Gentler Hair Health Options
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hair, Gently
We have previously talked about the medicinal options for combatting the thinning hair that comes with age especially for men, but also for a lot of women. You can read about those medicinal options here:
Hair-Loss Remedies, By Science
We also did a whole supplement spotlight research review for saw palmetto! You can read about how that might help you keep your hair present and correct, here:
One Man’s Saw Palmetto Is Another Woman’s Serenoa Repens
Today we’re going to talk options that are less “heavy guns”, and/but still very useful.
Supplementation
First, the obvious. Taking vitamins and minerals, especially biotin, can help a lot. This writer takes 10,000µg (that’s micrograms, not milligrams!) biotin gummies, similar to this example product on Amazon (except mine also has other vitamins and minerals in, but the exact product doesn’t seem to be available on Amazon).
When thinking “what vitamins and minerals help hair?”, honestly, it’s most of them. So, focus on the ones that count for the most (usually: biotin and zinc), and then cover your bases for the rest with good diet and additional supplementation if you wish.
Caffeine (topical)
It may feel silly, giving one’s hair a stimulant, but topical caffeine application really does work to stimulate hair growth. And not “just a little help”, either:
❝Specifically, 0.2% topical caffeine-based solutions are typically safe with very minimal adverse effects for long-term treatment of AGA, and they are not inferior to topical 5% minoxidil therapy❞
(AGA = Androgenic Alopecia)
Argan oil
As with coconut oil, argan oil is great on hair. It won’t do a thing to improve hair growth or decrease hair shedding, but it will help you hair stay moisturized and thus reduce breakage—thus, may not be relevant for everyone, but for those of us with hair long enough to brush, it’s important.
Bonus: get an argan oil based hair serum that also contains keratin (the protein used to make hair), as this helps strengthen the hair too.
Here’s an example product on Amazon
Silk pillowcases
Or a silk hair bonnet to sleep in! They both do the same thing, which is prevent damaging the hair in one’s sleep by reducing the friction that it may have when moving/turning against the pillow in one’s sleep.
- Pros of the bonnet: if you have lots of hair and a partner in bed with you, your hair need not be in their face, and you also won’t get it caught under you or them.
- Pros of the pillowcase: you don’t have to wear a bonnet
Both are also used widely by people without hair loss issues, but with easily damaged and/or tangled hair—Black people especially with 3C or tighter curls in particular often benefit from this. Other people whose hair is curly and/or gray also stand to gain a lot.
Here are Amazon example products of a silk pillowcase (it’s expensive, but worth it) and a silk bonnet, respectively
Want to read more?
You might like this article:
From straight to curly, thick to thin: here’s how hormones and chemotherapy can change your hair
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Cancer Code − by Dr. William Fung
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We have previously reviewed, by the same author, “The Obesity Code” and “The Diabetes Code”, so, what does this one offer that’s new?
Mostly, it’s just a new focus, because the dietary approach is basically the same (because all three are fundamentally metabolism-related), with some small tweaks for cancer-specificity. If you’ve read one or more of the other books, you can probably comfortably get away with skipping this one, unless you or a loved one presently has cancer and you’re doing your best to squeeze out any extra 1% of anticancer potential.
Indeed, the former two books assumed that you are affected by obesity or diabetes, respectively, and this one assumes you are at least particularly concerned by cancer—he doesn’t assume you have it (although he does cover that too); he assumes however that you perhaps have a known risk factor or some other similar reason to be focusing on this.
To oversimplify a lot, the dietary approach recommended involves practising intermittent fasting, and also adjusting one’s diet to reduce fasting blood sugar levels and postprandial (after eating) blood sugar and insulin levels. Shocking nobody, he advocates for a lot of plants; he does however recommend a moderately low-carb diet (e.g. legumes are fine but maybe skip the fries).
The style is on the hard end of pop-science, while still quite readable provided one takes one’s time, and there are more than 30 pages of scientific references.
Bottom line: if you’d like to make your diet as anticancer as possible, this book will show you how.
Click there to check out The Cancer Code, and eat to beat cancer!
Share This Post
-
From eye exams to blood tests and surgery: how doctors use light to diagnose disease
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is the next article in our ‘Light and health’ series, where we look at how light affects our physical and mental health in sometimes surprising ways. Read other articles in the series.
You’re not feeling well. You’ve had a pounding headache all week, dizzy spells and have vomited up your past few meals.
You visit your GP to get some answers and sit while they shine a light in your eyes, order a blood test and request some medical imaging.
Everything your GP just did relies on light. These are just some of the optical technologies that have had an enormous impact in how we diagnose disease.
megaflopp/Shutterstock 1. On-the-spot tests
Point-of-care diagnostics allow doctors to test patients on the spot and get answers in minutes, rather than sending samples to a lab for analysis.
The “flashlight” your GP uses to view the inside of your eye (known as an ophthalmoscope) is a great example. This allows doctors to detect abnormal blood flow in the eye, deformations of the cornea (the outermost clear layer of the eye), or swollen optical discs (a round section at the back of the eye where the nerve link to the brain begins). Swollen discs are a sign of elevated pressure inside your head (or in the worst case, a brain tumour) that could be causing your headaches.
The invention of lasers and LEDs has enabled many other miniaturised technologies to be provided at the bedside or clinic rather than in the lab.
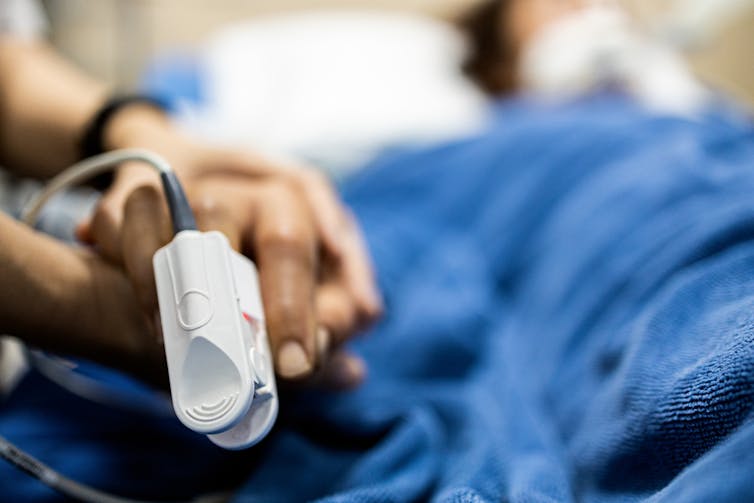
Pulse oximetry is a famous example, where a clip attached to your finger reports how well your blood is oxygenated. It does this by measuring the different responses of oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood to different colours of light.
Pulse oximetry is used at hospitals (and sometimes at home) to monitor your respiratory and heart health. In hospitals, it is also a valuable tool for detecting heart defects in babies.
See that clip on the patient’s finger? That’s a pulse oximeter, which relies on light to monitor respiratory and heart health. CGN089/Shutterstock 2. Looking at molecules
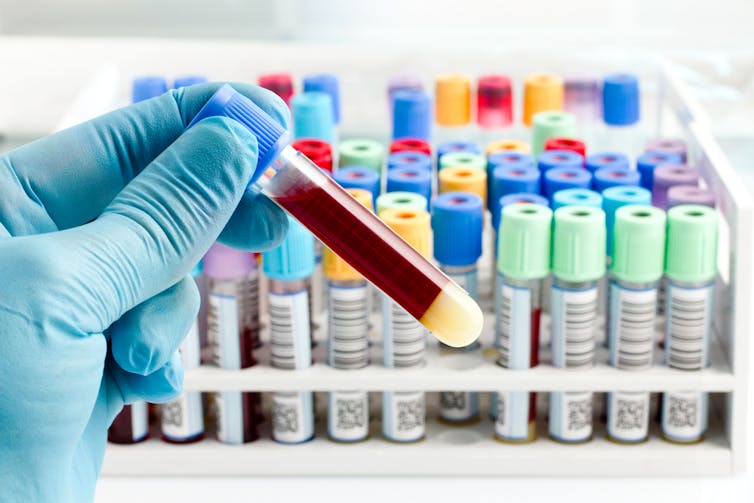
Now, back to that blood test. Analysing a small amount of your blood can diagnose many different diseases.
A machine called an automated “full blood count analyser” tests for general markers of your health. This machine directs focused beams of light through blood samples held in small glass tubes. It counts the number of blood cells, determines their specific type, and reports the level of haemoglobin (the protein in red blood cells that distributes oxygen around your body). In minutes, this machine can provide a snapshot of your overall health.
For more specific disease markers, blood serum is separated from the heavier cells by spinning in a rotating instrument called a centrifuge. The serum is then exposed to special chemical stains and enzyme assays that change colour depending on whether specific molecules, which may be the sign of a disease, are present.
These colour changes can’t be detected with the naked eye. However, a light beam from an instrument called a spectrometer can detect tiny amounts of these substances in the blood and determine if the biomarkers for diseases are present, and at what levels.
Light shines through the blood sample and tells us whether biomarkers for disease are present. angellodeco/Shutterstock 3. Medical imaging
Let’s re-visit those medical images your GP ordered. The development of fibre-optic technology, made famous for transforming high-speed digital communications (such as the NBN), allows light to get inside the body. The result? High-resolution optical imaging.
A common example is an endoscope, where fibres with a tiny camera on the end are inserted into the body’s natural openings (such as your mouth or anus) to examine your gut or respiratory tracts.
Surgeons can insert the same technology through tiny cuts to view the inside of the body on a video screen during laparoscopic surgery (also known as keyhole surgery) to diagnose and treat disease.
Doctors can insert this flexible fibre-optic tube with a camera on the end into your body. Eduard Valentinov/Shutterstock How about the future?
Progress in nanotechnology and a better understanding of the interactions of light with our tissues are leading to new light-based tools to help diagnose disease. These include:
- nanomaterials (materials on an extremely small scale, many thousands of times smaller than the width of a human hair). These are being used in next-generation sensors and new diagnostic tests
- wearable optical biosensors the size of your fingernail can be included in devices such as watches, contact lenses or finger wraps. These devices allow non-invasive measurements of sweat, tears and saliva, in real time
- AI tools to analyse how blood serum scatters infrared light. This has allowed researchers to build a comprehensive database of scatter patterns to detect any cancer
- a type of non-invasive imaging called optical coherence tomography for more detailed imaging of the eye, heart and skin
- fibre optic technology to deliver a tiny microscope into the body on the tip of a needle.
So the next time you’re at the GP and they perform (or order) some tests, chances are that at least one of those tests depend on light to help diagnose disease.
Matthew Griffith, Associate Professor and ARC Future Fellow and Director, UniSA Microscopy and Microanalysis Facilities, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
53 Studies Later: The Best Way to Improve VO2 Max
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
VO2 max measures maximum oxygen usage during intense exercise and reflects overall health and performance. To have a high VO2 max, efficient functioning of lungs, heart, red blood cells, muscles, and mitochondria is crucial. So, how to get those?
Let’s HIIT it!
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) outperforms moderate-intensity exercise, by a long way. Further, based on the data from the 53 studies mentioned in the title, we can know which of the protocols tested work best, and they are:
- 15×15 Interval Training: 15 seconds sprint (90–95% max heart rate) + 15 seconds active rest (70% max heart rate), repeated 47 times.
- 4×4 Interval Training: 4 minutes sprint (90–95% max heart rate) + 3 minutes active rest (70% max heart rate), repeated 4 times.
Whichever you choose, it is best to then do that 3x per week.
Note that “sprint” can mean any maximum-effort cardio exercise; it doesn’t have to be running specifically. Cycling or swimming, for example, are fine options too, as is jumping rope.
For more on each of these, plus how the science got there, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Not all ultra-processed foods are bad for your health, whatever you might have heard
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In recent years, there’s been increasing hype about the potential health risks associated with so-called “ultra-processed” foods.
But new evidence published this week found not all “ultra-processed” foods are linked to poor health. That includes the mass-produced wholegrain bread you buy from the supermarket.
While this newly published research and associated editorial are unlikely to end the wrangling about how best to define unhealthy foods and diets, it’s critical those debates don’t delay the implementation of policies that are likely to actually improve our diets.
What are ultra-processed foods?
Ultra-processed foods are industrially produced using a variety of processing techniques. They typically include ingredients that can’t be found in a home kitchen, such as preservatives, emulsifiers, sweeteners and/or artificial colours.
Common examples of ultra-processed foods include packaged chips, flavoured yoghurts, soft drinks, sausages and mass-produced packaged wholegrain bread.
In many other countries, ultra-processed foods make up a large proportion of what people eat. A recent study estimated they make up an average of 42% of total energy intake in Australia.
How do ultra-processed foods affect our health?
Previous studies have linked increased consumption of ultra-processed food with poorer health. High consumption of ultra-processed food, for example, has been associated with a higher risk of type 2 diabetes, and death from heart disease and stroke.
Ultra-processed foods are typically high in energy, added sugars, salt and/or unhealthy fats. These have long been recognised as risk factors for a range of diseases.
Ultra-processed foods are usually high is energy, salt, fat, or sugar. Olga Dubravina/Shutterstock It has also been suggested that structural changes that happen to ultra-processed foods as part of the manufacturing process may lead you to eat more than you should. Potential explanations are that, due to the way they’re made, the foods are quicker to eat and more palatable.
It’s also possible certain food additives may impair normal body functions, such as the way our cells reproduce.
Is it harmful? It depends on the food’s nutrients
The new paper just published used 30 years of data from two large US cohort studies to evaluate the relationship between ultra-processed food consumption and long-term health. The study tried to disentangle the effects of the manufacturing process itself from the nutrient profile of foods.
The study found a small increase in the risk of early death with higher ultra-processed food consumption.
But importantly, the authors also looked at diet quality. They found that for people who had high quality diets (high in fruit, vegetables, wholegrains, as well as healthy fats, and low in sugary drinks, salt, and red and processed meat), there was no clear association between the amount of ultra-processed food they ate and risk of premature death.
This suggests overall diet quality has a stronger influence on long-term health than ultra-processed food consumption.
People who consume a healthy diet overall but still eat ultra-processed foods aren’t at greater risk of early death. Grusho Anna/Shutterstock When the researchers analysed ultra-processed foods by sub-category, mass-produced wholegrain products, such as supermarket wholegrain breads and wholegrain breakfast cereals, were not associated with poorer health.
This finding matches another recent study that suggests ultra-processed wholegrain foods are not a driver of poor health.
The authors concluded, while there was some support for limiting consumption of certain types of ultra-processed food for long-term health, not all ultra-processed food products should be universally restricted.
Should dietary guidelines advise against ultra-processed foods?
Existing national dietary guidelines have been developed and refined based on decades of nutrition evidence.
Much of the recent evidence related to ultra-processed foods tells us what we already knew: that products like soft drinks, alcohol and processed meats are bad for health.
Dietary guidelines generally already advise to eat mostly whole foods and to limit consumption of highly processed foods that are high in refined grains, saturated fat, sugar and salt.
But some nutrition researchers have called for dietary guidelines to be amended to recommend avoiding ultra-processed foods.
Based on the available evidence, it would be difficult to justify adding a sweeping statement about avoiding all ultra-processed foods.
Advice to avoid all ultra-processed foods would likely unfairly impact people on low-incomes, as many ultra-processed foods, such as supermarket breads, are relatively affordable and convenient.
Wholegrain breads also provide important nutrients, such as fibre. In many countries, bread is the biggest contributor to fibre intake. So it would be problematic to recommend avoiding supermarket wholegrain bread just because it’s ultra-processed.
So how can we improve our diets?
There is strong consensus on the need to implement evidence-based policies to improve population diets. This includes legislation to restrict children’s exposure to the marketing of unhealthy foods and brands, mandatory Health Star Rating nutrition labelling and taxes on sugary drinks.
Taxes on sugary drinks would reduce their consumption. MDV Edwards/Shutterstock These policies are underpinned by well-established systems for classifying the healthiness of foods. If new evidence unfolds about mechanisms by which ultra-processed foods drive health harms, these classification systems can be updated to reflect such evidence. If specific additives are found to be harmful to health, for example, this evidence can be incorporated into existing nutrient profiling systems, such as the Health Star Rating food labelling scheme.
Accordingly, policymakers can confidently progress food policy implementation using the tools for classifying the healthiness of foods that we already have.
Unhealthy diets and obesity are among the largest contributors to poor health. We can’t let the hype and academic debate around “ultra-processed” foods delay implementation of globally recommended policies for improving population diets.
Gary Sacks, Professor of Public Health Policy, Deakin University; Kathryn Backholer, Co-Director, Global Centre for Preventive Health and Nutrition, Deakin University; Kathryn Bradbury, Senior Research Fellow in the School of Population Health, University of Auckland, Waipapa Taumata Rau, and Sally Mackay, Senior Lecturer Epidemiology and Biostatistics, University of Auckland, Waipapa Taumata Rau
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Train For The Event Of Your Life!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mobility As A Sporting Pursuit
As we get older, it becomes increasingly important to treat life like a sporting event. By this we mean:
As an “athlete of life”, there are always events coming up for which we need to train. Many of these events will be surprise tests!
Such events/tests might include:
- Not slipping in the shower and breaking a hip (or worse)
- Reaching an item from a high shelf without tearing a ligament
- Getting out of the car at an awkward angle without popping a vertebra
- Climbing stairs without passing out light-headed at the top
- Descending stairs without making it a sled-ride-without-a-sled
…and many more.
Train for these athletic events now
Not necessarily this very second; we appreciate you finishing reading first. But, now generally in your life, not after the first time you fail such a test; it can (and if we’re not attentive: will) indeed happen to us all.
With regard to falling, you might like to revisit our…
…which covers how to not fall, and to not injure yourself if you do.
You’ll also want to be able to keep control of your legs (without them buckling) all the way between standing and being on the ground.
Slav squats or sitting squats (same exercise, different names, amongst others) are great for building and maintaining this kind of strength and suppleness:
(Click here for a refresher if you haven’t recently seen Zuzka’s excellent video explaining how to do this, especially if it’s initially difficult for you, “The Most Anti-Aging Exercise”)
this exercise is, by the way, great for pretty much everything below the waist!
You will also want to do resistance exercises to keep your body robust:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
And as for those shoulders? If it is convenient for you to go swimming, then backstroke is awesome for increasing and maintaining shoulder mobility (and strength).
If swimming isn’t a viable option for you, then doing the same motion with your arms, while standing, will build the same flexibility. If you do it while holding a small weight (even just 1kg is fine, but feel free to increase if you so wish and safely can) in each hand will build the necessary strength as you go too.
As for why even just 1kg is fine: read on
About that “and strength”, by the way…
Stretching is not everything. Stretching is great, but mobility without strength (in that joint!) is just asking for dislocation.
You don’t have to be built like the Terminator, but you do need to have the structural integrity to move your body and then a little bit more weight than that (or else any extra physical work could be enough to tip you to breaking point) without incurring damage from the strain. So, it needs to not be a strain! See again, the aforementioned resistance exercises.
That said, even very gentle exercise helps too; see for example the impact of walking on osteoporosis:
Living near green spaces linked to higher bone density and lower osteoporosis risk
and…
So you don’t have to run marathons—although you can if you want:
Marathons in Mid- and Later-Life
…to keep your hips and more in good order.
Want to test yourself now?
Check out:
Building & Maintaining Mobility
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What is ‘doll therapy’ for people with dementia? And is it backed by science?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The way people living with dementia experience the world can change as the disease progresses. Their sense of reality or place in time can become distorted, which can cause agitation and distress.
One of the best ways to support people experiencing changes in perception and behaviour is to manage their environment. This can have profound benefits including reducing the need for sedatives.
One such strategy is the use of dolls as comfort aids.
Jack Cronkhite/Shutterstock What is ‘doll therapy’?
More appropriately referred to as “child representation”, lifelike dolls (also known as empathy dolls) can provide comfort for some people with dementia.
Memories from the distant past are often more salient than more recent events in dementia. This means that past experiences of parenthood and caring for young children may feel more “real” to a person with dementia than where they are now.
Hallucinations or delusions may also occur, where a person hears a baby crying or fears they have lost their baby.
Providing a doll can be a tangible way of reducing distress without invalidating the experience of the person with dementia.
Some people believe the doll is real
A recent case involving an aged care nurse mistreating a dementia patient’s therapy doll highlights the importance of appropriate training and support for care workers in this area.
For those who do become attached to a therapeutic doll, they will treat the doll as a real baby needing care and may therefore have a profound emotional response if the doll is mishandled.
It’s important to be guided by the person with dementia and only act as if it’s a real baby if the person themselves believes that is the case.
What does the evidence say about their use?
Evidence shows the use of empathy dolls may help reduce agitation and anxiety and improve overall quality of life in people living with dementia.
Child representation therapy falls under the banner of non-pharmacological approaches to dementia care. More specifically, the attachment to the doll may act as a form of reminiscence therapy, which involves using prompts to reconnect with past experiences.
Interacting with the dolls may also act as a form of sensory stimulation, where the person with dementia may gain comfort from touching and holding the doll. Sensory stimulation may support emotional well-being and aid commnication.
However, not all people living with dementia will respond to an empathy doll.
It depends on a person’s background. Shutterstock The introduction of a therapeutic doll needs to be done in conjunction with careful observation and consideration of the person’s background.
Empathy dolls may be inappropriate or less effective for those who have not previously cared for children or who may have experienced past birth trauma or the loss of a child.
Be guided by the person with dementia and how they respond to the doll.
Are there downsides?
The approach has attracted some controversy. It has been suggested that child representation therapy “infantilises” people living with dementia and may increase negative stigma.
Further, the attachment may become so strong that the person with dementia will become upset if someone else picks the doll up. This may create some difficulties in the presence of grandchildren or when cleaning the doll.
The introduction of child representation therapy may also require additional staff training and time. Non-pharmacological interventions such as child representation, however, have been shown to be cost-effective.
Could robots be the future?
The use of more interactive empathy dolls and pet-like robots is also gaining popularity.
While robots have been shown to be feasible and acceptable in dementia care, there remains some contention about their benefits.
While some studies have shown positive outcomes, including reduced agitation, others show no improvement in cognition, behaviour or quality of life among people with dementia.
Advances in artificial intelligence are also being used to help support people living with dementia and inform the community.
Viv and Friends, for example, are AI companions who appear on a screen and can interact with the person with dementia in real time. The AI character Viv has dementia and was co-created with women living with dementia using verbatim scripts of their words, insights and experiences. While Viv can share her experience of living with dementia, she can also be programmed to talk about common interests, such as gardening.
These companions are currently being trialled in some residential aged care facilities and to help educate people on the lived experience of dementia.
How should you respond to your loved one’s empathy doll?
While child representation can be a useful adjunct in dementia care, it requires sensitivity and appropriate consideration of the person’s needs.
People living with dementia may not perceive the social world the same way as a person without dementia. But a person living with dementia is not a child and should never be treated as one.
Ensure all family, friends and care workers are informed about the attachment to the empathy doll to help avoid unintentionally causing distress from inappropriate handling of the doll.
If using an interactive doll, ensure spare batteries are on hand.
Finally, it is important to reassess the attachment over time as the person’s response to the empathy doll may change.
Nikki-Anne Wilson, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Neuroscience Research Australia (NeuRA), UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: