Sesame Chocolate Fudge
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’d like a sweet treat without skyrocketing your blood sugars with, well, rocket fuel… Today’s recipe can help you enjoy a taste of decadence that’s not bad for your blood sugars, and good for your heart and brain.
You will need
- ½ cup sesame seeds
- ¼ cup cocoa powder
- 3 tbsp maple syrup
- 1 tbsp coconut oil (plus a little extra for the pan)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Lightly toast the sesame seeds in a pan until golden brown. Remove from the heat and allow to cool.
2) Put them in a food processor, and blend on full speed until they start to form a dough-like mixture. This may take a few minutes, so be patient. We recommend doing it in 30-second sessions with a 30-second rest between them, to avoiding overheating the motor.
3) Add the rest of the ingredients and blend to combine thoroughly—this should go easily now and only take 10 seconds or so, but judge it by eye.
4) Grease an 8″ square baking tin with a little coconut oil, and add the mixture, patting it down to fill the tin, making sure it is well-compressed.
5) Allow to chill in the fridge for 6 hours, until firm.
6) Turn the fudge out onto a chopping board, and cut into the size squares you want. Serve, or store in the fridge until ready to serve.
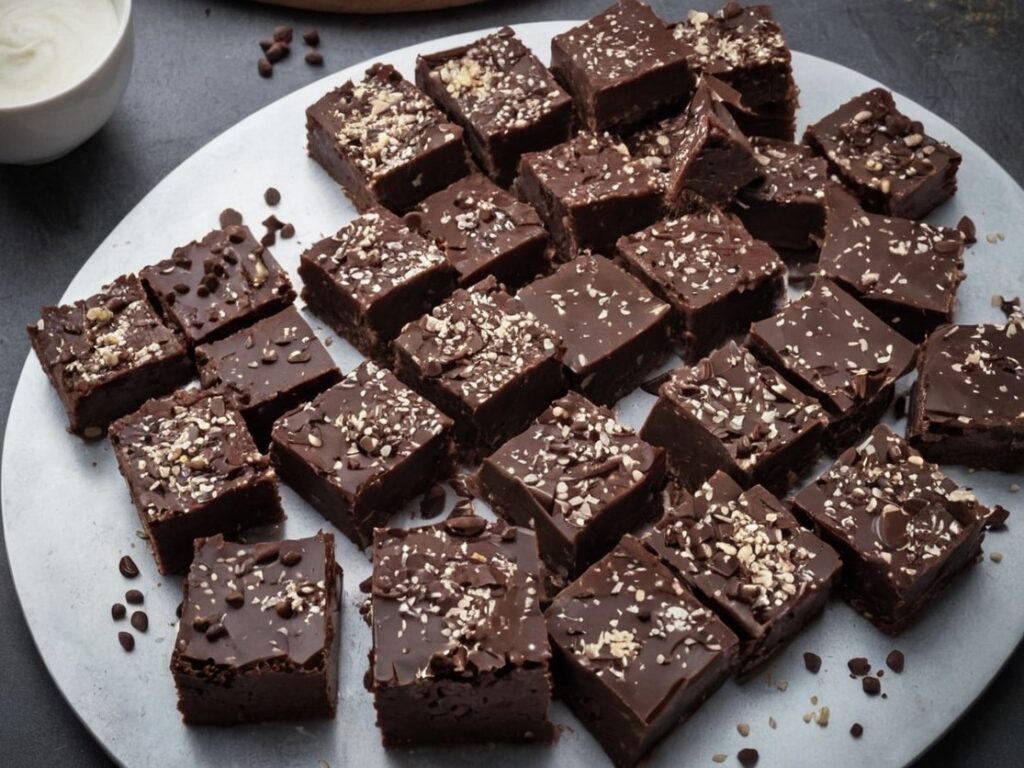

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Tasty Polyphenols For Your Heart & Brain
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
- Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
More Things Dopamine Does For Us
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In this week’s news roundup, we have two dopamine items and one other for variety:
The real “dopamine switch”
Dopamine is well-known as “the reward chemical”, and indeed it is that, but it also plays a central role in many neurological processes, including:
- Linear task processing
- Motivation
- Learning and memory
- Motor functions
- Language faculties
Recent research has now shown its importance in cognitive flexibility, i.e. the ability to adapt to circumstances, and switch approaches appropriately to such, and generally not get stuck in a cognitive rut:
Read in full: Scientists confirm neurobiochemical link between dopamine and cognitive flexibility
Related: The Dopamine Myth
You may like the sound of this
It’s been known for a while that dopamine is involved in learning and memory (as mentioned above), but this has been established largely by associative studies, e.g. “people with lower dopamine levels learn less easily”. But scientists have now mapped out more of how it actually does that.
One more reason to ensure we have and maintain healthy dopamine levels!
Read in full: Songbirds highlight dopamine’s role in learning
Related: 10 Ways To Naturally Boost Dopamine
Resist Or Run!
When it comes to protecting against bone loss, resistance exercise remains key, but impact-laden activities such as running (but not lower-level everyday activity) can help too. There have been studies on the extent to which walking (a load-bearing activity) may be protective against bone loss, and the results of those studies have mostly been inconclusive.
This study looked into the incidence (or not, as the case may be) of bone-loading impacts in everyday movements, using accelerometers, and measured bone mineral density before and after testing periods. Those that had higher-intensity bone-loading movements (so, resistance training or running, for example) retained the best measures of bone density through menopause into postmenopause:
Read in full: Everyday physical activity does not slow bone loss during menopause, finds study
Related: The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Plant-Based Diet Revolution – by Dr. Alan Desomond
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is this just another gut-healthy cooking guide? Not entirely…
For a start, it’s not just about giving you a healthy gut; it also covers a healthy heart and a healthy brain. There’s lots of science in here!
It’s also aimed as a transitional guide to eating more plants and fewer animal products, if you so choose. And if you don’t so choose, at least having the flexibility to cook both ways.
The recipes themselves (organized into basics, breakfasts, lunches, mains, desserts) are clear and easy while also being calculated to please readers (and their families) who are used to eating more meat. There are, for instance, plenty of healthy proteins, healthy fats, and comfort foods.
The “28 days” of the title refers to a meal plan using the recipes from the book; it’s not a big feature of the book though, so use it or don’t, but the cooking advice itself is more than worth the price of the book and the recipes are certainly great.
Bottom line: if you’re thinking of taking a “Meatless Mondays” approach to making your diet healthier, this book can help you do that in style!
Click here to check out The Plant-Based Diet Revolution, and upgrade your culinary repertoire!
Share This Post
-
Why Do We Have Crooked Teeth When Our Ancestors Didn’t?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Evidence shows that people in ancient times typically had straight teeth set well into strong jaws, with even wisdom teeth fitting properly.
So, what went wrong? Did evolution do us a disservice?
Some information to chew on
Transition from hard-to-chew diets to processed, refined foods over millennia has reduced jaw size while tooth size stayed constant. Smaller jaws lead to tooth crowding, crookedness, and impacted wisdom teeth, requiring braces or extractions in modern times.
However, all is not lost!
Studies on non-human animals show softer diets reduce jaw and facial growth, causing dental crowding. In other words: dental crowding is primarily attributed to dietary and lifestyle changes, though genetics may play a role.
And notably, when it comes to humans, populations with less processed diets experience fewer dental problems, suggesting lifestyle modifications could help prevent tooth crowding.
And no, it is not too late. Remember, you are rebuilding your body all the time, including your bones!
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Exercises That Can Fix Sinus Problems (And More) ← this also improves the jaw structure
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
When You “Should” Be In Better Shape
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s easy to think that we “should” be many things that we aren’t. However, it can be counterproductive to implementing real change:
The problem with “should”
The word “should” often sabotages changes in mindset and habit formation. Saying things like “I should be further along” typically leads to frustration, feelings of failure, and ultimately a lack of motivation to take action. Yes, in the first instance, “I should…” can be a motivator, but when your goals are not achieved by the second session, and the “I should…” is still there, the subconscious says “well, clearly this is not working”. Even though the conscious mind can easily see the fallacy in that dysfunctional line of thinking, the subconscious is easily swayed by such things, and in turn easily sways our actual behaviors.
Also, even before that, if goals feel impossible, people often do nothing instead of making small, manageable changes.
So, what should we do instead?
Step 1: assess your current lifestyle and priorities. Your current results are a reflection of past habits and actions, including dieting practices, inconsistent workouts, and lack of planning. Instead of searching for a “perfect plan,” first acknowledge your current lifestyle and priorities. Then, identify which habits are beneficial, which ones hold you back, and what common excuses you make. By understanding where you are now, you can create a sustainable plan that fits your life rather than fighting against it.
Step 2: define your future lifestyle. It’s not enough to just set goals—you need to define what the lifestyle associated with those goals looks like. Recognize that real change requires adjustments in habits and routines. Don’t stress over whether these changes feel overwhelming; simply identify what might be necessary. Writing things down (and then consulting them often, not just putting them away never to be seen again) makes them more tangible and helps create a roadmap for progress.
Step 3: make one small change today. Rather than making vague or overwhelming changes, start with one small, realistic step that aligns with your goals. Building momentum through cumulatively beneficial small actions leads to longer-lasting motivation. Also, instead of focusing on what you need to cut out, look for positive habits to add, as this makes change easier. Track your progress visibly—like using a checklist—and commit to revisiting and adding new changes weekly.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
How To Plan For The Unplannable And Always Follow Through
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Severe Complications for Pregnant Veterans Nearly Doubled in the Last Decade, a GAO Report Finds
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
ProPublica is a Pulitzer Prize-winning investigative newsroom. Sign up for The Big Story newsletter to receive stories like this one in your inbox.
Series: Post-Roe America:Abortion Access Divides the Nation
After the Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade, ending nearly 50 years of federal protection for abortion, some states began enforcing strict abortion bans while others became new havens for the procedure. ProPublica is investigating how sweeping changes to reproductive health care access in America are affecting people, institutions and governments.
Over the past decade, the rate of veterans suffering severe pregnancy complications has risen dramatically, a new federal report found.
Veterans have raced to the hospital with dangerous infections, kidney failure, aneurysms or blood loss. They’ve required hysterectomies, breathing machines and blood transfusions to save their lives. Between 2011 and 2020, 13 veterans died after such complications.
The report found that among people getting health care benefits through the Department of Veterans Affairs, the rate of severe complications nearly doubled during that time, from about 93 per 10,000 hospitalizations in 2011 to just over 184 per 10,000 hospitalizations in 2020. Black veterans had the highest rates.
The report, which was put together by the Government Accountability Office, also made recommendations for reducing the problem, which focus on conducting more routine screenings throughout pregnancy and in the postpartum period.
“It is imperative that the VA help ensure veterans have the healthiest pregnancy outcomes possible,” the report said, highlighting the increasing number of veterans using the agency’s maternity benefits as well as the troublesome complication rates faced by Black women.
The report’s findings are an unfortunate trend, said Alyssa Hundrup, director of health care at the GAO. The office analyzed data on 40,000 hospitalizations related to deliveries paid for by the VA. It captures a time period before 21 states banned or greatly restricted abortion and the military was thrust into a political battle over whether it would pay for active service members to travel for abortion care if a pregnancy was a risk to their health.
Hundrup, who led the review, said the analysis included hospital records from days after delivery to a year postpartum. The report was mandated after Congress passed a law in 2021 that aimed to address the maternal health crisis among veterans. The law led to a $15 million investment in maternity care coordination programs for veterans.
The report recommended that the VA analyze and collect more data on severe complications as well as data on the mental health, race and ethnicity of veterans who experience complications to understand the causes behind the increase and the reasons for the disparity. The report also states that oversight is needed to ensure screenings are being completed.
Studies show there’s a connection between mental health conditions and pregnancy-related complications, VA officials said.
The report recommended expanding the screening questions that providers ask patients at appointments to glean more information about their mental health, including anxiety and PTSD symptoms. It urged the VA to review the data more regularly.
“You don’t know what you don’t measure,” Hundrup said in an interview with ProPublica.
The VA health system, which historically served a male population, does not provide maternity care at its facilities. Instead, the agency has outsourced maternity care. But when patients were treated by those providers, the VA failed to track whether they were getting screened for other health issues and mental health problems.
Officials hope the improved data collection will help the VA study underlying issues that may lead to complications. For example, do higher rates of anxiety have a connection to rates of high blood pressure in pregnant people?
VA officials are working with a maternal health review committee to monitor the data as it is gathered. The agency recently conducted its first review of data going back five years about pregnancy-related complications, said Dr. Amanda Johnson, acting head of the VA’s Office of Women’s Health, who is overseeing the implementation of the report’s recommendations.
The VA has created a dashboard to monitor pregnant veterans’ health outcomes. The VA’s data analysis team will also examine the impact of veterans’ ages on complications and whether they differ for people who live in urban and rural areas.
VA officials will begin to review mental health screenings conducted by maternal care coordinators in March. The coordinators advocate for veterans, helping them between health care visits, whether their providers are inside or outside the VA.
Johnson said that reducing racial and ethnic disparities is a priority for the agency. In 2018, ProPublica published “Lost Mothers,” a series that shed light on the country’s maternal health crisis. Studies have shown that in the general population, Black women are three times more likely than white women to die from pregnancy-related complications. While deaths made up only a small portion of the bad outcomes for Black veterans cited in the report, VA care could not spare them from elevated rates of severe complications. Johnson said the maternal health crisis also persists within the VA.
“There is a disparity,” Johnson said. “We are not immune to that.”
Research shows pregnant people who have used the VA’s coverage have higher rates of trauma and mental conditions that can increase their risks of complications and bad outcomes.
This may be because many people who join the military enter it having already faced trauma, said Dr. Laura Miller, a psychiatrist and the medical director of reproductive mental health at the VA.
She said veterans with PTSD have higher rates of complications such as preeclampsia, a potentially fatal condition related to high blood pressure, gestational diabetes and postpartum depression. If untreated during pregnancy, depression also increases the likelihood of preterm birth and lingering problems for babies.
Hundrup said she hopes this proactive work will improve maternal health.
“We want these numbers trending in the other direction,” Hundrup said.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Beet “Kvass” With Ginger
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Kvass is a popular drink throughout Eastern Europe, with several countries claiming it, but the truth is, kvass is older than nations (as in: nations, in general, any of them; nation states are a newer concept than is often realized), and its first recorded appearance was in the city state of Kyiv.
This one is definitely not a traditional recipe, as kvass is usually made from rye, but keeping true to its Eastern European roots with (regionally popular) beetroot, it’s nevertheless a great fermented drink, full of probiotic benefits, and this time, with antioxidants too.
It’s a little saltier than most things we give recipes for here, so enjoy it on hot sunny days as a great way to replenish electrolytes!
You will need (for 1 quart / 1 liter)
- 2¾ cups filtered or spring water
- 2 beets, roughly chopped
- 1 tbsp chopped fresh ginger
- 2 tsp salt (do not omit or substitute)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Sterilize a 1-quart jar with boiling water (carefully please)
2) Put all the ingredients in the jar and stir until the salt dissolves
3) Close the lid tightly and store in a cool dark place to ferment for 2 weeks
4) Strain the beets and ginger (they are now pickled and can be enjoyed in a salad or as a kimchi-like snack), pouring the liquid into a clean jar/bottle. This can be kept in the fridge for up to a month. Next time you make it, if you use ¼ cup of this as a “starter” to replace an equal volume of water in the original recipe, the fermentation will take days instead of weeks.
5) Serve! Best served chilled, but without ice, on a hot sunny day.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- What To Eat, Take, And Do Before A Workout
- Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: