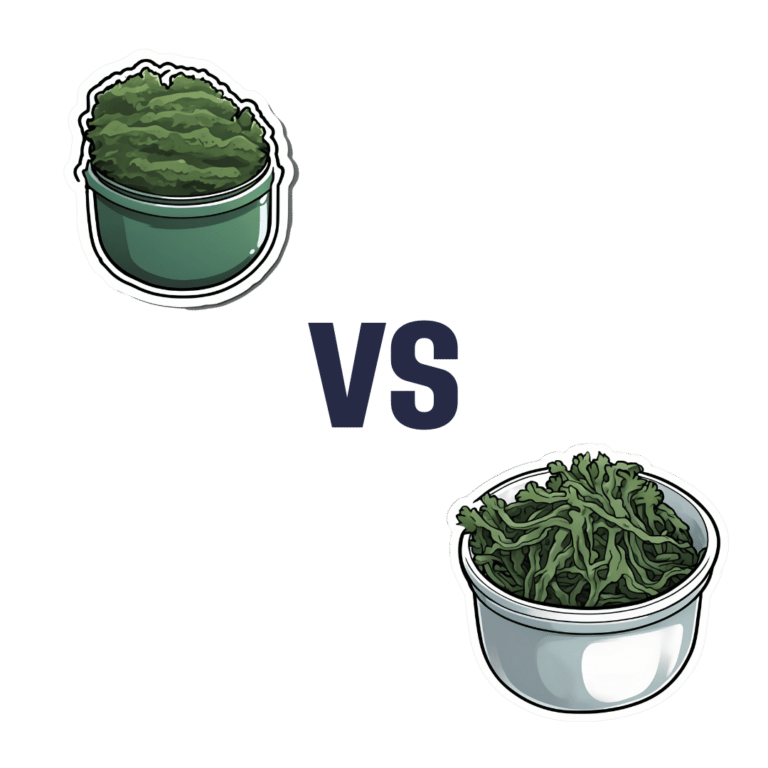
Celery vs Chard – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing celery to chard, we picked the chard.
Why?
In terms of macros, chard has more fiber, carbs, and protein, making it the more nutrient-dense option and thus the winner of the macros category.
In the category of vitamins, celery has more of vitamins B5 and B9, while chard has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, C, E, K, and choline—another win for chard.
When it comes to minerals, celery is not higher in any minerals, while chard has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. One more very clear win for chard!
Looking at polyphenols, celery has very little to boast, about 3mg/100g furanocoumarins and nothing else, while chard has an impressive array of polyphenols, with 9mg/100g kaempferol and 7.5mg/100g quercetin atop the list of 12 polyphenols. Yet another win for chard.
Adding up the sections is not difficult arithmetic today: chard sweeps every category. But by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen ← the “dozen” in question includes getting a good amount of of leafy greens per day
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Physical Exercises That Build Your Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Jim Kwik: from broken brain to brain coach
Image from Kwik Learning This is Jim Kwik. He suffered a traumatic brain injury as a small child, and later taught himself to read and write by reading comic books. He became fascinated with the process of learning, and in his late 20s he set up Kwik Learning, to teach accelerated learning in classrooms and companies, which he continued until 2009 when he launched his online learning platform. His courses have now been enjoyed by people in 195 countries.
So, since accelerated learning is his thing, you might wonder…
What does he have to share that we can benefit from in the next five minutes?
Three brain exercises to improve memory and concentration
A lot of problems we have with working memory are a case of executive dysfunction, but there are tricks we can use to get our brains into gear and make them cumulatively stronger:
First exercise
You can strengthen your corpus callosum (the little bridge between the two hemispheres of the brain) by performing a simple kinesiological exercise, such as alternating touching your left elbow to your right knee, and touching your right elbow to your left knee.
Do it for about a minute, but the goal here is not a cardio exercise, it’s accuracy!
You want to touch your elbow and opposite knee to each other as precisely as possible each time. Not missing slightly off to the side, not falling slightly short, not hitting it too hard.
Second exercise
Put your hands out in front of you, as though you’re about to type at a keyboard. Now, turn your hands palm-upwards. Now back to where they were. Now palm-upwards again. Got it? Good.
That’s not the exercise, the exercise is:
You’re now going to do the same thing, but do it twice as quickly with one hand than the other. So they’ll still be flipping to the same basic “beat”, put it in musical terms, the tempo on one hand will now be twice that of the other. When you get the hang of that, switch hands and do the other side.
This is again about the corpus callosum, but it’s now adding an extra level of challenge because of holding the two rhythms separately, which is also working the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex.
The pre-frontal cortex in particular is incredibly important to executive function, self-discipline, and being able to “do” delayed gratification. So this exercise is really important!
Third exercise
This one works the same features of the brain, but most people find it harder. So, consider it a level-up on the previous:
Imagine there’s a bicycle wheel in front of you (as though the bike is facing you at chest-height). Turn the wheel towards you with your hands, one on each side.
Now, do the same thing, but each of your hands is going in the opposite direction. So one is turning the wheel towards you; the other is turning it away from you.
Now, do the same thing, but one hand goes twice as quickly as the other.
Switch sides.
Why is this harder for most people than the previous? Because the previous involved processing discrete (distinct from each other) movements while this one involves analog continuous movements.
It’s like reading an analog clock vs a digital clock, but while using both halves of your brain, your corpus callosum, your pre-frontal cortex, and the motor cortex too.
Want to learn more?
You might enjoy his book, which as well as offering exercises like the above, also offers a lot about learning strategies, memory processes, and generally building a quicker more efficient brain:
Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life
Share This Post
-
Languishing – by Prof. Corey Keyes
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about depression and “flourishing” but what about when one isn’t exactly flourishing, but is not necessarily in the depths of depression either? That’s what this book is about.
Prof. Keyes offers, from his extensive research, hope for those who do not check enough of the boxes to be considered depressed, but who are also definitely more in the lane of “surviving” than “thriving”.
Specifically, he outlines five key ways to make the step from languishing to flourishing, based not on motivational rhetoric, but actual data-based science:
- Learn (creating your personal story of self-growth)
- Connect (building relationships, on the individual level and especially on the community level)
- Transcend (developing psychological resilience to the unexpected)
- Help (others! This is about finding your purpose, and then actively living it)
- Play (this is a necessary “recharge” element that many people miss, especially as we get older)
With regard to finding one’s purpose being given the one-word summary of “help”, this is a callback to our tribal origins, and how we thrive and flourish best and feel happiest when we have a role to fulfil and provide value to those around us)
Bottom line: if you’re not at the point of struggling to get out of bed each day, but you’re also not exactly leaping out of bed with a smile, this book can help get you from one place to the other.
Share This Post
-
Eat More, Live Well – by Dr. Megan Rossi
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Often, eating healthily can feel restrictive. Don’t eat this, skip that, eliminate the other. Where is the joy?
Dr. Megan Rossi brings a scientific angle on positive dieting, that is to say, looking at what to add, rather than what to subtract. Now, the idea isn’t to have sugar-laden chocolate cake with berries on top and call it a net positive because of the berries, though. Rather, Dr. Rossi lays out how to include as many diverse vegetables and fruits as possible, with tasty recipes so that we’re too busy with those to crave junk food.
Speaking of recipes, there are 80, and they are easy to follow. She describes them as “plant-based”, and by this what she really means is “plant-centric” or such; she does include the use of some animal products.
This is important to note, because general convention is to use “plant-based” to mean functionally vegan, but being about the food rather than the ideology; a relevant distinction in both society and science. In the case of this book, it’s neither, but it is very healthy.
Bottom line: if you’d like to introduce more healthy diversity to your diet, rather than eating the same three fruits and five vegetables, but you’re not sure how, this book will get you where you need to be.
Click here to check out Eat More, Live Well, and diversify your diet!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Healthy Living in a Contaminated World – by Dr. Donald Hoernschemeyer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s a lot going on here, as this book tackles very many kinds of common contaminants, from waste products and industrial chemicals (such as from fracking), pesticides that are banned in most places but not the US, smog and soot from coal and oil power, mercury and other heavy metals, dioxins, Teflon and its close relatives, phthalates, BPA, and other things again regulated out of use in many countries but not entirely in the US (which bans them only in some things, like baby bottles), drinking water issues of various kinds, and much more.
Indeed, there’s a whole chapter on the US and international regulation of toxic substances; the problem is often that on a political level, the same people who are against nebulous “chemicals” are also against environmentalist regulations that would ban them. This is mostly not a political book though, and rather is chiefly a book of chemistry (the author’s field).
It does also cover the medical maladies associated with various contaminants, while the bulk of the data is on the chemistry side of such things as “elimination times for toxic chemicals”, “amounts of pesticides in fruit and vegetables”, “antibiotics and hormones used in animal agriculture”, and so forth.
The style is dense, and/but it is clear the author has made an effort to not be too dry. Still, this is not a fun read; it’s depressing in content and the style is more suited to academia. There are appendices containing glossaries and acronym tables, but reading front-to-back, there’s a lot that’s not explained so unless you also are a PhD chemist, chances are you’ll be needing to leaf forwards and backwards a lot.
Bottom line: this book is not thrilling, but what you don’t know, can kill you.
Click here to check out Healthy Living In A Contaminated World, and improve your odds!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Strong Bones Forever − by Dr. Raymond Hinish
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This doctor of pharmacy would like for fewer people to take (or need to take) osteoporosis medications. Indeed, as the subtitle suggests, the focus here is on drug-free solutions.
And not just because “natural is better” as an argument without evidence, rather, he talks about the limitations and drawbacks of osteoporosis medications (which we wrote about previously, but he has more room to go into more detail), whereupon some osteoporosis meds may do more harm than good.
His method boasts improvements in bone density by 11% or more in two years, and covers such topics as:
- which calcium (and why no, dairy is not what you want; it contains things that inhibit calcium absorption, so the calcium will be stuck in your arteries instead of your bones)
- which minerals are more important than calcium, and why
- common mistakes that many people make that sabotage their bone density
It’s about more than just diet though; he does also talk about hormones, and not just other lifestyle factors, but also many “industry secrets” that aren’t really secrets per se, it’s just, people outside of the industry don’t usually know them—pertaining to things like how to get the most out of bone density tests (i.e. how to get better accuracy), how to meaningfully assess fracture risk, and, if choosing to take osteoporosis meds, how to minimize the risks and maximize the benefits.
The style is very direct and informational, very easy to read, remarkably jargon-free, and our only criticism is that there is no bibliography.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your bone density, this book can certainly help with that.
Click here to check out Strong Bones Forever, and have strong bones forever!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Surgery is the default treatment for ACL injuries in Australia. But it’s not the only way
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
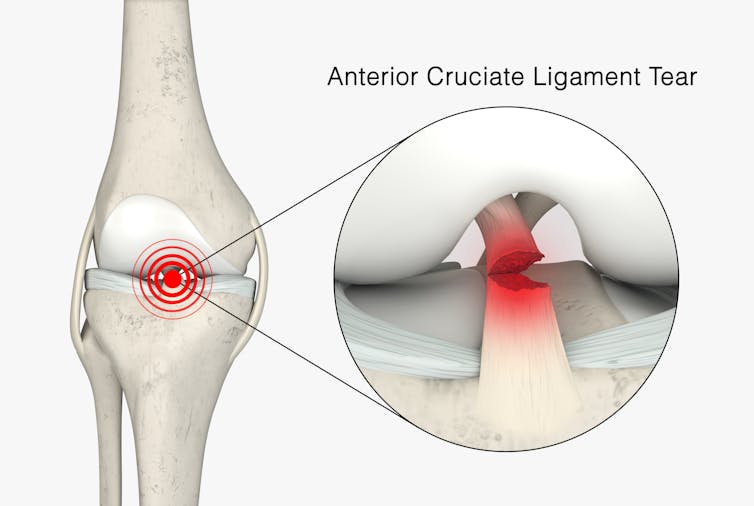
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is an important ligament in the knee. It runs from the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia) and helps stabilise the knee joint.
Injuries to the ACL, often called a “tear” or a “rupture”, are common in sport. While a ruptured ACL has just sidelined another Matildas star, people who play sport recreationally are also at risk of this injury.
For decades, surgical repair of an ACL injury, called a reconstruction, has been the primary treatment in Australia. In fact, Australia has among the highest rates of ACL surgery in the world. Reports indicate 90% of people who rupture their ACL go under the knife.
Although surgery is common – around one million are performed worldwide each year – and seems to be the default treatment for ACL injuries in Australia, it may not be required for everyone.
PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock What does the research say?
We know ACL ruptures can be treated using reconstructive surgery, but research continues to suggest they can also be treated with rehabilitation alone for many people.
Almost 15 years ago a randomised clinical trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine compared early surgery to rehabilitation with the option of delayed surgery in young active adults with an ACL injury. Over half of people in the rehabilitation group did not end up having surgery. After five years, knee function did not differ between treatment groups.
The findings of this initial trial have been supported by more research since. A review of three trials published in 2022 found delaying surgery and trialling rehabilitation leads to similar outcomes to early surgery.
A 2023 study followed up patients who received rehabilitation without surgery. It showed one in three had evidence of ACL healing on an MRI after two years. There was also evidence of improved knee-related quality of life in those with signs of ACL healing compared to those whose ACL did not show signs of healing.
Experts used to think an ACL tear couldn’t heal without surgery – now there’s evidence it can. SKYKIDKID/Shutterstock Regardless of treatment choice the rehabilitation process following ACL rupture is lengthy. It usually involves a minimum of nine months of progressive rehabilitation performed a few days per week. The length of time for rehabilitation may be slightly shorter in those not undergoing surgery, but more research is needed in this area.
Rehabilitation starts with a physiotherapist overseeing simple exercises right through to resistance exercises and dynamic movements such as jumping, hopping and agility drills.
A person can start rehabilitation with the option of having surgery later if the knee remains unstable. A common sign of instability is the knee giving way when changing direction while running or playing sports.
To rehab and wait, or to go straight under the knife?
There are a number of reasons patients and clinicians may opt for early surgical reconstruction.
For elite athletes, a key consideration is returning to sport as soon as possible. As surgery is a well established method, athletes (such as Matilda Sam Kerr) often opt for early surgical reconstruction as this gives them a more predictable timeline for recovery.
At the same time, there are risks to consider when rushing back to sport after ACL reconstruction. Re-injury of the ACL is very common. For every month return to sport is delayed until nine months after ACL reconstruction, the rate of knee re-injury is reduced by 51%.
For people who opt to try rehabilitation, the option of having surgery later is still there. PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock Historically, another reason for having early surgical reconstruction was to reduce the risk of future knee osteoarthritis, which increases following an ACL injury. But a review showed ACL reconstruction doesn’t reduce the risk of knee osteoarthritis in the long term compared with non-surgical treatment.
That said, there’s a need for more high-quality, long-term studies to give us a better understanding of how knee osteoarthritis risk is influenced by different treatments.
Rehab may not be the only non-surgical option
Last year, a study looking at 80 people fitted with a specialised knee brace for 12 weeks found 90% had evidence of ACL healing on their follow-up MRI.
People with more ACL healing on the three-month MRI reported better outcomes at 12 months, including higher rates of returning to their pre-injury level of sport and better knee function. Although promising, we now need comparative research to evaluate whether this method can achieve similar results to surgery.
What to do if you rupture your ACL
First, it’s important to seek a comprehensive medical assessment from either a sports physiotherapist, sports physician or orthopaedic surgeon. ACL injuries can also have associated injuries to surrounding ligaments and cartilage which may influence treatment decisions.
In terms of treatment, discuss with your clinician the pros and cons of management options and whether surgery is necessary. Often, patients don’t know not having surgery is an option.
Surgery appears to be necessary for some people to achieve a stable knee. But it may not be necessary in every case, so many patients may wish to try rehabilitation in the first instance where appropriate.
As always, prevention is key. Research has shown more than half of ACL injuries can be prevented by incorporating prevention strategies. This involves performing specific exercises to strengthen muscles in the legs, and improve movement control and landing technique.
Anthony Nasser, Senior Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of Technology Sydney; Joshua Pate, Senior Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of Technology Sydney, and Peter Stubbs, Senior Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of Technology Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: