both meals and snacks are important for overall diet quality, snacks are often unplanned, which means food environments and situations may have a greater impact on what we snack on.
Foods consumed as snacks are often sugary drinks, confectionery, chips and cakes. However, snacks can also be healthy (for example, fruits, nuts and seeds).
Try removing unhealthy foods, particularly packaged snacks, from the house, or not buying them in the first place. This means temptations are removed, which can be especially helpful for those who may be more susceptible to their food environment.
Planning social events around non-food activities can help reduce social influences on eating. For example, why not catch up with friends for a walk instead of lunch at a fast-food restaurant.
Creating certain rules and habits can reduce cues for eating. For example, not eating at your desk, in the car, or in front of the TV will, over time, lessen the effects of these situations as cues for eating.
You could also try keeping a food diary to identify what moods and emotions trigger eating. Once you’ve identified these triggers, develop a plan to help break these habits. Strategies may include doing another activity you enjoy such as going for a short walk or listening to music – anything that can help manage the mood or emotion where you would have typically reached for the fridge.
Write (and stick to) a grocery list and avoid shopping for food when hungry. Plan and prepare meals and snacks ahead of time so eating decisions are made in advance of situations where you might feel especially hungry or tired or be influenced by your food environment.
Georgie Russell, Senior Lecturer, Institute for Physical Activity and Nutrition (IPAN), Deakin University and Rebecca Leech, NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow, School of Exercise and Nutrition Sciences, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Move over, COVID and Flu! We Have “Hybrid Viruses” To Contend With Now
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Move over, COVID and Flu! We have “hybrid viruses” to contend with now
COVID and influenza viruses can be serious, of course, so let’s be clear up front that we’re not being dismissive of those. But, most people are hearing a lot about them, whereas respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) has flown under a lot of radars.
Simply put, until recently it hasn’t been considered much of a threat except to the young, the old, or people with other respiratory illnesses. Only these days, the prevalence of “other respiratory illnesses” is a lot higher than it used to be!
It’s not just a comorbidity
It’s easy to think “well of course if you have more than one illness at once, especially similar ones, that’s going to suck” but it’s a bit more than that; it produces newer, more interesting, hybrid viruses. Here’s a research paper from last year’s “flu season”:
Coinfection by influenza A virus and respiratory syncytial virus produces hybrid virus particles
Best to be aware of this if you’re in the “older” age-range
It’s not just that the older we are, the more likely we are to get it. Critically, the older we are, the more likely we are to be hospitalized by it.
And..the older we are, the less likely we are to come back from hospital if hospitalized by it.
Some years back, the intensive care and mortality rates for people over the age of 65 were 8% and 7%, respectively:
Respiratory syncytial virus infection in elderly and high-risk adults
…but a new study this year has found the rates like to be 2.2x that, i.e. 15% intensive care rate and 18% mortality, respectively:
Want to know more?
Here are some hot-off-the-press news articles on the topic:
- Better awareness of RSV in older adults is needed to reduce hospitalizations
- Is there also a connection between RSV and asthma?
- Respiratory syncytial virus coinfections conspire to worsen disease
And as for what to do…
Same general advice as for COVID and Flu, just, ever-more important:
- Try to keep to well-ventilated places as much as possible
- Get any worrying symptoms checked out quickly
- Mask up when appropriate
- Get your shots as appropriate
See also:
Harvard Health Review | Fall shots: Who’s most vulnerable to RSV, COVID, and the flu, and which shots are the right choice for you to help protect against serious illness and hospitalization?
Stay safe!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Gravitas – by Caroline Goyder
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A no-nonsense guide to (more than!) public speaking that isn’t just “tell jokes in your speech and imagine the audience naked”.
Because this isn’t just about speech-writing or speech delivery, so much as giving you important life skills. The kind that weren’t taught in school, but that nevertheless make a huge impact on success… whether you’re giving a presentation or hosting a party or negotiating a deal or just attending a social event. Or making a phonecall, even.
Whereas a lot of books of this kind treat “the audience” as a nebulous and purely responsive passive crowd of extras, Goyder does better. People are individuals, even if they’re all facing the same way for a moment. She works with that! She also teaches how to deal with not just hecklers, but also simply those people who sap your confidence and find fault with you and anything you do or say.b
Bottom line is: if you for whatever reason communicate with people, and would like them to think better of you, this is the book for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
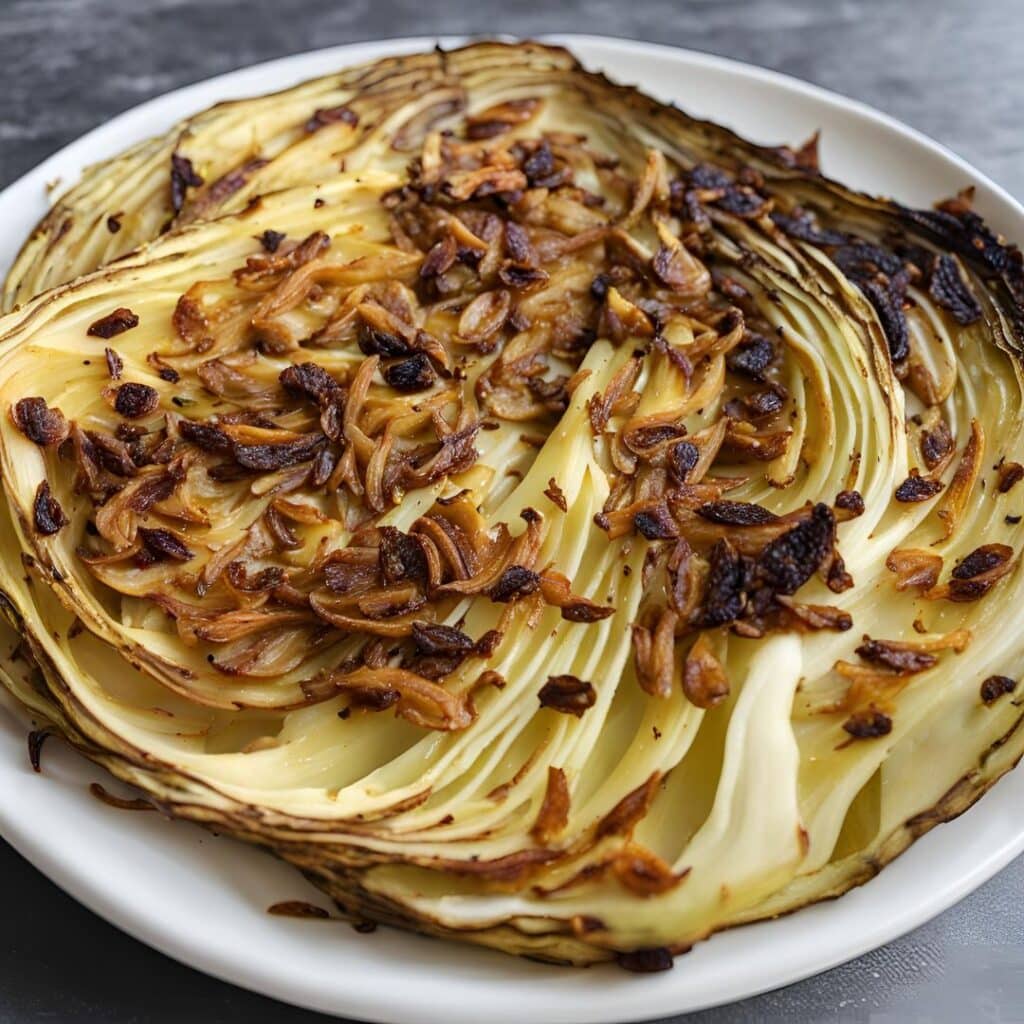
Caramelized Caraway Cabbage
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cabbage is an underrated vegetable for its many nutrients and its culinary potential—here’s a great way to make it a delectable starter or respectable side.
You will need
- 1 medium white cabbage, sliced into 1″ thick slabs
- 1 tbsp extra-virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp caraway seeds
- 1 tsp black pepper
- ½ tsp turmeric
- ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃.
2) Combine the non-cabbage ingredients in a small bowl, whisking to mix thoroughly—with a tiny whisk if you have one, but a fork will work if necessary.
3) Arrange the cabbage slices on a lined baking tray and brush the seasoning-and-oil mixture over both sides of each slice.
4) Roast for 20–25 minutes until the cabbage is tender and beginning to caramelize.
5) Serve warm.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Curcumin (Turmeric) is worth its weight in gold
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: