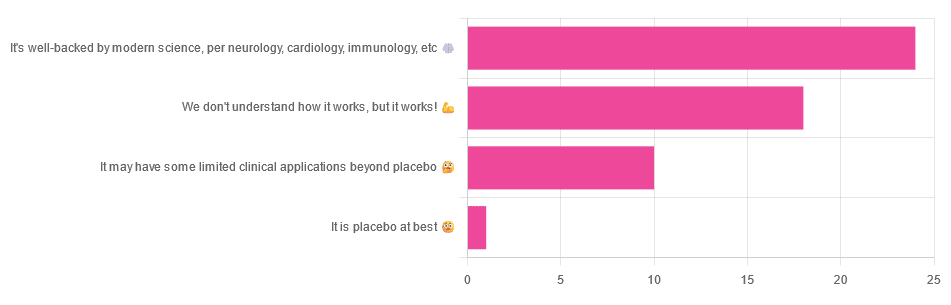‘It’s okay to poo at work’: new health campaign highlights a common source of anxiety
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For most people, the daily or near-daily ritual of having a bowel motion is not something we give a great deal of thought to. But for some people, the need to do a “number two” in a public toilet or at work can be beset with significant stress and anxiety.
In recognition of the discomfort people may feel around passing a bowel motion at work, the Queensland Department of Health recently launched a social media campaign with the message “It’s okay to poo at work”.
The campaign has gained significant traction on Instagram and Facebook. It has been praised by health and marketing experts for its humorous handling of a taboo topic.
A colourful Instagram post is accompanied by a caption warning of the health risks of “holding it in”, including haemorrhoids and other gastrointestinal problems. The caption also notes:
If you find it extremely difficult to poo around other people, you might have parcopresis.

What is parcopresis?
Parcopresis, sometimes called “shy bowel”, occurs when people experience a difficulty or inability to poo in public toilets due to fear of perceived scrutiny by others.
People with parcopresis may find it difficult to go to the toilet in public places such as shopping centres, restaurants, at work or at school, or even at home when friends or family are around.
They may fear being judged by others about unpleasant smells or sounds when they have a bowel motion, or how long they take to go, for example.
Living with a gastrointestinal condition (at least four in ten Australians do) may contribute to parcopresis due to anxiety about the need to use a toilet frequently, and perceived judgment from others when doing so. Other factors, such as past negative experiences or accessibility challenges, may also play a role.

For sufferers, anxiety can present in the form of a faster heart rate, rapid breathing, sweating, muscle tension, blushing, nausea, trembling, or a combination of these symptoms. They may experience ongoing worry about situations where they may need to use a public toilet.
Living with parcopresis can affect multiple domains of life and quality of life overall. For example, sufferers may have difficulties relating to employment, relationships and social life. They might avoid travelling or attending certain events because of their symptoms.
How common is parcopresis?
We don’t really know how common parcopresis is, partly due to the difficulty of evaluating this behaviour. It’s not necessarily easy or appropriate to follow people around to track whether they use or avoid public toilets (and their reasons if they do). Also, observing individual bathroom activities may alter the person’s behaviour.
I conducted a study to try to better understand how common parcopresis is. The study involved 714 university students. I asked participants to respond to a series of vignettes, or scenarios.
In each vignette participants were advised they were at a local shopping centre and they needed to have a bowel motion. In the vignettes, the bathrooms (which had been recently cleaned) had configurations of either two or three toilet stalls. Each vignette differed by the configuration of stalls available.
The rate of avoidance was just over 14% overall. But participants were more likely to avoid using the toilet when the other stalls were occupied.
Around 10% avoided going when all toilets were available. This rose to around 25% when only the middle of three toilets was available. Men were significantly less likely to avoid going than women across all vignettes.
For those who avoided the toilet, many either said they would go home to poo, use an available disabled toilet, or come back when the bathroom was empty.
Parcopresis at work
In occupational settings, the rates of anxiety about using shared bathrooms may well be higher for a few reasons.
For example, people may feel more self-conscious about their bodily functions being heard or noticed by colleagues, compared to strangers in a public toilet.
People may also experience guilt, shame and fear about being judged by colleagues or supervisors if they need to make extended or frequent visits to the bathroom. This may particularly apply to people with a gastrointestinal condition.
Reducing restroom anxiety
Using a public toilet can understandably cause some anxiety or be unpleasant. But for a small minority of people it can be a real problem, causing severe distress and affecting their ability to engage in activities of daily living.
If doing a poo in a toilet at work or another public setting causes you anxiety, be kind to yourself. A number of strategies might help:
- identify and challenge negative thoughts about using public toilets and remind yourself that using the bathroom is normal, and that most people are not paying attention to others in the toilets
- try to manage stress through relaxation techniques such as deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation, which involves tensing and relaxing different muscles around the body
- engaging in gradual exposure can be helpful, which means visiting public toilets at different times and locations, so you can develop greater confidence in using them
- use grounding or distraction techniques while going to the toilet. These might include listening to music, watching something on your phone, or focusing on your breathing.
If you feel parcopresis is having a significant impact on your life, talk to your GP or a psychologist who can help identify appropriate approaches to treatment. This might include cognitive behavioural therapy.
Simon Robert Knowles, Associate Professor and Clinical Psychologist, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Would a Second Trump Presidency Look Like for Health Care?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
On the presidential campaign trail, former President Donald Trump is, once again, promising to repeal and replace the Affordable Care Act — a nebulous goal that became one of his administration’s splashiest policy failures.
“We’re going to fight for much better health care than Obamacare. Obamacare is a catastrophe,” Trump said at a campaign stop in Iowa on Jan. 6.
The perplexing revival of one of Trump’s most politically damaging crusades comes at a time when the Obama-era health law is even more popular and widely used than it was in 2017, when Trump and congressional Republicans proved unable to pass their own plan to replace it. That failed effort was a big part of why Republicans lost control of the House of Representatives in the 2018 midterms.
Despite repeated promises, Trump never presented his own Obamacare replacement. And much of what Trump’s administration actually accomplished in health care has been reversed by the Biden administration.
Still, Trump secured some significant policy changes that remain in place today, including efforts to bring more transparency to prices charged by hospitals and paid by health insurers.
Trying to predict Trump’s priorities in a second term is even more difficult given that he frequently changes his positions on issues, sometimes multiple times.
The Trump campaign did not respond to a request for comment.
Perhaps Trump’s biggest achievement is something he rarely talks about on the campaign trail. His administration’s “Operation Warp Speed” managed to create, test, and bring to market a covid-19 vaccine in less than a year, far faster than even the most optimistic predictions.
Many of Trump’s supporters, though, don’t support — and some even vehemently oppose — covid vaccines.
Here is a recap of Trump’s health care record:
Public Health
Trump’s pandemic response dominates his overall record on health care.
More than 400,000 Americans died from covid over Trump’s last year in office. His travel bans and other efforts to prevent the global spread of the virus were ineffective, his administration was slower than other countries’ governments to develop a diagnostic test, and he publicly clashed with his own government’s health officials over the response.
Ahead of the 2020 election, Trump resumed large rallies and other public campaign events that many public health experts regarded as reckless in the face of a highly contagious, deadly virus. He personally flouted public health guidance after contracting covid himself and ending up hospitalized.
At the same time, despite what many saw as a politicization of public health by the White House, Trump signed a massive covid relief bill (after first threatening to veto it). He also presided over some of the largest boosts for the National Institutes of Health’s budget since the turn of the century. And the mRNA-based vaccines Operation Warp Speed helped develop were an astounding scientific breakthrough credited with helping save millions of lives while laying the groundwork for future shots to fight other diseases including cancer.
Abortion
Trump’s biggest contribution to abortion policy was indirect: He appointed three Supreme Court justices, who were instrumental in overturning the constitutional right to an abortion.
During his 2024 campaign, Trump has been all over the place on the red-hot issue. Since the Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade in 2022, Trump has bemoaned the issue as politically bad for Republicans; criticized one of his rivals, Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis, for signing a six-week abortion ban; and vowed to broker a compromise with “both sides” on abortion, promising that “for the first time in 52 years, you’ll have an issue that we can put behind us.”
He has so far avoided spelling out how he’d do that, or whether he’d support a national abortion ban after any number of weeks.
More recently, however, Trump appears to have mended fences over his criticism of Florida’s six-week ban and more with key abortion opponents, whose support helped him get elected in 2016 — and whom he repaid with a long list of policy changes during his presidency.
Among the anti-abortion actions taken by the Trump administration were a reinstatement of the “Mexico City Policy” that bars giving federal funds to international organizations that support abortion rights; a regulation to bar Planned Parenthood and other organizations that provide abortions from the federal family planning program, Title X; regulatory changes designed to make it easier for health care providers and employers to decline to participate in activities that violate their religious and moral beliefs; and other changes that made it harder for NIH scientists to conduct research using fetal tissue from elective abortions.
All of those policies have since been overturned by the Biden administration.
Health Insurance
Unlike Trump’s policies on reproductive health, many of his administration’s moves related to health insurance still stand.
For example, in 2020, Trump signed into law the No Surprises Act, a bipartisan measure aimed at protecting patients from unexpected medical bills stemming from payment disputes between health care providers and insurers. The bill was included in the $900 billion covid relief package he opposed before signing, though Trump had expressed support for ending surprise medical bills.
His administration also pushed — over the vehement objections of health industry officials — price transparency regulations that require hospitals to post prices and insurers to provide estimated costs for procedures. Those requirements also remain in place, although hospitals in particular have been slow to comply.
Medicaid
While first-time candidate Trump vowed not to cut popular entitlement programs like Medicare, Medicaid, and Social Security, his administration did not stick to that promise. The Affordable Care Act repeal legislation Trump supported in 2017 would have imposed major cuts to Medicaid, and his Department of Health and Human Services later encouraged states to require Medicaid recipients to prove they work in order to receive health insurance.
Drug Prices
One of the issues the Trump administration was most active on was reducing the price of prescription drugs for consumers — a top priority for both Democratic and Republican voters. But many of those proposals were blocked by the courts.
One Trump-era plan that never took effect would have pegged the price of some expensive drugs covered by Medicare to prices in other countries. Another would have required drug companies to include prices in their television advertisements.
A regulation allowing states to import cheaper drugs from Canada did take effect, in November 2020. However, it took until January 2024 for the FDA, under Trump’s successor, to approve the first importation plan, from Florida. Canada has said it won’t allow exports that risk causing drug shortages in that country, leaving unclear whether the policy is workable.
Trump also signed into law measures allowing pharmacists to disclose to patients when the cash price of a drug is lower than the cost using their insurance. Previously pharmacists could be barred from doing so under their contracts with insurers and pharmacy benefit managers.
Veterans’ Health
Trump is credited by some advocates for overhauling Department of Veterans Affairs health care. However, while he did sign a major bill allowing veterans to obtain care outside VA facilities, White House officials also tried to scuttle passage of the spending needed to pay for the initiative.
Medical Freedom
Trump scored a big win for the libertarian wing of the Republican Party when he signed into law the “Right to Try Act,” intended to make it easier for patients with terminal diseases to access drugs or treatments not yet approved by the FDA.
But it is not clear how many patients have managed to obtain treatment using the law because it is aimed at the FDA, which has traditionally granted requests for “compassionate use” of not-yet-approved drugs anyway. The stumbling block, which the law does not address, is getting drug companies to release doses of medicines that are still being tested and may be in short supply.
Trump said in a Jan. 10 Fox News town hall that the law had “saved thousands and thousands” of lives. There’s no evidence for the claim.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
How Does One Test Acupuncture Against Placebo Anyway?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pinpointing The Usefulness Of Acupuncture
We asked you for your opinions on acupuncture, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of answers:
- A little under half of all respondents voted for “It’s well-backed by modern science, per neurology, cardiology, immunology, etc”
- Slightly fewer respondents voted for “We don’t understand how it works, but it works!”
- A little under a fifth of respondents voted for “It may have some limited clinical applications beyond placebo”
- One (1) respondent voted for for “It’s placebo at best”
When we did a main feature about homeopathy, a couple of subscribers wrote to say that they were confused as to what homeopathy was, so this time, we’ll start with a quick definition first.
First, what is acupuncture? For the convenience of a quick definition so that we can move on to the science, let’s borrow from Wikipedia:
❝Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine in which thin needles are inserted into the body.
Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientific knowledge, and it has been characterized as quackery.❞
Now, that’s not a promising start, but we will not be deterred! We will instead examine the science itself, rather than relying on tertiary sources like Wikipedia.
It’s worth noting before we move on, however, that there is vigorous debate behind the scenes of that article. The gist of the argument is:
- On one side: “Acupuncture is not pseudoscience/quackery! This has long been disproved and there are peer-reviewed research papers on the subject.”
- On the other: “Yes, but only in disreputable quack journals created specifically for that purpose”
The latter counterclaim is a) potentially a “no true Scotsman” rhetorical ploy b) potentially true regardless
Some counterclaims exhibit specific sinophobia, per “if the source is Chinese, don’t believe it”. That’s not helpful either.
Well, the waters sure are muddy. Where to begin? Let’s start with a relatively easy one:
It may have some clinical applications beyond placebo: True or False?
True! Admittedly, “may” is doing some of the heavy lifting here, but we’ll take what we can get to get us going.
One of the least controversial uses of acupuncture is to alleviate chronic pain. Dr. Vickers et al, in a study published under the auspices of JAMA (a very respectable journal, and based in the US, not China), found:
❝Acupuncture is effective for the treatment of chronic pain and is therefore a reasonable referral option. Significant differences between true and sham acupuncture indicate that acupuncture is more than a placebo.
However, these differences are relatively modest, suggesting that factors in addition to the specific effects of needling are important contributors to the therapeutic effects of acupuncture❞
Source: Acupuncture for Chronic Pain: Individual Patient Data Meta-analysis
If you’re feeling sharp today, you may be wondering how the differences are described as “significant” and “relatively modest” in the same text. That’s because these words have different meanings in academic literature:
- Significant = p<0.05, where p is the probability of the achieved results occurring randomly
- Modest = the differences between the test group and the control group were small
In other words, “significant modest differences” means “the sample sizes were large, and the test group reliably got slightly better results than placebo”
We don’t understand how it works, but it works: True or False
Broadly False. When it works, we generally have an idea how.
Placebo is, of course, the main explanation. And even in examples such as the above, how is placebo acupuncture given?
By inserting acupuncture needles off-target rather than in accord with established meridians and points (the lines and dots that, per Traditional Chinese Medicine, indicate the flow of qi, our body’s vital energy, and welling-points of such).
So, if a patient feels that needles are being inserted randomly, they may no longer have the same confidence that they aren’t in the control group receiving placebo, which could explain the “modest” difference, without there being anything “to” acupuncture beyond placebo. After all, placebo works less well if you believe you are only receiving placebo!
Indeed, a (Korean, for the record) group of researchers wrote about this—and how this confounding factor cuts both ways:
❝Given the current research evidence that sham acupuncture can exert not only the originally expected non-specific effects but also sham acupuncture-specific effects, it would be misleading to simply regard sham acupuncture as the same as placebo.
Therefore, researchers should be cautious when using the term sham acupuncture in clinical investigations.❞
Source: Sham Acupuncture Is Not Just a Placebo
It’s well-backed by modern science, per neurology, cardiology, immunology, etc: True or False?
False, for the most part.
While yes, the meridians and points of acupuncture charts broadly correspond to nerves and vasculature, there is no evidence that inserting needles into those points does anything for one’s qi, itself a concept that has not made it into Western science—as a unified concept, anyway…
Note that our bodies are indeed full of energy. Electrical energy in our nerves, chemical energy in every living cell, kinetic energy in all our moving parts. Even, to stretch the point a bit, gravitational potential energy based on our mass.
All of these things could broadly be described as qi, if we so wish. Indeed, the ki in the Japanese martial art of aikido is the latter kinds; kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy based on our mass. Same goes, therefore for the ki in kiatsu, a kind of Japanese massage, while the ki in reiki, a Japanese spiritual healing practice, is rather more mystical.
The qi in Chinese qigong is mostly about oxygen, thus indirectly chemical energy, and the electrical energy of the nerves that are receiving oxygenated blood at higher or lower levels.
On the other hand, the efficacy of the use of acupuncture for various kinds of pain is well-enough evidenced. Indeed, even the UK’s famously thrifty NHS (that certainly would not spend money on something it did not find to work) offers it as a complementary therapy for some kinds of pain:
❝Western medical acupuncture (dry needling) is the use of acupuncture following a medical diagnosis. It involves stimulating sensory nerves under the skin and in the muscles.
This results in the body producing natural substances, such as pain-relieving endorphins. It’s likely that these naturally released substances are responsible for the beneficial effects experienced with acupuncture.❞
Source: NHS | Acupuncture
Meanwhile, the NIH’s National Cancer Institute recommends it… But not as a cancer treatment.
Rather, they recommend it as a complementary therapy for pain management, and also against nausea, for which there is also evidence that it can help.
Frustratingly, while they mention that there is lots of evidence for this, they don’t actually link the studies they’re citing, or give enough information to find them. Instead, they say things like “seven randomized clinical trials found that…” and provide links that look reassuring until one finds, upon clicking on them, that it’s just a link to the definition of “randomized clinical trial”:
Source: NIH | Nactional Cancer Institute | Acupuncture (PDQ®)–Patient Version
However, doing our own searches finds many studies (mostly in specialized, potentially biased, journals such as the Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies) finding significant modest outperformance of [what passes for] placebo.
Sometimes, the existence of papers with promising titles, and statements of how acupuncture might work for things other than relief of pain and nausea, hides the fact that the papers themselves do not, in fact, contain any evidence to support the hypothesis. Here’s an example:
❝The underlying mechanisms behind the benefits of acupuncture may be linked with the regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (adrenal) axis and activation of the Wnt/β-catenin and OPG/RANKL/RANK signaling pathways.
In summary, strong evidence may still come from prospective and well-designed clinical trials to shed light on the potential role of acupuncture in preserving bone loss❞
Source: Acupuncture for Osteoporosis: a Review of Its Clinical and Preclinical Studies
So, here they offered a very sciencey hypothesis, and to support that hypothesis, “strong evidence may still come”.
“We must keep faith” is not usually considered evidence worthy of inclusion in a paper!
PS: the above link is just to the abstract, because the “Full Text” link offered in that abstract leads to a completely unrelated article about HIV/AIDS-related cryptococcosis, in a completely different journal, nothing to do with acupuncture or osteoporosis).
Again, this is not the kind of professionalism we expect from peer-reviewed academic journals.
Bottom line:
Acupuncture reliably performs slightly better than sham acupuncture for the management of pain, and may also help against nausea.
Beyond placebo and the stimulation of endorphin release, there is no consistently reliable evidence that is has any other discernible medical effect by any mechanism known to Western science—though there are plenty of hypotheses.
That said, absence of evidence is not evidence of absence, and the logistical difficulty of testing acupuncture against placebo makes for slow research. Maybe one day we’ll know more.
For now:
- If you find it helps you: great! Enjoy
- If you think it might help you: try it! By a licensed professional with a good reputation, please.
- If you are not inclined to having needles put in you unnecessarily: skip it! Extant science suggests that at worst, you’ll be missing out on slight relief of pain/nausea.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
6-Minute Core Strength – by Dr. Jonathan Su
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We don’t normally do author biographies here, but in this case it’s worth noting that Dr. Su is a physiotherapist, military rehab expert, and an IAYT yoga therapist. So, these things together certainly do lend weight to his advice.
About the “6-minute” thing: this is in the style of the famous “7-minute workout” and “5 Minutes’ Physical Fitness” etc, and refers to how long each exercise session should take. The baseline is one such session per day, though of course doing more than one set of 6 minutes each time is a bonus if you wish to do so.
The exercises are focused on core strength, but they also include hip and shoulder exercises, since these are after all attached to the core, and hip and shoulder mobility counts for a lot.
A particular strength of the book is in troubleshooting mistakes of the kind that aren’t necessarily visible from photos; in this case, Dr. Su explains what you need to go for in a certain exercise, and how to know if you are doing it correctly. This alone is worth the cost of the book, in this reviewer’s opinion.
Bottom line: if you want core strength and want it simple yet comprehensive, this book can guide you.
Click here to check out 6-Minute Core Strength, and strengthen yours!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Dating apps could have negative effects on body image and mental health, our research shows
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Around 350 million people globally use dating apps, and they amass an estimated annual revenue of more than US$5 billion. In Australia, 49% of adults report using at least one online dating app or website, with a further 27% having done so in the past.
But while dating apps have helped many people find romantic partners, they’re not all good news.
In a recent review, my colleagues and I found using dating apps may be linked to poorer body image, mental health and wellbeing.
Dikushin Dmitry/Shutterstock We collated the evidence
Our study was a systematic review, where we collated the results of 45 studies that looked at dating app use and how this was linked to body image, mental health or wellbeing.
Body image refers to the perceptions or feelings a person has towards their own appearance, often relating to body size, shape and attractiveness.
Most of the studies we included were published in 2020 onwards. The majority were carried out in Western countries (such as the United States, the United Kingdom and Australia). Just under half of studies included participants of all genders. Interestingly, 44% of studies observed men exclusively, while only 7% included just women.
Of the 45 studies, 29 looked at the impact of dating apps on mental health and wellbeing and 22 considered the impact on body image (some looked at both). Some studies examined differences between users and non-users of dating apps, while others looked at whether intensity of dating app use (how often they’re used, how many apps are used, and so on) makes a difference.
More than 85% of studies (19 of 22) looking at body image found significant negative relationships between dating app use and body image. Just under half of studies (14 of 29) observed negative relationships with mental health and wellbeing.
The studies noted links with problems including body dissatisfaction, disordered eating, depression, anxiety and low self-esteem.
Dating apps are becoming increasingly common. But could their use harm mental health? Rachata Teyparsit/Shutterstock It’s important to note our research has a few limitations. For example, almost all studies included in the review were cross-sectional – studies that analyse data at a particular point in time.
This means researchers were unable to discern whether dating apps actually cause body image, mental health and wellbeing concerns over time, or whether there is simply a correlation. They can’t rule out that in some cases the relationship may go the other way, meaning poor mental health or body image increases a person’s likelihood of using dating apps.
Also, the studies included in the review were mostly conducted in Western regions with predominantly white participants, limiting our ability to generalise the findings to all populations.
Why are dating apps linked to poor body image and mental health?
Despite these limitations, there are plausible reasons to expect there may be a link between dating apps and poorer body image, mental health and wellbeing.
Like a lot of social media, dating apps are overwhelmingly image-centric, meaning they have an emphasis on pictures or videos. Dating app users are initially exposed primarily to photos when browsing, with information such as interests or hobbies accessible only after manually clicking through to profiles.
Because of this, users often evaluate profiles based primarily on the photos attached. Even when a user does click through to another person’s profile, whether or not they “like” someone may still often be determined primarily on the basis of physical appearance.
This emphasis on visual content on dating apps can, in turn, cause users to view their appearance as more important than who they are as a person. This process is called self-objectification.
People who experience self-objectification are more likely to scrutinise their appearance, potentially leading to body dissatisfaction, body shame, or other issues pertaining to body image.
Dating apps are overwhelmingly image-centric. Studio Romantic/Shutterstock There could be several reasons why mental health and wellbeing may be impacted by dating apps, many of which may centre around rejection.
Rejection can come in many forms on dating apps. It can be implied, such as having a lack of matches, or it can be explicit, such as discrimination or abuse. Users who encounter rejection frequently on dating apps may be more likely to experience poorer self-esteem, depressive symptoms or anxiety.
And if rejection is perceived to be based on appearance, this could lead again to body image concerns.
What’s more, the convenience and game-like nature of dating apps may lead people who could benefit from taking a break to keep swiping.
What can app developers do? What can you do?
Developers of dating apps should be seeking ways to protect users against these possible harms. This could, for example, include reducing the prominence of photos on user profiles, and increasing the moderation of discrimination and abuse on their platforms.
The Australian government has developed a code of conduct – to be enforced from April 1 this year – to help moderate and reduce discrimination and abuse on online dating platforms. This is a positive step.
Despite the possible negatives, research has also found dating apps can help build confidence and help users meet new people.
If you use dating apps, my colleagues and I recommend choosing profile images you feel display your personality or interests, or photos with friends, rather than semi-clothed images and selfies. Engage in positive conversations with other users, and block and report anyone who is abusive or discriminatory.
It’s also sensible to take breaks from the apps, particularly if you’re feeling overwhelmed or dejected.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14. The Butterfly Foundation provides support for eating disorders and body image issues, and can be reached on 1800 334 673.
Zac Bowman, PhD Candidate, College of Education, Psychology & Social Work, Flinders University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hope Not Nope – by Dr. Dillon Caswell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author a Doctor of Physical Therapy, writes from both professional expertise and personal experience, when it comes to the treatment of long term injury / disability / chronic illness.
His position here is that while suffering is unavoidable, we don’t have to suffer as much or as long as many might tell us. We can do things to crawl and claw our way to a better position, and we do not have to settle for any outcome we don’t want. That doesn’t mean there’s always a miracle cure—we don’t get to decide that—but we do get to decide whether we keep trying.
Dr. Caswell’s advice is based mostly in psychology—a lot of it in sports psychology, which is no surprise given his long history as an athlete as well as his medical career.
The style is very easy-reading, and a combination of explanation, illustrative (often funny) anecdotes, and a backbone of actual research to keep everything within the realms of science rather than mere wishful thinking—he strikes a good balance.
Bottom line: if your current health outlook is more of an uphill marathon, then this book can give you the tools to carry yourself through the healthcare system that’s been made for numbers, not people.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
For Many Rural Women, Finding Maternity Care Outweighs Concerns About Abortion Access
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
BAKER CITY, Ore. — In what has become a routine event in rural America, a hospital maternity ward closed in 2023 in this small Oregon town about an hour from the Idaho border.
For Shyanne McCoy, 23, that meant the closest hospital with an obstetrician on staff when she was pregnant was a 45-mile drive away over a mountain pass.
When McCoy developed symptoms of preeclampsia last January, she felt she had the best chance of getting the care she needed at a larger hospital in Boise, Idaho, two hours away. She spent the final week of her pregnancy there, too far from home to risk leaving, before giving birth to her daughter.
Six months later, she said it seems clear to her that the health care needs of rural young women like her are largely ignored.
For McCoy and others, figuring out how to obtain adequate care to safely have a baby in Baker City has quickly eclipsed concerns about another medical service lacking in the area: abortion. But in Oregon and elsewhere in the country, progressive lawmakers’ attempts to expand abortion access sometimes clash with rural constituencies.
Oregon is considered one of the most protective states in the country when it comes to abortion. There are no legal limits on when someone can receive an abortion in the state, and the service is covered by its Medicaid system. Still, efforts to expand access in the rural, largely conservative areas that cover most of the state have encountered resistance and incredulity.
It’s a divide that has played out in elections in such states as Nevada, where voters passed a ballot measure in November that seeks to codify abortion protections in the state constitution. Residents in several rural counties opposed the measure.
In Oregon, during the months just before the Baker City closure was announced, Democratic state lawmakers were focused on a proposed pilot program that would launch two mobile reproductive health care clinics in rural areas. The bill specified that the van-based clinics would include abortion services.
State Rep. Christine Goodwin, a Republican from a southwestern Oregon district, called the proposal the “latest example” of urban legislators telling rural leaders what their communities need.
The mobile health clinic pilot was eventually removed from the bill that was under discussion. That means no new abortion options in Oregon’s Baker County — and no new state-funded maternity care either.
“I think if you expanded rural access in this community to abortions before you extended access to maternal health care, you would have an uprising on your hands,” said Paige Witham, 27, a member of the Baker County health care steering committee and the mother of two children, including an infant born in October.
A study published in JAMA in early December that examined nearly 5,000 acute care hospitals found that by 2022, 52% of rural hospitals lacked obstetrics care after more than a decade of unit closures. The health implications of those closures for young women, the population most likely to need pregnancy care, and their babies can be significant. Research has shown that added distance between a patient and obstetric care increases the likelihood the baby will be admitted to a neonatal intensive care unit, or NICU.
Witham said that while she does not support abortion, she believes the government should not “legislate it away completely.” She said that unless the government provides far more support for young families, like free child care and better mental health care, abortion should remain legal.
Conversations with a liberal school board member, a moderate owner of a timber company, members of Baker City’s Republican Party chapter, a local doula, several pregnant women, and the director of the Baker County Health Department — many of whom were not rigidly opposed to abortion — all turned up the same answer: No mobile clinics offering abortions here, please.
Kelle Osborn, a nurse supervisor for the Baker County Health Department, loved the idea of a mobile clinic that would provide education and birth control services to people in outlying areas. She was less thrilled about including abortion services in a clinic on wheels.
“It’s not something that should just be handed out from a mobile van,” she said of abortion services. She said people in her conservative rural county would probably avoid using the clinics for anything if they were understood to provide abortion services.
Both Osborn and Meghan Chancey, the health department’s director, said they would rank many health care priorities higher, including the need for a general surgeon, an ICU, and a dialysis clinic.
Nationally, reproductive health care services of all types tend to be limited for people in rural areas, even within states that protect abortion access. More than two-thirds of people in “maternity care deserts” — all of which are in rural counties — must drive more than a half-hour to get obstetric care, according to a 2024 March of Dimes report. For people in the Southern states where lawmakers installed abortion bans, abortion care can be up to 700 miles away, according to a data analysis by Axios.
Nathan Defrees grew up in Baker City and has practiced medicine here since 2017. He works for a family medicine clinic. If a patient asks about abortion, he provides information about where and how one can be obtained, but he doesn’t offer abortions himself.
“There’s not a lot of anonymity in small towns for physicians who provide that care,” he said. “Many of us aren’t willing to sacrifice the rest of our career for that.”
He also pointed to the small number of patients requesting the service locally. Just six people living in Baker County had an abortion in 2023, according to data from the Oregon Department of Public Health. Meanwhile, 125 residents had a baby that year.
A doctor with obstetric training living in another rural part of the state has chosen to quietly provide early-stage abortions when asked. The doctor, concerned for their family’s safety in the small, conservative town where they live, asked not to be identified.
The idea that better access to abortion is not needed in rural areas seems naive, the doctor said. People most in need of abortion often don’t have access to any medical service not already available in town, the doctor pointed out. The first patient the doctor provided an abortion for at the clinic was a meth user with no resources to travel or to manage an at-home medication abortion.
“It seemed entirely inappropriate for me to turn her away for care I had the training and the tools to do,” the doctor said.
Defrees said it has been easier for Baker County residents to get an abortion since the U.S. Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade.
A new Planned Parenthood clinic in Ontario, Oregon, 70 miles away in neighboring Malheur County, was built primarily to provide services to people from the Boise metro area, but it also created an option for many living in rural eastern Oregon.
Idaho is one of the 16 states with near-total bans on abortion. Like many states with bans, Idaho has struggled to maintain its already small fleet of fetal medicine doctors. The loss of regional expertise touches Baker City, too, Defrees said.
For example, he said, the treatment plan for women who have a desired pregnancy but need a termination for medical reasons is now far less clear. “It used to be those folks could go to Boise,” he said. “Now they can’t. That does put us in a bind.”
Portland is the next closest option for that type of care, and that means a 300-mile drive along a set of highways that can be treacherous in winter.
“It’s a lot scarier to be pregnant now in Baker City than it ever has been,” Defrees said.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: