Parenting a perfectionist? Here’s how you can respond
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some children show signs of perfectionism from early on. Young children might become frustrated and rip up their drawing if it’s not quite right. Older children might avoid or refuse to do homework because they’re afraid to make a mistake.
Perfectionism can lead to children feeling overwhelmed, angry and frustrated, or sad and withdrawn.
And yet perfectionism isn’t considered all bad in our society. Being called a “perfectionist” can be a compliment – code for being a great worker or student, someone who strives to do their best and makes sure all jobs are done well.
These seemingly polarised views reflect the complex nature of perfectionism.

What is perfectionism?
Researchers often separate perfectionism into two parts:
- perfectionistic strivings: being determined to meet goals and achieve highly
- perfectionistic concerns: worry about being able to meet high standards, and self-criticism about performance.
While perfectionistic strivings can be positive and lead to high achievement, perfectionistic concerns can lead to a higher chance of children developing eating disorders or anxiety and depression, and having lower academic achievement.
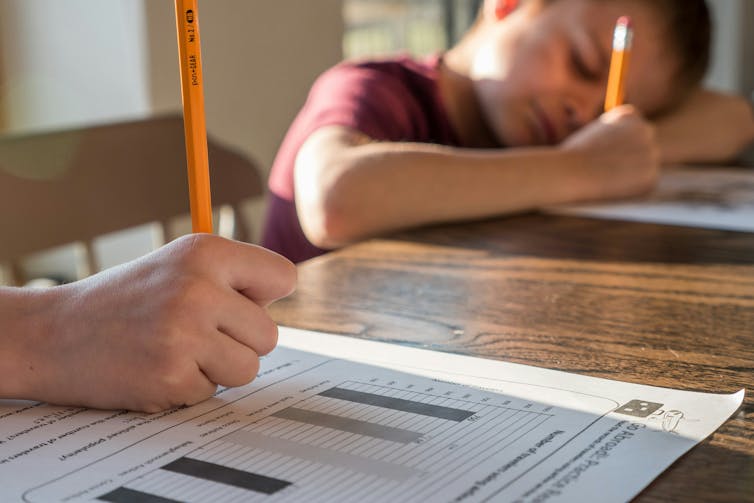

Children and adolescents may experience perfectionism in relation to school work, sport, performance in art or music, or in relation to their own body.
Signs of perfectionistic concerns in children and adolescents may include:
- children being highly critical of themselves
- their reactions to mistakes seeming to be an overreaction
- intense preoccupation and worry over their standards and goals and/or procrastination
- significant change in performance, for example, lower academic results
- irritability and negative emotions, stress and feelings of worthlessness
- social problems with peers and friends, such as bullying and alienating themselves from peers.
A range of genetic, biological and environmental factors influence perfectionism in children. And as a parent, our role is important. While research evidence suggests we can’t successfully increase positive perfectionistic strivings in our children, harsh or controlling parenting can increase negative perfectionistic concerns in children.
Parents who are perfectionistic themselves can also model this to their children.
So, how can we walk the line between supporting our child’s interests and helping them to achieve their potential, without pressuring them and increasing the risk of negative outcomes?
Give them space to grow
A great metaphor is the gardener versus the carpenter described by psychology professor Alison Gopnik.
Instead of trying to build and shape our children by controlling them and their environment (like a carpenter), parents can embrace the spirit of the gardener – providing lots of space for children to grow in their own direction, and nourishing them with love, respect and trust.
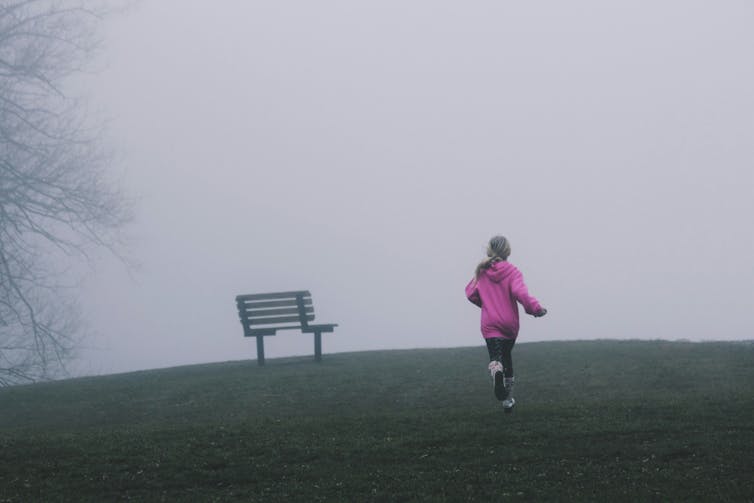

We can’t control who they become, so it’s better to sit back, enjoy the ride, and look forward to watching the person they grow into.
However, there is still plenty we can do as parents if our child is showing signs of perfectionism. We can role model to our children how to set realistic goals and be flexible when things change or go wrong, help our children manage stress and negative emotions, and create healthy balance in our family daily routine.
Set realistic goals
People with perfectionistic tendencies will often set unattainable goals. We can support the development of flexibility and realistic goal setting by asking curious questions, for example, “what would you need to do to get one small step closer to this goal?” Identifying upper and lower limits for goals is also helpful.
If your child is fixed on a high score at school, for example, set that as the “upper limit” and then support them to identify a “lower limit” they would find acceptable, even if they are less happy with the outcome.
This strategy may take time and practice to widen the gap between the two, but is useful to create flexibility over time.
If a goal is performance-based and the outcome cannot be guaranteed (for example, a sporting competition), encourage your child to set a personal goal they have more control over.

We can also have conversations about perfectionism from early on, and explain that everyone makes mistakes. In fact, it’s great to model this to our children – talking about our own mistakes and feelings, to show them that we ourselves are not perfect.
Talk aloud practices can help children to see that we “walk the walk”. For example, if you burn dinner you could reflect:
I’m disappointed because I put time and effort into that and it didn’t turn out as I expected. But we all make mistakes. I don’t get things right every time.
Manage stress and negative emotions
Some children and adolescents have a natural tendency towards perfectionism. Rather than trying to control their behaviour, we can provide gentle, loving support.
When our child or adolescent becomes frustrated, angry, sad or overwhelmed, we support them best by helping them to name, express and validate all of their emotions.
Parents may fear that acknowledging their child’s negative emotions will make the emotions worse, but the opposite is true.
Creating healthy balance
The building blocks of healthy child development are strong loving family relationships, good nutrition, creative play and plenty of physical activity, sleep and rest.
Perfectionism is associated with rigidity, and thinking that there is only one correct way to succeed. We can instead encourage flexibility and creativity in children.
Children’s brains grow through play. There is strong research evidence showing that creative, child-led play is associated with higher emotion regulation skills, and a range of cognitive skills, including problem-solving, memory, planning, flexibility and decision-making.
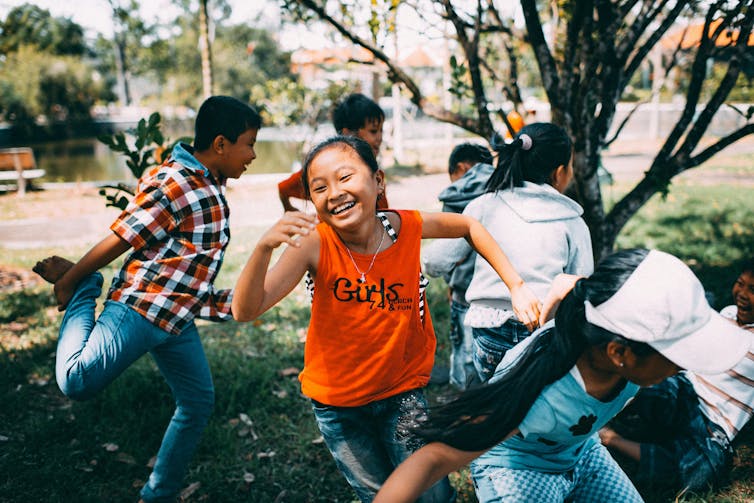

Play isn’t just for young children either – there’s evidence that explorative, creative play of any kind also benefits adolescents and adults.
There is also evidence that getting active outdoors in nature can promote children’s coping skills, emotion regulation and cognitive development.
Elizabeth Westrupp, Associate Professor in Psychology, Deakin University; Gabriella King, Associate Research Fellow, Deakin University, and Jade Sheen, Associate Professor, School of Psychology, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
I Will Make You Passionate About Exercise – by Bevan Eyles
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What this isn’t: a “just do it!” motivational pep-talk.
What this is:a compassionate and thoughtful approach to help non-exercisers become regular exercisers, by looking at the real life factors of what holds people back (learning from his own early failures as a coach, by paying attention now to things he inadvertently neglected back then), both in the material/practical and in the psychological/emotional.
Further, he gives a 10-step method, for those who would like to be walked through it by the hand, making the transition to exercising regularly (and as a leisure habit, rather than as a chore) as frictionless as possible.
The style is friendly and energetic, and very easy-reading throughout.
Bottom line: if you are someone who finds exercising to be a chore, this book can definitely help you “get from here to there” in terms of finding joy in it, and finding exercise even easier than not exercising. Yes, really.
Share This Post
-
Younger Next Year: The Exercise Program – by Chris Crowley & Dr. Henry Lodge
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We previously reviewed the same authors’ original “Younger Next Year”, and now here’s the more specific book about exercise for increasing healthspan and reversing markers of biological aging, going into much more detail in that regard.
How much more? Well, it’s a very hand-holding book in the sense that it walks the reader through everything step-by-step, tells not only what kind of exercise and how much, but also how to do, what things to do to prepare, how to avoid not erring in various ways, what metrics to keep an eye on to ensure you are making progress, and more.
There are also whole sections on specific common age-related issues including osteoporosis and arthritis, as well as how to train around injuries (especially of the kind that basically aren’t likely to ever fully go away).
As with the previous book, there’s a blend of motivational pep talk and science—this book is heavily weighted towards the former. It has, however, enough science to keep it on the right track throughout. Hence the two authors! Crowley for motivational pep and training tips, and Dr. Lodge for the science.
Bottom line: if you’d like to be biologically younger next year, that exercise will be an important component of that, and this book is really quite comprehensive for its relative brevity (weighing in at 176 pages).
Click here to check out Younger Next Year: The Exercise Program, and make that progress!
Share This Post
-
Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Capsaicin’s Hot Benefits
Capsaicin, the compound in hot peppers that makes them spicy, is a chemical irritant and a neurotoxin. However, humans being humans, we decided to eat them for fun.
In contrast to many other ways in which humans recreationally enjoy things that are objectively poisonous, consuming capsaicin (in moderation) is considered to have health benefits, such as aiding weight loss (by boosting metabolism) and reducing inflammation.
Let’s see what the science says…
First: is it safe?
Capsaicin is classified as “Generally Recognized As Safe”. That said, the same mechanism that causes them to boost metabolism, does increase blood pressure:
Mechanisms underlying the hypertensive response induced by capsaicin
If you are in good cardiovascular health, this increase should be slight and not pose any threat, unless for example you enter a chili-eating contest when not acclimated to such:
Capsaicin and arterial hypertensive crisis
As ever, if unsure, do check with your doctor first, especially if you are taking any blood pressure medications, or otherwise have known blood pressure issues.
Does it really boost metabolism?
It certainly does; it works by increasing oxygen consumption and raising body temperature, both of which mean more calories will be burned for the same amount of work:
Dietary capsaicin and its anti-obesity potency: from mechanism to clinical implications
This means, of course, that chili peppers enjoy the status of being functionally a “negative calorie” food, and a top-tier one at that:
Chili pepper as a body weight-loss food
Here’s a good quality study that showed a statistically significant* fat loss improvement over placebo:
*To put it in numbers, the benefit was:
- 5.91 percentage points lower body fat percentage than placebo
- 6.68 percentage points greater change in body fat mass than placebo
See also: Difference between percentages and percentage points
For those who prefer big reviews than single studies, we’ve got you covered:
Does it really reduce inflammation?
Counterintuitive as it may seem, yes. By means of reducing oxidative stress. Given that things that reduce oxidative stress tend to reduce inflammation, and in turn tend to reduce assorted disease risks (from diabetes to cancer to Alzheimer’s), this probably has more knock-on benefits too, but we don’t have room to explore all of those today.
Fresh peppers are best for this, but dried peppers (such as when purchased as a ground spice in the supermarket, or when purchased as a capsule-based supplement) still have a very respectable anti-inflammatory effect:
- Capsaicinoids, Polyphenols and Antioxidant Activities of Capsicum annuum: Comparative Study of the Effect of Ripening Stage and Cooking Methods
- A Review on the Effect of Drying on Antioxidant Potential of Fruits and Vegetables
How much should we take?
It’s recommended to start at a low dose and gradually increase it, but 2–6mg of capsaicin per day is the standard range used in studies.
If you’re getting this from peppers, then for example cayenne pepper (a good source of capsaicin) contains around 2.5mg of capsaicin per 1 gram of cayenne.
In the case of capsules, if for example you don’t like eating hot pepper, this will usually mean taking 2–6 capsules per day, depending on dosage.
Make sure to take it with plenty of water!
Where can we get it?
Fresh peppers or ground spice from your local grocery store is fine. Your local health food store probably sells the supplements, too.
If you’d like to buy it online, here is an example product on Amazon.
Note: options on Amazon were more limited than usual, so this product is not vegan, and probably not halal or kosher, as the capsule contains an unspecified gelatin.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How long does back pain last? And how can learning about pain increase the chance of recovery?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Back pain is common. One in thirteen people have it right now and worldwide a staggering 619 million people will have it this year.
Chronic pain, of which back pain is the most common, is the world’s most disabling health problem. Its economic impact dwarfs other health conditions.
If you get back pain, how long will it take to go away? We scoured the scientific literature to find out. We found data on almost 20,000 people, from 95 different studies and split them into three groups:
- acute – those with back pain that started less than six weeks ago
- subacute – where it started between six and 12 weeks ago
- chronic – where it started between three months and one year ago.
We found 70%–95% of people with acute back pain were likely to recover within six months. This dropped to 40%–70% for subacute back pain and to 12%–16% for chronic back pain.
Clinical guidelines point to graded return to activity and pain education under the guidance of a health professional as the best ways to promote recovery. Yet these effective interventions are underfunded and hard to access.
More pain doesn’t mean a more serious injury
Most acute back pain episodes are not caused by serious injury or disease.
There are rare exceptions, which is why it’s wise to see your doctor or physio, who can check for signs and symptoms that warrant further investigation. But unless you have been in a significant accident or sustained a large blow, you are unlikely to have caused much damage to your spine.
Your doctor or physio can rule out serious damage.
DG fotostock/ShutterstockEven very minor back injuries can be brutally painful. This is, in part, because of how we are made. If you think of your spinal cord as a very precious asset (which it is), worthy of great protection (which it is), a bit like the crown jewels, then what would be the best way to keep it safe? Lots of protection and a highly sensitive alarm system.
The spinal cord is protected by strong bones, thick ligaments, powerful muscles and a highly effective alarm system (your nervous system). This alarm system can trigger pain that is so unpleasant that you cannot possibly think of, let alone do, anything other than seek care or avoid movement.
The messy truth is that when pain persists, the pain system becomes more sensitive, so a widening array of things contribute to pain. This pain system hypersensitivity is a result of neuroplasticity – your nervous system is becoming better at making pain.
Reduce your chance of lasting pain
Whether or not your pain resolves is not determined by the extent of injury to your back. We don’t know all the factors involved, but we do know there are things that you can do to reduce chronic back pain:
- understand how pain really works. This will involve intentionally learning about modern pain science and care. It will be difficult but rewarding. It will help you work out what you can do to change your pain
- reduce your pain system sensitivity. With guidance, patience and persistence, you can learn how to gradually retrain your pain system back towards normal.
How to reduce your pain sensitivity and learn about pain
Learning about “how pain works” provides the most sustainable improvements in chronic back pain. Programs that combine pain education with graded brain and body exercises (gradual increases in movement) can reduce pain system sensitivity and help you return to the life you want.
Some programs combine education with gradual increases in movement.
Halfpoint/ShutterstockThese programs have been in development for years, but high-quality clinical trials are now emerging and it’s good news: they show most people with chronic back pain improve and many completely recover.
But most clinicians aren’t equipped to deliver these effective programs – good pain education is not taught in most medical and health training degrees. Many patients still receive ineffective and often risky and expensive treatments, or keep seeking temporary pain relief, hoping for a cure.
When health professionals don’t have adequate pain education training, they can deliver bad pain education, which leaves patients feeling like they’ve just been told it’s all in their head.
Community-driven not-for-profit organisations such as Pain Revolution are training health professionals to be good pain educators and raising awareness among the general public about the modern science of pain and the best treatments. Pain Revolution has partnered with dozens of health services and community agencies to train more than 80 local pain educators and supported them to bring greater understanding and improved care to their colleagues and community.
But a broader system-wide approach, with government, industry and philanthropic support, is needed to expand these programs and fund good pain education. To solve the massive problem of chronic back pain, effective interventions need to be part of standard care, not as a last resort after years of increasing pain, suffering and disability.
Sarah Wallwork, Post-doctoral Researcher, University of South Australia and Lorimer Moseley, Professor of Clinical Neurosciences and Foundation Chair in Physiotherapy, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Get On It! – by Jane Aronovitch, Miriane Taylor, & Colleen Craig
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Balance is important; without it, we die early. That’s quite a strong selling point for improving one’s balance, but why this book in particular?
This is—with one drawback—the best book of balance ball exercises we’ve seen. Notwithstanding the cover photo, many exercises do, by the way, involve standing on it with one or both feet, doing various kinds of squats, lunges, get-ups, and so forth. The ball (it’s not really a ball so much as an oblate hemisphere) can also be flipped and used the other way around, with a flat platform that will now wobble per your weight distribution, and train balance in different ways (dome-up trains large stabilizing muscles more; platform-up trains smaller stabilizing muscles more).
Indeed, that’s where the brand name Bosu, often stylized “BOSU”, comes from: both sides up!
So, what’s the drawback? Alas, the photos are black and white, which means in some cases they’re not as clear as they could be. Nothing that will prevent understanding the exercises, which are well-explained in any case, but it does mean that sometimes it’s necessary to look closely to see which leg is in front of the other for a given exercise, for example.
Still, with 80 different exercises it really does cover the whole body, and even gives workout program varieties for those who want that, including targeted to particular areas, e.g. lower body, core, upper body, or complete.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your balance (and have, or are willing to acquire, a balance ball like the Bosu), then this book will give you everything else you need in that regard.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Seven Principles for Making Marriage Work – by Dr. John Gottman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of relationship advice can seem a little wishy-washy. Hardline clinical work, on the other hand, can seem removed from the complex reality of married life. Dr. Gottman, meanwhile, strikes a perfect balance.
He looks at huge datasets, and he listens to very many couples. He famously isolated four relational factors that predict divorce with 91% accuracy, his “Four Horsemen”:
- Criticism
- Contempt
- Defensiveness
- Stonewalling
He also, as the title of this book promises (and we get a chapter-by-chapter deep-dive on each of them) looks at “Seven principles for making marriage work”. They’re not one-word items, so including them here would take up the rest of our space, and this is a book review not a book summary. However…
Dr. Gottman’s seven principles are, much like his more famous “four horsemen”, deeply rooted in science, while also firmly grounded in the reality of individual couples. Essentially, by listening to very many couples talk about their relationships, and seeing how things panned out with each of them in the long-term, he was able to see what things kept on coming up each time in the couples that worked out. What did they do differently?
And, that’s the real meat of the book. Science yes, but lots of real-world case studies and examples, from couples that worked and couples that didn’t.
In so doing, he provides a roadmap for couples who are serious about making their marriage the best it can be.
Bottom line: this is a must-have book for couples in general, no matter how good or bad the relationship.
- For some it’ll be a matter of realising “You know what; this isn’t going to work”
- For others, it’ll be a matter of “Ah, relief, this is how we can resolve that!”
- For still yet others, it’ll be a matter of “We’re doing these things right; let’s keep them forefront in our minds and never get complacent!”
- And for everyone who is in a relationship or thinking of getting into one, it’s a top-tier manual.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: