Pear vs Peach – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pears to peaches, we picked the peaches.
Why?
Both are great! But peaches are exceptional in some ways that pears just can’t match up to:
In terms of macros, pears have more carbs and fiber, the ratio of which results in an approximately equal glycemic index. Thus, we’ll say that pears win this round by virtue of being the nutritionally denser option.
Looking at the vitamins, pears have (slightly) more of vitamins B6, B9, and K, while peaches have (much) more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B7, C, E, and choline—thus sweeping this category easily for peaches.
In the category of minerals, pears have more calcium and copper, while peaches have more iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. This time, the margins of difference for each mineral are comparably low (i.e. pears are close behind peaches on all those minerals), but still, by strength of numbers, it’s a clear win for peaches.
When it comes to polyphenols, not only do peaches have more, but also, they have anticancer properties that pears don’t—see our link below for more about that!
Meanwhile, adding up the sections makes for an overall win for peaches, but as ever when it comes to fruits, by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← peaches in the #2 spot! They induce cell death in cancer cells while sparing healthy ones
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Apricot vs Banana – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing apricot to banana, we picked the banana.
Why?
Both are great, and it was close!
In terms of macros, apricot has more protein, while banana has more carbs and fiber; both are low glycemic index foods, and we’ll call this category a tie.
In the category of vitamins, apricot has more of vitamins A, C, E, and K, while banana has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, and choline, giving banana the win by strength of numbers. It’s worth noting though that apricots are one of the best fruits for vitamin A in particular.
When it comes to minerals, apricot has slightly more calcium, iron, and zinc, while banana has a lot more magnesium, manganese, potassium, and selenium, meaning a moderate win for banana here.
Adding up the sections makes for an overall win for banana—but of course, by all means enjoy either or both!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← we argue for apricots as bonus number 9 on the list
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Toe-Tapping Tip For Better Balance
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Balance is critical for health especially in older age, since it’s amazing how much else can go dramatically and suddenly wrong after a fall. So, here’s an exercise to give great balance and stability:
How to do it
You will need:
- Something to hold onto, such as a countertop
- A target on the floor, such as a mark or a coin
The steps:
- Lift one leg up, bring your foot forward, and tap the object in front of you.
- Then, bring that foot back to where it started.
- Next, switch to the other leg and tap.
- Alternate between your right and left legs, shifting back and forth.
- Your goal is to do this for 10 repetitions on each leg without holding on.
How it works:
Whenever you tap, you have to lift one leg up and reach it out in front of you. Doing this requires you to stand on one leg while moving a weight (namely: your other leg), which is something many people, especially upon getting older, are hesitant to do. If you’re unable to stand on one leg, let alone move your center of gravity (per the counterbalance of the other leg) while doing so, you may end up shuffling and walking with your feet sliding across the ground—something you really want to avoid.
For more on all of this plus a visual demonstration, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Fall Special ← this is about not falling, or, failing that, minimizing injury if you do
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Healthiest Bread Recipe You’ll Probably Find
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝[About accidental scalding with water] Is cold water actually the best immediate treatment for a burn? Maybe there is something better, or something I should apply after the cold water.❞
If this is a case of spilled tea or similar—as in your story, which (apologies) we clipped for brevity—indeed, cold running water is best, and nothing else should be needed. It’s up to you whether you want to invest the time based on the extent of the scalding, but 10 minutes is recommended to minimize tissue damage.
If it’s a more severe scalding or burning, seek medical attention immediately. If it’s a burn to anywhere other than the airway, cold running water is still best for 10 minutes, but if you have to choose between that and professional medical attention, don’t delay the help.
If it’s a burn you’ve given 10 minutes of cold running water and it still hurts and/or has blistered, cover it in a sterile, non-adhesive dressing that extends well beyond the visible burn (because the actual damage probably extends further, and you don’t want to find this out the hard way later). If the burn is to the face, do still irrigate but not cover it; wait for help.
Do not apply any kind of cream, lotion, oil, etc. No matter how tempting, no matter where the burn is.
All of the above also goes for splashed oil, chemical burns, and electrical burns too (but obviously, make sure to get away from the electricity first).
Source: this ex-military writer was trained for this sort of thing and, suffice it to say, has dealt with more serious things than spilled tea before now.
Legal note: notwithstanding the above, we are a health science newsletter, not paramedics. Also, circumstances may differ, and best practices may change. In the case of serious injury, call emergency services first, and follow their instructions over ours.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Running or yoga can help beat depression, research shows – even if exercise is the last thing you feel like
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
At least one in ten people have depression at some point in their lives, with some estimates closer to one in four. It’s one of the worst things for someone’s wellbeing – worse than debt, divorce or diabetes.
One in seven Australians take antidepressants. Psychologists are in high demand. Still, only half of people with depression in high-income countries get treatment.
Our new research shows that exercise should be considered alongside therapy and antidepressants. It can be just as impactful in treating depression as therapy, but it matters what type of exercise you do and how you do it.
Walk, run, lift, or dance away depression
We found 218 randomised trials on exercise for depression, with 14,170 participants. We analysed them using a method called a network meta-analysis. This allowed us to see how different types of exercise compared, instead of lumping all types together.
We found walking, running, strength training, yoga and mixed aerobic exercise were about as effective as cognitive behaviour therapy – one of the gold-standard treatments for depression. The effects of dancing were also powerful. However, this came from analysing just five studies, mostly involving young women. Other exercise types had more evidence to back them.
Walking, running, strength training, yoga and mixed aerobic exercise seemed more effective than antidepressant medication alone, and were about as effective as exercise alongside antidepressants.
But of these exercises, people were most likely to stick with strength training and yoga.
Antidepressants certainly help some people. And of course, anyone getting treatment for depression should talk to their doctor before changing what they are doing.
Still, our evidence shows that if you have depression, you should get a psychologist and an exercise plan, whether or not you’re taking antidepressants.
Join a program and go hard (with support)
Before we analysed the data, we thought people with depression might need to “ease into it” with generic advice, such as “some physical activity is better than doing none.”
But we found it was far better to have a clear program that aimed to push you, at least a little. Programs with clear structure worked better, compared with those that gave people lots of freedom. Exercising by yourself might also make it hard to set the bar at the right level, given low self-esteem is a symptom of depression.
We also found it didn’t matter how much people exercised, in terms of sessions or minutes a week. It also didn’t really matter how long the exercise program lasted. What mattered was the intensity of the exercise: the higher the intensity, the better the results.
Yes, it’s hard to keep motivated
We should exercise caution in interpreting the findings. Unlike drug trials, participants in exercise trials know which “treatment” they’ve been randomised to receive, so this may skew the results.
Many people with depression have physical, psychological or social barriers to participating in formal exercise programs. And getting support to exercise isn’t free.
We also still don’t know the best way to stay motivated to exercise, which can be even harder if you have depression.
Our study tried to find out whether things like setting exercise goals helped, but we couldn’t get a clear result.
Other reviews found it’s important to have a clear action plan (for example, putting exercise in your calendar) and to track your progress (for example, using an app or smartwatch). But predicting which of these interventions work is notoriously difficult.
A 2021 mega-study of more than 60,000 gym-goers found experts struggled to predict which strategies might get people into the gym more often. Even making workouts fun didn’t seem to motivate people. However, listening to audiobooks while exercising helped a lot, which no experts predicted.
Still, we can be confident that people benefit from personalised support and accountability. The support helps overcome the hurdles they’re sure to hit. The accountability keeps people going even when their brains are telling them to avoid it.
So, when starting out, it seems wise to avoid going it alone. Instead:
- join a fitness group or yoga studio
get a trainer or an exercise physiologist
- ask a friend or family member to go for a walk with you.
Taking a few steps towards getting that support makes it more likely you’ll keep exercising.
Let’s make this official
Some countries see exercise as a backup plan for treating depression. For example, the American Psychological Association only conditionally recommends exercise as a “complementary and alternative treatment” when “psychotherapy or pharmacotherapy is either ineffective or unacceptable”.
Based on our research, this recommendation is withholding a potent treatment from many people who need it.
In contrast, The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists recommends vigorous aerobic activity at least two to three times a week for all people with depression.
Given how common depression is, and the number failing to receive care, other countries should follow suit and recommend exercise alongside front-line treatments for depression.
I would like to acknowledge my colleagues Taren Sanders, Chris Lonsdale and the rest of the coauthors of the paper on which this article is based.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14.
Michael Noetel, Senior Lecturer in Psychology, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
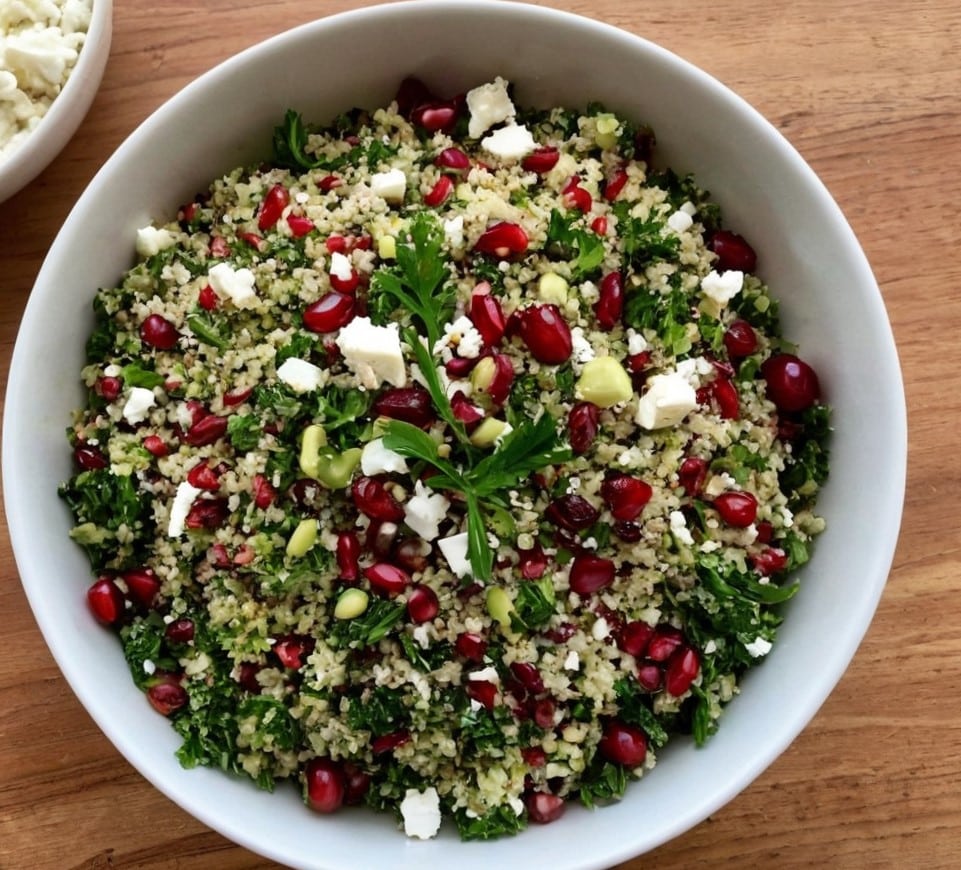
Quercetin Quinoa Probiotic Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This quercetin-rich salad is a bit like a tabbouleh in feel, with half of the ingredients switched out to maximize phenolic and gut-healthy benefits.
You will need
- ½ cup quinoa
- ½ cup kale, finely chopped
- ½ cup flat leaf parsley, finely chopped
- ½ cup green olives, thinly sliced
- ½ cup sun-dried tomatoes, roughly chopped
- 1 pomegranate, peel and pith removed
- 1 preserved lemon, finely chopped
- 1 oz feta cheese or plant-based equivalent, crumbled
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tbsp capers
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
Note: you shouldn’t need salt or similar here, because of the diverse gut-healthy fermented products bringing their own salt with them
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Rinse the quinoa, add the tbsp of chia seeds, cook as normal for quinoa (i.e. add hot water, bring to boil, simmer for 15 minutes or so until pearly and tender), carefully (don’t lose the chia seeds; use a sieve) drain and rinse with cold water to cool. Shake off excess water and/or pat dry on kitchen paper if necessary.
2) Mix everything gently but thoroughly.
3) Serve:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Tasty Tabbouleh with Tahini ← in case you want an actual tabbouleh
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Fight Inflammation & Protect Your Brain, With Quercetin
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fully Present – by Dr. Susan Smalley and Diana Winston
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“The Science and the Art of…” tends to be a bit of a fuzzy obfuscation, but in this case, it’s accurate, especially in this presentation. The authors are, indeed, a scientist and an artist—and both practitioners, meeting in the middle.
As such, we get the clinical insights of a researcher and professor of psychiatry, and the grounded-yet-spiritual insights of an erstwhile Buddhist nun.
While the book is pop psychology in essence, the format is much more that of a textbook than a self-help book. Will it be useful for helping yourself anyway, though? Yes, absolutely, if you apply the information contained within.
Don’t be fooled into thinking that a textbook format makes it dry, though—the writing is very compelling, and you’ll find yourself turning pages eagerly. There’s no time like the present, after all!
Bottom line: if you find the scientific evidence-base for the usefulness of mindfulness appealing, but find a lot of guides a little fluffy, this one is perfectly balanced—and very well written, too.
Click here to check out Fully Present, bring yourself into the moment, always!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: