Bird flu has been detected in a pig in the US. Why does that matter?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The United States Department of Agriculture last week reported that a pig on a backyard farm in Oregon was infected with bird flu.
As the bird flu situation has evolved, we’ve heard about the A/H5N1 strain of the virus infecting a range of animals, including a variety of birds, wild animals and dairy cattle.
Fortunately, we haven’t seen any sustained spread between humans at this stage. But the detection of the virus in a pig marks a worrying development in the trajectory of this virus.

How did we get here?
The most concerning type of bird flu currently circulating is clade 2.3.4.4b of A/H5N1, a strain of influenza A.
Since 2020, A/H5N1 2.3.4.4b has spread to a vast range of birds, wild animals and farm animals that have never been infected with bird flu before.
While Europe is a hotspot for A/H5N1, attention is currently focused on the US. Dairy cattle were infected for the first time in 2024, with more than 400 herds affected across at least 14 US states.
Bird flu has enormous impacts on farming and commercial food production, because infected poultry flocks have to be culled, and infected cows can result in contaminated diary products. That said, pasteurisation should make milk safe to drink.
While farmers have suffered major losses due to H5N1 bird flu, it also has the potential to mutate to cause a human pandemic.
Birds and humans have different types of receptors in their respiratory tract that flu viruses attach to, like a lock (receptors) and key (virus). The attachment of the virus allows it to invade a cell and the body and cause illness. Avian flu viruses are adapted to birds, and spread easily among birds, but not in humans.
So far, human cases have mainly occurred in people who have been in close contact with infected farm animals or birds. In the US, most have been farm workers.
The concern is that the virus will mutate and adapt to humans. One of the key steps for this to happen would be a shift in the virus’ affinity from the bird receptors to those found in the human respiratory tract. In other words, if the virus’ “key” mutated to better fit with the human “lock”.
A recent study of a sample of A/H5N1 2.3.4.4b from an infected human had worrying findings, identifying mutations in the virus with the potential to increase transmission between human hosts.
Why are pigs a problem?
A human pandemic strain of influenza can arise in several ways. One involves close contact between humans and animals infected with their own specific flu viruses, creating opportunities for genetic mixing between avian and human viruses.
Pigs are the ideal genetic mixing vessel to generate a human pandemic influenza strain, because they have receptors in their respiratory tracts which both avian and human flu viruses can bind to.
This means pigs can be infected with a bird flu virus and a human flu virus at the same time. These viruses can exchange genetic material to mutate and become easily transmissible in humans.
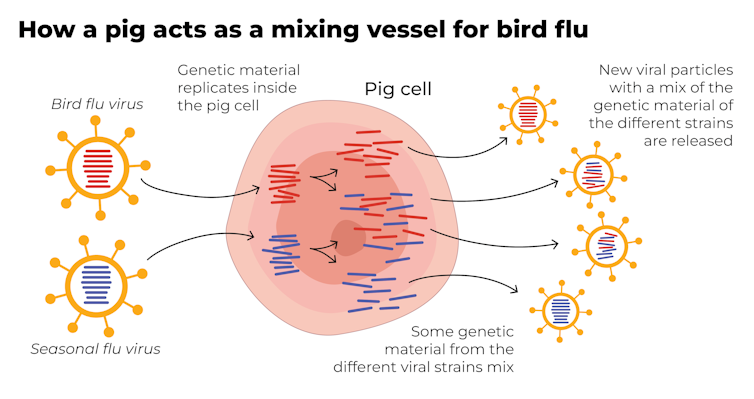
Interestingly, in the past pigs were less susceptible to A/H5N1 viruses. However, the virus has recently mutated to infect pigs more readily.
In the recent case in Oregon, A/H5N1 was detected in a pig on a non-commercial farm after an outbreak occurred among the poultry housed on the same farm. This strain of A/H5N1 was from wild birds, not the one that is widespread in US dairy cows.
The infection of a pig is a warning. If the virus enters commercial piggeries, it would create a far greater level of risk of a pandemic, especially as the US goes into winter, when human seasonal flu starts to rise.
How can we mitigate the risk?
Surveillance is key to early detection of a possible pandemic. This includes comprehensive testing and reporting of infections in birds and animals, alongside financial compensation and support measures for farmers to encourage timely reporting.
Strengthening global influenza surveillance is crucial, as unusual spikes in pneumonia and severe respiratory illnesses could signal a human pandemic. Our EPIWATCH system looks for early warnings of such activity, which can speed up vaccine development.
If a cluster of human cases occurs, and influenza A is detected, further testing (called subtyping) is essential to ascertain whether it’s a seasonal strain, an avian strain from a spillover event, or a novel pandemic strain.
Early identification can prevent a pandemic. Any delay in identifying an emerging pandemic strain enables the virus to spread widely across international borders.
Australia’s first human case of A/H5N1 occurred in a child who acquired the infection while travelling in India, and was hospitalised with illness in March 2024. At the time, testing revealed Influenza A (which could be seasonal flu or avian flu), but subtyping to identify A/H5N1 was delayed.
This kind of delay can be costly if a human-transmissible A/H5N1 arises and is assumed to be seasonal flu because the test is positive for influenza A. Only about 5% of tests positive for influenza A are subtyped further in Australia and most countries.
In light of the current situation, there should be a low threshold for subtyping influenza A strains in humans. Rapid tests which can distinguish between seasonal and H5 influenza A are emerging, and should form part of governments’ pandemic preparedness.
A higher risk than ever before
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that the current risk posed by H5N1 to the general public remains low.
But with H5N1 now able to infect pigs, and showing worrying mutations for human adaptation, the level of risk has increased. Given the virus is so widespread in animals and birds, the statistical probability of a pandemic arising is higher than ever before.
The good news is, we are better prepared for an influenza pandemic than other pandemics, because vaccines can be made in the same way as seasonal flu vaccines. As soon as the genome of a pandemic influenza virus is known, the vaccines can be updated to match it.
Partially matched vaccines are already available, and some countries such as Finland are vaccinating high-risk farm workers.
C Raina MacIntyre, Professor of Global Biosecurity, NHMRC L3 Research Fellow, Head, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute, UNSW Sydney and Haley Stone, Research Associate, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute & CRUISE lab, Computer Science and Engineering, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
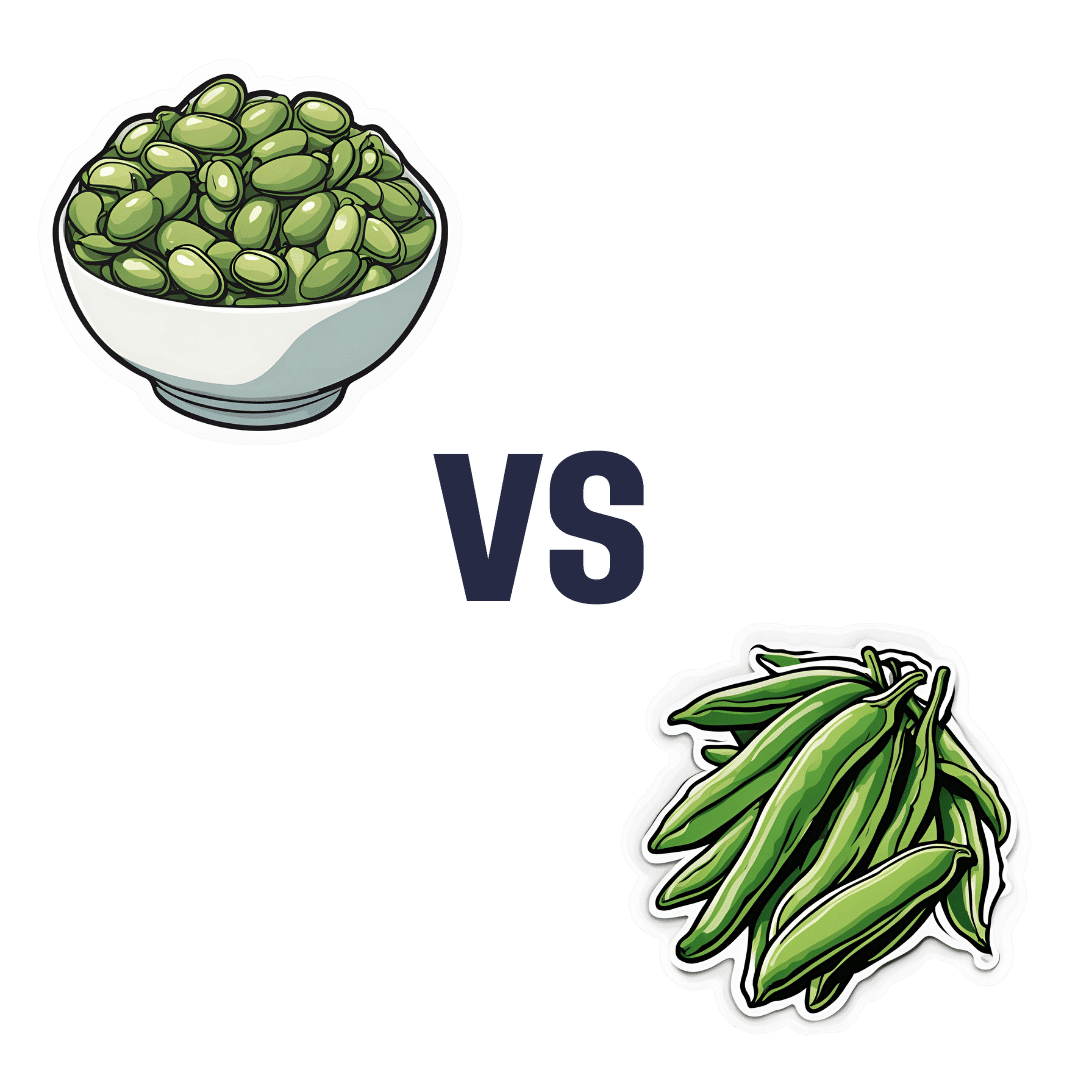
Broad Beans vs Green Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing broad beans to green beans, we picked the broad.
Why?
It’s quite a straightforward one today:
In terms of macros, broad beans have 2.5x the protein, and slightly more fiber and carbs, so we pick the broad beans as the more nutrient-dense option here.
In the category of vitamins, broad beans have more of vitamins B1, B3, B9, and C, while green beans have more of vitamins A and B6 (with comparable margins of difference for both beans’ winning vitamins), so another win for broad beans, based on the 4:2 numerical advantage.
When it comes to minerals, broad beans have more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while green beans have more calcium and manganese. Again, comparable mostly margins of difference (except for broad beans bing 5x richer in selenium, which is a bit of an outlier, but it’s not because broad beans are an amazing source of selenium, but rather, that green beans have only a tiny amount), so it’s a clear 7:2 win for broad beans.
Adding up the three wins for broad beans makes an overall win for them, but by all means, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
How to Prevent Dementia – by Dr. Richard Restak
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written about this topic here, we know. But there’s a lot more we can do to be on guard against, and pre-emptively strengthen ourselves against, dementia.
The author, a neurologist, takes us on a detailed exploration of dementia in general, with a strong focus on Alzheimer’s in particular, as that accounts for more than half of all dementia cases.
But what if you can’t avoid it? It could be that with the wrong genes and some other factor(s) outside of your control, it will get you if something else doesn’t get you first.
Rather than scaremongering, Dr. Restak tackles this head-on too, and discusses how symptoms can be managed, to make the illness less anxiety-inducing, and look to maintain quality of life as much as possible.
The style of the book is… it reads a lot like an essay compilation. Good essays, then organized and arranged in a sensible order for reading, but distinct self-contained pieces. There are ten or eleven chapters (depending on how we count them), each divided into few or many sections. All this makes for:
- A very “read a bit now and a bit later and a bit the next day” book, if you like
- A feeling of a very quick pace, if you prefer to sit down and read it in one go
Either way, it’s a very informative read.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand the many-headed beast that is dementia, this book gives a far more comprehensive overview than we could here, and also explains the prophylactic interventions available.
Share This Post
-
What Macronutrient Balance Is Right For You?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝I want to learn more about macros. Can you cover that topic?❞
That’s a little broader than we usually go for, given the amount of space we have, but let’s give it a go!
Macronutrients, or “macros”, are the nutrients that we typically measure in grams rather than milligrams or micrograms, and are:
- Carbohydrates
- …and what kinds, of which usually the focus is on how much is sugars as opposed to more complex carbs that take longer to break down. See also: Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
- …and of the sugars, the interested may further categorize them into sucrose, fructose, etc. See also: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
- Proteins
- …of which, the amino acid make-up is generally considered a matter of micronutrients. See also: Protein: How Much Do We Need, Really?
- Fats
- …and what kinds, i.e. monounsaturated vs polyunsaturated vs saturated. See also: Saturated Fat: What’s The Truth?
- …and then the interested may further categorize them for their fatty acids / triglycerides profile, etc. See also: What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
- Fiber
- …which often gets ignored by people counting macros, as “stuff that doesn’t do anything”, despite it in fact being very important for health. See also: Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Water
- …which again tends to get disregarded but is very arguably a critical macronutrient. See also: Busting The Myth of “Eight Glasses Of Water A Day”
In terms of how much we need of each, you can read more in the above-linked articles, but:
- General scientific consensus is we need plenty of fiber (30 or 40g per day is good) and water (highly dependent on climate and activity), and there’s a clear minimum requisite for protein (usually put at around 1g of protein per day per 1kg of body weight).
- There is vigorous debate in the general health community about what the best ratio of carbs to fat is.
The reality is that humans are quite an adaptable species, and while we absolutely do need at least some of both (carbohydrates and fats), we can play around with the ratios quite a bit, provided we don’t get too extreme about it.
While some influence is social and often centered around weight loss (see for example keto which seeks to minimize carbs, and volumetrics, which seeks maximise volume-to-calorie ratio, which de facto tends to minimize fats), some of what drives us to lean one way or the other will be genetics, too—dependent on what our ancestors ate more or less of.
Writer’s example: my ancestors could not grow much grain (or crops in general) where they were, so they got more energy from such foods as whale and seal fat (with protein coming more from reindeer). Now, biology is not destiny, and I personally enjoy a vegan diet, but my genes are probably why I am driven to get most of my daily calories from fat (of which, a lot of fatty nuts (don’t tell almonds, but I prefer walnuts and cashews) and healthy oils such as olive oil, avocado oil, and coconut oil).
However! About that adaptability. Provided we make changes slowly, we can usually adjust our diet to whatever we want it to be, including whether we get our energy more from carbs or fats. The reason we need to make changes slowly is because our gut needs time to adjust. For example, if your vegan writer here were to eat her ancestrally-favored foods now, I’d be very ill, because my gut microbiome has no idea what to do with animal products anymore, no matter what genes I have. In contrast, if an enthusiastic enjoyer of a meat-heavy diet were to switch to my fiber-rich diet overnight, they’d be very ill.
So: follow your natural inclinations, make any desired changes slowly, and if in doubt, it’s hard to go wrong with enjoying carbs and fats in moderation.
Learn more: Intuitive Eating Might Not Be What You Think
Take care!
Share This Post
- Carbohydrates
Related Posts
-
Galveston Diet Cookbook for Beginners – by Martha McGrew
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We recently reviewed “The Galveston Diet”, and here’s a cookbook (by a nutritionist) to support that.
For the most part, it’s essentially keto-leaning, with an emphasis on protein and fats, but without quite the carb-cut that keto tends to have. It’s also quite plant-centric, but it’s not by default vegan or even vegetarian; you will find meat and fish in here. As you might expect from an anti-inflammatory cookbook, it’s light on the dairy too, though fermented dairy products such as yogurt do feature as well.
The recipes are quite simple and easy to follow, with suggestions of alternative ingredients along the way, making for extra variety as well as convenience.
If you are going to buy this book, you might want to take a look at the buying options, to ensure you get a full-color version, as recent reprints have photos in black and white, whereas older runs have color throughout.
Bottom line: if you’d like to cook the Galveston Diet way, this is as good a way to start as any.
Click here to check out the Galveston Diet Cookbook for Beginners, and get cooking!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can You Get Addicted To MSG, Like With Sugar?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Hello, I love your newsletter 🙂 Can I have a question? While browsing through your recepies, I realised many contained MSG. As someone based in Europe, I am not used to using MSG while cooking (of course I know that processed food bought in supermarket containes MSG). There is a stigma, that MSG is not particulary healthy, but rather it should be really bad and cause negative effects like headaches. Is this true? Also, can you get addicted to MSG, just like you get addicted to sugar? Thank you :)❞
Thank you for the kind words, and the interesting questions!
Short answer: no and no 🙂
Longer answer: most of the negative reputation about MSG comes from a single piece of satire written in the US in the 1960s, which the popular press then misrepresented as a genuine concern, and the public then ran with, mostly due to racism/xenophobia/sinophobia specifically, given the US’s historically not fabulous relations with China, and the moniker of “Chinese restaurant syndrome”, notwithstanding that MSG was first isolated in Japan, not China, more than 100 years ago.
The silver lining that comes out of this is that because of the above, MSG has been one of the most-studied food additives in recent decades, with many teams of scientists in many countries trying to determine its risks and not finding any (except insofar as anything in extreme quantities can kill you, including water or oxygen).
You can read more about this and other* myths about MSG, here:
Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
*such as pertaining to gluten sensitivity, which in reality MSG has no bearing on whatsoever as it does not contain gluten and is not even made of the same basic stuff; gluten being a protein made of (amongst other things) the amino acid glutamine, not a glutamate salt. Glutamate is as closely related to gluten as cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) is to cyanide (the famous poison).
PS: if you didn’t click the above link to read that article, then 1) we really do recommend it 2) we did some LD50 calculations there and looked at available research, and found that for someone of this writer’s (very medium) size, eating 1kg of MSG at once is sufficient to cause toxicity, and injecting >250g of MSG may cause heart problems. So we don’t recommend doing that.
However, ½ tsp in a recipe that gives multiple portions is not going to get you anywhere close to the danger zone, unless you consume that entire meal by yourself hundreds of times per day. And if you do, the MSG is probably the least of your concerns.
(2 tsp of cassia cinnamon, however, is enough to cause coumarin toxicity; for this reason we recommend Ceylon (or “True” or “Sweet”) cinnamon in our recipes, as it has almost undetectable levels of coumarin)
With regard to your interesting question about addiction, first of all let’s speak briefly about sugar addiction:
Sugar addiction is, by broad scientific consensus, agreed-upon as an extant thing that does exist, and contemporary research is more looking into the “hows” and “whys” and “whats” rather than the “whether”. It is a somewhat complicated topic, because it’s halfway between what science would usually consider a chemical addiction, and what science would usually consider a behavioral addiction:
The Not-So-Sweet Science Of Sugar Addiction
The reasonable prevailing hypothesis, therefore, is that sugar simply has two moderate mechanisms of addiction, rather than one strong one.
The biochemical side of sugar addiction comes from the body’s metabolism of sugar, so this cannot be a thing for MSG, because there is nothing to metabolize in the same sense of the word (MSG being an inorganic compound with zero calories).
People can crave salt, especially when deficient in it, and MSG does contain sodium (it’s what the “S” stands for), but it contains a little under ⅓ of the sodium that table salt does (sodium chloride in whatever form, be it sea salt, rock salt, or such):
MSG vs. Salt: Sodium Comparison ← we do molecular calculations here!
Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier? ← this one for a head-to-head
However, even craving salt does not constitute an addiction; nobody is shamefully hiding their rock salt crystals under their bed and getting a fix when they feel low, and nor does withdrawal cause adverse side effects, except insofar as (once again) a person deficient in salt will crave salt.
Finally, the only other way we know of that one might wonder if MSG could be addictive, is about glutamate and glutamate receptors. The glutamate in MSG is the same glutamate (down to the atoms) as the glutamate formed if one consumes tomatoes in the presence of salt, and triggers the same glutamate receptors in the same way. We have the same number of receptors either way, and uptake is exactly the same (because again, it’s exactly the same chemical) so there is a maximum to how strong this effect can be, and that maximum is the same whatever the source of the glutamate was.
In this respect, if MSG is addictive, then so is a tomato salad with a pinch of salt: it’s not—it’s just tasty.
We haven’t cited papers in today’s article, but it’s just because we cited them already in the articles we linked, and so we avoided doubling up. Most of them are in that first link we gave 🙂
One final note
Technically anyone can develop a sensitivity to anything, so in theory someone could develop a sensitivity to MSG, just like they could for any other ingredient. Our usual legal/medical disclaimer applies.
However, it’s certainly not a common trigger, putting it well below common allergens like nuts (or less common allergens like, say, bananas), not even in the same league as common intolerances such as gluten, and less worthy of health risk warnings than, say, spinach (high in oxalates; fine for most people but best avoided if you have kidney problems).
The reason we use it in the recipes we use it in, is simply because it’s a lower-sodium alternative to salt, and while it contains a (very) tiny bit less sodium than low-sodium salt (which itself has about ⅓ the sodium of regular salt), it has more of a flavor-enhancing effect, such that one can use half as much, for a more than sixfold total sodium reduction. Which for most of us in the industrialized world, is beneficial.
Want to try some?
If today’s article has inspired you to give MSG a try, here’s an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Truth About Handwashing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Washing Our Hands Of It
In Tuesdays’s newsletter, we asked you how often you wash your hands, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of self-reported answers:
- About 54% said “More times per day than [the other options]”
- About 38% said “Whenever using the bathroom or kitchen
- About 5% said “Once or twice per day”
- Two (2) said “Only when visibly dirty”
- Two (2) said “I prefer to just use sanitizer gel”
What does the science have to say about this?
People lie about their handwashing habits: True or False?
True and False (since some people lie and some don’t), but there’s science to this too. Here’s a great study from 2021 that used various levels of confidentiality in questioning (i.e., there were ways of asking that made it either obvious or impossible to know who answered how), and found…
❝We analysed data of 1434 participants. In the direct questioning group 94.5% of the participants claimed to practice proper hand hygiene; in the indirect questioning group a significantly lower estimate of only 78.1% was observed.❞
Note: the abstract alone doesn’t make it clear how the anonymization worked (it is explained later in the paper), and it was noted as a limitation of the study that the participants may not have understood how it works well enough to have confidence in it, meaning that the 78.1% is probably also inflated, just not as much as the 94.5% in the direct questioning group.
Here’s a pop-science article that cites a collection of studies, finding such things as for example…
❝With the use of wireless devices to record how many people entered the restroom and used the pumps of the soap dispensers, researchers were able to collect data on almost 200,000 restroom trips over a three-month period.
The found that only 31% of men and 65% of women washed their hands with soap.❞
Source: Study: Men Wash Their Hands Much Less Often Than Women (And People Lie About Washing Their Hands)
Sanitizer gel does the job of washing one’s hands with soap: True or False?
False, though it’s still not a bad option for when soap and water aren’t available or practical. Here’s an educational article about the science of why this is so:
UCI Health | Soap vs. Hand Sanitizer
There’s also some consideration of lab results vs real-world results, because while in principle the alcohol gel is very good at killing most bacteria / inactivating most viruses, it can take up to 4 minutes of alcohol gel contact to do so, as in this study with flu viruses:
In contrast, 20 seconds of handwashing with soap will generally do the job.
Antibacterial soap is better than other soap: True or False?
False, because the main way that soap protects us is not in its antibacterial properties (although it does also destroy the surface membrane of some bacteria and for that matter viruses too, killing/inactivating them, respectively), but rather in how it causes pathogens to simply slide off during washing.
Here’s a study that found that handwashing with soap reduced disease incidence by 50–53%, and…
❝Incidence of disease did not differ significantly between households given plain soap compared with those given antibacterial soap.❞
Read more: Effect of handwashing on child health: a randomised controlled trial
Want to wash your hands more than you do?
There have been many studies into motivating people to wash their hands more (often with education and/or disgust-based shaming), but an effective method you can use for yourself at home is to simply buy more luxurious hand soap, and generally do what you can to make handwashing a more pleasant experience (taking a moment to let the water run warm is another good thing to do if that’s more comfortable for you).
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: