Maximize Your Misery! (7 Great Methods)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Let’s imagine that instead of being healthily fulfilled in life, you wanted to spend your days as miserable as possible. What should you do?
Here are a few pointers:
Stay still
Avoid physical activity and/or outdoor exposure, to avoid any mood-lifting neurochemicals. In fact, remain indoors as much as possible, preferably in the same room.
If you want to absolutely maximize your misery, make your bedroom the sole space for all activities that it’s possible to do there.
Disrupt your sleep
Keep an irregular sleep schedule by varying your bedtime and wake-up times frequently. Sleep in as much as possible, and make up for it by staying up late to ensure ongoing exhaustion.
Maximize screentime
Use digital entertainment as much as possible to distract you from meaningful activities and rest—as a bonus, this will also help you to avoid self-reflection.
Begin and end your day with a device in hand.
Fuel negative emotions
If you’re going to focus on something, focus on problems you cannot control, to stoke the fires of anger and angst.
A good way of doing this is by staying informed about distressing events, while avoiding meaningful actions to address them. Contribute only in token gestures, and then lament the lack of change.
Follow your impulses
Act on short-term desires without considering long-term consequences, while avoiding behaviors that you know might improve your mood or wellbeing.
Trust that doing the same things that have not previously resulted in happiness, will continue to reliably deliver unhappiness.
Set goals to miss
It’s important that your goals should be vague, and overly ambitious in their scope and/or deliverability. Ideally you should also disregard any preparatory work that a person would normally do before embarking on such a project.
Bonus tip: you can further sabotage any chances of progress, by waiting for motivation to strike before you take any action.
Pursue happiness
Focus on chasing happiness itself, instead of improving your situation or skills. Treat happiness as an end goal, instead of a by-product of worthwhile activities.
Want to learn more?
If you’d like to know many more ways to be miserable, we featured these 7 from this book of 40, which we haven’t reviewed yet, but probably will one of these days:
How to Be Miserable: 40 Strategies You Already Use – by Dr. Randy Paterson
Alternatively…
If for some strange reason you’d rather not do those things, you might consider a previous article of ours:
How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to Eat (And Still Lose Weight) – by Dr. Andrew Jenkinson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may be wondering: what diet is he recommending?
The answer is: some guiding principles aside…. He’s not recommending a diet, per se.
What this book does instead is outline why we eat too much ← link is to where we previously had this author as a spotlight featured expert on this topic! Check it out!
He goes into a lot more detail than we ever could have in our little article, though, and this book is one of those where the reader may feel as though we have had a few classes at medical school. The style, however, is very comprehensible and accessible; there’s no obfuscating jargon here.
Once we understand the signalling that goes on in terms of hunger/satiety, and the signalling that goes on in terms of fat storage/metabolism, we can simply choose to not give our bodies the wrong signals. Yes, it’s really that simple. It feels quite like a cheat code!
Bottom line: if you’d like a better understanding of what regulates our body’s “set point” in weight/adiposity, and what can change it (for better or for worse), then this is the book for you.
Share This Post
-
How To Out-Cheat “Cheat Days”
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Out-Cheating “Cheat Days” (Or Even Just “Cheat Meals”)
If you are in the habit of eating healthily, the idea of a “cheat day” probably isn’t appealing—because you simply don’t crave junk food; it’s not what your gut is used to.
Nevertheless, sometimes cheat days, or at least cheat meals, choose us rather than the other way around. If your social group is having a pizza night or meeting up at the burger bar, probably you’re going to be having a meal that’s not ideal.
So, what to do about it?
Well, first of all, relax. If it really is an exception and not a regular occurrence, it’s not going to have a big health impact. Assuming that your basic dietary requirements are taken care of (e.g. free from allergens as necessary, vegan/vegetarian if that’s appropriate for you, adhering to any religious restrictions that are important to you, etc), then you’re going to have a good time, which is what scientists call a “pro-social activity” and is not a terrible thing.
See also: Is Fast Food Really All That Bad? ← answer: yes it is, but the harm is cumulative and won’t all happen the instant you take a bite of a chicken nugget
Think positive
No, not in the “think positive thoughts” sense (though feel free, if that’s your thing), but rather: focus on adding things rather than subtracting things.
It’s said:
❝It’s not the calories in your food that make the biggest impact on your health; it’s the food in your calories❞e
…and that’s generally true. The same goes for “bad things” in the food, e.g. added sugar, salt, seed oils, etc. They really are bad! But, in this case you’re going to be eating them and they’re going to be nearly impossible to avoid in the social scenarios we described. So, forget that sunk treasure, and instead, add nutrients.
10almonds tip: added nutrients remain added nutrients, even if the sources were not glowing with health-appeal and/or you ate them alongside something unhealthy:
- Those breaded garlic mushrooms are still full of magnesium and fiber and ergothioneine.
- The chili-and-mint peas that came as an overpriced optional side-dish with your burger are still full of protein, fiber, and a stack of polyphenols.
…and so on. And, the more time you spend eating those things, the less time you spend eating the real empty-calorie foods.
Fix the flaw
We set out to offer this guide without arguing for abstemiousness or making healthy substitutions, because we assume you knew already that you can not eat things, and as for substitutions, often they are not practical, especially if dining out or ordering in.
Also, sometimes even when home-cooking something unhealthy, taking the bad ingredient out takes some of the joy out with it.
Writers example: I once incorrectly tried to solve the fat conundrum of my favorite shchi (recipe here) by trying purely steaming the vegetables instead of my usual frying/sautéing them, and let’s just say, that errant-and-swiftly-abandoned version got recorded in my nutrition-tracker app as “sad shchi”.
So instead, fix the flaw by countering it if possible:
- The meal is devoid of fiber? Preload with some dried figs (you can never have too many dried figs in your pantry)
- The meal is high in saturated fat? Enjoy fiber before/during/after, per what’s convenient for you. Fiber helps clear out excess cholesterol, which is usually the main issue with saturated fat.
- The meal is salty? Double down on your hydration before, during, and after. If that sounds like a chore, then remember, it’s more fun than getting bloated (which results, counterintuitively, from dehydration—because your body detects the salt, and panics and tries to retain as much water as possible to restore homeostasis, resulting in bloating) and hypertensive (which results from the combination of the blood having too much salt and too little water, and cells retaining too much water and pressing inwards because it is the cells themselves that are bloated). So, tending to your hydration can help mitigate all of the above.
- The meal is full of high-GI carbs? Preload with fiber, enjoy the carbs together with fats, and have something acidic (e.g. some kind of vinegar, or citrus fruit) with it if that’s a reasonable option. Yes, this does mean that a Whiskey Sour is better for your blood sugars than an Old Fashioned, by the way, and/but no, it doesn’t make either of them healthy.
- The meal is inflammatory? Doing all of the above things will help, as will eating it slowly/mindfully, which latter makes it less of a shock to your system.
See also: How To Get More Nutrition From The Same Food
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Debate over tongue tie procedures in babies continues. Here’s why it can be beneficial for some infants
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There is increasing media interest about surgical procedures on new babies for tongue tie. Some hail it as a miracle cure, others view it as barbaric treatment, though adverse outcomes are rare.
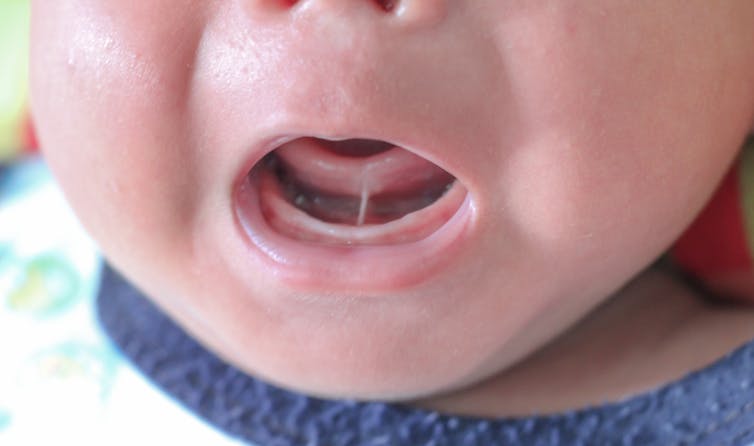
Tongue tie occurs when the tissue under the tongue is attached to the lower gum or floor of the mouth in a way that can restrict the movement or range of the tongue. This can impact early breastfeeding in babies. It affects an estimated 8% of children under one year of age.
While there has been an increase in tongue tie releases (also called division or frenotomy), it’s important to keep this in perspective relative to the increase in breastfeeding rates.
The World Health Organization recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life, with breastfeeding recommended into the second year of life and beyond for the health of mother and baby as well as optimal growth. Global rates of breastfeeding infants for the first six months have increased from 38% to 48% over the past decade. So, it is not surprising there is also an increase in the number of babies being referred globally with breastfeeding challenges and potential tongue tie.
An Australian study published in 2023 showed that despite a 25% increase in referrals for tongue tie division between 2014 and 2018, there was no increase in the number of tongue tie divisions performed. Tongue tie surgery rates increased in Australia in the decade from 2006 to 2016 (from 1.22 per 1,000 population to 6.35) for 0 to 4 year olds. There is no data on surgery rates in Australia over the last eight years.
Tongue tie division isn’t always appropriate but it can make a big difference to the babies who need it. More referrals doesn’t necessarily mean more procedures are performed.
chomplearn/Shutterstock How tongue tie can affect babies
When tongue tie (ankyloglossia) restricts the movement of the tongue, it can make it more difficult for a baby to latch onto the mother’s breast and painlessly breastfeed.
Earlier this month, the International Consortium of oral Ankylofrenula Professionals released a tongue tie position statement and practice guideline. Written by a range of health professionals, the guidelines define tongue tie as a functional diagnosis that can impact breastfeeding, eating, drinking and speech. The guidelines provide health professionals and families with information on the assessment and management of tongue tie.
Tongue tie release has been shown to improve latch during breastfeeding, reduce nipple pain and improve breast and bottle feeding. Early assessment and treatment are important to help mothers breastfeed for longer and address any potential functional problems.
The frenulum is a band of tissue under the tongue that is attached to the gumline base of the mouth. Akkalak Aiempradit/Shutterstock Where to get advice
If feeding isn’t going well, it may cause pain for the mother or there may be signs the baby isn’t attaching properly to the breast or not getting enough milk. Parents can seek skilled help and assessment from a certified lactation consultant or International Board-Certified Lactation Consultant who can be found via online registry.
Alternatively, a health professional with training and skills in tongue tie assessment and division can assist families. This may include a doctor, midwife, speech pathologist or dentist with extended skills, training and experience in treating babies with tongue tie.
When access to advice or treatment is delayed, it can lead to unnecessary supplementation with bottle feeds, early weaning from breastfeeding and increased parental anxiety.
Getting a tongue tie assessment
During assessment, a qualified health professional will collect a thorough case history, including pregnancy and birth details, do a structural and functional assessment, and conduct a comprehensive breastfeeding or feeding assessment.
They will view and thoroughly examine the mouth, including the tongue’s movement and lift. The appearance of where the tissue attaches to the underside of the tongue, the ability of the tongue to move and how the baby can suck also needs to be properly assessed.
Treatment decisions should focus on the concerns of the mother and baby and the impact of current feeding issues. Tongue tie division as a baby is not recommended for the sole purpose of avoiding speech problems in later life if there are no feeding concerns for the baby.
A properly qualified lactation consultant can help with positioning and attachment. HarryKiiM Stock/Shutterstock Treatment options
The Australian Dental Association’s 2020 guidelines provide a management pathway for babies diagnosed with tongue tie.
Once feeding issues are identified and if a tongue tie is diagnosed, non-surgical management to optimise positioning, latch and education for parents should be the first-line approach.
If feeding issues persist during follow-up assessment after non-surgical management, a tongue tie division may be considered. Tongue tie release may be one option to address functional challenges associated with breastfeeding problems in babies.
There are risks associated with any procedure, including tongue tie release, such as bleeding. These risks should be discussed with the treating practitioner before conducting any laser, scissor or scalpel tongue tie procedure.
Post-release support by a certified lactation consultant or feeding specialist is necessary after a tongue tie division. A post-release treatment plan should be developed by a team of health professionals including advice and support for breastfeeding to address both the mother and baby’s individual needs.
We would like to acknowledge the contribution of Raymond J. Tseng, DDS, PhD, (Paediatric Dentist) to the writing of this article.
Sharon Smart, Lecturer and Researcher (Speech Pathology) – School of Allied Health, Curtin University; David Todd, Associate Professor, Neonatology, ANU Medical School, Australian National University, and Monica J. Hogan, PhD student, ANU School of Medicine and Psychology, Australian National University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
I’m Moving Forward and Facing the Uncertainty of Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It takes a lot of courage to grow old.
I’ve come to appreciate this after conversations with hundreds of older adults over the past eight years for nearly 200 “Navigating Aging” columns.
Time and again, people have described what it’s like to let go of certainties they once lived with and adjust to new circumstances.
These older adults’ lives are filled with change. They don’t know what the future holds except that the end is nearer than it’s ever been.
And yet, they find ways to adapt. To move forward. To find meaning in their lives. And I find myself resolving to follow this path as I ready myself for retirement.
Patricia Estess, 85, of the Brooklyn borough of New York City spoke eloquently about the unpredictability of later life when I reached out to her as I reported a series of columns on older adults who live alone, sometimes known as “solo agers.”
Estess had taken a course on solo aging. “You realize that other people are in the same boat as you are,” she said when I asked what she had learned. “We’re all dealing with uncertainty.”
Consider the questions that older adults — whether living with others or by themselves — deal with year in and out: Will my bones break? Will my thinking skills and memory endure? Will I be able to make it up the stairs of my home, where I’m trying to age in place?
Will beloved friends and family members remain an ongoing source of support? If not, who will be around to provide help when it’s needed?
Will I have enough money to support a long and healthy life, if that’s in the cards? Will community and government resources be available, if needed?
It takes courage to face these uncertainties and advance into the unknown with a measure of equanimity.
“It’s a question of attitude,” Estess told me. “I have honed an attitude of: ‘I am getting older. Things will happen. I will do what I can to plan in advance. I will be more careful. But I will deal with things as they come up.’”
For many people, becoming old alters their sense of identity. They feel like strangers to themselves. Their bodies and minds aren’t working as they used to. They don’t feel the sense of control they once felt.
That requires a different type of courage — the courage to embrace and accept their older selves.
Marna Clarke, a photographer, spent more than a dozen years documenting her changing body and her life with her partner as they grew older. Along the way, she learned to view aging with new eyes.
“Now, I think there’s a beauty that comes out of people when they accept who they are,” she told me in 2022, when she was 70, just before her 93-year-old husband died.
Arthur Kleinman, a Harvard professor who’s now 83, gained a deeper sense of soulfulness after caring for his beloved wife, who had dementia and eventually died, leaving him grief-stricken.
“We endure, we learn how to endure, how to keep going. We’re marked, we’re injured, we’re wounded. We’re changed, in my case for the better,” he told me when I interviewed him in 2019. He was referring to a newfound sense of vulnerability and empathy he gained as a caregiver.
Herbert Brown, 68, who lives in one of Chicago’s poorest neighborhoods, was philosophical when I met him at his apartment building’s annual barbecue in June.
“I was a very wild person in my youth. I’m surprised I’ve lived this long,” he said. “I never planned on being a senior. I thought I’d die before that happened.”
Truthfully, no one is ever prepared to grow old, including me. (I’m turning 70 in February.)
Chalk it up to denial or the limits of imagination. As May Sarton, a writer who thought deeply about aging, put it so well: Old age is “a foreign country with an unknown language.” I, along with all my similarly aged friends, are surprised we’ve arrived at this destination.
For me, 2025 is a turning point. I’m retiring after four decades as a journalist. Most of that time, I’ve written about our nation’s enormously complex health care system. For the past eight years, I’ve focused on the unprecedented growth of the older population — the most significant demographic trend of our time — and its many implications.
In some ways, I’m ready for the challenges that lie ahead. In many ways, I’m not.
The biggest unknown is what will happen to my vision. I have moderate macular degeneration in both eyes. Last year, I lost central vision in my right eye. How long will my left eye pick up the slack? What will happen when that eye deteriorates?
Like many people, I’m hoping scientific advances outpace the progression of my condition. But I’m not counting on it. Realistically, I have to plan for a future in which I might become partially blind.
It’ll take courage to deal with that.
Then, there’s the matter of my four-story Denver house, where I’ve lived for 33 years. Climbing the stairs has helped keep me in shape. But that won’t be possible if my vision becomes worse.
So my husband and I are taking a leap into the unknown. We’re renovating the house, installing an elevator, and inviting our son, daughter-in-law, and grandson to move in with us. Going intergenerational. Giving up privacy. In exchange, we hope our home will be full of mutual assistance and love.
There are no guarantees this will work. But we’re giving it a shot.
Without all the conversations I’ve had over all these years, I might not have been up for it. But I’ve come to see that “no guarantees” isn’t a reason to dig in my heels and resist change.
Thank you to everyone who has taken time to share your experiences and insights about aging. Thank you for your openness, honesty, and courage. These conversations will become even more important in the years ahead, as baby boomers like me make their way through their 70s, 80s, and beyond. May the conversations continue.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Beetroot vs Pumpkin – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing beetroot to pumpkin, we picked the beetroot.
Why?
It was close! And an argument could be made for either.
In terms of macros, beetroot has about 3x more protein and about 3x more fiber, as well as about 2x more carbs, making it the “more food per food” option. While both have a low glycemic index, we picked the beetroot here for its better numbers overall.
In the category of vitamins, beetroot has more of vitamins B6 and B9, while pumpkin has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B5, E, and K. So, a fair win for pumpkin this time.
When it comes to minerals, though, beetroot has more calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while pumpkin has a tiny bit more copper. An easy win for beetroot here.
In short, both are great, and although pumpkin shines in the vitamin category, beetroot wins on overall nutritional density.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
No, beetroot isn’t vegetable Viagra. But here’s what it can do
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Watch Out For Lipedema
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Lipedema occurs mostly in women, mostly in times of hormonal change, with increasing risk as time goes by (so for example, puberty yields a lower risk than pregnancy, which yields a lower risk than menopause).
Its name literally means “fat swelling”, and can easily be mistaken for obesity or, in its earlier stages, just pain old cellulite.
Cellulite, by the way, is completely harmless and is also not, per se, an indicator of bad health. But if you have it and don’t like it, you can reduce it:
Obesity is more of a complex matter, and one that we’ve covered here:
Lipedema is actively harmful
Lipedema can become a big problem, because lifestyle change does not reduce lipedema fat, the fat is painful, can lead to obesity if one was not already obese, causes gait and joint abnormalities, causes fatigue, can lead to lymphedema (beyond the scope of today’s article—perhaps another time!) and very much psychosocial distress.
Like many conditions that mostly affect women, the science is… Well, here’s a recent example review that was conducted and published:
Fun fact: in Romanian there is an expression “one eye is laughing; the other is crying”, and it seems appropriate here.
Spot the signs
Because it’s most readily mistaken for cellulite in first presentation, let’s look at the differences between them:
- Cellulite is characterized by dimpled, bumpy, or even skin; lipedema is the same but with swelling too.
- Cellulite is a connective tissue condition; lipedema is too (at least in part), but also involves the abnormal accumulation and deposition of fat cells, rather than just pulling some down a bit.
- Cellulite has no additional symptoms; lipedema soon also brings swollen limbs, joint pain, and/or skin that’s “spongy” and easily bruised.
What to do about it
First, get it checked out by a doctor.
If the doctor says it is just cellulite or obesity, ask them what difference(s) they are basing that on, and ask that they confirm in writing having dismissed your concerns (having this will be handy later if it turns out to be lipedema after all).
If it is lipedema, you will want to catch it early; there is no known cure, but advanced symptoms are a lot easier to keep at bay than they are to reverse once they’ve shown up.
Weight maintenance, skin care (including good hydration), and compression therapy have all been shown to help slow the progression.
If it is allowed to progress unhindered, that’s when a lot more fat accumulation and joint pain is likely to occur. Liposuction and surgery are options, but even they are only a temporary solution, and are obviously not fun things to have to go through.
Prevention is, as ever, much better than
curetreatment ← because there is no known cureOne last thing
Lipedema’s main risk factor is genetic. The bad news is, there’s not much that can be done about that for now, but the good news is, you can at least get the heads-up about whether you are at increased risk or not, and be especially vigilant if you’re in the increased risk group. See also:
One Test, Many Warnings: The Real Benefit Of Genetic Testing
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: