Chickpeas vs Mung Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing chickpeas to mung beans, we picked the chickpeas.
Why?
Both are great! But there’s a clear winner here:
In terms of macros, chickpeas have more protein, carbs, and fiber, as well as the lower glycemic index. The difference is very small, but it’s a nominal win for chickpeas.
When it comes to vitamins, chickpeas have more of vitamins A, B2, B6, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while mung beans have more of vitamins B1, B3, and B5. Again the differences aren’t huge, but by strength of numbers they’re in chickpeas’ favor, so it’s another win for chickpeas here.
In the category of minerals, chickpeas have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while mung beans are not higher in any mineral. An easy win for chickpeas on this one.
Adding up the sections makes for a clear overall win for chickpeas, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Alzheimer’s may have once spread from person to person, but the risk of that happening today is incredibly low
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
An article published this week in the prestigious journal Nature Medicine documents what is believed to be the first evidence that Alzheimer’s disease can be transmitted from person to person.
The finding arose from long-term follow up of patients who received human growth hormone (hGH) that was taken from brain tissue of deceased donors.
Preparations of donated hGH were used in medicine to treat a variety of conditions from 1959 onwards – including in Australia from the mid 60s.
The practice stopped in 1985 when it was discovered around 200 patients worldwide who had received these donations went on to develop Creuztfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), which causes a rapidly progressive dementia. This is an otherwise extremely rare condition, affecting roughly one person in a million.
What’s CJD got to do with Alzehimer’s?
CJD is caused by prions: infective particles that are neither bacterial or viral, but consist of abnormally folded proteins that can be transmitted from cell to cell.
Other prion diseases include kuru, a dementia seen in New Guinea tribespeople caused by eating human tissue, scrapie (a disease of sheep) and variant CJD or bovine spongiform encephalopathy, otherwise known as mad cow disease. This raised public health concerns over the eating of beef products in the United Kingdom in the 1980s.
Human growth hormone used to come from donated organs
Human growth hormone (hGH) is produced in the brain by the pituitary gland. Treatments were originally prepared from purified human pituitary tissue.
But because the amount of hGH contained in a single gland is extremely small, any single dose given to any one patient could contain material from around 16,000 donated glands.
An average course of hGH treatment lasts around four years, so the chances of receiving contaminated material – even for a very rare condition such as CJD – became quite high for such people.
hGH is now manufactured synthetically in a laboratory, rather than from human tissue. So this particular mode of CJD transmission is no longer a risk.
Human growth hormone is now produced in a lab.
National Cancer Institute/UnsplashWhat are the latest findings about Alzheimer’s disease?
The Nature Medicine paper provides the first evidence that transmission of Alzheimer’s disease can occur via human-to-human transmission.
The authors examined the outcomes of people who received donated hGH until 1985. They found five such recipients had developed early-onset Alzheimer’s disease.
They considered other explanations for the findings but concluded donated hGH was the likely cause.
Given Alzheimer’s disease is a much more common illness than CJD, the authors presume those who received donated hGH before 1985 may be at higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease is caused by presence of two abnormally folded proteins: amyloid and tau. There is increasing evidence these proteins spread in the brain in a similar way to prion diseases. So the mode of transmission the authors propose is certainly plausible.
However, given the amyloid protein deposits in the brain at least 20 years before clinical Alzheimer’s disease develops, there is likely to be a considerable time lag before cases that might arise from the receipt of donated hGH become evident.
When was this process used in Australia?
In Australia, donated pituitary material was used from 1967 to 1985 to treat people with short stature and infertility.
More than 2,000 people received such treatment. Four developed CJD, the last case identified in 1991. All four cases were likely linked to a single contaminated batch.
The risks of any other cases of CJD developing now in pituitary material recipients, so long after the occurrence of the last identified case in Australia, are considered to be incredibly small.
Early-onset Alzheimer’s disease (defined as occurring before the age of 65) is uncommon, accounting for around 5% of all cases. Below the age of 50 it’s rare and likely to have a genetic contribution.
Early onset Alzheimer’s means it occurs before age 65.
perfectlab/ShutterstockThe risk is very low – and you can’t ‘catch’ it like a virus
The Nature Medicine paper identified five cases which were diagnosed in people aged 38 to 55. This is more than could be expected by chance, but still very low in comparison to the total number of patients treated worldwide.
Although the long “incubation period” of Alzheimer’s disease may mean more similar cases may be identified in the future, the absolute risk remains very low. The main scientific interest of the article lies in the fact it’s first to demonstrate that Alzheimer’s disease can be transmitted from person to person in a similar way to prion diseases, rather than in any public health risk.
The authors were keen to emphasise, as I will, that Alzheimer’s cannot be contracted via contact with or providing care to people with Alzheimer’s disease.
Steve Macfarlane, Head of Clinical Services, Dementia Support Australia, & Associate Professor of Psychiatry, Monash University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Do we need animal products to be healthy?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Do we need animal products to be healthy?
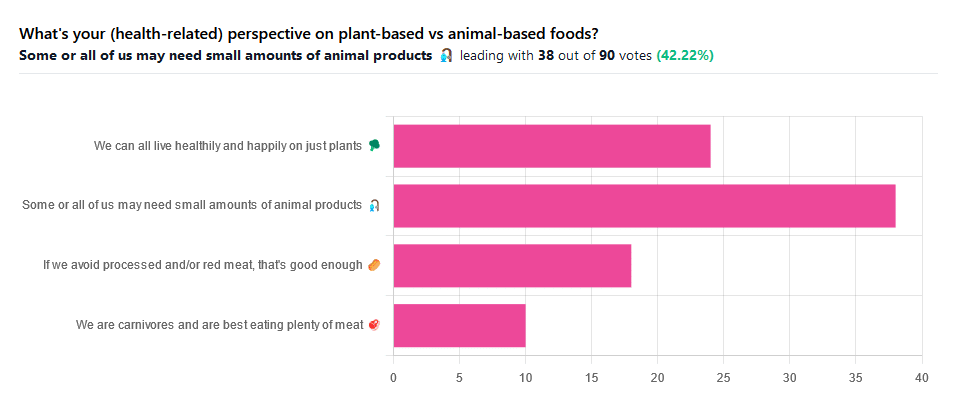
We asked you for your (health-related) perspective on plant-based vs anima-based foods, and got the above-pictured spread of answers.
“Some or all of us may need small amounts of animal products” came out on top with more votes than the two more meat-eatery options combined, and the second most popular option was the hard-line “We can all live healthily and happily on just plants”.
Based on these answers, it seems our readership has quite a lot of vegans, vegetarians, and perhaps “flexitarians” who just have a little of animal products here and there.
Perhaps we should have seen this coming; the newsletter is “10almonds”, not “10 rashers of bacon”, after all.
But what does the science say?
We are carnivores and are best eating plenty of meat: True or False?
False. Let’s just rip the band-aid off for this one.
In terms of our anatomy and physiology, we are neither carnivores nor herbivores:
- We have a mid-length digestive tract (unlike carnivores and herbivores who have short and long ones, respectively)
- We have a mouthful of an assortment of teeth; molars and premolars for getting through plants from hard nuts to tough fibrous tubers, and we have incisors for cutting into flesh and (vestigial, but they’re there) canines that really serve us no purpose now but would have been a vicious bite when they were bigger, like some other modern-day primates.
- If we look at our closest living relatives, the other great apes, they are mostly frugivores (fruit-eaters) who supplement their fruity diet with a small quantity of insects and sometimes other small animals—of which they’ll often eat only the fatty organ meat and discard the rest.
And then, there’s the health risks associated with meat. We’ll not linger on this as we’ve talked about it before, but for example:
- Processed Meat Consumption and the Risk of Cancer: A Critical Evaluation of the Constraints of Current Evidence from Epidemiological Studies
- Red Meat Consumption (Heme Iron Intake) and Risk for Diabetes and Comorbidities?
- Health Risks Associated with Meat Consumption: A Review of Epidemiological Studies
- Associations of Processed Meat, Unprocessed Red Meat, Poultry, or Fish Intake With Incident Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality
- Meat consumption: Which are the current global risks? A review of recent (2010-2020) evidences
If we avoid processed and/or red meat, that’s good enough: True or False?
True… Ish.
Really this one depends on one’s criteria for “good enough”. The above-linked studies, and plenty more like them, give the following broad picture:
- Red and/or processed meats are unequivocally terrible for the health in general
- Other mammalian meats, such as from pigs, are really not much better
- Poultry, on the other hand, the science is less clear on; the results are mixed, and thus so are the conclusions. The results are often barely statistically significant. In other words, when it comes to poultry, in the matter of health, the general consensus is that you can take it or leave it and will be fine. Some studies have found firmly for or against it, but the consensus is a collective scientific shrug.
- Fish, meanwhile, has almost universally been found to be healthful in moderation. You may have other reasons for wanting to avoid it (ethics, environmentalism, personal taste) but those things are beyond the scope of this article.
Some or all of us may need small amounts of animal products: True or False?
True! With nuances.
Let’s divide this into “some” and “all”. Firstly, some people may have health conditions and/or other mitigating circumstances that make an entirely plant-based diet untenable.
We’re going light on quotations from subscriber comments today because otherwise this article will get a bit long, but here’s a great example that’s worth quoting, from a subscriber who voted for this option:
❝I have a rare genetic disease called hereditary fructose intolerance. It means I lack the enzyme, Aldolase B, to process fructose. Eating fruits and veggies thus gives me severe hypoglycemia. I also have anemia caused by two autoimmune diseases, so I have to eat meat for the iron it supplies. I also supplement with iron pills but the pills alone can’t fix the problem entirely.❞
And, there’s the thing. Popular vegan talking-points are very good at saying “if you have this problem, this will address it; if you have that problem, that will address it”, etc. For every health-related objection to a fully plant-based diet there’s a refutation… Individually.
But actual real-world health doesn’t work like that; co-morbidities are very common, and in some cases, like our subscriber above, one problem undermines the solution to another. Add a third problem and by now you really just have to do what you need to do to survive.
For this reason, even the Vegan Society’s definition of veganism includes the clause “so far as is possible and practicable”.
Now, as for the rest of us “all”.
What if we’re really healthy and are living in optimal circumstances (easy access to a wide variety of choice of food), can we live healthily and happily just on plants?
No—on a technicality.
Vegans famously need to supplement vitamin B12, which is not found in plants. Ironically, much of the B12 in animal products comes from the animals themselves being given supplements, but that’s another matter. However, B12 can also be enjoyed from yeast. Popular options include the use of yeast extract (e.g. Marmite) and/or nutritional yeast in cooking.
Yeast is a single-celled microorganism that’s taxonomically classified as a fungus, even though in many ways it behaves like an animal (which series of words may conjure an amusing image, but we mean, biologically speaking).
However, it’s also not technically a plant, hence the “No—on a technicality”
Bottom line:
By nature, humans are quite versatile generalists when it comes to diet:
- Most of us can live healthily and happily on just plants if we so choose.
- Some people cannot, and will require varying kinds (and quantities) of animal products.
- As for red and/or processed meats, we’re not the boss of you, but from a health perspective, the science is clear: unless you have a circumstance that really necessitates it, just don’t.
- Same goes for pork, which isn’t red and may not be processed, but metabolically it’s associated with the same problems.
- The jury is out on poultry, but it strongly appears to be optional, healthwise, without making much of a difference either way
- Fish is roundly considered healthful in moderation. Enjoy it if you want, don’t if you don’t.
Share This Post
-
How often should you wash your sheets and towels?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Everyone seems to have a different opinion when it comes to how often towels and bed sheets should be washed. While many people might wonder whether days or weeks is best, in one survey from the United Kingdom, almost half of single men reported not washing their sheets for up to four months at a time.
It’s fairly clear that four months is too long to leave it, but what is the ideal frequency?
Bed linen and towels are quite different and so should be washed at different intervals. While every week or two will generally suffice for sheets, towels are best washed every few days.
Anyway, who doesn’t love the feeling of a fresh set of sheets or the smell of a newly laundered towel?
Why you should wash towels more often
When you dry yourself, you deposit thousands of skin cells and millions of microbes onto the towel. And because you use your towel to dry yourself after a shower or bath, your towel is regularly damp.
You also deposit a hefty amount of dead skin, microbes, sweat and oils onto your sheets every night. But unless you’re a prolific night sweater, your bedding doesn’t get wet after a night’s sleep.
Towels are also made of a thicker material than sheets and therefore tend to stay damp for longer.
So what is it about the dampness that causes a problem? Wet towels are a breeding ground for bacteria and moulds. Moulds especially love damp environments. Although mould won’t necessarily be visible (you would need significant growth to be able to see it) this can lead to an unpleasant smell.
As well as odours, exposure to these microbes in your towels and sheets can cause asthma, allergic skin irritations, or other skin infections.
People don’t always agree on how often to change the sheets.
http://rawpixel.com/ShutterstockSo what’s the ideal frequency?
For bedding, it really depends on factors such as whether you have a bath or shower just before going to bed, or if you fall into bed after a long, sweaty day and have your shower in the morning. You will need to wash your sheets more regularly in the latter case. As a rule of thumb, once a week or every two weeks should be fine.
Towels should ideally be washed more regularly – perhaps every few days – while your facecloth should be cleaned after every use. Because it gets completely wet, it will be wet for a longer time, and retain more skin cells and microbes.
Wash your towels at a high temperature (for example, 65°C) as that will kill many microbes. If you are conscious of saving energy, you can use a lower temperature and add a cup of vinegar to the wash. The vinegar will kill microbes and prevent bad smells from developing.
Clean your washing machine regularly and dry the fold in the rubber after every wash, as this is another place microbes like to grow.
Smelly towels
What if you regularly wash your towels, but they still smell bad? One of the reasons for this pong could be that you’ve left them in the washing machine too long after the wash. Especially if it was a warm wash cycle, the time they’re warm and damp will allow microbes to happily grow. Under lab conditions the number of these bacteria can double every 30 minutes.
It’s important to hang your towel out to dry after use and not to leave towels in the washing machine after the cycle has finished. If possible, hang your towels and bedding out in the sun. That will dry them quickly and thoroughly and will foster that lovely fresh, clean cotton smell. Using a dryer is a good alternative if the weather is bad, but outdoors in the sun is always better if possible.
Also, even if your towel is going to be washed, don’t throw a wet towel into the laundry basket, as the damp, dirty towel will be an ideal place for microbes to breed. By the time you get to doing your washing, the towel and the other laundry around it may have acquired a bad smell. And it can be difficult to get your towels smelling fresh again.
Towels should be washed more often than sheets.
New Africa/ShutterstockWhat about ‘self-cleaning’ sheets and towels?
Some companies sell “quick-dry” towels or “self-cleaning” towels and bedding. Quick-dry towels are made from synthetic materials that are weaved in a way to allow them to dry quickly. This would help prevent the growth of microbes and the bad smells that develop when towels are damp for long periods of time.
But the notion of self-cleaning products is more complicated. Most of these products contain nanosilver or copper, antibacterial metals that kill micro-organisms. The antibacterial compounds will stop the growth of bacteria and can be useful to limit smells and reduce the frequency with which you need to clean your sheets and towels.
However, they’re not going to remove dirt like oils, skin flakes and sweat. So as much as I would love the idea of sheets and towels that clean themselves, that’s not exactly what happens.
Also, excessive use of antimicrobials such as nanosilver can lead to microbes becoming resistant to them.
Rietie Venter, Associate professor, Clinical and Health Sciences, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Well Plated Cookbook – by Erin Clarke
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Clarke’s focus here is on what she calls “stealthy healthy”, with the idea of dishes that feel indulgent while being great for the health.
The recipes, of which there are well over 100, are indeed delicious and easy to make without being oversimplified, and since she encourages the use of in-season ingredients, many recipes come with a “market swaps” substitution guide, to make each recipe seasonal.
The book is largely not vegetarian, let alone vegan, but the required substitutions will be second-nature to any seasoned vegetarian or vegan. Indeed, “skip the meat sometimes” is one of the advices she offers near the beginning of the book, in the category of tips to make things even healthier.
Bottom line: if you want to add dishes to your repertoire that are great for entertaining and still super-healthy, this book will be a fine addition to your collection.
Click here to check out The Well Plated Cookbook, and get cooking!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Are you over 75? Here’s what you need to know about vitamin D
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Vitamin D is essential for bone health, immune function and overall wellbeing. And it becomes even more crucial as we age.
New guidelines from the international Endocrine Society recommend people aged 75 and over should consider taking vitamin D supplements.
But why is vitamin D so important for older adults? And how much should they take?
OPPO Find X5 Pro/Unsplash Young people get most vitamin D from the sun
In Australia, it is possible for most people under 75 to get enough vitamin D from the sun throughout the year. For those who live in the top half of Australia – and for all of us during summer – we only need to have skin exposed to the sun for a few minutes on most days.
The body can only produce a certain amount of vitamin D at a time. So staying in the sun any longer than needed is not going to help increase your vitamin D levels, while it will increase your risk of skin cancer.
But it’s difficult for people aged over 75 to get enough vitamin D from a few minutes of sunshine, so the Endocrine Society recommends people get 800 IU (international units) of vitamin D a day from food or supplements.
Why you need more as you age
This is higher than the recommendation for younger adults, reflecting the increased needs and reduced ability of older bodies to produce and absorb vitamin D.
Overall, older adults also tend to have less exposure to sunlight, which is the primary source of natural vitamin D production. Older adults may spend more time indoors and wear more clothing when outdoors.
As we age, our skin also becomes less efficient at synthesising vitamin D from sunlight.
The kidneys and the liver, which help convert vitamin D into its active form, also lose some of their efficiency with age. This makes it harder for the body to maintain adequate levels of the vitamin.
All of this combined means older adults need more vitamin D.
Deficiency is common in older adults
Despite their higher needs for vitamin D, people over 75 may not get enough of it.
Studies have shown one in five older adults in Australia have vitamin D deficiency.
In higher-latitude parts of the world, such as the United Kingdom, almost half don’t reach sufficient levels.
This increased risk of deficiency is partly due to lifestyle factors, such as spending less time outdoors and insufficient dietary intakes of vitamin D.
It’s difficult to get enough vitamin D from food alone. Oily fish, eggs and some mushrooms are good sources of vitamin D, but few other foods contain much of the vitamin. While foods can be fortified with the vitamin D (margarine, some milk and cereals), these may not be readily available or be consumed in sufficient amounts to make a difference.
In some countries such as the United States, most of the dietary vitamin D comes from fortified products. However, in Australia, dietary intakes of vitamin D are typically very low because only a few foods are fortified with it.
Why vitamin D is so important as we age
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, which is essential for maintaining bone density and strength. As we age, our bones become more fragile, increasing the risk of fractures and conditions like osteoporosis.
Keeping bones healthy is crucial. Studies have shown older people hospitalised with hip fractures are 3.5 times more likely to die in the next 12 months compared to people who aren’t injured.
People over 75 often have less exposure to sunlight. Aila Images/Shutterstock Vitamin D may also help lower the risk of respiratory infections, which can be more serious in this age group.
There is also emerging evidence for other potential benefits, including better brain health. However, this requires more research.
According to the society’s systematic review, which summarises evidence from randomised controlled trials of vitamin D supplementation in humans, there is moderate evidence to suggest vitamin D supplementation can lower the risk of premature death.
The society estimates supplements can prevent six deaths per 1,000 people. When considering the uncertainty in the available evidence, the actual number could range from as many as 11 fewer deaths to no benefit at all.
Should we get our vitamin D levels tested?
The Endocrine Society’s guidelines suggest routine blood tests to measure vitamin D levels are not necessary for most healthy people over 75.
There is no clear evidence that regular testing provides significant benefits, unless the person has a specific medical condition that affects vitamin D metabolism, such as kidney disease or certain bone disorders.
Routine testing can also be expensive and inconvenient.
In most cases, the recommended approach to over-75s is to consider a daily supplement, without the need for testing.
You can also try to boost your vitamin D by adding fortified foods to your diet, which might lower the dose you need from supplementation.
Even if you’re getting a few minutes of sunlight a day, a daily vitamin D is still recommended.
Elina Hypponen, Professor of Nutritional and Genetic Epidemiology, University of South Australia and Joshua Sutherland, PhD Candidate – Nutrition and Genetic Epidemiology, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hazelnuts vs Pecans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing hazelnuts to pecans, we picked the hazelnuts.
Why?
In terms of macros, hazelnuts have more protein, carbs, and fiber, though the difference is not big in the latter two cases, and the glycemic indices are resultantly about the same. Meanwhile, pecans have a little more fat, but the fat is healthy in both cases. Everything taken into account, we’re calling it a tie on macros.
When it comes to vitamins, hazelnuts have more of vitamins B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while pecans have more of vitamins A, B1, and B2. An easy win for hazelnuts here.
In the category of minerals, hazelnuts have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium, while pecans have more selenium and zinc. Another clear win for hazelnuts.
In short, enjoy either or both (unless you’re allergic, in which case, don’t), but hazelnuts are ultimately the more nutritionally dense of the two.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: