Reading As A Cognitive Exercise
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Reading, Better
It is relatively uncontroversial to say that reading is good for cognitive health, but we don’t like to make claims without science if we can help it, so let’s get started:
There was a 2021 study, which found that even when controlling for many other factors, including highest level of education, socioeconomic status, and generalized pre-morbid intelligence:
❝high reading activity, as defined by almost daily reading, was associated with lower odds of cognitive decline, compared to low reading activity❞
Source: Can reading increase cognitive reserve?
However, not all reading is the same. And this isn’t just about complexity or size of vocabulary, either. It’s about engagement.
And that level of engagement remains the key factor, no matter how quickly or slowly someone reads, as the brain tends to automatically adjust reading speed per complexity, because the brain’s “processing speed” remains the same:
Read more: Cognitive coupling during reading
Everyone’s “processing speed” is different (and is associated with generalized intelligence and executive functions), though as a general rule of thumb, the more we practice it, the faster our processing speed gets. So if you balked at the notion of “generalized intelligence” being a factor, be reassured that this association goes both ways.
So is the key to just read more?
That’s a great first step! But…
The key factor still remains: engagement.
So what does that mean?
It is not just the text that engages you. You must also engage the text!
This is akin to the difference between learning to drive by watching someone else do it, and learning by getting behind the wheel and having a go.
When it comes to reading, it should not be a purely passive thing. Sure, if you are reading a fiction book at bedtime, get lost in it, by all means. But when it comes to non-fiction reading, engage with it actively!
For example, I (your writer here, hi), when reading non-fiction:
- Read at what is generally considered an unusually fast pace, but
- Write so many notes in the margins of physical books, and
- Write so many notes using the “Notes” function on my Kindle
And this isn’t just like a studious student taking notes. Half the time I am…
- objecting to content (disagreeing with the author), or
- at least questioning it, or which is especially important, or
- noting down questions that came to my mind as a result of what I am reading.
This latter is a bit like:
- when you are reading 10almonds, sometimes you will follow our links and go off down a research rabbit-hole of your own, and that’s great!
- sometimes you will disagree with something and write to tell us, and that’s great too (when this happens, one or the other or all of us will learn something, and yes, we have published corrections before now)!
- sometimes what you read here will prompt a further question, and you’ll send that to us, and guess what, also great! We love questions.
Now, if your enjoyment of 10almonds is entirely passive, don’t let us stop you (we know our readers like quick-and-easy knowledge, and that’s good too), it’s just, the more you actively engage with it, the more you’ll get out of it.
This, by the way, was also a lifelong habit of Leonardo da Vinci, which you can read about here:
How to Think Like Leonardo da Vinci: Seven Steps to Genius Every Day – by Michael J. Gelb
a very good book that we reviewed last year
How you read (i.e. what medium) matters too!
Are you reading this on a desktop/laptop, or a mobile device? That difference could matter more than the difference between paper and digital, according to this study from 2020 that found…
❝The cumulation of evidence from this and previous studies suggests that reading on a tablet affords different interactions between the reader and the text than reading on a computer screen.
Reading on a tablet might be more similar to reading on paper, and this may impact the attentional processes during reading❞
What if my mind wanders easily?
You can either go with it, or train to improve focus.
Going with it: just make sure you have more engaging reading to get distracted by. It’s all good.
Training focus: this is trickier, but worthwhile, as executive function (you will remember from earlier) was an important factor too, and training focus is training executive function.
As for one way to do that…
If you’d like a primer for getting going with that, then you may enjoy our previous main feature:
No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Not To Die – by Dr. Michael Greger
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We previously reviewed this book some years ago, but we’re revisiting it now because:
- It really is a book that should be in every healthspan-enjoyer’s collection
- Our book reviews back then were not as comprehensive as now (though we still generally try to fit into the “it takes about one minute to read this review” idea, sometimes we’ll spend a little extra time).
Dr. Greger (of “Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen” fame) outlines for us in cold hard facts and stats what’s most likely to be our cause of death. While this is not a cheery premise for a book, he then sets out to work back from there—what could have prevented those specific things?
Thus, while the book doesn’t confer immortality (the title is not “how to not die”, after all), it does teach us how not to die—i.e, from heart disease, lung diseases, brain diseases, digestive cancers, infections, diabetes, high blood pressure, liver disease, blood cancers, kidney disease, breast cancer, suicidal depression, prostate cancer, Parkinson’s disease, and even iatrogenic causes.
This it does with a lot of solid science, explained for the layperson, and/but without holding back when it comes to big words, and a lot of them, at that. If you want to add in daily exercises, just lifting the book could be a start; weighing in at 678 pages, it’s an information-dense tome that’s more likely to be sifted through than read cover-to-cover.
The style is thus dense science somewhat editorialized for lay readability, and well-evidenced with around 3,000 citations. That’s not a typo; there are 178 pages of bibliography at the back with about 15–20 scientific references per page.
In terms of practical use, he does also devote chapters to that, it’s not just all textbook. Indeed, he discusses the reasonings behind the items, portion sizes, and quantities of his “daily dozen” foods, so that the reader will understand how much bang-for-buck they deliver, and then it’ll seem a lot less like an arbitrary list, and more likely to be adopted and maintained.
Bottom line: if you care about not getting life-threatening illnesses (which at the end of the day, come to most people at some point), then this book is a must-read.
Share This Post
-
Lose Weight (Healthily!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Do You Have To Lose?
For something that’s a very commonly sought-after thing, we’ve not yet done a main feature specifically about how to lose weight, so we’re going to do that today, and make it part of a three-part series about changing one’s weight:
- Losing weight (specifically, losing fat)
- Gaining weight (specifically, gaining muscle)
- Gaining weight (specifically, gaining fat)
And yes, that last one is something that some people want/need to do (healthily!), and want/need help with that.
There will be, however, no need for a “losing muscle” article, because (even though sometimes a person might have some reason to want to do this), it’s really just a case of “those things we said for gaining muscle? Don’t do those and the muscle will atrophy naturally”.
One reason we’ve not covered this before is because the association between weight loss and good health is not nearly so strong as the weight loss industry would have you believe:
And, while BMI is not a useful measure of health in general, it’s worth noting that over the age of 65, a BMI of 27 (which is in the high end of “overweight”, without being obese) is associated with the lowest all-cause mortality:
BMI and all-cause mortality in older adults: a meta-analysis
Important: the above does mean that for very many of our readers, weight loss would not actually be healthy.
Today’s article is intended as a guide only for those who are sure that weight loss is the correct path forward. If in doubt, please talk to your doctor.
With that in mind…
Start in the kitchen
You will not be able to exercise well if your body is malnourished.
Counterintuitively, malnourishment and obesity often go hand-in-hand, partly for this reason.
Important: it’s not the calories in your food; it’s the food in your calories
See also: Mythbusting Calories
The kind of diet that most readily produces unhealthy overweight, the diet that nutritional scientists often call the “Standard American Diet”, or “SAD” for short, is high on calories but low on nutrients.
So you will want to flip this, and focus on enjoying nutrient-dense whole foods.
The Mediterranean Diet is the current “gold standard” in this regard, so for your interest we offer:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet
And since you may be wondering:
Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
The dining room is the next most important place
Many people do not appreciate food enough for good health. The trick here is, having prepared a nice meal, to actually take the time to enjoy it.
It can be tempting when hungry (or just plain busy) to want to wolf down dinner in 47 seconds, but that is the metabolic equivalent of “oh no, our campfire needs more fuel, let’s spray it with a gallon of gasoline”.
To counter this, here’s the very good advice of Dr. Rupy Aujla, “The Kitchen Doctor”:
Interoception & Mindful Eating
The bedroom is important too
You snooze, you lose… Visceral belly fat, anyway! We’ve talked before about how waist circumference is a better indicator of metabolic health than BMI, and in our article about trimming that down, we covered how good sleep is critical for one’s waistline:
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It
Exercise, yes! But in one important way.
There are various types of exercise that are good for various kinds of health, but there’s only one type of exercise that is good for boosting one’s metabolism.
Whereas most kinds of exercise will raise one’s metabolism while exercising, and then lower it afterwards (to below its previous metabolic base rate!) to compensate, high-intensity interval training (HIIT) will raise your metabolism while training, and for two hours afterwards:
…which means that unlike most kinds of exercise, HIIT actually works for fat loss:
So if you’d like to take up HIIT, here’s how:
How (And Why) To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Want more?
Check out our previous article about specifically how to…
Burn! How To Boost Your Metabolism
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Coconut Milk vs Soy Milk – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing coconut milk to soy milk, we picked the soy.
Why?
First, because there are many kinds of both, let’s be clear which ones we’re comparing. For both, we picked the healthiest options commonly available, which were:
- Soy milk, unsweetened, fortified
- Coconut milk, raw (liquid expressed from grated meat and water)
Macronutrients are our first consideration; coconut milk has about 3x the carbs and about 14x the fat. Now, the fats are famously healthy medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), but still, one cup of coconut milk contains about 2.5x the recommended daily amount of saturated fat, so it’s wise to go easy on that. Coconut milk also has about 4x the fiber, but still, because the saturated fat difference, we’re calling this one a win for soy milk.
In the category of vitamins, the fortified soy milk wins. In case you’re curious: milk in general (animal or plant) is generally fortified with vitamin D (in N. America, anyway; other places may vary), and vitamin B12. In this case, the soy milk has those, plus some natural vitamins, meaning it has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, and D, while coconut milk has more of vitamins B3, B5, and C. A fair win for soy milk.
When it comes to minerals, the only fortification for the soy milk is calcium, of which it has more than 7x what coconut milk has. The coconut milk, however, has more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium. An easy win for coconut milk.
Adding up the sections gives us a win for soy milk—but if consumed in moderation as part of a diet otherwise low in saturated fat, a case could be made for the coconut.
The real take-away here today is not this specific head-to-head but rather: milks (animal or plant) vary a lot, have a lot of different fortifications and/or additives, and yes that goes even for brands (cow milk brands do this a lot) who don’t advertise their additives because their branding is going for a “natural” look. So, read labels, and make informed decisions about which additives you do or don’t want.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Healthy Habits for Managing & Reversing Prediabetes – by Dr. Marie Feldman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The book doesn’t assume prior knowledge, and does explain the science of diabetes, prediabetes, the terms and the symptoms, what’s going on inside, etc—before getting onto the main meat of the book, the tips.
The promised 100 tips are varied in their application; they range from diet and exercise, to matters of sleep, stress, and even love.
There are bonus tips too! For example, an appendix covers “tips for healthier eating out” (i.e. in restaurants etc) and a grocery list to ensure your pantry is good for defending you against prediabetes.
The writing style is very accessible pop-science; this isn’t like reading some dry academic paper—though it does cite its sources for claims, which we always love to see.
Bottom line: if you’d like to proof yourself against prediabetes, and are looking for “small things that add up” habits to get into to achieve that, this book is an excellent first choice.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How light tells you when to sleep, focus and poo
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is the next article in our ‘Light and health’ series, where we look at how light affects our physical and mental health in sometimes surprising ways. Read other articles in the series.
Exposure to light is crucial for our physical and mental health, as this and future articles in the series will show.
But the timing of that light exposure is also crucial. This tells our body to wake up in the morning, when to poo and the time of day to best focus or be alert. When we’re exposed to light also controls our body temperature, blood pressure and even chemical reactions in our body.
But how does our body know when it’s time to do all this? And what’s light got to do with it?
nymphoenix/Shutterstock What is the body clock, actually?
One of the key roles of light is to re-set our body clock, also known as the circadian clock. This works like an internal oscillator, similar to an actual clock, ticking away as you read this article.
But rather than ticking you can hear, the body clock is a network of genes and proteins that regulate each other. This network sends signals to organs via hormones and the nervous system. These complex loops of interactions and communications have a rhythm of about 24 hours.
In fact, we don’t have one clock, we have trillions of body clocks throughout the body. The central clock is in the hypothalamus region of the brain, and each cell in every organ has its own. These clocks work in concert to help us adapt to the daily cycle of light and dark, aligning our body’s functions with the time of day.
However, our body clock is not precise and works to a rhythm of about 24 hours (24 hours 30 minutes on average). So every morning, the central clock needs to be reset, signalling the start of a new day. This is why light is so important.
The central clock is directly connected to light-sensing cells in our retinas (the back of the eye). This daily re-setting of the body clock with morning light is essential for ensuring our body works well, in sync with our environment.
In parallel, when we eat food also plays a role in re-setting the body clock, but this time the clock in organs other than the brain, such as the liver, kidneys or the gut.
So it’s easy to see how our daily routines are closely linked with our body clocks. And in turn, our body clocks shape how our body works at set times of the day.
What time of day?
Matt Garrow/The Conversation. Adapted from Delos, CC BY Let’s take a closer look at sleep
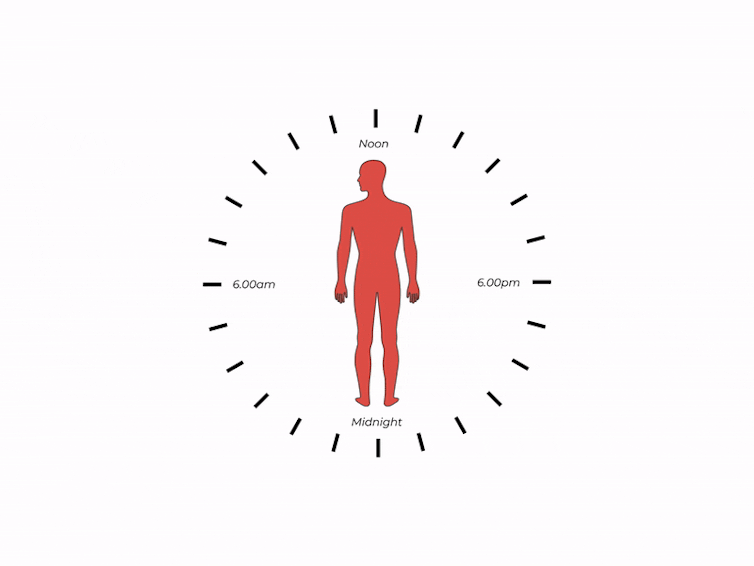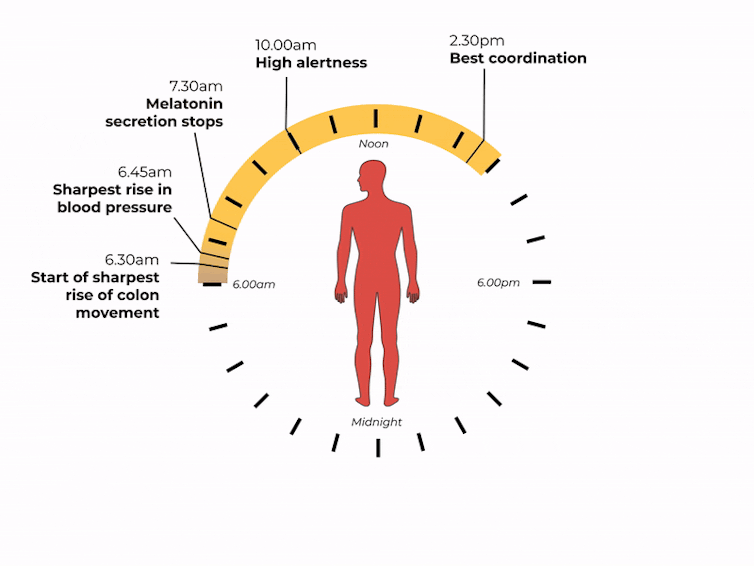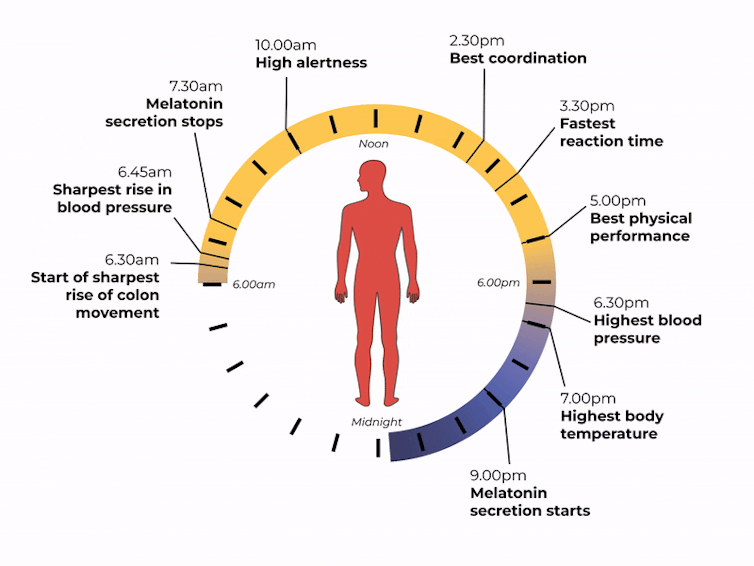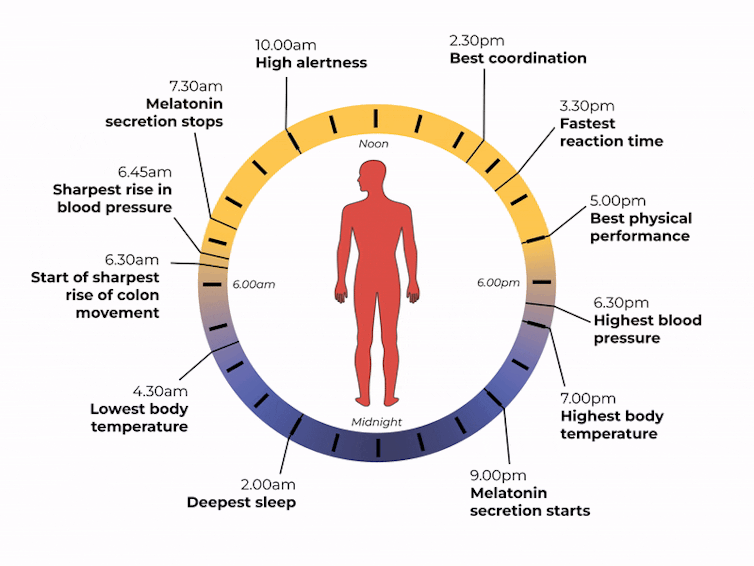
The naturally occurring brain hormone melatonin is linked to our central clock and makes us feel sleepy at certain times of day. When it’s light, our body stops making melatonin (its production is inhibited) and we are alert. Closer to bedtime, the hormone is made, then secreted, making us feel drowsy.
Our sleep is also partly controlled by our genes, which are part of our central clock. These genes influence our chronotype – whether we are a “lark” (early riser), “night owl” (late sleeper) or a “dove” (somewhere in between).
But exposure to light at night when we are supposed to be sleeping can have harmful effects. Even dim light from light pollution can impair our heart rate and how we metabolise sugar (glucose), may lead to psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety and bipolar disorder, and increases the overall risk of premature death.
The main reason for these harmful effects is that light “at the wrong time” disturbs the body clock, and these effects are more pronounced for “night owls”.
This “misaligned” exposure to light is also connected to the detrimental health effects we often see in people who work night shifts, such as an increased risk of cancer, diabetes and heart disease.
How about the gut?
Digestion also follows a circadian rhythm. Muscles in the colon that help move waste are more active during the day and slow down at night.
The most significant increase in colon movement starts at 6.30am. This is one of the reasons why most people feel the urge to poo in the early morning rather than at night.
The gut’s day-night rhythm is a direct result of the action of the gut’s own clock and the central clock (which synchronises the gut with the rest of the body). It’s also influenced by when we eat.
At 6.30am, your gut really begins to get going for the day. Rendra Dria Septia Aji/Shutterstock How about focusing?
Our body clock also helps control our attention and alertness levels by changing how our brain functions at certain times of day. Attention and alertness levels improve in the afternoon and evening but dip during the night and early morning.
Those fluctuations impact performance and can lead to decreased productivity and an increased risk of errors and accidents during the less-alert hours.
So it’s important to perform certain tasks that require our attention at certain times of day. That includes driving. In fact, disruption of the circadian clock at the start of daylight savings – when our body hasn’t had a chance to adapt to the clocks changing – increases the risk of a car accident, particularly in the morning.
What else does our body clock control?
Our body clock influences many other aspects of our biology, including:
- physical performance by controlling the activity of our muscles
- blood pressure by controlling the system of hormones involved in regulating our blood volume and blood vessels
- body temperature by controlling our metabolism and our level of physical activity
- how our body handles drugs and toxins by controlling enzymes involved in how the liver and kidneys eliminate these substances from the body.
If you can, avoid driving long distances at night, as you’ll be less alert. trendobjects/Shutterstock Morning light is important
But what does this all mean for us? Exposure to light, especially in the morning, is crucial for synchronising our circadian clock and bodily functions.
As well as setting us up for a good night’s sleep, increased morning light exposure benefits our mental health and reduces the risk of obesity. So boosting our exposure to morning light – for example, by going for a walk, or having breakfast outside – can directly benefit our mental and metabolic health.
However, there are other aspects about which we have less control, including the genes that control our body clock.
Frederic Gachon, Associate Professor, Physiology of Circadian Rhythms, Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland and Benjamin Weger, NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Doctors From 15 Specialties Tell The Worst Common Mistakes People Make
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Whatever your professional background, you probably know many things about it that are very obvious to you, but that most people don’t know. So it is for doctors too; here are the things that doctors from 15 specialties would never do, and thus advise people against doing:
Better safe than sorry
We’ll leap straight into it:
- General Surgery: avoid rushing into musculoskeletal or spinal surgery unless absolutely necessary; conservative treatments like physical therapy are often effective.
- Interventional Gastroenterology: avoid long-term, around-the-clock use of anti-inflammatory pain medications (e.g. Ibuprofen and friends) to prevent stomach ulcers.
- Podiatry: never place feet on the car dashboard due to the risk of severe injuries from airbag deployment.
- Rheumatology: avoid daily use of high heels to prevent joint and foot deformities, bunions, and pain.
- Otorhinolaryngology: never smoke, as it can lead to severe consequences like laryngectomy and other life-altering conditions.
- Pediatrics: avoid dangerous activities for children, such as swimming alone, eating choking hazards, biking or skiing without a helmet, or consuming raw meat/fish/dairy. Also, be cautious with firearms in homes.
- Orthopedic Surgery: avoid riding motorcycles and handling fireworks due to high risks of accidents.
- Emergency Medicine: never drink and drive or ride ATVs. Always use eye protection during activities like woodworking.
- Ophthalmology: always wear safety glasses during activities like grinding metal or woodworking. Sunglasses are essential to prevent UV damage even on cloudy days.
- Urology: avoid shaving pubic hair if diabetic or immunocompromised to prevent severe infections like Fournier’s gangrene.
- Gastroenterology: do not use gut health supplements as they lack proven efficacy and are often a waste of money*
- Plastic Surgery: avoid contour threads (barbed sutures for facial rejuvenation) and butt implants due to risks like infection, complications, and poor outcomes.
- Psychiatry: never take recreational drugs from unknown sources to avoid accidental overdoses, especially from substances laced with fentanyl. Carry Narcan for emergencies.
- Dermatology: use sunscreen daily to prevent skin cancer, aging, pigmentation issues, and texture problems caused by UV exposure.
- Cardiology: avoid the carnivore diet as it increases heart disease risks due to its negligible fiber content and high saturated fat intake.
*We had an article about this a while back; part of the problem is that taking probiotics without prebiotics can mean your new bacteria just die in about 20 minutes, which is their approximate lifespan in which to multiply or else die out. Similar problems arise if taking them with sugar that feeds their competitors instead. See: Stop Sabotaging Your Gut!
For more on each of these, in the words of the respective doctors, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: