Popcorn vs Peanuts – Which is Healthier
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing air-popped popcorn to peanuts (without an allergy), we picked the peanuts.
Why?
Peanuts, if we were to list popular nuts in order of healthfulness, would not be near the top of the list. Many other nuts have more nutrients and fewer/lesser drawbacks.
But the comparison to popcorn shines a different light on it:
Popcorn has very few nutrients. It’s mostly carbs and fiber; it’s just not a lot of carbs because the manner of its consumption makes it a very light snack (literally). You can eat a bowlful and it was perhaps 30g. It has some small amounts of some minerals, but nothing that you could rely on it for. It’s mostly fresh air wrapped in fiber.
Peanuts, in contrast, are a much denser snack. High in calories yes, but also high in protein, their fats are mostly healthy, and they have not only a fair stock of vitamins and minerals, but also a respectable complement of beneficial phytochemicals: mostly assorted antioxidant polyphenols, but also oleic acid (as in olives, good for healthy triglyceride levels).
Another thing worth a mention is their cholesterol-reducing phytosterols (these reduce the absorption of dietary cholesterol, “good” and “bad”, so this is good for most people, bad for some, depending on the state of your cholesterol and what you ate near in time to eating the nuts)
Peanuts do have their clear downsides too: its phytic acid content can reduce the bioavailability of iron and zinc taken at the same time.
In summary: while popcorn’s greatest claim to dietary beneficence is its fiber content and that it’s close to being a “zero snack”, peanuts (eaten in moderation, say, the same 30g as the popcorn) have a lot to contribute to our daily nutritional requirements.
We do suggest enjoying other nuts though!
Read more: Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
We looked at 700 plant-based foods to see how healthy they really are. Here’s what we found
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
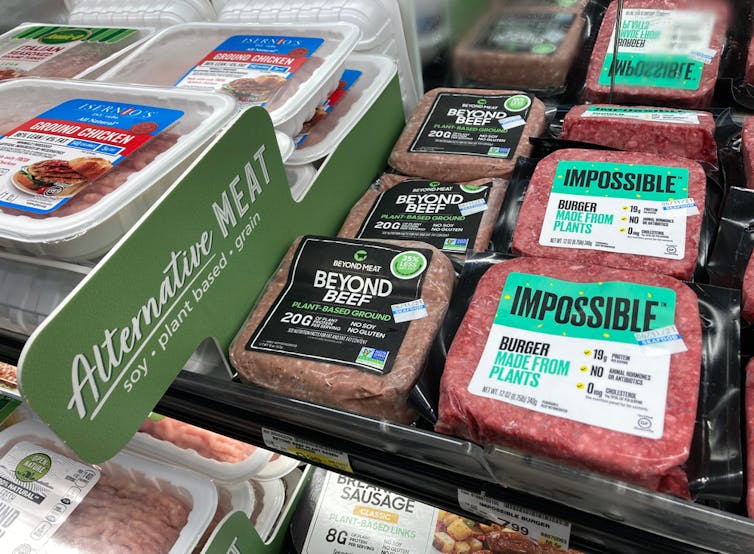
If you’re thinking about buying plant-based foods, a trip to the supermarket can leave you bewildered.
There are plant-based burgers, sausages and mince. The fridges are loaded with non-dairy milk, cheese and yoghurt. Then there are the tins of beans and packets of tofu.
But how much is actually healthy?
Our nutritional audit of more than 700 plant-based foods for sale in Australian supermarkets has just been published. We found some products are so high in salt or saturated fat, we’d struggle to call them “healthy”.
We took (several) trips to the supermarket
In 2022, we visited two of each of four major supermarket retailers across Melbourne to collect information on the available range of plant-based alternatives to meat and dairy products.
We took pictures of the products and their nutrition labels.
We then analysed the nutrition information on the packaging of more than 700 of these products. This included 236 meat substitutes, 169 legumes and pulses, 50 baked beans, 157 dairy milk substitutes, 52 cheese substitutes and 40 non-dairy yoghurts.
Plant-based meats were surprisingly salty
We found a wide range of plant-based meats for sale. So, it’s not surprising we found large variations in their nutrition content.
Sodium, found in added salt and which contributes to high blood pressure, was our greatest concern.
The sodium content varied from 1 milligram per 100 grams in products such as tofu, to 2,000mg per 100g in items such as plant-based mince products.
This means we could eat our entire daily recommended sodium intake in just one bowl of plant-based mince.
An audit of 66 plant-based meat products in Australian supermarkets conducted in 2014 found sodium ranged from 316mg in legume-based products to 640mg in tofu products, per 100g. In a 2019 audit of 137 products, the range was up to 1,200mg per 100g.
In other words, the results of our audit seems to show a consistent trend of plant-based meats getting saltier.
Looking for plant-based meat? Check the label for the sodium content.
Michael Vi/Shutterstock
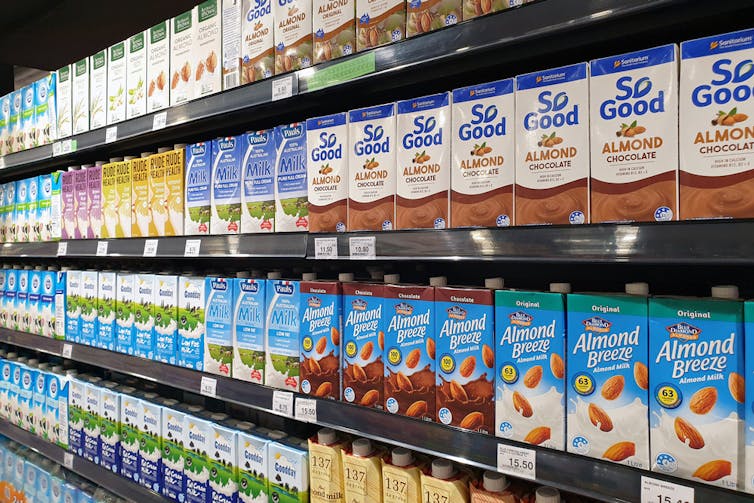
What about plant-based milks?
Some 70% of the plant-based milks we audited were fortified with calcium, a nutrient important for bone health.
This is good news as a 2019-2020 audit of 115 plant-based milks from Melbourne and Sydney found only 43% of plant-based milks were fortified with calcium.
Of the fortified milks in our audit, almost three-quarters (73%) contained the recommended amount of calcium – at least 100mg per 100mL.
We also looked at the saturated fat content of plant-based milks.
Coconut-based milks had on average up to six times higher saturated fat content than almond, oat or soy milks.
Previous audits also found coconut-based milks were much higher in saturated fat than all other categories of milks.
Some plant-based milks were healthier than others.
TY Lim/Shutterstock
A first look at cheese and yoghurt alternatives
Our audit is the first study to identify the range of cheese and yoghurt alternatives available in Australian supermarkets.
Calcium was only labelled on a third of plant-based yoghurts, and only 20% of supermarket options met the recommended 100mg of calcium per 100g.
For plant-based cheeses, most (92%) were not fortified with calcium. Their sodium content varied from 390mg to 1,400mg per 100g, and saturated fat ranged from 0g to 28g per 100g.
So, what should we consider when shopping?
As a general principle, try to choose whole plant foods, such as unprocessed legumes, beans or tofu. These foods are packed with vitamins and minerals. They’re also high in dietary fibre, which is good for your gut health and keeps you fuller for longer.
If opting for a processed plant-based food, here are five tips for choosing a healthier option.
1. Watch the sodium
Plant-based meat alternatives can be high in sodium, so look for products that have around 150-250mg sodium per 100g.
2. Pick canned beans and legumes
Canned chickpeas, lentils and beans can be healthy and low-cost additions to many meals. Where you can, choose canned varieties with no added salt, especially when buying baked beans.
3. Add herbs and spices to your tofu
Tofu can be a great alternative to meat. Check the label and pick the option with the highest calcium content. We found flavoured tofu was higher in salt and sugar content than minimally processed tofu. So it’s best to pick an unflavoured option and add your own flavours with spices and herbs.
4. Check the calcium
When choosing a non-dairy alternative to milk, such as those made from soy, oat, or rice, check it is fortified with calcium. A good alternative to traditional dairy will have at least 100mg of calcium per 100g.
5. Watch for saturated fat
If looking for a lower saturated fat option, almond, soy, rice and oat varieties of milk and yoghurt alternatives have much lower saturated fat content than coconut options. Pick those with less than 3g per 100g.
Laura Marchese, PhD Student at the Institute for Physical Activity and Nutrition, Deakin University and Katherine Livingstone, NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow and Senior Research Fellow at the Institute for Physical Activity and Nutrition, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Resistance Beyond Weights
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Resistance, Your Way
We’ve talked before about the importance of resistance training:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
And we’ve even talked about how to make resistance training more effective:
(High Intensity Interval Training, but make it High Intensity Resistance Training)
Which resistance training exercises are best?
There are two reasonable correct answers here:
- The resistance training exercises that you will actually do (because it’s no good knowing the best exercise ever if you’re not going to do it because it is in some way offputting to you)
- The resistance training exercises that will prevent you from getting a broken bone in the event of some accident or incident
This latter is interesting, because when people think resistance training, the usually immediate go-to exercises are often things like the bench press, or the chest machine in the gym.
But ask yourself: how often do we hear about some friend or relative who in their old age has broken their humerus?
It can happen, for sure, but it’s not as often as breaking a hip, a tarsal (ankle bones), or a carpal (wrist bones).
So, how can we train to make those bones strong?
Strong bones grow under strong muscles
When archaeologists dig up a skeleton from a thousand years ago, one of the occupations that’s easy to recognize is an archer. Why?
An archer has an unusual frequent exercise: pushing with their left arm while pulling with their right arm. This will strengthen different muscles on each side, and thus, increase bone density in different places on each arm. The left first metacarpal and right first and second metacarpals and phalanges are also a giveaway.
This is because: one cannot grow strong muscles on weak bones (or else the muscles would just break the bones), so training muscles will force the body to strengthen the relevant bones.
So: if you want strong bones, train the muscles attached to those bones
This answers the question of “how am I supposed to exercise my hips” etc.
Weights, bodyweight, resistance bands
If you go to the gym, there’s a machine for everything, and a member of gym staff will be able to advise which of their machines will strengthen which muscles.
If you train with free weights at home:
- Wrist curls (forearm supported and stationary, lifting a dumbbell in your hand, palm-upwards) will strengthen the wrist
- The farmer’s walk (carrying a heavy weight in each hand) will also strengthen your wrist
- A modified version of this involves holding the weight with just your fingertips, and then raising and lowering it by curling and uncurling your fingers)
- Lateral leg raises (you will need ankle-weights for this) will strengthen your ankles and your hips, as will hip abductions (as in today’s featured video), especially with a weight attached.
- Ankle raises (going up on your tip-toes and down again, repeat) while holding weights in your hands will strengthen your ankles
If you don’t like weights:
- Press-ups will strengthen your wrists
- Fingertip press-ups are even better: to do these, do your press-ups as normal, except that the only parts of your hands in contact with the ground are your fingertips
- This same exercise can be done the other way around, by doing pull-ups
- And that same “even better” works by doing pull-ups, but holding the bar only with one’s fingertips, and curling one’s fingers to raise oneself up
- Lateral leg raises and hip abductions can be done with a resistance band instead of with weights. The great thing about these is that whereas weights are a fixed weight, resistance bands will always provide the right amount of resistance (because if it’s too easy, you just raise your leg further until it becomes difficult again, since the resistance offered is proportional to how much tension the band is under).
Remember, resistance training is still resistance training even if “all” you’re resisting is gravity!
If it fells like work, then it’s working
As for the rest of preparing to get older?
Check out:
Training Mobility Ready For Later Life
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Reflexology: What The Science Says
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How Does Reflexology Work, Really?
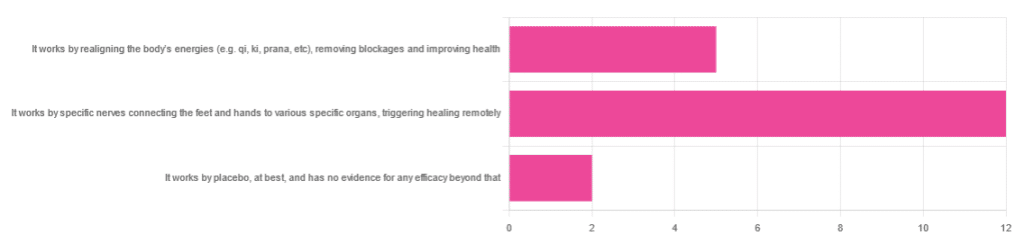
In Wednesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion of reflexology, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- About 63% said “It works by specific nerves connecting the feet and hands to various specific organs, triggering healing remotely”
- About 26% said “It works by realigning the body’s energies (e.g. qi, ki, prana, etc), removing blockages and improving health“
- About 11% said “It works by placebo, at best, and has no evidence for any efficacy beyond that”
So, what does the science say?
It works by realigning the body’s energies (e.g. qi, ki, prana, etc), removing blockages and improving health: True or False?
False, or since we can’t prove a negative: there is no reliable scientific evidence for this.
Further, there is no reliable scientific evidence for the existence of qi, ki, prana, soma, mana, or whatever we want to call it.
To save doubling up, we did discuss this in some more detail, exploring the notion of qi as bioelectrical energy, including a look at some unreliable clinical evidence for it (a study that used shoddy methodology, but it’s important to understand what they did wrong, to watch out for such), when we looked at [the legitimately very healthful practice of] qigong, a couple of weeks ago:
Qigong: A Breath Of Fresh Air?
As for reflexology specifically: in terms of blockages of qi causing disease (and thus being a putative therapeutic mechanism of action for attenuating disease), it’s an interesting hypothesis but in terms of scientific merit, it was pre-emptively supplanted by germ theory and other similarly observable-and-measurable phenomena.
We say “pre-emptively”, because despite orientalist marketing, unless we want to count some ancient pictures of people getting a foot massage and say it is reflexology, there is no record of reflexology being a thing before 1913 (and that was in the US, by a laryngologist working with a spiritualist to produce a book that they published in 1917).
It works by specific nerves connecting the feet and hands to various specific organs, triggering healing remotely: True or False?
False, or since we can’t prove a negative: there is no reliable scientific evidence for this.
A very large independent review of available scientific literature found the current medical consensus on reflexology is that:
- Reflexology is effective for: anxiety (but short lasting), edema, mild insomnia, quality of sleep, and relieving pain (short term: 2–3 hours)
- Reflexology is not effective for: inflammatory bowel disease, fertility treatment, neuropathy and polyneuropathy, acute low back pain, sub acute low back pain, chronic low back pain, radicular pain syndromes (including sciatica), post-operative low back pain, spinal stenosis, spinal fractures, sacroiliitis, spondylolisthesis, complex regional pain syndrome, trigger points / myofascial pain, chronic persistent pain, chronic low back pain, depression, work related injuries of the hip and pelvis
Source: Reflexology – a scientific literary review compilation
(the above is a fascinating read, by the way, and its 50 pages go into a lot more detail than we have room to here)
Now, those items that they found it effective for, looks suspiciously like a short list of things that placebo is often good for, and/or any relaxing activity.
Another review was not so generous:
❝The best evidence available to date does not demonstrate convincingly that reflexology is an effective treatment for any medical condition❞
~ Dr. Edzard Ernst (MD, PhD, FMedSci)
Source: Is reflexology an effective intervention? A systematic review of randomised controlled trials
In short, from the available scientific literature, we can surmise:
- Some researchers have found it to have some usefulness against chiefly psychosomatic conditions
- Other researchers have found the evidence for even that much to be uncompelling
It works by placebo, at best, and has no evidence for any efficacy beyond that: True or False?
Mostly True; of course reflexology runs into similar problems as acupuncture when it comes to testing against placebo:
How Does One Test Acupuncture Against Placebo Anyway?
…but not quite as bad, since it is easier to give a random foot massage while pretending it is a clinical treatment, than to fake putting needles into key locations.
However, as the paper we cited just above (in answer to the previous True/False question) shows, reflexology does not appear to meaningfully outperform placebo—which points to the possibility that it does work by placebo, and is just a placebo treatment on the high end of placebo (because the placebo effect is real, does work, isn’t “nothing”, and some placebos work better than others).
For more on the fascinating science and useful (applicable in daily life!) practicalities of how placebo does work, check out:
How To Leverage Placebo Effect For Yourself
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Insomnia Decoded – by Dr. Audrey Porter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written about sleep books before, so what makes this one different? Its major selling point is: most of the focus isn’t on the things that everyone already knows.
Yes, there’s a section on sleep hygiene and yes it’ll tell you to cut the caffeine and alcohol, but most of the advice here is beyond that.
Rather, it looks at finding out (if you don’t already know for sure) what is keeping you from healthy sleep, be it environmental, directly physical, or psychological, and breaking out of the stress-sleep cycle that often emerges from such.
The style is light and conversational, but includes plenty of science too; Dr. Porter knows her stuff.
Bottom line: if you feel like you know what you should be doing, but somehow life keeps conspiring to stop you from doing it, then this is the book that could help you break out that cycle.
Click here to check out Insomnia Decoded, and get regular healthy sleep!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Flexible Dieting Really Means
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When Flexibility Is The Dish Of The Day
This is Alan Aragon. Notwithstanding not being a “Dr. Alan Aragon”, he’s a research scientist with dozens of peer-reviewed nutrition science papers to his name, as well as being a personal trainer and fitness educator. Most importantly, he’s an ardent champion of making people’s pursuit of health and fitness more evidence-based.
We’ll be sharing some insights from a book of his that we haven’t reviewed yet, but we will link it at the bottom of today’s article in any case.
What does he want us to know?
First, get out of the 80s and into the 90s
In the world of popular dieting, the 80s were all about calorie-counting and low-fat diets. They did not particularly help.
In the 90s, it was discovered that not only was low-fat not the way to go, but also, regardless of the diet in question, rigid dieting leads to “disinhibition”, that is to say, there comes a point (usually not far into a diet) whereby one breaks the diet, at which point, the floodgates open and the dieter binges unhealthily.
Aragon would like to bring our attention to a number of studies that found this in various ways over the course of the 90s measuring various different metrics including rigid vs flexible dieting’s impacts on BMI, weight gain, weight loss, lean muscle mass changes, binge-eating, anxiety, depression, and so forth), but we only have so much room here, so here’s a 1999 study that’s pretty much the culmination of those:
Flexible vs. Rigid Dieting Strategies: Relationship with Adverse Behavioral Outcomes
So in short: trying to be very puritan about any aspect of dieting will not only not work, it will backfire.
Next, get out of the 90s into the 00s
…which is not only fun if you read “00s” out loud as “naughties”, but also actually appropriate in this case, because it is indeed important to be comfortable being a little bit naughty:
In 2000, Dr. Marika Tiggemann found that dichotomous perceptions of food (e.g. good/bad, clean/dirty, etc) were implicated as a dysfunctional cognitive style, and predicted not only eating disorders and mood disorders, but also adverse physical health outcomes:
Dieting and Cognitive Style: The Role of Current and Past Dieting Behaviour and Cognitions
This was rendered clearer, in terms of physical health outcomes, by Dr. Susan Byrne & Dr. Emma Dove, in 2009:
❝Weight loss was negatively associated with pre-treatment depression and frequency of treatment attendance, but not with dichotomous thinking. Females who regard their weight as unacceptably high and who think dichotomously may experience high levels of depression irrespective of their actual weight, while depression may be proportionate to the degree of obesity among those who do not think dichotomously❞
Aragon’s advice based on all this: while yes, some foods are better than others, it’s more useful to see foods as being part of a spectrum, rather than being absolutist or “black and white” about it.
Next: hit those perfect 10s… Imperfectly
The next decade expanded on this research, as science is wont to do, and for this one, Aragon shines a spotlight on Dr. Alice Berg’s 2018 study with obese women averaging 69 years of age, in which…
In other words (and in fact, to borrow Dr. Berg’s words from that paper),
❝encouraging a flexible approach to eating behavior and discouraging rigid adherence to a diet may lead to better intentional weight loss for overweight and obese older women❞
You may be wondering: what did this add to the studies from the 90s?
And the key here is: rather than being observational, this was interventional. In other words, rather than simply observing what happened to people who thought one way or another, this study took people who had a rigid, dichotomous approach to food, and gave them a 6-month behavioral intervention (in other words, support encouraging them to be more flexible and open in their approach to food), and found that this indeed improved matters for them.
Which means, it’s not a matter of fate or predisposition, as it could have been back in the 90s, per “some people are just like that; who’s to say which factor causes which”. Instead, now we know that this is an approach that can be adopted, and it can be expected to work.
Beyond weight loss
Now, so far we’ve talked mostly about weight loss, and only touched on other health outcomes. This is because:
- weight loss a very common goal for many
- it’s easy to measure so there’s a lot of science for it
Incidentally, if it’s a goal of yours, here’s what 10almonds had to say about that, along with two follow-up articles for other related goals:
Spoiler: we agree with Aragon, and recommend a relaxed and flexible approach to all three of these things
Aragon’s evidence-based approach to nutrition has found that this holds true for other aspects of healthy eating, too. For example…
To count or not to count?
It’s hard to do evidence-based anything without counting, and so Aragon talks a lot about this. Indeed, he does a lot of counting in scientific papers of his own, such as:
and
The effect of protein timing on muscle strength and hypertrophy: a meta-analysis
…as well as non-protein-related but diet-related topics such as:
But! For the at-home health enthusiast, Aragon recommends that the answer to the question “to count or not to count?” is “both”:
- Start off by indeed counting and tracking everything that is important to you (per whatever your current personal health intervention is, so it might be about calories, or grams of protein, or grams of carbs, or a certain fat balance, or something else entirely)
- Switch to a more relaxed counting approach once you get used to the above. By now you probably know the macros for a lot of your common meals, snacks, etc, and can tally them in your head without worrying about weighing portions and knowing the exact figures.
- Alternatively, count moderately standardized portions of relevant foods, such as “three servings of beans or legumes per day” or “no more than one portion of refined carbohydrates per day”
- Eventually, let habit take the wheel. Assuming you have established good dietary habits, this will now do you just fine.
This latter is the point whereby the advice (that Aragon also champions) of “allow yourself an unhealthy indulgence of 10–20% of your daily food”, as a budget of “discretionary calories”, eventually becomes redundant—because chances are, you’re no longer craving that donut, and at a certain point, eating foods far outside the range of healthiness you usually eat is not even something that you would feel inclined to do if offered.
But until that kicks in, allow yourself that budget of whatever unhealthy thing you enjoy, and (this next part is important…) do enjoy it.
Because it is no good whatsoever eating that cream-filled chocolate croissant and then feeling guilty about it; that’s the dichotomous thinking we had back in the 80s. Decide in advance you’re going to eat and enjoy it, then eat and enjoy it, then look back on it with a sense of “that was enjoyable” and move on.
The flipside of this is that the importance of allowing oneself a “little treat” is that doing so actively helps ensure that the “little treat” remains “little”. Without giving oneself permission, then suddenly, “well, since I broke my diet, I might as well throw the whole thing out the window and try again on Monday”.
On enjoying food fully, by the way:
Mindful Eating: How To Get More Nutrition Out Of The Same Food
Want to know more from Alan Aragon?
Today we’ve been working heavily from this book of his; we haven’t reviewed it yet, but we do recommend checking it out:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Mediterranean Air Fryer Cookbook – by Naomi Lane
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are Mediterranean Diet cookbooks, and there are air fryer cookbooks. And then there are (a surprisingly large intersection of!) Mediterranean Diet air fryer cookbooks. We wanted to feature one of them in today’s newsletter… And as part of the selection process, looked through quite a stack of them, and honestly, were quite disappointed with many. This one, however, was one of the ones that stood out for its quality of both content and clarity, and after a more thorough reading, we now present it to you:
Naomi Lane is a professional dietician, chef, recipe developer, and food writer… And it shows, on all counts.
She covers what the Mediterranean diet is, and she covers far more than this reviewer knew it was even possible to know about the use of an air fryer. That alone would make the book a worthy purchase already.
The bulk of the book is the promised 200 recipes. They cover assorted dietary requirements (gluten-free, dairy-free, etc) while keeping to the Mediterranean Diet.
The recipes are super clear, just what you need to know, no reading through a nostalgic storytime first to find things. Also no pictures, which will be a plus for some readers and a minus for others. The recipes also come complete with nutritional information for each meal (including sodium), so you don’t have to do your own calculations!
Bottom line: this is the Mediterranean Diet air fryer cook book. Get it, thank us later!
Get your copy of “Mediterranean Air Fryer Cookbook” on Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: