Surgery is the default treatment for ACL injuries in Australia. But it’s not the only way
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
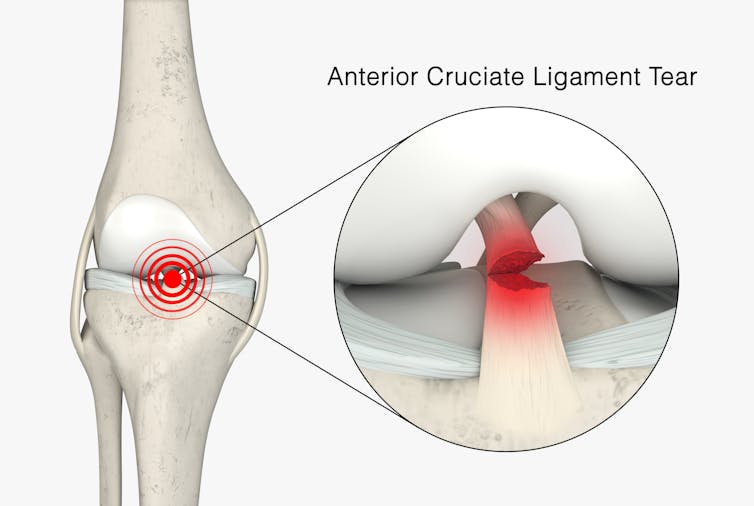
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is an important ligament in the knee. It runs from the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia) and helps stabilise the knee joint.
Injuries to the ACL, often called a “tear” or a “rupture”, are common in sport. While a ruptured ACL has just sidelined another Matildas star, people who play sport recreationally are also at risk of this injury.
For decades, surgical repair of an ACL injury, called a reconstruction, has been the primary treatment in Australia. In fact, Australia has among the highest rates of ACL surgery in the world. Reports indicate 90% of people who rupture their ACL go under the knife.
Although surgery is common – around one million are performed worldwide each year – and seems to be the default treatment for ACL injuries in Australia, it may not be required for everyone.

What does the research say?
We know ACL ruptures can be treated using reconstructive surgery, but research continues to suggest they can also be treated with rehabilitation alone for many people.
Almost 15 years ago a randomised clinical trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine compared early surgery to rehabilitation with the option of delayed surgery in young active adults with an ACL injury. Over half of people in the rehabilitation group did not end up having surgery. After five years, knee function did not differ between treatment groups.
The findings of this initial trial have been supported by more research since. A review of three trials published in 2022 found delaying surgery and trialling rehabilitation leads to similar outcomes to early surgery.
A 2023 study followed up patients who received rehabilitation without surgery. It showed one in three had evidence of ACL healing on an MRI after two years. There was also evidence of improved knee-related quality of life in those with signs of ACL healing compared to those whose ACL did not show signs of healing.
Regardless of treatment choice the rehabilitation process following ACL rupture is lengthy. It usually involves a minimum of nine months of progressive rehabilitation performed a few days per week. The length of time for rehabilitation may be slightly shorter in those not undergoing surgery, but more research is needed in this area.
Rehabilitation starts with a physiotherapist overseeing simple exercises right through to resistance exercises and dynamic movements such as jumping, hopping and agility drills.
A person can start rehabilitation with the option of having surgery later if the knee remains unstable. A common sign of instability is the knee giving way when changing direction while running or playing sports.
To rehab and wait, or to go straight under the knife?
There are a number of reasons patients and clinicians may opt for early surgical reconstruction.
For elite athletes, a key consideration is returning to sport as soon as possible. As surgery is a well established method, athletes (such as Matilda Sam Kerr) often opt for early surgical reconstruction as this gives them a more predictable timeline for recovery.
At the same time, there are risks to consider when rushing back to sport after ACL reconstruction. Re-injury of the ACL is very common. For every month return to sport is delayed until nine months after ACL reconstruction, the rate of knee re-injury is reduced by 51%.

Historically, another reason for having early surgical reconstruction was to reduce the risk of future knee osteoarthritis, which increases following an ACL injury. But a review showed ACL reconstruction doesn’t reduce the risk of knee osteoarthritis in the long term compared with non-surgical treatment.
That said, there’s a need for more high-quality, long-term studies to give us a better understanding of how knee osteoarthritis risk is influenced by different treatments.
Rehab may not be the only non-surgical option
Last year, a study looking at 80 people fitted with a specialised knee brace for 12 weeks found 90% had evidence of ACL healing on their follow-up MRI.
People with more ACL healing on the three-month MRI reported better outcomes at 12 months, including higher rates of returning to their pre-injury level of sport and better knee function. Although promising, we now need comparative research to evaluate whether this method can achieve similar results to surgery.
What to do if you rupture your ACL
First, it’s important to seek a comprehensive medical assessment from either a sports physiotherapist, sports physician or orthopaedic surgeon. ACL injuries can also have associated injuries to surrounding ligaments and cartilage which may influence treatment decisions.
In terms of treatment, discuss with your clinician the pros and cons of management options and whether surgery is necessary. Often, patients don’t know not having surgery is an option.
Surgery appears to be necessary for some people to achieve a stable knee. But it may not be necessary in every case, so many patients may wish to try rehabilitation in the first instance where appropriate.
As always, prevention is key. Research has shown more than half of ACL injuries can be prevented by incorporating prevention strategies. This involves performing specific exercises to strengthen muscles in the legs, and improve movement control and landing technique.
Anthony Nasser, Senior Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of Technology Sydney; Joshua Pate, Senior Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of Technology Sydney, and Peter Stubbs, Senior Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of Technology Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why You Can’t Just “Get Over” Trauma
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Time does not, in fact, heal all wounds. Sometimes they even compound themselves over time. Dr. Tracey Marks explains the damage that trauma does—the physiological presentation of “the axe forgets but the tree remembers”—and how to heal from that actual damage.
The science of healing
Trauma affects the mind and body (largely because the brain is, of course, both—and affects pretty much everything else), which can ripple out into all areas of life.
On the physical level, brain areas affected by trauma include:
- Amygdalae: becomes hyperactive, keeping a person in a heightened state of vigilance.
- Hippocampi: can shrink, causing fragmented or missing memories.
- Prefrontal cortex: reduces in activity, impairing decision-making and emotional regulation.
Trauma also activates the body’s fight or flight response, releasing stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These are great things to have a pinch, but having them elevated all the time is equivalent to only ever driving your car at top speed—the only question becomes whether you’ll crash and burn before you break down.
However, there is hope! Neuroplasticity (the brain’s ability to rewire itself) can make trauma recovery possible through various interventions.
Evidence-based therapies for trauma include:
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): this can help reprocess traumatic memories and reduce emotional intensity.
- Trauma-focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): this can help change unhelpful thought patterns and includes exposure therapy.
- Somatic therapies: these focus on the body and nervous system to release stored tension.
In this latter category, embodiment is key to trauma recovery—this may sound “wishy-washy”, but the evidence shows that reconnecting with the body does help manage emotional stress responses. Mind-body practices like mindfulness, yoga, and breathwork help cultivate embodiment and reduce trauma-related stress.
In short: you can’t just “get over” it, but with the right support and interventions, it’s possible to rewire the brain and body toward resilience and healing.
For more on all of this from Dr. Marks, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- PTSD, But, Well…. Complex.
- Undoing The Damage Of Life’s Hard Knocks
- A Surprisingly Powerful Tool: Eye Movement Desensitization & Reprocessing
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Yes, you still need to use sunscreen, despite what you’ve heard on TikTok
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Summer is nearly here. But rather than getting out the sunscreen, some TikTokers are urging followers to chuck it out and go sunscreen-free.
They claim it’s healthier to forgo sunscreen to get the full benefits of sunshine.
Here’s the science really says.
Karolina Grabowska/Pexels How does sunscreen work?
Because of Australia’s extreme UV environment, most people with pale to olive skin or other risk factors for skin cancer need to protect themselves. Applying sunscreen is a key method of protecting areas not easily covered by clothes.
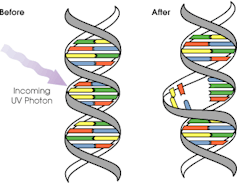
Sunscreen works by absorbing or scattering UV rays before they can enter your skin and damage DNA or supportive structures such as collagen.
When UV particles hit DNA, the excess energy can damage our DNA. This damage can be repaired, but if the cell divides before the mistake is fixed, it causes a mutation that can lead to skin cancers.
The energy from a particle of UV (a photon) causes DNA strands to break apart and reconnect incorrectly. This causes a bump in the DNA strand that makes it difficult to copy accurately and can introduce mutations. NASA/David Herring The most common skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Melanoma is less common, but is the most likely to spread around the body; this process is called metastasis.
Two in three Australians will have at least one skin cancer in their lifetime, and they make up 80% of all cancers in Australia.
Around 99% of skin cancers in Australia are caused by excessive exposure to UV radiation.
Excessive exposure to UV radiation also affects the appearance of your skin. UVA rays are able to penetrate deep into the skin, where they break down supportive structures such as elastin and collagen.
This causes signs of premature ageing, such as deep wrinkling, brown or white blotches, and broken capillaries.
Sunscreen can help prevent skin cancers
Used consistently, sunscreen reduces your risk of skin cancer and slows skin ageing.
In a Queensland study, participants either used sunscreen daily for almost five years, or continued their usual use.
At the end of five years, the daily-use group had reduced their risk of squamous cell carcinoma by 40% compared to the other group.
Ten years later, the daily use group had reduced their risk of invasive melanoma by 73%
Does sunscreen block the health-promoting properties of sunlight?
The answer is a bit more complicated, and involves personalised risk versus benefit trade-offs.
First, the good news: there are many health benefits of spending time in the sun that don’t rely on exposure to UV radiation and aren’t affected by sunscreen use.
Sunscreen only filters UV rays, not all light. Ron Lach/Pexels Sunscreen only filters UV rays, not visible light or infrared light (which we feel as heat). And importantly, some of the benefits of sunlight are obtained via the eyes.
Visible light improves mood and regulates circadian rhythm (which influences your sleep-wake cycle), and probably reduces myopia (short-sightedness) in children.
Infrared light is being investigated as a treatment for several skin, neurological, psychiatric and autoimmune disorders.
So what is the benefit of exposing skin to UV radiation?
Exposing the skin to the sun produces vitamin D, which is critical for healthy bones and muscles.
Vitamin D deficiency is surprisingly common among Australians, peaking in Victoria at 49% in winter and being lowest in Queensland at 6% in summer.
Luckily, people who are careful about sun protection can avoid vitamin D deficiency by taking a supplement.
Exposing the skin to UV radiation might have benefits independent of vitamin D production, but these are not proven. It might reduce the risk of autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis or cause release of a chemical that could reduce blood pressure. However, there is not enough detail about these benefits to know whether sunscreen would be a problem.
What does this mean for you?
There are some benefits of exposing the skin to UV radiation that might be blunted by sunscreen. Whether it’s worth foregoing those benefits to avoid skin cancer depends on how susceptible you are to skin cancer.
If you have pale skin or other factors that increase you risk of skin cancer, you should aim to apply sunscreen daily on all days when the UV index is forecast to reach 3.
If you have darker skin that rarely or never burns, you can go without daily sunscreen – although you will still need protection during extended times outdoors.
For now, the balance of evidence suggests it’s better for people who are susceptible to skin cancer to continue with sun protection practices, with vitamin D supplementation if needed.
Katie Lee, PhD Candidate, Dermatology Research Centre, The University of Queensland and Rachel Neale, Principal research fellow, QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
What is mitochondrial donation? And how might it help people have a healthy baby one day?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mitochondria are tiny structures in cells that convert the food we eat into the energy our cells need to function.
Mitochondrial disease (or mito for short) is a group of conditions that affect this ability to generate the energy organs require to work properly. There are many different forms of mito and depending on the form, it can disrupt one or more organs and can cause organ failure.
There is no cure for mito. But an IVF procedure called mitochondrial donation now offers hope to families affected by some forms of mito that they can have genetically related children free from mito.
After a law to allow mitochondrial donation in Australia was passed in 2022, scientists are now preparing for a clinical trial to see if mitochondrial donation is safe and works.
Jonathan Borba/Pexels What is mitochondrial disease?
There are two types of mitochondrial disease.
One is caused by faulty genes in the nuclear DNA, the DNA we inherit from both our parents and which makes us who we are.
The other is caused by faulty genes in the mitochondria’s own DNA. Mito caused by faulty mitochondrial DNA is passed down through the mother. But the risk of disease is unpredictable, so a mother who is only mildly affected can have a child who develops serious disease symptoms.
Mitochondrial disease is the most common inherited metabolic condition affecting one in 5,000 people.
Some people have mild symptoms that progress slowly, while others have severe symptoms that progress rapidly. Mito can affect any organ, but organs that need a lot of energy such as brain, muscle and heart are more often affected than other organs.
Mito that manifests in childhood often involves multiple organs, progresses rapidly, and has poor outcomes. Of all babies born each year in Australia, around 60 will develop life-threatening mitochondrial disease.
What is mitochondrial donation?
Mitochondrial donation is an experimental IVF-based technique that offers people who carry faulty mitochondrial DNA the potential to have genetically related children without passing on the faulty DNA.
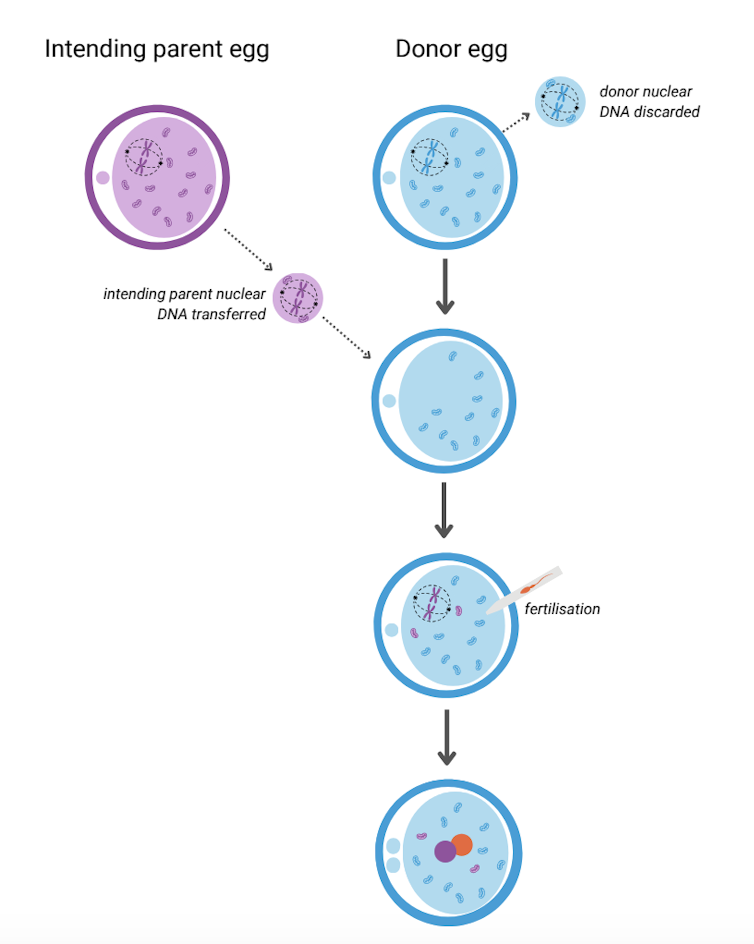
It involves removing the nuclear DNA from the egg of someone who carries faulty mitochondrial DNA and inserting it into a healthy egg donated by someone not affected by mito, which has had its nuclear DNA removed.
The donor egg (in blue) has had its nuclear DNA removed. Author provided The resulting egg has the nuclear DNA of the intending parent and functioning mitochondria from the donor. Sperm is then added and this allows the transmission of both intending parents’ nuclear DNA to the child.
A child born after mitochondrial donation will have genetic material from the three parties involved: nuclear DNA from the intending parents and mitochondrial DNA from the egg donor. As a result the child will likely have a reduced risk of mito, or no risk at all.
The procedure removes the faulty DNA to reduce the chance of it passing on to the baby. Josh Willink/Pexels This highly technical procedure requires specially trained scientists and sophisticated equipment. It also requires both the person with mito and the egg donor to have hormone injections to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. The eggs are then retrieved in an ultrasound-guided surgical procedure.
Mitochondrial donation has been pioneered in the United Kingdom where a handful of babies have been born as a result. To date there have been no reports about whether they are free of mito.
Maeve’s Law
After three years of public consultation The Mitochondrial Donation Law Reform (Maeve’s Law) Bill 2021 was passed in the Australian Senate in 2022, making mitochondrial donation legal in a research and clinical trial setting.
Maeve’s law stipulates strict conditions including that clinics need a special licence to perform mitochondrial donation.
To make sure mitochondrial donation works and is safe before it’s introduced into Australian clinical practice, the law also specifies that initial licences will be issued for pre-clinical and clinical trial research and training.
We’re expecting one such licence to be issued for the mitoHOPE (Healthy Outcomes Pilot and Evaluation) program, which we are part of, to perfect the technique and conduct a clinical trial to make sure mitochondrial donation is safe and effective.
Before starting the trial, a preclinical research and training program will ensure embryologists are trained in “real-life” clinical conditions and existing mitochondrial donation techniques are refined and improved. To do this, many human eggs are needed.
The need for donor eggs
One of the challenges with mitochondrial donation is sourcing eggs. For the preclinical research and training program, frozen eggs can be used, but for the clinical trial “fresh” eggs will be needed.
One possible source of frozen eggs is from people who have stored eggs they don’t intend to use.
A recent study looked at data on the outcomes of eggs stored at a Melbourne clinic from 2012 to 2021. Over the ten-year period, 1,132 eggs from 128 patients were discarded. No eggs were donated to research because the clinics where the eggs were stored did not conduct research requiring donor eggs.
However, research shows that among people with stored eggs, the number one choice for what to do with eggs they don’t need is to donate them to research.
This offers hope that, given the opportunity, those who have eggs stored that they don’t intend to use might be willing to donate them to mitochondrial donation preclinical research.
As for the “fresh” eggs needed in the future clinical trial, this will require individuals to volunteer to have their ovaries stimulated and eggs retrieved to give those people impacted by mito a chance to have a healthy baby. Egg donors may be people who are friends or relatives of those who enter the trial, or it might be people who don’t know someone affected by mito but would like to help them conceive.
At this stage, the aim is to begin enrolling participants in the clinical trial in the next 12 to 18 months. However this may change depending on when the required licences and ethics approvals are granted.
Karin Hammarberg, Senior Research Fellow, Global and Women’s Health, School of Public Health & Preventive Medicine, Monash University; Catherine Mills, Professor of Bioethics, Monash University; Mary Herbert, Professor, Anatomy & Developmental Biology, Monash University, and Molly Johnston, Research fellow, Monash Bioethics Centre, Monash University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Drug & Supplement Combo That Reverses Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So far, its effects have been dramatic (in a good way) in mice; human trials are now underway.
How does it work?
It builds from previous work, in which a Japanese research team created an “anti-aging vaccine”, that responded to a problem more specific than aging as a whole, namely atherosclerosis.
They found that a certain* protein was upregulated (i.e., it was made at a greater rate resulting in greater quantities) in patients (mouse and human alike) with atherosclerosis. So, they immunized the mice against that protein, and long story short, everything improved for them, from their atherosclerosis to general markers of aging—including growing back fur that had been lost due to age-related balding (just like in humans). They also lived longer, as is to be expected of a mouse who is now biologically younger.
*To avoid being mysterious: it was glycoprotein nonmetastatic melanoma protein B, known to its friends as GPNMB.
You may be wondering: how can one be immunized against a protein? If so, do bear in mind, a virus is also a protein. In this case, they developed an RNA vaccine, that works in a similar way to the COVID vaccines we all know and love (albeit with a different target).
You can read about this in abundant detail here: Senolytic vaccination improves normal and pathological age-related phenotypes and increases lifespan in progeroid mice
Hot on the heels of that, new approaches were found, including…
The combination
We’ll not keep you waiting; the combination is dasatinib plus quercetin, or else fisetin alone.
It’s about killing senescent (aging) “zombie cells” while sparing healthy cells, which that drug (dasatinib) and those supplements (quercetin and fisetin) do.
The researchers noted:
❝Senescent cells are resistant to apoptosis, which is governed through the upregulation of senescent cell anti-apoptotic pathways (SCAPs). Compounds were subsequently identified that disrupted the SCAPs, inducing death of senescent cells while leaving healthy cells unaffected. Forty-six potential senolytic agents were discovered through this process. To advance translational efforts, the majority of research has focused on agents with known safety profiles and limited off-target effects (Kirkland and Tchkonia, 2020).
The best characterized senolytic agents are dasatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor approved for use in humans for cancer treatment, and quercetin, a naturally occurring plant flavonoid. The agents have a synergistic effect, making their combination more potent for senescent cell clearance (Zhu et al., 2015). As senescent cells do not divide and accumulate over a period of weeks, they can be administered using an intermittent approach, which further serves to reduce the risk of side effects (Kirkland and Tchkonia, 2020).
In preclinical trials, the combination of dasatinib and quercetin (D + Q) have been found to alleviate numerous chronic medical conditions including vascular stiffness, osteoporosis, frailty, and hepatic stenosis❞
Source: A geroscience motivated approach to treat Alzheimer’s disease: Senolytics move to clinical trials
As to how they expanded on this research:
❝In our study, oral D + Q were intermittently administered to tau transgenic mice with late-stage pathology (approximated to a 70-year-old human with advanced AD) (Musi et al., 2018). The treatment effectively reduced cellular senescence and associated senescence-associated secretory phenotype incidence. The 35 % reduction in neurofibrillary tangles was accompanied by enhanced neuron density, decreased ventricular enlargement, diminished tau accumulation, and restoration of aberrant cerebral blood flow. A subsequent preclinical study validated the findings, reporting that intermittently administered D + Q cleared senescent cells in the central nervous system, reduced amyloid-β plaques, attenuated neuroinflammation, and enhanced cognition❞
Source: Ibid.
And now taking it to humans:
❝The first clinical trial of D + Q for early-stage Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) has completed enrollment (Gonzales et al., 2021). The primary aim of the open-label pilot study was to examine the central nervous system penetrance of D and Q in a small sample of older adults with early-stage AD (NCT04063124). In addition, two placebo-controlled trials of D + Q for neurodegenerative disease are underway (NCT04685590 and NCT04785300).
One of the trials in development is a multi-site, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of senolytic therapy in older adults with amnestic mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or early-stage dementia (Clinical Dementia Rating Scale (CDR) Global 0.5–1) due to AD (elevated CSF total tau/Aβ42 ratio).
The treatment regimen will consist of 12-weeks of intermittently administered oral D + Q.❞
Source: Ibid.
The study is actually completed now, but its results are not yet published (again, at time of writing). Which means: they have the data, and now they’re writing the paper.
We look forward to providing an update about that, when the paper is published!
In the meantime…
Dasatinib is a drug usually prescribed to people with certain kinds of leukemia, and suffice it to say, it’s prescription-only. And unlike drugs that are often prescribed off-label (such as metformin for weight loss), getting your doctor to prescribe you an anticancer drug is unlikely unless you have the cancer in question.
You may be wondering: how is an anticancer drug helpful against aging? And the answer is that cancer and aging are very interrelated, and both have to do with “these old cells just won’t die, and are using the resources needed for young healthy cells”. So in both cases, killing those “zombie cells” while sparing healthy ones, is what’s needed. However, your doctor will probably not buy that as a reason to prescribe you a drug that is technically chemotherapy.
Quercetin, on the other hand, is a readily-available supplement, as is fisetin, and both have glowing (in a good way) safety profiles.
Want to know more?
You can read more about each of quercetin and fisetin (including how to get them), here:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Before You Eat Breakfast: 3 Surprising Facts About Intermittent Fasting
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. William Li is well-known for his advocacy of “eating to beat disease”, and/but today he has advice for us about not eating to beat disease. In moderation, of course, thus: intermittent fasting.
The easy way
Dr. Li explains the benefits of intermittent fasting; how it improves the metabolism and gives the body a chance to do much-needed maintainance, including burning off any excess fat we had hanging around.
However, rather than calling for us to do anything unduly Spartan, he points out that it’s already very natural for us to fast while sleeping, so we only need to add a couple of hours before and after sleeping (assuming an 8 hour sleep), to make it to a 12-hour fast for close to zero effort and probably no discomfort.
And yes, he argues that a 12-hour fast is beneficial, and even if 16 hours would be better, we do not need to beat ourselves up about getting to 16; what is more important is sustainability of the practice.
Dr. Li advocates for flexibility in fasting, and that it should be done by what manner is easiest, rather than trying to stick to something religiously (of course, if you do fast for religious reasons, that is another matter, and/but beyond the scope of this today).
For more information on each of these, as well as examples and tips, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Intermittent Fasting: What’s the truth?
- 16/8 Intermittent Fasting For Beginners
- Meal Timings & Health: How Important Is Breakfast?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fasting Cancer – by Dr. Valter Longo
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Dr. Longo’s “The Longevity Diet”, and whereas that one was about eating, this one is (superficially, at least) about not eating. Nor is this any kind of dissonance, because, in fact, it’s important to do both!
That said, he discusses not just fasting per se, but also the use of a personalized fast-mimicking diet, to accomplish the same goal of not overloading the metabolism—as overloading the metabolism results in metabolic disease, and cancer is, ultimately, a metabolic disease of immune dysfunction with genetic disorder*—which makes for quite a deadly trifecta.
*not in the sense of “hereditary”, though certainly genes can influence cancer risk, but rather, in the sense of “your gene-copying process becomes disordered”.
The first three chapters (after the introduction, which we’ll comment on shortly) are devoted to explaining the principles at hand:
- Fasting cancer while feeding patients
- Genes, aging, and cancer
- Fasting, nutrition, and physical activity in cancer prevention
In those chapters, he details a lot of the science for exactly how and why it is possible to “feed the patient and starve the cancer” at the same time.
After that, the rest of the book—another nine chapters, not counting appendices etc—are given over to fasting and nutrition in the context of nine main types of cancer, one chapter per type. These are not hyperspecific, though, and are rather categorizations, such as “blood cancers”, and “gynecological cancers” and so forth. It’s comprehensive, and while it could be argued that it may mean chapters feel irrelevant to some people (à la “I have never smoked and have no pressing concern about my lung cancer risk” etc), the reality is that it’s good to know how to avoid them all, because if nothing else, it’d be super embarrassing to get a cancer you “thought you couldn’t get”. So, it’s honestly worth the time to read each chapter.
In the category of criticism, he did open the introduction with a handful of anecdotes to defend the consumption of (well-established group 1 carcinogens) red meat and alcohol as “secondary concerns that might not be such a big deal”, even discussing how surprised his colleagues in the field are that he has this view. Suffice it to say, it’s contrary to the overwhelming body of evidence, and reads suspiciously like a man who simply doesn’t want to give up his steak and wine despite his own longevity diet forswearing them.
The style is self-indulgently autobiographical and very complimentary, and (in this reviewer’s opinion) it can be tedious to wade through that to get to the science, but at the end of the day, his self-accolades might be needless fluff, but they don’t actually remove anything from the science in question.
Bottom line: as you can see, there are good and bad things to say about this book, but the information contained in the good makes it well worth reading through the stylistically questionable to get it.
Click here to check out Fasting Cancer, and starve cancer cells while nourishing your healthy ones!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: