Get Better Sleep: Beyond The Basics
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First though, for the sake of being methodical, let’s quickly note the basics:
- Aim for 7–9 hours per night
- Set a regular bedtime and (equally important!) regular getting-up time
- Have a 2-hour wind-down period before bed, to decompress from any stresses of the day
- Minimal device/screen usage before bed
- Abstain from stimulants for as long before bed as reasonably possible (caffeine elimination halflife is 4–8 hours depending on your genes, call it 6 hours average to eliminate half (not the whole lot), and you’ll see it’s probably best to put a cap on it earlier rather than later).
- Abstain from alcohol, ideally entirely, but allow at least 1hr/unit before bed. So for example, 1hr for a 1oz single shot of spirits, or 2–3 hours for a glass of wine (depending on size), or 3–4 hours for a martini (depending on recipe). Not that that is not the elimination time, nor even the elimination halflife of alcohol, it’s just a “give your body a chance at least” calculation. If you like to have a drink to relax before bed, then well, only you can decide what you like more: that or actually getting restorative sleep.
- Consider a warm bath/shower before bed, if that suits your schedule.
- Wash and change your bedsheets more often than seems necessary. Or if that’s too onerous, at least change the pillowcases more often, which makes quite a difference already.
- Lower the temperature of your bedroom shortly before bedtime; this will help cue the body to produce melatonin
- Make your bedroom as dark as reasonably possible. Invest in blackout blinds/curtains, and remove any pesky electronics, or at least cover their little LEDs if it’s something that reasonably needs to remain on.
Ok, now, onwards…
Those 7–9 hours? Yes, it goes for you too.
A lot of people mistake getting 6 hours sleep per night for only needing 6 hours sleep per night. Sure, you may still be alive after regularly getting 6 hours, but (unless you have a rare mutation of the ADRB1 gene) it will be causing harm, and yes, that includes later in life; we don’t stop needing so much sleep, even stop getting it:
Why You Probably Need More Sleep
With this in mind, it becomes important to…
Prioritize your sleep—which means planning for it!
When does your bedtime routine start? According to sleep scientist Dr. Lisa Matricciani, it starts before breakfast. This is because the things we do earlier in the day can greatly affect the amount (and quality) of sleep we get later. For example, a morning moderate-to-intense exercise session greatly improves sleep at night:
Planning Ahead For Better Sleep
As for quality, that is as important as quantity, and it’s not just about “soundness” of sleep:
The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter)
“What gets measured, gets done” goes for sleep too
Sleep-deprived people usually underestimate how sleep-deprived they are. This is for the same reason as why drunk people usually underestimate how drunk they are—to put it in words that go for both situations: a cognitively impaired person lacks the cognitive function to realize how cognitively impaired they are.
Here’s the science on that, by the way:
How Sleep-Deprived Are You, Really?
For that reason, we recommend using sleep-tracking software (there are many apps for that) on your phone or, ideally, a wearable device (such as a smartwatch or similar).
A benefit of doing so is that we don’t think “well, I slept from 10pm to 6am, so that’s 8 hours”, if our device tells us we slept between 10:43pm and 5:56 am with 74% sleep efficiency because we woke up many times.
As an aside, sleep efficiency should be about 85%, by the way. Why not 100%, you ask? It’s because if your body is truly out like a light for the entire night, something is wrong (either you were very sleep-deprived, or you have been drugged, that kind of thing). See also:
An unbroken night’s sleep is a myth. Here’s what good sleep looks like.
So waking up during the night is normal, and nothing to worry about per se. If you do find trouble getting back to sleep, though:
How to Fall Back Asleep After Waking Up in the Middle of the Night
Be careful about how you try to supplement sleep
This goes both for taking substances of various kinds, and napping. Some sleep aids can help, but many are harmful and/or do not really work as such; here’s a rundown of examples of those:
Safe Effective Sleep Aids For Seniors?
And when it comes to napping, timing is everything:
How To Nap Like A Pro (No More “Sleep Hangovers”!)
Want to know a lot more?
This is the book on sleep:
Why We Sleep – by Dr. Matthew Walker
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
4 Tips To Stand Without Using Hands
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The “sit-stand” test, getting up off the floor without using one’s hands, is well-recognized as a good indicator of healthy aging, and predictor of longevity. But what if you can’t do it? Rather than struggling, there are exercises to strengthen the body to be able to do this vital movement.
Step by step
Teresa Shupe has been teaching Pilates professionally full-time for over 25 years, and here’s what she has to offer in the category of safe and effective ways of improving balance and posture while doing the sitting-to-standing movement:
- Squat! Doing squats (especially deep ones) regularly strengthens all the parts necessary to effectively complete this movement. If your knees aren’t up to it at first, do the squats with your back against a wall to start with.
- Roll! On your back, cross your feet as though preparing to stand, and rock-and-roll your body forwards. To start with you can “cheat” and use your fingertips to give a slight extra lift. This exercise builds mobility in the various necessary parts of the body, and also strengthens the core—as well as getting you accustomed to using your bodyweight to move your body forwards.
- Lift! This one’s focusing on that last part, and taking it further. Because it may be difficult to get enough momentum initially, you can practice by holding small weights in your hands, to shift your centre of gravity forwards a bit. Unlike many weights exercises, in this case you’re going to transition to holding less weight rather than more, though.
- Complete! Continue from the above, without weights now; use the blades of your feet to stand. If you need to, use your fingertips to give you a touch more lift and stability, and reduce the fingers that you use until you are using none.
For more on each of these as well as a visual demonstration, enjoy this short video:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Further reading
For more exercises with a similar approach, check out:
Mobility As A Sporting Pursuit
Take care!
Share This Post
-
We Hope This Email Blows Your Tits Clean Off
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Right Kind Of “Email Hacks”!
Are you a Gmailer or an Outlookista? Whatever your preference, you’re probably facing many of the same challenges that most of us face in our work and personal lives:
Email’s greatest strength (its ease of accessibility) brings about its greatest problem (our inboxes are cluttered and chaotic), not to mention that each of us are usually managing a whole flock of email addresses.
Sometimes we put productivity resources up against each other; that’s not what we’re going to do today! Each of these can play a role alongside each other; grab as many as will make your life easier:
ProtonMail: this is an email client; it’s the nicest, simplest, easiest, free email client that doesn’t track, let alone share, everything you do.
Bonus: there also exists ProtonCalendar (it’s a calendar that doesn’t share your data), ProtonDrive (it’s a cloud storage provider that doesn’t share your data) and, because they’re indeed serious about your privacy, ProtonVPN (it’s a VPN that, of course, doesn’t share your data).
Clean Email: maybe you’re stuck with the email provider you have. It happens. But it doesn’t have to be a chaotic mess. This tool will make tidying your email (and keeping it tidy!) a simplified dream.
See How Clean Your Email Can Get With Just A Few Clicks!
Right Inbox: a Gmail extension with many useful features, including read receipts, emails scheduled for later (e.g: time your email to send at 7am to look like a morning lark when in fact you’re peacefully snoozing), add unforwardable “For Your Eyes Only” notes to emails, and more.
Power Up Your Gmail With The Right Inbox Extension!
Email Finder: find the verified work email address of any person, so long as you know what company you’re looking for them in! No more “I thought it was lastname.firstname@ and it was firstname.lastname@”, no more “the wrong John Smith”, no more “undelivered” bounceback notices. Just: your email delivered.
Never Hear From The Mailer Daemon Again, With Email Finder!
Unroll.me: love your subscriptions, but hate the clutter? Unroll.me aggregates them for you in a virtual roll-up, with an “unroll” button to read them.
Get What You Really Want From Your Subscriptions, With Unroll.Me!
On which note, anything you’d like to hear more of from us? Let us know! You can always just hit reply, or use the feedback widget at the bottom of this email
Share This Post
-
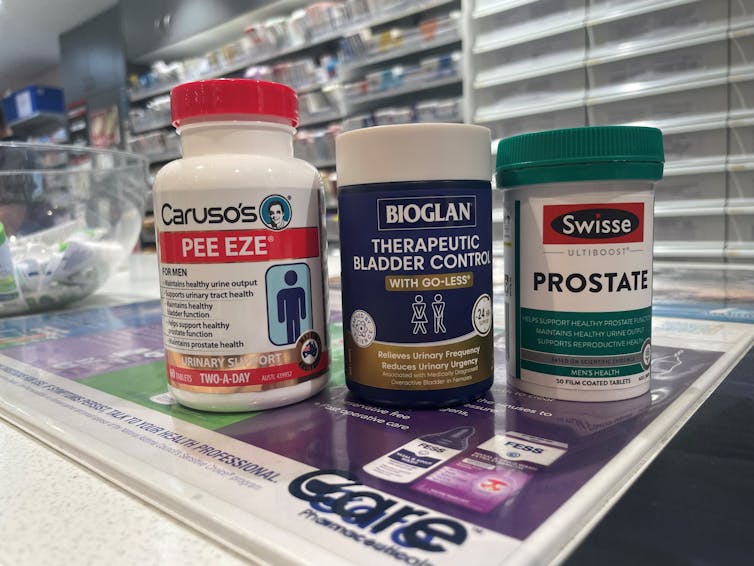
What’s in the supplements that claim to help you cut down on bathroom breaks? And do they work?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
With one in four Australian adults experiencing problems with incontinence, some people look to supplements for relief.
With ingredients such as pumpkin seed oil and soybean extract, a range of products promise relief from frequent bathroom trips.
But do they really work? Let’s sift through the claims and see what the science says about their efficacy.
Christian Moro/Shutterstock What is incontinence?
Incontinence is the involuntary loss of bladder or bowel control, leading to the unintentional leakage of urine or faeces. It can range from occasional minor leaks to a complete inability to control urination and defecation.
This condition can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life, and affects women more often than it affects men.
Some people don’t experience bladder leakage but can sometimes feel an urgent need to go to the bathroom. This is known as overactive bladder syndrome, and occurs when the muscles around the bladder tighten on their own, which greatly reduces its capacity. The result is the person feels the need to go to the bathroom much more frequently.
There are many potential causes of incontinence and overactive bladders, including menopause, pregnancy and child birth, urinary tract infections, pelvic floor disorders, and an enlarged prostate. Conditions such as diabetes, neurological disorders and certain medications (such as diuretics, sleeping pills, antidepressants and blood-pressure drugs) can also contribute.
While pelvic muscle rehabilitation and behavioural techniques for bladder retraining can be helpful, some people are interested in pharmaceutical solutions.
What’s in these products?
A number of supplements are available in Australia that include ingredients used in traditional medicine for urinary incontinence and overactive bladders. The three most common ingredients are:
- Cucurbita pepo (pumpkin seed extract)
- glycine max (soybean extract)
- an extract from the bark of the Crateva magna or nurvala (Varuna) tree.
The supplements have common ingredients. Author How are they supposed to work?
Pumpkin seeds are rich in plant sterols that are thought to reduce the testosterone-related enlargement of the prostate, as well as having broader anti-inflammatory effects. The seed extracts can also contain oleic acid, which may help increase bladder capacity by relaxing the muscles around the organ.
Soybean extracts are rich in isoflavones, especially daidzen and genistein. Like olieic acid, these are thought to act on the muscles around the bladder. Because isoflavones are similar in structure to the female hormone oestrogen, soy extracts may be most beneficial for postmenopausal women who have overactive bladders.
Crateva extract is rich in lupeol- and sterol-based chemicals which have strong anti-inflammatory effects. This has benefits not just for enlarged prostates but possibly also for reducing urinary tract infections.
Do they actually work?
It’s important to note that the government has only approved these types of supplements as “listed medicines”. This means the ingredients have only been assessed for safety. The companies behind the products have not had to provide evidence they actually work.
A 2014 clinical trial examined a combined pumpkin seed and soybean extract called cucurflavone on people with overactive bladders. The 120 participants received either a placebo or a daily 1,000mg dose of the herbal mixture over a period of 12 weeks.
By the end of study, those in the cucurflavone group went to the bathroom around three fewer times per day, compared with people in the control group, who only went to the bathroom on average one fewer time each day.
In a different trial, researchers examined a combination of Crateva bark extract with herbal extracts of horsetail and Japanese evergreen spicebush, called Urox.
For the 150 participants, the Urox formulation helped participants go to the bathroom less frequently when compared with placebo treatment.
After eight weeks of treatment, participants in the placebo group were going to the bathroom to urinate 11 times per day. Those in the Urox group were only going around to 7.5 times per day. And those who took Urox also needed to go to the bathroom one fewer time during the night.
Finally, another study also examined a Creteva, horsetail and Japanese spicebush combination, but this time in children. They were given either a 420mg dose of the supplement or a placebo, and then monitored for how many times they wet the bed.
After two months of taking the supplement, slightly more than 40% of the 24 kids in the supplement group wet the bed less often.
While these results may look promising, there are considerable limitations to the studies which means the data may not be reliable. For example, the trials didn’t include enough participants to have reliable data. To conclusively provide efficacy, final-stage clinical trials require data for between 300 and 3,000 patients.
From the studies, it is also not clear whether some participants were also taking other medicines as well as the supplement. This is important, as medications can interfere with how the supplements work, potentially making them less or more effective.
What if you want to take them?
If you have incontinence or an overactive bladder, you should always discuss this with your doctor, as it may due to a serious or treatable underlying condition.
Otherwise, your GP may give you strategies or exercises to improve your bladder control, prescribe medications or devices, or refer you to a specialist.
If you do decide to take a supplement, discuss this with your doctor and local pharmacist so they can check that any product you choose will not interfere with any other medications you may be taking.
Nial Wheate, Professor of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Macquarie University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Power of Hormones – by Dr. Max Nieuwdorp
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First a quick note on the author: he’s an MD & PhD, internist, endocrinologist, and professor. He knows his stuff.
There are a lot of books with “the new science of” in the title, and they don’t often pertain to science that is actually new, and in this case, for the most part the science contained within this book is quite well-established.
A strength of this book is that it’s not talking about hormones in just one specific aspect (e.g. menopause, pregnancy, etc) but rather, in the full span of human health, across the spectra of ages and sexes—and yes, also covering hormones that are not sex hormones, so for example also demystifying the different happiness-related neurotransmitters, as well as the hormones responsible for hunger and satiety, weight loss and gain, sleep and wakefulness, etc.
Which is all very good, because there’s a lot of overlap and several hormones fall into several categories there.
Moreover, the book covers how your personal cocktail of hormones impacts how you look, feel, behave, and more—there’s a lot about chronic health issues here too, and how to use the information in this book to if not outright cure, then at least ameliorate, many conditions.
Bottom line: this is an information-dense book with a lot of details great and small; if you read this, you’ll come away with a much better understanding of hormones than you had previously!
Click here to check out The Power of Hormones, and harness that power for yourself!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Guava vs Passion Fruit – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing guava to passion fruit, we picked the guava.
Why?
There aren’t many fruits that can beat passion fruit for nutritional density! And even in this case, it wasn’t completely so in every category:
In terms of macros, passion fruit has more carbs and fiber, the ratio of which give it the slightly lower glycemic index. Thus, a modest win for passion fruit in this category.
In the category of vitamins, guava has more of vitamins B1, B5, B6, B9, C, E, and K, while passion fruit has more of vitamins A, B2, and B3. A clear win for guava this time.
When it comes to minerals, it’s a little closer, but: guava has more calcium, copper, manganese, potassium, and zinc, while passion fruit has more iron, magnesium, and phosphorus. So, another win for guava.
Adding up the sections makes for guava winning the day, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Fruit Is Healthy; Juice Isn’t (Here’s Why)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Seniors: Improve Blood Flow & Circulation In Your Legs
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Doug Weiss, a physiotherapist (and thus: a doctor of physical therapy), has advice on how and why to increase blood flow and circulation in your legs, keeping yourself healthier for longer and avoiding a lot of potential unpleasantries.
The exercises
The exercises here are not complex; they are as follows, and he suggests 3 sets of 10 reps of each, daily:
- Sitting ankle pumps: sitting on a chair or the edge of a bed, lift the toes up, then heels up, squeezing the muscles.
- Sitting knee extensions: sitting as before, kick one leg up until knee is straight, then switch legs.
- Heel raises: standing this time, with a sturdy support such as a countertop, raise on toes as high as possible, then lower heels back to the ground
- Pillow squats: placing pillows on a chair, cross hands on chest, and simply stand up and sit down—similar to the “getting up off the floor without using your hands” exercise, but an easier version.
For visuals on these, and more details including the specific benefits of each, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
4 Tips To Stand Without Using Hands ← this time it’s the full movement, from the floor, and this is a really important movement to be able to do, as it’s a big indicator of healthy longevity
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: