Tahini vs Hummus – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing tahini to hummus, we picked the tahini.
Why?
Both are great! But tahini is so nutritionally dense, that it makes even the wonder food that is hummus look bad next to it.
In terms of macros, tahini is higher in everything except water. So, higher in protein, carbs, fats, and fiber. In terms of those fats, the fat breakdown is similar for both, being mostly polyunsaturated and monounsaturated, with a small percentage of saturated. Tahini has the lower glycemic index, but both are so low that it makes no practical difference.
In terms of vitamins, tahini has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B9, E, and choline, while hummus is higher in vitamin B6.
This is a good reason to embellish hummus with some red pepper (vitamin A), a dash of lemon (vitamin C), etc, but we’re judging these foods in their most simple states, for fairness.
When it comes to minerals, tahini has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. Meanwhile, hummus is higher in sodium.
Note: hummus is a good source of all those minerals too! Tahini just has more.
In short… Enjoy both, but tahini is the more nutritionally dense by far. On the other hand, if for whatever reason you’re looking for something lower in carbs, fats, and calories, then hummus is where it’s at.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dates vs Banana – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing dates to banana, we picked the dates.
Why?
It was close, and bananas do have some strengths too! We pitted these two against each other as they’re both sweet fruits often used as a sweetening and consistency-altering ingredient in desserts and sweet snacks, so if you’re making a choice between them, here are the things to consider:
In terms of macros, dates have more than 3x the fiber, more than 2x the protein, and a little over 3x the carbs. You may be wondering how this adds up in terms of glycemic index: dates have the lower GI. So, we pick dates, here, for that reason and overall nutritional density too.
When it comes to vitamins, bananas have their moment, albeit barely: dates have more of vitamins B1, B3, B5, and K, while bananas have more of vitamins A, B6, C, E, and choline, making for a marginal victory for bananas in this category.
Looking at minerals next, however, it’s quite a different story: dates have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while bananas are not higher in any mineral. No, not even potassium, for which they are famous—dates have nearly 2x more potassium than bananas.
Adding up these sections makes for a clear win for dates in general!
Enjoy either/both, but dates are the more nutritious snack/ingredient.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
We looked at 700 plant-based foods to see how healthy they really are. Here’s what we found
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’re thinking about buying plant-based foods, a trip to the supermarket can leave you bewildered.
There are plant-based burgers, sausages and mince. The fridges are loaded with non-dairy milk, cheese and yoghurt. Then there are the tins of beans and packets of tofu.
But how much is actually healthy?
Our nutritional audit of more than 700 plant-based foods for sale in Australian supermarkets has just been published. We found some products are so high in salt or saturated fat, we’d struggle to call them “healthy”.
We took (several) trips to the supermarket
In 2022, we visited two of each of four major supermarket retailers across Melbourne to collect information on the available range of plant-based alternatives to meat and dairy products.
We took pictures of the products and their nutrition labels.
We then analysed the nutrition information on the packaging of more than 700 of these products. This included 236 meat substitutes, 169 legumes and pulses, 50 baked beans, 157 dairy milk substitutes, 52 cheese substitutes and 40 non-dairy yoghurts.
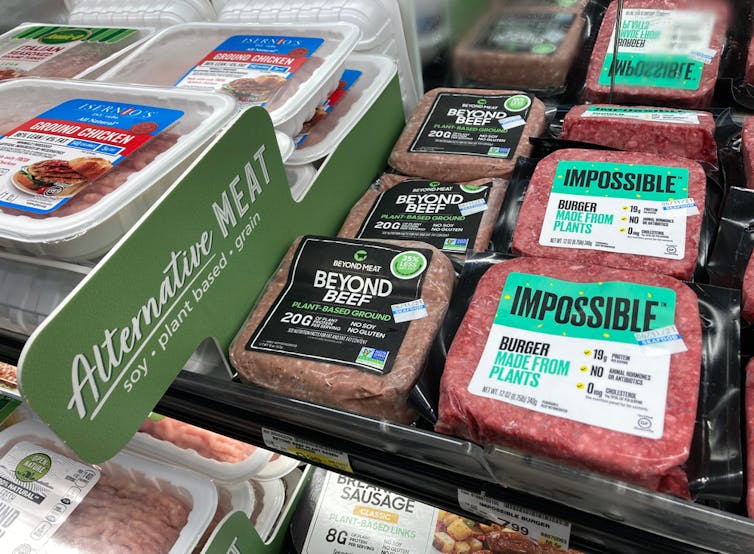
Plant-based meats were surprisingly salty
We found a wide range of plant-based meats for sale. So, it’s not surprising we found large variations in their nutrition content.
Sodium, found in added salt and which contributes to high blood pressure, was our greatest concern.
The sodium content varied from 1 milligram per 100 grams in products such as tofu, to 2,000mg per 100g in items such as plant-based mince products.
This means we could eat our entire daily recommended sodium intake in just one bowl of plant-based mince.
An audit of 66 plant-based meat products in Australian supermarkets conducted in 2014 found sodium ranged from 316mg in legume-based products to 640mg in tofu products, per 100g. In a 2019 audit of 137 products, the range was up to 1,200mg per 100g.
In other words, the results of our audit seems to show a consistent trend of plant-based meats getting saltier.
Looking for plant-based meat? Check the label for the sodium content.
Michael Vi/Shutterstock
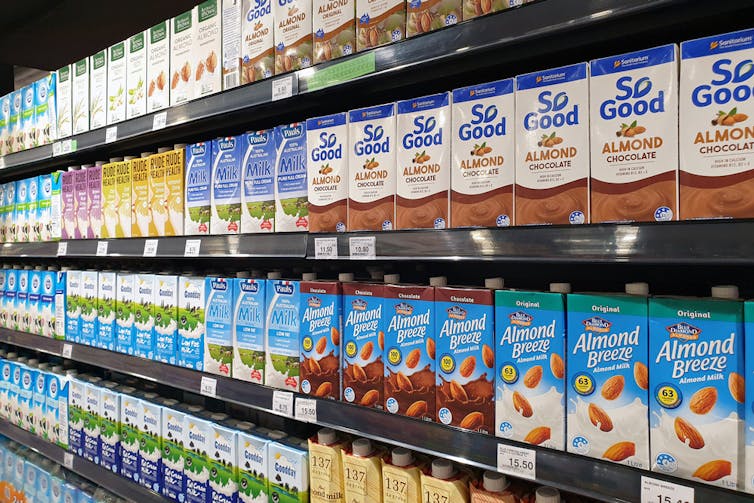
What about plant-based milks?
Some 70% of the plant-based milks we audited were fortified with calcium, a nutrient important for bone health.
This is good news as a 2019-2020 audit of 115 plant-based milks from Melbourne and Sydney found only 43% of plant-based milks were fortified with calcium.
Of the fortified milks in our audit, almost three-quarters (73%) contained the recommended amount of calcium – at least 100mg per 100mL.
We also looked at the saturated fat content of plant-based milks.
Coconut-based milks had on average up to six times higher saturated fat content than almond, oat or soy milks.
Previous audits also found coconut-based milks were much higher in saturated fat than all other categories of milks.
Some plant-based milks were healthier than others.
TY Lim/Shutterstock
A first look at cheese and yoghurt alternatives
Our audit is the first study to identify the range of cheese and yoghurt alternatives available in Australian supermarkets.
Calcium was only labelled on a third of plant-based yoghurts, and only 20% of supermarket options met the recommended 100mg of calcium per 100g.
For plant-based cheeses, most (92%) were not fortified with calcium. Their sodium content varied from 390mg to 1,400mg per 100g, and saturated fat ranged from 0g to 28g per 100g.
So, what should we consider when shopping?
As a general principle, try to choose whole plant foods, such as unprocessed legumes, beans or tofu. These foods are packed with vitamins and minerals. They’re also high in dietary fibre, which is good for your gut health and keeps you fuller for longer.
If opting for a processed plant-based food, here are five tips for choosing a healthier option.
1. Watch the sodium
Plant-based meat alternatives can be high in sodium, so look for products that have around 150-250mg sodium per 100g.
2. Pick canned beans and legumes
Canned chickpeas, lentils and beans can be healthy and low-cost additions to many meals. Where you can, choose canned varieties with no added salt, especially when buying baked beans.
3. Add herbs and spices to your tofu
Tofu can be a great alternative to meat. Check the label and pick the option with the highest calcium content. We found flavoured tofu was higher in salt and sugar content than minimally processed tofu. So it’s best to pick an unflavoured option and add your own flavours with spices and herbs.
4. Check the calcium
When choosing a non-dairy alternative to milk, such as those made from soy, oat, or rice, check it is fortified with calcium. A good alternative to traditional dairy will have at least 100mg of calcium per 100g.
5. Watch for saturated fat
If looking for a lower saturated fat option, almond, soy, rice and oat varieties of milk and yoghurt alternatives have much lower saturated fat content than coconut options. Pick those with less than 3g per 100g.
Laura Marchese, PhD Student at the Institute for Physical Activity and Nutrition, Deakin University and Katherine Livingstone, NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow and Senior Research Fellow at the Institute for Physical Activity and Nutrition, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
How weight bias in health care can harm patients with obesity: Research
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Patients who weigh more than what medical authorities generally consider healthy often avoid seeing doctors for fear of being judged, insulted or misdiagnosed, decades of research find. Meanwhile, academic studies consistently show many health care professionals discriminate against heavier patients and that weight bias can drive people with obesity to gain weight.
Weight bias refers to negative attitudes, stereotypes and discrimination aimed at individuals with excess body fat. When scholars reviewed 41 studies about weight bias in health care, published from 1989 to 2021, they found it comes in many forms: contemptuous language, inappropriate gestures, expressing a preference for thinner patients, avoiding physical touch and eye contact, and attributing all of a person’s health issues to their weight.
“Weight bias has been reported in physicians, nurses, dietitians, physiotherapists, and psychologists, as well as nutritionists and exercise professionals, and it is as pervasive among medical professionals as it is within the general population,” write the authors of the research review, published in 2021 in the journal Obesity.
That’s a problem considering an estimated 4 out of 10 U.S. adults aged 20 years and older have obesity, a complex and often misunderstood illness that the American Medical Association voted in 2013 to recognize as a disease. By 2030, half of U.S. adults will have obesity, researchers project in a 2020 paper in the International Journal of Epidemiology.
Worldwide, the obesity rate among adults aged 18 and older was 13% in 2016, according to the World Health Organization. If current trends continue, the World Obesity Federation projects that, by 2035, 51% of the global population will be living with overweight or obesity.
The harms of weight bias
Weight stigma — the societal devaluation of people perceived to be carrying excess weight — drives weight bias. It’s so physically and emotionally damaging that a panel of 36 international experts issued a consensus statement in 2020 to raise awareness about and condemn it. Dozens of medical and academic organizations, including 15 scholarly journals, endorsed the document, published in Nature Medicine.
The release of a consensus statement is a significant event in research, considering it represents the collective position that experts in a particular field have taken on an issue, based on an analysis of all the available evidence.
Research to date indicates heavier individuals who experience weight bias and stigma often:
- Avoid doctors and other health care professionals, skipping routine screenings as well as needed treatments.
- Change doctors frequently.
- Are at a higher risk for depression, anxiety, mood disorders and other mental health problems.
- Avoid or put off exercise.
- Consume more food and calories.
- Gain weight.
- Have disrupted sleep.
The consensus statement notes that educating health care providers, journalists, policymakers and others about obesity is key to changing the narrative around the disease.
“Weight stigma is reinforced by misconceived ideas about body-weight regulation and lack of awareness of current scientific evidence,” write the experts, led by Francesco Rubino, the chair of metabolic and bariatric surgery at Kings College London.
“Despite scientific evidence to the contrary, the prevailing view in society is that obesity is a choice that can be reversed by voluntary decisions to eat less and exercise more. These assumptions mislead public health policies, confuse messages in popular media, undermine access to evidence-based treatments, and compromise advances in research.”
Weight bias and stigma appear to stimulate the secretion of the stress hormone cortisol and promote weight gain, researchers write in a 2016 paper published in Obesity.
A. Janet Tomiyama, a psychology professor at UCLA who directs the university’s Dieting, Stress, and Health research lab, describes weight stigma as “a ‘vicious cycle’ — a positive feedback loop wherein weight stigma begets weight gain.”
“This happens through increased eating behavior and increased cortisol secretion governed by behavioral, emotional, and physiological mechanisms, which are theorized to ultimately result in weight gain and difficulty of weight loss,” Tomiyama writes in her 2014 paper, “Weight Stigma is Stressful. A Review of Evidence for the Cyclic Obesity/Weight-Based Stigma Model.”
The consensus statement spotlights 13 recommendations for eliminating weight bias and stigma, some of which are specifically aimed at health care providers, the media, researchers or policymakers. One of the recommendations for the health care community: “[Health care providers] specialized in treating obesity should provide evidence of stigma-free practice skills. Professional bodies should encourage, facilitate, and develop methods to certify knowledge of stigma and its effects, along with stigma-free skills and practices.”
The one recommendation for the media: “We call on the media to produce fair, accurate, and non-stigmatizing portrayals of obesity. A commitment from the media is needed to shift the narrative around obesity.”
Why obesity is a complicated disease
It’s important to point out that having excess body fat does not, by itself, mean an individual is unhealthy, researchers explain in a 2017 article in The Conversation, which publishes research-based news articles and essays. But it is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, including stroke, as well as diabetes, some types of cancer, and musculoskeletal disorders such as osteoarthritis.
Doctors often look at patients’ body mass index — a number that represents their weight in relation to their height — to gauge the amount of fat on their bodies. A BMI of 18.5 to 24.9 is ideal, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A BMI of 25.0 to 29.9, indicates excess body fat, or “overweight,” while a BMI of 30 and above indicates obesity.
In June, the American Medical Association announced a new policy clarifying how BMI can be used to diagnose obesity. Because it’s an imperfect measure for body fat, the organization suggests BMI be used in conjunction with other measures such as a patient’s waist circumference and skin fold thickness.
Two specialists who have been working for years to dispel myths and misconceptions about obesity are Fatima Cody Stanford, an obesity physician and associate professor at Harvard Medical School, and Rebecca Puhl, the deputy director of the Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity at the University of Connecticut.
Cody Stanford has called obesity “a brain disease” because the brain tells the body how much to eat and what to do with the food consumed. One pathway in the brain directs the body to eat less and store less fat, she explains in a February 2023 podcast produced by the American Medical Association.
“For people that signal really great down this pathway, they tend to be very lean, not struggle with their weight in the same way that people that have excess weight do,” she says during the podcast, adding that people with obesity receive signals from an alternate pathway that “tells us to eat more and store more.”
Academic studies demonstrate that a wide variety of factors can affect weight regulation, including sleep quality and duration, gut health, genetics, medication, access to healthy foods and even early life experiences.
For example, a 2020 paper in the journal JAMA Network Open suggests female infants born by cesarean delivery have a higher risk of obesity during adulthood than female infants born by vaginal delivery. The study of 33,226 U.S. women born between 1946 and 1964 found that a cesarean delivery is associated with an 11% higher risk of developing obesity and a 46% higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Scholars have also found that traumatic childhood experiences such as abuse and neglect are linked to adult obesity, according to a research review published in 2020.
Income inequality seems to play a role as well. When researchers from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health studied the link between income inequality and obesity for a sample of 36,665 U.S. adults, they discovered women with lower incomes are more likely to have obesity than women with higher incomes.
Their analysis indicates the opposite is true for men, whose odds of obesity rise with their income, the researchers write in a 2021 paper in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
Weight bias among doctor trainees
While scholars have learned a lot about obesity and weight bias in recent decades, the information might not be reaching people training to become doctors. A study published in October finds that some resident physicians believe obesity to be the result of poor choices and weak willpower.
Researchers asked 3,267 resident physicians who graduated from a total of 49 U.S. medical schools a series of questions to gauge their knowledge of obesity and attitudes toward heavier patients. What they learned: Nearly 40% of resident physicians agreed with the statement, “Fat people tend to be fat pretty much through their own fault.” Almost half agreed with the statement, “Some people are fat because they have no willpower.”
The study also reveals that about one-third of participants said they “feel more irritated when treating an obese patient than a non-obese patient.”
“Notably, more than a quarter of residents expressed slight-to-strong agreement with the item ‘I dislike treating obese patients,’” the researchers write.
Another takeaway from the paper: Resident physicians specializing in orthopedic surgery, anesthesiology and urology expressed the highest levels of dislike of heavier patients. Of the 16 medical specialties represented, residents in family medicine, psychiatry and pediatrics reported the lowest levels of dislike.
Kimberly Gudzune, medical director of the American Board of Obesity Medicine, asserts that doctors and medical students need to be educated about obesity. The topic “is grossly neglected” in medical schools and medical training programs worldwide, research has found.
Many physicians don’t understand obesity, Gudzune explains in a July 2023 interview on the internal medicine podcast “The Curbsiders.”
“I think back to when I was a medical student, when I was a resident, I really didn’t learn much about obesity and how to treat it, yet it’s a problem that affects the majority of our patients,” she tells podcast listeners. “I think there’s a lot of evidence out there showing that primary care physicians don’t really know where to start.”
In 2011, the American Board of Obesity Medicine established a program through which doctors could become certified in obesity medicine. Since then, a total of 6,729 U.S. doctors have earned certification, the vast majority of whom specialize in family and internal medicine.
What health care providers think
The experts who created the consensus statement on weight bias and stigma noted health care providers’ shortcomings in the document. They write that the common themes they discovered in the research include “contemptuous, patronizing, and disrespectful treatment” of patients, a lack of training, poor communication and assumptions about weight gain.
Puhl, the deputy director of the Rudd Center at the University of Connecticut, is a pioneer in weight bias research and one of the experts who wrote the consensus statement. During an episode of “The Leading Voices in Food,” a podcast created by Duke University’s World Food Policy Center, she shares details about what she has learned over the years.
“[Health care providers’] views that patients with obesity are lazy or lacking control, are to blame for their weight or noncompliant with treatment,” she says during the interview. “We know, for example, that some physicians spend less time in their appointments with patients [who] have a larger body size. They give them less education about health. They’re more reluctant to perform certain screenings. They talk about treating patients with obesity as being a greater waste of their time than providing care to thinner patients. And we know that patients seem to be aware of these biases from providers and that can really contribute to patients avoiding health care because they just don’t want to repeat those negative experiences of bias.”
To set the record straight, the experts who wrote the the consensus statement listed the following five common assumptions as being “at odds with a definitive body of biological and clinical evidence.”
1. Body weight = calories in – calories out.
This equation oversimplifies the relationship between body weight and energy consumed and used, the experts write. “Both variables of the equation depend on factors additional to just eating and exercising. For instance, energy intake depends on the amount of food consumed, but also on the amount of food-derived energy absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract, which in turn is influenced by multiple factors, such as digestive enzymes, bile acids, microbiota, gut hormones, and neural signals, none of which are under voluntary control.”
2. Obesity is primarily caused by voluntary overeating and a sedentary lifestyle.
According to the experts, overeating and forgoing exercise might be symptoms of obesity rather than the root causes. There are many possible causes and contributors “including geneticand epigenetic factors, foodborne factors, sleep deprivation and circadian dysrhythmia, psychological stress, endocrine disruptors, medications, and intrauterine and intergenerational effects. These factors do not require overeating or physical inactivity to explain excess weight.” they write.
3. Obesity is a lifestyle choice.
“People with obesity typically recognize obesity as a serious health problem, rather than a conscious choice,” the experts write. “Given the negative effects of obesity on quality of life, the well-known risks of serious complications and reduced life expectancy associated with it, it is a misconception to define obesity as a choice.”
4. Obesity is a condition, not a disease.
The criteria generally used to determine disease status “are clearly fulfilled in many individuals with obesity as commonly defined, albeit not all,” the experts explain. “These criteria include specific signs or symptoms (such as increased adiposity), reduced quality of life, and/or increased risk of further illness, complications, and deviation from normal physiology — or well-characterized pathophysiology (for example, inflammation, insulin resistance, and alterations of hormonal signals regulating satiety and appetite).”
5. Severe obesity is usually reversible by voluntarily eating less and exercising more.
“A large body of clinical evidence has shown that voluntary attempts to eat less and exercise more render only modest effects on body weight in most individuals with severe obesity,” the experts write. “When fat mass decreases, the body responds with reduced resting energy expenditure and changes in signals that increase hunger and reduce satiety (for example, leptin, ghrelin). These compensatory metabolic and biologic adaptations promote weight regain and persist for as long as persons are in the reduced-energy state, even if they gain some weight back.”
Health care facility improvements
The expert panel also determined that many health care facilities aren’t equipped to treat people with obesity. Examination gowns, blood pressure cuffs, chairs and examination tables often are too small, patients have reported.
When researchers from the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center and Mayo Clinic studied the quality of care that patients with obesity receive, they learned that a clinic’s physical environment can have a big effect on a patient’s experience.
They write in a 2015 study published in Obesity Reviews: “Waiting room chairs with armrests can be uncomfortable or too small. Equipment such as scales, blood pressure cuffs, examination gowns and pelvic examination instruments are often designed for use with smaller patients. When larger alternatives are not available, or are stored in a place that suggests infrequent use, it can signal to patients that their size is unusual and that they do not belong. These experiences, which are not delivered with malicious intent, can be humiliating.”
When medical equipment is the wrong size, it may not work correctly. For instance, chances are high that a blood pressure reading will be inaccurate if a health care professional uses a blood pressure cuff that’s too small on a patient with obesity, a 2022 paper finds.
To create a comfortable environment for patients with high body weights, the Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity recommends that health care facilities provide, among other things, extra-large exam gowns, chairs that can support more than 300 pounds and do not have arms, and wide exam tables that are bolted to the floor so they don’t move.
The consensus statement also recommends improvements to health care facilities.
“Given the prevalence of obesity and obesity-related diseases,” the 36 international experts write, “appropriate infrastructure for the care and management of people with obesity, including severe obesity, must be standard requirement for accreditation of medical facilities and hospitals.”
Source list:
Weight Bias Among Health Care Professionals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Blake J. Lawrence; et al. Obesity, November 2021.Joint International Consensus Statement for Ending Stigma of Obesity
Francesco Rubino, et al. Nature Medicine, March 2020.Perceived Weight Discrimination and Chronic Biochemical Stress: A Population-Based Study Using Cortisol in Scalp Hair
Sarah E. Jackson, Clemens Kirschbaum and Andrew Steptoe. Obesity, December 2016.Weight Stigma is Stressful. A Review of Evidence for the Cyclic Obesity/Weight-Based Stigma Model
A. Janet Tomiyama. Appetite, November 2014.Association of Birth by Cesarean Delivery with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Among Adult Women
Jorge E. Chavarro. JAMA Network Open, April 2020.Adverse Childhood Experiences and Adult Obesity: A Systematic Review of Plausible Mechanisms and Meta-Analysis of Cross-Sectional Studies
David A. Wiss and Timothy D. Brewerton. Physiology & Behavior, September 2020.Income Inequality and Obesity among U.S. Adults 1999–2016: Does Sex Matter?
Hossein Zare, Danielle D. Gaskin and Roland J. Thorpe Jr. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, July 2021.Comparisons of Explicit Weight Bias Across Common Clinical Specialties of U.S. Resident Physicians
Samantha R. Philip, Sherecce A. Fields, Michelle Van Ryn and Sean M. Phelan. Journal of General Internal Medicine, October 2023.Impact of Weight Bias and Stigma on Quality of Care and Outcomes for Patients with Obesity
S.M. Phelan; et al. Obesity Reviews, April 2015.One Size Does Not Fit All: Impact of Using A Regular Cuff For All Blood Pressure Measurements
Tammy. M. Brady; et al. Circulation, April 2022.This article first appeared on The Journalist’s Resource and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How gender-affirming care improves trans mental health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In recent years, a growing number of states have passed laws restricting or banning gender-affirming care for transgender people, particularly minors. As conversations about gender-affirming care increase, so do false narratives about it, with some opponents falsely suggesting that it’s harmful to mental health.
Despite widespread attacks against gender-affirming care, research clearly shows that it improves mental health outcomes for transgender people.
Read on to learn more about what gender-affirming care is, how it benefits mental well-being, and how you can access it.
What is gender-affirming care?
Gender-affirming care describes a range of medical interventions that help align people’s bodies with their gender identities. While anyone can seek gender-affirming care in the form of laser hair removal, breast augmentation, erectile dysfunction medication, or hormone therapy, among other treatments, most conversations about gender-affirming care center around transgender people, whose gender identity or gender expression does not conform to their sex assigned at birth.
Gender-affirming care for trans people varies based on age. For example, some trans adults seek hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or gender-affirming surgeries that help their bodies match their internal sense of gender.
Trans kids entering adolescence might be prescribed puberty blockers, which temporarily delay the production of hormones that initiate puberty, to give them more time to figure out their gender identities before deciding on next steps. This is the same medication given to cisgender kids—whose gender identities match the sex they were assigned at birth—experiencing early puberty.
What is gender dysphoria?
Gender dysphoria describes a feeling of unease that some trans people experience when their perceived gender doesn’t match their gender identity. This can lead to a range of mental health conditions that affect their quality of life
Some trans people may manage gender dysphoria by wearing gender-affirming clothing, opting for a gender-affirming hairstyle, or asking others to refer to them by a name and pronouns that authentically represent them. Others may need gender-affirming care to feel at home in their bodies.
Trans people who desire gender-affirming care and have not been able to access it experience psychological distress, including depression, anxiety, self-harm, and suicidal ideation. The Trevor Project’s 2023 U.S. National Survey on the Mental Health of LGBTQ Young People found that roughly half of trans youth “seriously considered attempting suicide in the past year.”
How does gender-affirming care improve mental health?
For trans adults, gender-affirming care can alleviate gender dysphoria, which has been shown to improve both short-term and long-term mental health. A 2018 study found that trans adults who do not undergo HRT are four times more likely to experience depression than those who do, although not all trans people desire HRT.
Extensive research has shown that gender-affirming care also alleviates gender dysphoria and improves mental health outcomes in trans kids, teens, and young adults. A 2022 study found that access to HRT and puberty blockers lowered the odds of depression in trans people between the ages of 13 and 20 by 60 percent and reduced the risk of self-harm and suicidal thoughts by 73 percent.
Both the Endocrine Society—which aims to advance hormone research—and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend that trans kids and teens have access to developmentally appropriate gender-affirming care.
How can I access gender-affirming care?
If you’re a trans adult seeking gender-affirming care or a guardian of a trans kid or teen who’s seeking gender-affirming care, talk to your health care provider about your options. You can find a trans-affirming provider by searching the World Professional Association for Transgender Health directory or visiting your local LGBTQ+ health center or Planned Parenthood.
Some gender-affirming care may not be covered by insurance. Learn how to make the most of your coverage from the National Center for Transgender Equality. Find insurance plans available through the Marketplace that cover gender-affirming care in some states through Out2Enroll.
Some states restrict or ban gender-affirming care. Learn about the laws in your state by visiting the Trans Legislation Tracker.
Where can trans people and their families find mental health support?
In addition to working with a trans-affirming therapist, trans people and their families can find mental health support through these free services:
- PFLAG offers resources for families and friends of LGBTQ+ people. Find a PFLAG chapter near you.
- The Trevor Project’s hotline has trained counselors who help LGBTQ+ youth in crisis. Call the TrevorLifeline 1-866-488-7386 or text START to 678-678.
- The Trans Lifeline was created by and for the trans community to support trans people in crisis. You can reach the Trans Lifeline hotline at 1-877-565-8860.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
If you or anyone you know is considering suicide or self-harm or is anxious, depressed, upset, or needs to talk, call the Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988 or text the Crisis Text Line at 741-741. For international resources, here is a good place to begin.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
100 No-Equipment Workouts – by Neila Rey
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For those of us who for whatever reason prefer to exercise at home rather than at the gym, we must make do with what exercise equipment we can reasonably install in our homes. This book deals with that from the ground upwards—literally!
If you have a few square meters of floorspace (and a ceiling that’s not too low, for exercises that involve any kind of jumping), then all 100 of these zero-equipment exercises are at-home options.
As to what kinds of exercises they are, they each marked as being one or both of “cardio” and “strength”.
They’re also marked as being of “difficulty level” 1, 2, or 3, so that someone who hasn’t exercised in a while (or hasn’t exercised like this at all), can know where best to start, and how best to progress.
The exercises come with clear explanations in the text, and clear line-drawing illustrations of how to do each exercise. Really, they could not be clearer; this is top quality pragmatism, and reads like a military manual.
Bottom line: whatever your strength and fitness goals, this book can see you well on your way to them (if not outright get you there already in many cases). It’s also an excellent “all-rounder” for full-body workouts.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Plant Power Doctor
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A Prescription For GLOVES
This is Dr. Gemma Newman. She’s a GP (General Practitioner, British equivalent to what is called a family doctor in America), and she realized that she was treating a lot of patients while nobody was actually getting better.
So, she set out to help people actually get better… But how?
The biggest thing
The single biggest thing she recommends is a whole foods plant-based diet, as that’s a starting point for a lot of other things.
Click here for an assortment of short videos by her and other health professionals on this topic!
Specifically, she advocates to “love foods that love you back”, and make critical choices when deciding between ingredients.
Click here to see her recipes and tips (this writer is going to try out some of these!)
What’s this about GLOVES?
We recently reviewed her book “Get Well, Stay Well: The Six Healing Health Habits You Need To Know”, and now we’re going to talk about those six things in more words than we had room for previously.
They are six things that she says we should all try to get every day. It’s a lot simpler than a lot of checklists, and very worthwhile:
Gratitude
May seem like a wishy-washy one to start with, but there’s a lot of evidence for this making a big difference to health, largely on account of how it lowers stress and anxiety. See also:
How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
Love
This is about social connections, mostly. We are evolved to be a social species, and while some of us want/need more or less social interaction than others, generally speaking we thrive best in a community, with all the social support that comes with that. See also:
How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Outside
This is about fresh air and it’s about moving and it’s about seeing some green plants (and if available, blue sky), marvelling at the wonder of nature and benefiting in many ways. See also:
Vegetables
We spoke earlier about the whole foods plant-based diet for which she advocates, so this is that. While reducing/skipping meat etc is absolutely a thing, the focus here is on diversity of vegetables; it is best to make a game of seeing how many different ones you can include in a week (not just the same three!). See also:
Three Critical Kitchen Prescriptions
Exercise
At least 150 minutes moderate exercise per week, and some kind of resistance work. It can be calisthenics or something; it doesn’t have to be lifting weights if that’s not your thing! See also:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
Sleep
Quality and quantity. Yes, 7–9 hours, yes, regardless of age. Unless you’re a child or a bodybuilder, in which case make it nearer 12. But for most of us, 7–9. See also:
Why You Probably Need More Sleep
Want to know more?
As well as the book we mentioned earlier, you might also like:
The Plant Power Doctor – by Dr. Gemma Newman
While the other book we mentioned is available for pre-order for Americans (it’s already released for the rest of the world), this one is available to all right now, so that’s a bonus too.
If books aren’t your thing (or even if they are), you might like her award-winning podcast:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: