Kate Middleton is having ‘preventive chemotherapy’ for cancer. What does this mean?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Catherine, Princess of Wales, is undergoing treatment for cancer. In a video thanking followers for their messages of support after her major abdominal surgery, the Princess of Wales explained, “tests after the operation found cancer had been present.”
“My medical team therefore advised that I should undergo a course of preventative chemotherapy and I am now in the early stages of that treatment,” she said in the two-minute video.
No further details have been released about the Princess of Wales’ treatment.
But many have been asking what preventive chemotherapy is and how effective it can be. Here’s what we know about this type of treatment.
It’s not the same as preventing cancer
To prevent cancer developing, lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise and sun protection are recommended.
Tamoxifen, a hormone therapy drug can be used to reduce the risk of cancer for some patients at high risk of breast cancer.
Aspirin can also be used for those at high risk of bowel and other cancers.
How can chemotherapy be used as preventive therapy?
In terms of treating cancer, prevention refers to giving chemotherapy after the cancer has been removed, to prevent the cancer from returning.
If a cancer is localised (limited to a certain part of the body) with no evidence on scans of it spreading to distant sites, local treatments such as surgery or radiotherapy can remove all of the cancer.
If, however, cancer is first detected after it has spread to distant parts of the body at diagnosis, clinicians use treatments such as chemotherapy (anti-cancer drugs), hormones or immunotherapy, which circulate around the body .
The other use for chemotherapy is to add it before or after surgery or radiotherapy, to prevent the primary cancer coming back. The surgery may have cured the cancer. However, in some cases, undetectable microscopic cells may have spread into the bloodstream to distant sites. This will result in the cancer returning, months or years later.
With some cancers, treatment with chemotherapy, given before or after the local surgery or radiotherapy, can kill those cells and prevent the cancer coming back.
If we can’t see these cells, how do we know that giving additional chemotherapy to prevent recurrence is effective? We’ve learnt this from clinical trials. Researchers have compared patients who had surgery only with those whose surgery was followed by additional (or often called adjuvant) chemotherapy. The additional therapy resulted in patients not relapsing and surviving longer.
How effective is preventive therapy?
The effectiveness of preventive therapy depends on the type of cancer and the type of chemotherapy.
Let’s consider the common example of bowel cancer, which is at high risk of returning after surgery because of its size or spread to local lymph glands. The first chemotherapy tested improved survival by 15%. With more intense chemotherapy, the chance of surviving six years is approaching 80%.
Preventive chemotherapy is usually given for three to six months.
How does chemotherapy work?
Many of the chemotherapy drugs stop cancer cells dividing by disrupting the DNA (genetic material) in the centre of the cells. To improve efficacy, drugs which work at different sites in the cell are given in combinations.
Chemotherapy is not selective for cancer cells. It kills any dividing cells.
But cancers consist of a higher proportion of dividing cells than the normal body cells. A greater proportion of the cancer is killed with each course of chemotherapy.
Normal cells can recover between courses, which are usually given three to four weeks apart.
What are the side effects?
The side effects of chemotherapy are usually reversible and are seen in parts of the body where there is normally a high turnover of cells.
The production of blood cells, for example, is temporarily disrupted. When your white blood cell count is low, there is an increased risk of infection.
Cell death in the lining of the gut leads to mouth ulcers, nausea and vomiting and bowel disturbance.
Certain drugs sometimes given during chemotherapy can attack other organs, such as causing numbness in the hands and feet.
There are also generalised symptoms such as fatigue.
Given that preventive chemotherapy given after surgery starts when there is no evidence of any cancer remaining after local surgery, patients can usually resume normal activities within weeks of completing the courses of chemotherapy.
Ian Olver, Adjunct Professsor, School of Psychology, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Adelaide
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
10 Ways To Lower Blood Pressure Naturally
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Increasingly many people, especially over a certain age, are taking so many medications that it precipitates a train of other medications to deal with the side effects of the previous ones. This is neither fun nor healthy. Of course, sometimes it’s a necessity, but often it’s not, so if you’d like to avoid blood pressure meds, here are some good first-line things, as recommended by Dr. Siobhan Deshauer:
No-med options
Dr. Deshauer recommends:
- Diet: follow the DASH diet by eating whole foods, lean / plant-based proteins, and reducing salt and processed foods to lower blood pressure by 5–6 points.
- Sodium reduction: limit sodium intake to 2g/day, focusing on reducing processed foods, which account for 80% of sodium consumption.
- Increase potassium intake: eat potassium-rich foods (e.g. fruit, vegetables) to lower blood pressure by 5–7 points but consult a doctor if you have kidney issues or take certain medications.
- Exercise: engage in isometric exercises like wall squats or planks, which lower systolic pressure by up to 8 points; any exercise is beneficial.
- Weight loss: lose weight (specifically: fat) if (and only if!) carrying excess fat, as each 1 kg (2.2 lbs) excess adiposity reduction can decrease blood pressure by 1 point.
- Limit alcohol: avoid consuming more than two alcoholic drinks per day, as it raises blood pressure.
- Quit smoking: stop smoking to prevent increased blood pressure and long-term vessel damage caused by nicotine.
- Improve sleep: aim for at least 6 hours of sleep per night, ideally 7–9, and seek medical advice if you suspect sleep apnea.
- Manage stress: adopt healthy stress management strategies to avoid the indirect effects of stress on blood pressure.
- Adopt a pet: pet ownership, particularly dogs, can lower blood pressure more effectively than some medications.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Ideal Blood Pressure Numbers Explained
Take care!
Share This Post
-
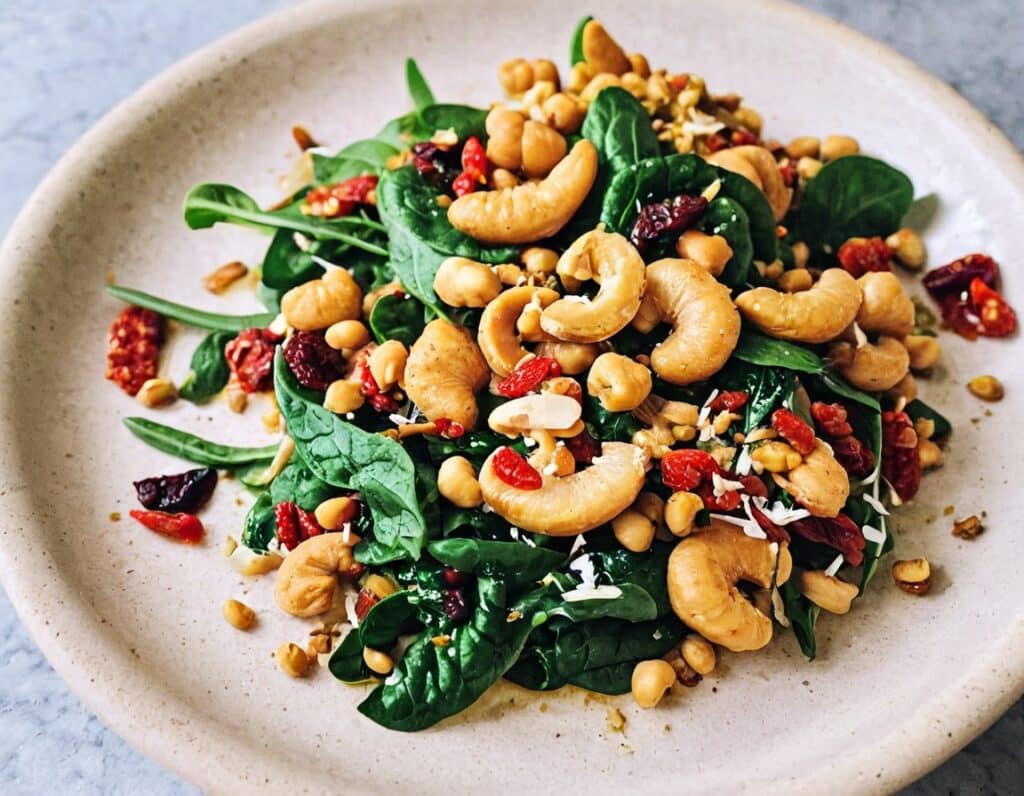
Protein Immune Support Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How to get enough protein from a salad, without adding meat? Cashews and chickpeas have you more than covered! Along with the leafy greens and an impressive array of minor ingredients full of healthy phytochemicals, this one’s good for your muscles, bones, skin, immune health, and more.
You will need
- 1½ cups raw cashews (if allergic, omit; the chickpeas and coconut will still carry the dish for protein and healthy fats)
- 2 cans (2x 14oz) chickpeas, drained
- 1½ lbs baby spinach leaves
- 2 large onions, finely chopped
- 3 oz goji berries
- ½ bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 2 tbsp dessicated coconut
- 1 tbsp dried cumin
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp chili flakes
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil, for cooking
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat a little oil in a pan; add the onions and cook for about 3 minutes.
2) Add the garlic and cook for a further 2 minutes.
3) Add the spinach, and cook until it wilts.
4) Add the remaining ingredients except the coconut, and cook for another three minutes.
5) Heat another pan (dry); add the coconut and toast for 1–2 minutes, until lightly golden. Add it to the main pan.
6) Serve hot as a main, or an attention-grabbing side:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
- What Matters Most For Your Heart?
- Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How long does back pain last? And how can learning about pain increase the chance of recovery?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Back pain is common. One in thirteen people have it right now and worldwide a staggering 619 million people will have it this year.
Chronic pain, of which back pain is the most common, is the world’s most disabling health problem. Its economic impact dwarfs other health conditions.
If you get back pain, how long will it take to go away? We scoured the scientific literature to find out. We found data on almost 20,000 people, from 95 different studies and split them into three groups:
- acute – those with back pain that started less than six weeks ago
- subacute – where it started between six and 12 weeks ago
- chronic – where it started between three months and one year ago.
We found 70%–95% of people with acute back pain were likely to recover within six months. This dropped to 40%–70% for subacute back pain and to 12%–16% for chronic back pain.
Clinical guidelines point to graded return to activity and pain education under the guidance of a health professional as the best ways to promote recovery. Yet these effective interventions are underfunded and hard to access.
More pain doesn’t mean a more serious injury
Most acute back pain episodes are not caused by serious injury or disease.
There are rare exceptions, which is why it’s wise to see your doctor or physio, who can check for signs and symptoms that warrant further investigation. But unless you have been in a significant accident or sustained a large blow, you are unlikely to have caused much damage to your spine.
Your doctor or physio can rule out serious damage.
DG fotostock/ShutterstockEven very minor back injuries can be brutally painful. This is, in part, because of how we are made. If you think of your spinal cord as a very precious asset (which it is), worthy of great protection (which it is), a bit like the crown jewels, then what would be the best way to keep it safe? Lots of protection and a highly sensitive alarm system.
The spinal cord is protected by strong bones, thick ligaments, powerful muscles and a highly effective alarm system (your nervous system). This alarm system can trigger pain that is so unpleasant that you cannot possibly think of, let alone do, anything other than seek care or avoid movement.
The messy truth is that when pain persists, the pain system becomes more sensitive, so a widening array of things contribute to pain. This pain system hypersensitivity is a result of neuroplasticity – your nervous system is becoming better at making pain.
Reduce your chance of lasting pain
Whether or not your pain resolves is not determined by the extent of injury to your back. We don’t know all the factors involved, but we do know there are things that you can do to reduce chronic back pain:
- understand how pain really works. This will involve intentionally learning about modern pain science and care. It will be difficult but rewarding. It will help you work out what you can do to change your pain
- reduce your pain system sensitivity. With guidance, patience and persistence, you can learn how to gradually retrain your pain system back towards normal.
How to reduce your pain sensitivity and learn about pain
Learning about “how pain works” provides the most sustainable improvements in chronic back pain. Programs that combine pain education with graded brain and body exercises (gradual increases in movement) can reduce pain system sensitivity and help you return to the life you want.
Some programs combine education with gradual increases in movement.
Halfpoint/ShutterstockThese programs have been in development for years, but high-quality clinical trials are now emerging and it’s good news: they show most people with chronic back pain improve and many completely recover.
But most clinicians aren’t equipped to deliver these effective programs – good pain education is not taught in most medical and health training degrees. Many patients still receive ineffective and often risky and expensive treatments, or keep seeking temporary pain relief, hoping for a cure.
When health professionals don’t have adequate pain education training, they can deliver bad pain education, which leaves patients feeling like they’ve just been told it’s all in their head.
Community-driven not-for-profit organisations such as Pain Revolution are training health professionals to be good pain educators and raising awareness among the general public about the modern science of pain and the best treatments. Pain Revolution has partnered with dozens of health services and community agencies to train more than 80 local pain educators and supported them to bring greater understanding and improved care to their colleagues and community.
But a broader system-wide approach, with government, industry and philanthropic support, is needed to expand these programs and fund good pain education. To solve the massive problem of chronic back pain, effective interventions need to be part of standard care, not as a last resort after years of increasing pain, suffering and disability.
Sarah Wallwork, Post-doctoral Researcher, University of South Australia and Lorimer Moseley, Professor of Clinical Neurosciences and Foundation Chair in Physiotherapy, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Guava vs Pineapple – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing guava to pineapple, we picked the guava.
Why?
Pineapple is great, but guava just beats it in most ways:
In terms of macros, guava has nearly 4x the fiber and nearly 5x the protein, for the same carbs, giving it the notably lower glycemic index. An easy win for guava in this category.
In the category of vitamins, guava has a lot more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B5, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while pineapple has marginally more vitamin B1. Another clear win for guava.
When it comes to minerals, guava has more calcium, copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while pineapple has more iron and manganese. One more win for guava.
One big thing in pineapple’s favor is that it contains bromelain, which is an enzyme* found in pineapple (and only in pineapple), that has many very healthful properties, some of them unique to bromelain (and thus: unique to pineapple)
*actually a combination of enzymes, but most often referred to collectively in the singular. But when you do see it referred to as “they”, that’s what that means.
However cool that is, we think it unfair to weight it against guava winning in every other category, so we still say guava gets the overall win.
Of course, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
Let’s Get Fruity: Bromelain vs Inflammation & Much More
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Flax Seeds vs Pumpkin Seeds – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing flax seeds to pumpkin seeds, we picked the flax.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, they are equal on protein, and flax seeds have a lot more fiber while pumpkin seeds have a lot more carbs. We’re going to prioritise fiber over carbs and call this a win for flax.
In terms of vitamins, flax seeds have a lot more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while pumpkin seeds have a tiny bit more vitamin A. An easy win for flax here.
When it comes to minerals, flax has multiples more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and selenium, while pumpkin seeds have more zinc. Another win for flax.
Adding up the sections makes for a clear overall win for flax, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score? ← seeds count as plants!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Edam vs Gouda – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing edam to gouda, we picked the edam.
Why?
There’s not a lot between them, but there are some differences:
In terms of macros, their numbers are all close enough that one may beat the other by decimal place rounding, so we’ll call this a tie. Same goes for their fat type breakdowns; per 100g they both have 18g saturated, 8g monounsaturated, and 1g polyunsaturated.
In the category of vitamins, edam has slightly more of vitamins A, B1, B2, and B3, while gouda has slightly more of vitamins B5 and B9. A modest 4:2 win for edam.
When it comes to minerals, edam has more calcium, iron, and potassium, while gouda is not higher in any minerals. A more convincing win for edam.
In short, enjoy either or both in moderation, but if you’re going to choose one over the other, edam is the way to go.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: