Garlic vs Ginger – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing garlic to ginger, we picked the ginger.
Why?
Both are great, and it is close!
Notwithstanding that (almost?) nobody eats garlic or ginger for the macros, let’s do a moment’s due diligence on that first: garlic has more than 3x the protein and about 2x the fiber (and slightly higher carbs). But, given the small quantities in which people usually consume these foods, these numbers aren’t too meaningful.
In the category of micronutrients, garlic has a lot more vitamins and minerals. We’ll not do a full breakdown for this though, because again, unless you’re eating it by the cupful, this won’t make a huge difference.
Which means that so far, we have two nominal wins for garlic.
Both plants have many medicinal properties. They are both cardioprotective and anticancer, and both full of antioxidants. The benefits of both are comparable in these regards.
Both have antidiabetic action also, but ginger’s effects are stronger when compared head-to head.
So that’s an actual practical win for ginger.
Each plant’s respective effects on the gastrointestinal tract sets them further apart—ginger has antiemetic effects and can be used for treating nausea and vomiting from a variety of causes. Garlic, meanwhile, can cause adverse gastrointestinal effects in some people—but it’s usually neutral for most people in this regard.
Another win for ginger in practical terms.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healthy Brain, Happy Life – by Dr. Wendy Suzuki
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We talked about Dr. Wendy Suzuki’s research in the category of exercise and brain-benefits in our main feature the other day. But she has more to say than we can fit into an article!
This book chronicles her discoveries, through her work in memory and neuroplasticity, to her discoveries about exercise, and her dive into broader neurology-based mental health. So what does neurology-based mental health look like?
The answer is: mitigating brain-busters such as stress and anxiety, revitalizing a fatigued brain, boosting creativity, and other such benefits.
Does she argue that exercise is a cure-all? No, not quite. Sometimes there are other things she’s recommending (such as in her chapter on challenging the neurobiology of the stress response, or her chapter on meditation and the brain).
The writing style is mostly casual, interspersed with occasional mini-lectures (complete with diagrams and other illustrations), and is very readable and informative throughout.
Bottom line: if you’d like the more in-depth details of Dr. Suzuki’s work, this book is a very accessible way to get 320 pages of that!
Click here to check out Healthy Brain, Happy Life, and give yours the best!
Share This Post
-
Addiction Myths That Are Hard To Quit
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Which Addiction-Quitting Methods Work Best?
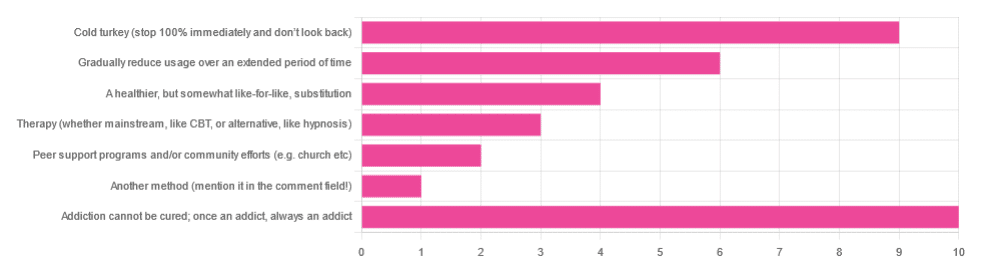
In Tuesday’s newsletter we asked you what, in your opinion, is the best way to cure an addiction. We got the above-depicted, below-described, interesting distribution of responses:
- About 29% said: “Addiction cannot be cured; once an addict, always an addict”
- About 26% said “Cold turkey (stop 100% and don’t look back)”
- About 17% said “Gradually reduce usage over an extended period of time”
- About 11% said “A healthier, but somewhat like-for-like, substitution”
- About 9% said “Therapy (whether mainstream, like CBT, or alternative, like hypnosis)”
- About 6% said “Peer support programs and/or community efforts (e.g. church etc)”
- About 3% said “Another method (mention it in the comment field)” and then did not mention it in the comment field
So what does the science say?
Addiction cannot be cured; once an addict, always an addict: True or False?
False, which some of the people who voted for it seemed to know, as some went on to add in the comment field what they thought was the best way to overcome the addiction.
The widespread belief that “once an addict, always an addict” is a “popular truism” in the same sense as “once a cheater, always a cheater”. It’s an observation of behavioral probability phrased as a strong generalization, but it’s not actually any kind of special unbreakable law of the universe.
And, certainly the notion that one cannot be cured keeps membership in many 12-step programs and similar going—because if you’re never cured, then you need to stick around.
However…
❝What is the definition of addiction?
Addiction is a treatable, chronic medical disease involving complex interactions among brain circuits, genetics, the environment, and an individual’s life experiences. People with addiction use substances or engage in behaviors that become compulsive and often continue despite harmful consequences.
Prevention efforts and treatment approaches for addiction are generally as successful as those for other chronic diseases.❞
~ American Society of Addiction Medicine
Or if we want peer-reviewed source science, rather than appeal to mere authority as above, then:
❝What is drug addiction?
Addiction is defined as a chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use despite adverse consequences. It is considered a brain disorder, because it involves functional changes to brain circuits involved in reward, stress, and self-control. Those changes may last a long time after a person has stopped taking drugs.
Addiction is a lot like other diseases, such as heart disease. Both disrupt the normal, healthy functioning of an organ in the body, both have serious harmful effects, and both are, in many cases, preventable and treatable.❞
~ Nora D. Volkow (Director, National Institute of Drug Abuse)
Read more: Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction
In short: part of the definition of addiction is the continued use; if the effects of the substance are no longer active in your physiology, and you are no longer using, then you are not addicted.
Just because you would probably become addicted again if you used again does not make you addicted when neither the substance nor its after-effects are remaining in your body. Otherwise, we could define all people as addicted to all things based on “well if they use in the future they will probably become addicted”.
This means: the effects of addiction can and often will last for long after cessation of use, but ultimately, addiction can be treated and cured.
(yes, you should still abstain from the thing to which you were formerly addicted though, or you indeed most probably will become addicted again)
Cold turkey is best: True or False?
True if and only if certain conditions are met, and then only for certain addictions. For all other situations… False.
To decide whether cold turkey is a safe approach (before even considering “effective”), the first thing to check is how dangerous the withdrawal symptoms are. In some cases (e.g. alcohol, cocaine, heroin, and others), the withdrawal symptoms can kill.
That doesn’t mean they will kill, so knowing (or being!) someone who quit this way does not refute this science by counterexample. The mortality rates that we saw while researching varied from 8% to 37%, so most people did not die, but do you really want (yourself or a loved one) to play those odds unnecessarily?
See also: Detoxification and Substance Abuse Treatment
Even in those cases where it is considered completely safe for most people to quit cold turkey, such as smoking, it is only effective when the quitter has appropriate reliable medical support, e.g.
- Without support: 3–5% success rate
- With support: 22% success rate
And yes, that 22% was for the “abrupt cessation” group; the “gradual cessation” group had a success rate of 15.5%. On which note…
Gradual reduction is the best approach: True or False?
False based on the above data, in the case of addictions where abrupt cessation is safe. True in other cases where abrupt cessation is not safe.
Because if you quit abruptly and then die from the withdrawal symptoms, then well, technically you did stay off the substance for the rest of your life, but we can’t really claim that as a success!
A healthier, but somewhat like-for-like substitution is best: True or False?
True where such is possible!
This is why, for example, medical institutions recommend the use of buprenorphine (e.g. Naloxone) in the case of opioid addiction. It’s a partial opioid receptor agonist, meaning it does some of the job of opioids, while being less dangerous:
It’s also why vaping—despite itself being a health hazard—is recommended as a method of quitting smoking:
Similarly, “zero alcohol drinks that seem like alcohol” are a popular way to stop drinking alcohol, alongside other methods:
This is also why it’s recommended that if you have multiple addictions, to quit one thing at a time, unless for example multiple doctors are telling you otherwise for some specific-to-your-situation reason.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Brown Rice vs Buckwheat – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing brown rice to buckwheat, we picked the buckwheat.
Why?
In terms of macros, brown rice has more carbs, while buckwheat has nearly 2x the fiber, and more protein. An easy choice here: buckwheat for the win.
In the category of vitamins, brown rice has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, and E, while buckwheat has more of vitamins B9, K, and choline. A win for brown rice this time, although as a point in buckwheat’s favor, while most of the margins of difference are comparable, buckwheat has nearly 10x the vitamin K.
When it comes to minerals, brown rice has more manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc, while buckwheat has more calcium, copper, iron, and magnesium. A win for buckwheat again this time.
A quick note on gluten: both of these are naturally gluten-free, so that’s not an issue here. Buckwheat, despite its name, is not a wheat, nor even closely related to wheat. It’s not even technically a grain; it’s a flowering plant of which we eat the groats. In taxonomic terms, buckwheat is about as related to wheat as a lionfish is to a lion.
Adding up the sections makes for an overall 2:1 win for buckwheat, though even if it weren’t for that, which is someone more likely to hear from a doctor, “you need to eat more fiber”, or “you need to eat more vitamin E”? Thus, even had the categories been tied (let’s imagine it had been tied on minerals, say) that’d have been a tiebreaker in favor of buckwheat. As it is, buckwheat already won by strength of numbers anyway.
Of course, do enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Grains: Bread Of Life, Or Cereal Killer?
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
No More Aches/Tripping When Walking: Strengthen This Oft-Neglected Muscle
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Aches and pains while walking (in the feet, shins, and/or knees), as well as fatigue, are actually mostly about the oft-neglected tibialis anterior muscle.
Fortunately, it’s quite easy to strengthen if you know how:
All about the tib
The tibialis anterior is located at the front of the shin. It lifts the toes when walking, preventing trips and stumbles. Weakness in this muscle can cause fatigue as other muscles compensate, tripping as feet catch the floor, and/or general instability while walking.
Happily, there is an easy exercise to do that gives results quite quickly:
Steps:
- Stand with back and shoulders against a wall, feet 12 inches away.
- Slightly bend knees and keep posture relaxed.
- Lift toes off the ground, hold for a few seconds, then lower.
- Repeat for 10–15 reps.
To increase difficulty:
- Step further away from the wall for more ankle movement.
- Perform a “Tib Plank” by lifting hips off the wall and keeping knees straight.
It’s recommended to do 3 sets per day, with 1-minute rests between.
For more on all of this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
The Secret to Better Squats: Foot, Knee, & Ankle Mobility
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Undo It! – by Dr. Dean Ornish & Anne Ornish
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Of course, no lifestyle changes will magically undo Type 1 Diabetes or Cerebral Palsy. But for many chronic diseases, a lot can be done. The question is,how does one book cover them all?
As authors Dr. Dean Ornish and Anne Ornish explain, very many chronic diseases are exacerbated, or outright caused, by the same factors:
- Gene expression
- Inflammation
- Oxidative stress
This goes for chronic disease from heart disease to type 2 diabetes to cancer and many autoimmune diseases.
We cannot change our genes, but we can change our gene expression (the authors explain how). And certainly, we can control inflammation and oxidative stress.
Then first part of the book is given over to dietary considerations. If you’re a regular 10almonds reader, you won’t be too surprised at their recommendations, but you may enjoy the 70 recipes offered.
Attention is also given to exercising in ways optimized to beat chronic disease, and to other lifestyle factors.
Limiting stress is important, but the authors go further when it comes to psychological and sociological factors. Specifically, what matters most to health, when it comes to intimacy and community.
Bottom line: this is a very good guide to a comprehensive lifestyle overhaul, especially if something recently has given you cause to think “oh wow, I should really do more to avoid xyz disease”.
Click here to check out Undo It, and better yet, prevent it in advance!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Beating Toxic Positivity
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
There have been many studies done regards optimism and health, and they generally come to the same conclusion: optimism is simply good for the health.
Here’s an example we’ve mentioned before, but it’s a good introduction to today’s main feature. It’s a longitudinal study, and it followed 121,700 women (what a sample size!) for eight years. It controlled for all kinds of other lifestyle factors (especially smoking, drinking, diet, and exercise habits, as well as pre-existing medical conditions), so this wasn’t a case of “people who are healthy are more optimistic as results. And, in the researchers’ own words…
❝We found strong and statistically significant associations of increasing levels of optimism with decreasing risks of mortality, including mortality due each major cause of death, such as cancer, heart disease, stroke, respiratory disease, and infection. Importantly, findings were maintained after close control for potential confounding factors, including sociodemographic characteristics and depression❞
Read: Optimism and Cause-Specific Mortality: A Prospective Cohort Study
And yet, toxic positivity can cause as many problems as it tries to fix.
What is toxic positivity?
- Toxic positivity is the well-meaning friend who says “I’m sure it’ll be ok” when you know full well it definitely will not.
- Toxic positivity is the allegorical frog-in-a-pan saying that the temperature rises due to climate change are gradual, so they’re nothing to worry about
- Toxic positivity is thinking that “good vibes” will outperform chemotherapy
Sometimes, a dose of realism is needed. So, can we do that and maintain a positive attitude?
The answer is: somewhat, yes! But first, a quick check-in:
❝I’m not a pessimist; I’m a realist!❞
~ every pessimist ever
To believe self-reports, the world is divided between optimists and realists. But how does your outlook measure up, really?
While like most free online tests, this is offered “as-is” with the usual caveats about not being a clinical diagnostic tool, this one actually has a fair amount of scientific weight behind it:
❝Empirical testing has indicated the validity of the Optimism Pessimism Instrument as published in the scientific journal Current Psychology: Research and Reviews.
The IDRlabs Optimism/Pessimism Test (IDR-OPT) was developed by IDRlabs. The IDR-OPT is based on the Optimism/Pessimism Instrument (OPI) developed by Dr. William Dember, Dr. Stephanie Martin, Dr. Mary Hummer, Dr. Steven Howe, and Dr. Richard Melton, at the University of Cincinnati.❞
Take This Short (1–2 mins) Test
How did you score? And what could you do to improve on that score?
First, it’s said that with a big enough “why”, one can overcome any “how”. So…
An attitude of gratitude
We know, we know, it’s very Oprah Winfrey. But also, it works. Take the time, ideally daily, to quickly list 3–5 things for which you feel grateful. Great or small, it can be anything from your spouse to your cup of coffee, provided you feel fortunate to have it.
How this works: our brains easily get stuck in loops, so it can help to nudge them into a more positive loop.
What about when we are treated unfairly? Are we supposed to be grateful?
Sometimes, our less positive emotions are necessary, to protect us and/or those around us, and to provide a motivational force. We can still maintain a positive attitude by noting the bad thing and some good, but watch out! Notice the difference:
- “How dare they take our healthcare away, but at least I’m not sick right now” (lasting impression: no action required)
- “At least I’m not sick right now, but how dare they take our healthcare away!” (lasting impression: action required)
It’s a well-known idea in neurolinguistic programming, that “but” negates whatever goes before it (think of “I’m sorry but”, or “I’m not racist but”, etc), so use it consciously and wisely, or else simply use “and” instead.
Cognitive reframing: problem, or opportunity?
Most problems can be opportunities, even if the problems themselves genuinely suck and are not intrinsically positive. A way of leveraging this can be replacing “I have to…” with “I get to…”.
This not only can reframe problems as opportunities, but also calls back to the gratitude idea.
- Instead of “I have to get my mammogram / prostate exam” (not generally considered fun activities), “I get to have the peace of mind of being free from cancer / I get to have the forewarning that will keep me safe”.
- Instead of “I have to go to work”, “I get to go to work” (many wish they were in your shoes!)
- Instead of “I have to rest”, “I get to rest”
When things are truly not great
Whether due to internal or external factors, whether you can control something or not, sometimes things are truly not great. The trick here is that in most contexts, one can replace negative talk, with verbally positive talk, no matter how dripping with scathing irony. You’ll still get to express the idea you wanted, but your brain will feel more positive and you’ll be in a positive loop rather than a negative one.
This, by the way, is the inverse of talking to a dog with a tone of voice that is completely the opposite of the meaning of the words. Whereas the dog will interpret the tone only, your brain will interpret the words only.
- You just spilled your drink over yourself at a social function? “Aren’t I the very model of grace and charm?”
- You made a costly mistake in your business dealings? “I am such a genius”
- You just got a diagnosis of a terrible disease? “Well, this is fabulous”
None of these things involve burying your head in the sand, in the manner of toxic positivity. You’ll still learn from your business mistake and correct it as best you can, or take appropriate action regards the disease, for example.
You’ll just feel better while you do it, and not get caught into a negative spiral that ruins your day, or even your next few months.
Sympathetic/Somatic Therapy:
Lastly, an easy one, leveraging the body’s tendency to get in sync with things around us:
For when you do just need a mood change, have an uplifting playlist available at the touch of a button. It’s hard to be consumed with counterproductive feelings to the tune of “Walking on Sunshine”!
Bonus tip: consider having the playlist start with something that is lyrically negative while musically upbeat. That way, your brain won’t resist it as antithetical to your mood, and by the second track, you’ll already be on your way to a better mood.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: