Who you are and where you live shouldn’t determine your ability to survive cancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In Canada, nearly everyone has a cancer story to share. It affects one in every two people, and despite improvements in cancer survivorship, one out of every four people affected by cancer still will die from it.
As a scientist dedicated to cancer care, I work directly with patients to reimagine a system that was never designed for them in the first place – a system in which your quality of care depends on social drivers like your appearance, your bank statements and your postal code.
We know that poverty, poor nutrition, housing instability and limited access to education and employment can contribute to both the development and progression of cancer. Quality nutrition and regular exercise reduce cancer risk but are contingent on affordable food options and the ability to stay active in safe, walkable neighbourhoods. Environmental hazards like air pollution and toxic waste elevate the risk of specific cancers, but are contingent on the built environment, laws safeguarding workers and the availability of affordable housing.
On a health-system level, we face implicit biases among care providers, a lack of health workforce competence in addressing the social determinants of health, and services that do not cater to the needs of marginalized individuals.
Indigenous peoples, racialized communities, those with low income and gender diverse individuals face the most discrimination in health care, resulting in inadequate experiences, missed diagnosis and avoidance of care. One patient living in subsidized housing told me, “You get treated like a piece of garbage – you come out and feel twice as bad.”
As Canadians, we benefit from a taxpayer funded health-care system that encompasses cancer care services. The average Canadian enjoys a life expectancy of more than 80 years and Canada boasts high cancer survival rates. While we have made incredible strides in cancer care, we must work together to ensure these benefits are equally shared amongst all people in Canada. We need to redesign systems of care so that they are:
- Anti-oppressive. We must begin by understanding and responding to historical and systemic racism that shapes cancer risk, access to care and quality of life for individuals facing marginalizing conditions. Without tackling the root causes, we will never be able to fully close the cancer care gap. This commitment involves undoing intergenerational trauma and harm through public policies that elevate the living and working conditions of all people.
- Patient-centric. We need to prioritize patient needs, preferences and values in all aspects of their health-care experience. This means tailoring treatments and services to individual patient needs. In policymaking, it involves creating policies that are informed by and responsive to the real-life experiences of patients. In research, it involves engaging patients in the research process and ensuring studies are relevant to and respectful of their unique perspectives and needs. This holistic approach ensures that patients’ perspectives are central to all aspects of health care.
- Socially just. We must strive for a society in which everyone has equal access to resources, opportunities and rights, and systemic inequalities and injustices are actively challenged and addressed. When redesigning the cancer care system, this involves proactive practices that create opportunities for all people, particularly those experiencing the most marginalization, to become involved in systemic health-care decision-making. A system that is responsive to the needs of the most marginalized will ultimately work better for all people.
Who you are, how you look, where you live and how much money you make should never be the difference between life and death. Let us commit to a future in which all people have the resources and support to prevent and treat cancer so that no one is left behind.
This article is republished from HealthyDebate under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Obesity Code – by Dr. Jason Fung
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Firstly, if you have already read Dr. Fung’s other book, The Diabetes Code, which we reviewed a little while ago, you can probably skip this one. It has mostly the same information, presented with a different focus.
While The Diabetes Code assumes you are diabetic, or prediabetic, or concerned about avoiding/reversing those conditions, The Obesity Code assumes you are obese, or heading in that direction, or otherwise are concerned about avoiding/reversing obesity.
What it’s not, though, is a weight loss book. Will it help if you want to lose weight? Yes, absolutely. But there is no talk here of weight loss goals, nor any motivational coaching, nor week-by-week plans, etc.
Instead, it’s more an informative textbook. With exactly the sort of philosophy we like here at 10almonds: putting information into people’s hands, so everyone can make the best decisions for themselves, rather than blindly following someone else’s program.
Dr. Fung explains why various dieting approaches don’t work, and how we can work around such things as our genetics, as well as most external factors except for poverty. He also talks us through how to change our body’s insulin response, and get our body working more like a lean machine and less like a larder for hard times.
Bottom line: this is a no-frills explanation of why your body does what it does when it comes to fat storage, and how to make it behave differently about that.
Share This Post
-
Fix Chronic Fatigue & Regain Your Energy, By Science
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chronic fatigue is on the rise. A lot of it appears to be Long COVID-related, but whether that’s the case for you or not, one thing that will make a big difference to your energy levels is something that French biochemist Jessie Inchauspé is here to explain:
Mitochondrial management
Inchauspé explains it in terms of a steam train; to keep running, it must have coal burning in its furnace. However, if more coal is delivered to the engine room faster than it can be put in the furnace and burned, and the coal just keeps on coming, the worker there will soon be overwhelmed trying to find places to put it all; the engine room will be full of coal, and the furnace will sputter and go out because the worker can’t even reach it on account of being buried in coal.
So it is with our glucose metabolism also. If we get spikes of glucose faster than our body can deal with them, it will overload the body’s ability to process that energy at all. Just like the steam train worker, our body will try! It’ll stuff that extra glucose wherever it can (storing as glycogen in the liver is a readily available option that’s easy to do and/but also gives you non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and isn’t quickly broken down into useable energy), and meanwhile, your actual mitochondria aren’t getting what they need (which is: a reliable, but gentle, influx of glucose).
You can imagine that the situation we described in the steam train isn’t good for the engine’s longevity, and the corresponding situation in the human body isn’t good for our mitochondria either (or our pancreas, or our liver, or… the list goes on). Indeed, damaged mitochondria affect exercise capacity and stress resilience—as well as being a long-term driver of cancer.
The remedy, of course, is blood sugar management. Specifically, avoiding glucose spikes. She has a list of 10 ways to do this (small changes to how we eat; what things to eat with what, in which order, etc) that make a huge measurable difference. For your convenience, we’ve linked those ten ways below; first though, if you’d like to hear it from Inchauspé directly (her style is very pleasant), enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- 10 Ways To Balance Your Blood Sugars ← this is the longer list she’s referring to in the video!
- How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver ← also relevant
Take care!
Share This Post
-
6 Daily Habits To Keep Your Brain Young & Sharp
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Without brain health, we do not have health. So here are six ways to keep it in order:
Food for thought
The six areas to focus on are as follows:
- Physical exercise: as we at 10almonds sometimes say, what’s good for the heart is good for the brain (because the brain is only as healthy as the circulation feeding it). For this reason, the recommendation here is for physical exercise that improves heart health—so, walking, running, swimming, dancing, etc.
- Healthy diet: shocking nobody, this is important too. Specifically, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy proteins and fats is important—partly for the heart benefits that give indirect benefits to the brain, and partly because the brain is built of stuff and so we have to consume that stuff in order to rebuild it (omega-3s features strongly here, for instance). Remember to hydrate, too! The body can’t do anything without water.
- Good sleep: yes, the famous 7–9 hours sleep per night, and yes, even at your age, whatever that might be. This is important for memory consolidation, cell repair, toxin removal, and more. Sleep deprivation, on the other hand, leads to cognitive decline and brain shrinkage.
- Mental stimulation: ideally, engaging those parts of the brain you most wish to protect (e.g. language, memory, or whatever is most important to you).
- Social interaction: this one gets underestimated a lot, but it’s important to have meaningful conversations (not just polite smalltalk from a small menu of stock phrases), and that these should be two-way, i.e. involving both listening/reading and speaking/writing. Ideally, all four of those, which for most people means online and offline social interactions.
- Stress management: because chronic stress damages brain cells and accelerates cognitive decline, it’s important to manage that; practices like mindfulness meditation go a very long way and make a big difference.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Physical Exercises That Build Your Brain ← this is different from just exercising for one’s heart and thus the brain by extension, and rather, is specific exercises that strengthen specific parts of the brain.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Almonds vs Macadamias – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing almonds to macadamias, we picked the almonds.
Why?
It’s not just our pro-almonds bias:
In terms of macros, almonds have 3x the protein and as well as more fiber and carbs, the ratio of which latter two give almonds the lower glycemic index, while macadamias have more total fat, and 4x the saturated fat percentage. All in all, we say this is a win for almonds in this category.
In the category of vitamins, almonds have more of vitamins B2, B3, B9, E, and choline, while macadamias have more of vitamins B1, B5, B6, and C. A modest 5:4 win for almonds, unless we consider that almonds have more than 47x as much vitamin E (almonds are an exceptionally good source of vitamin E), in which case, a stronger win for almonds.
When it comes to minerals, almonds have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while macadamias have more manganese. A very clear win for almonds.
Adding up the sections makes for a convincing overall win for almonds, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Want the health benefits of strength training but not keen on the gym? Try ‘exercise snacking’
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The science is clear: resistance training is crucial to ageing well. Lifting weights (or doing bodyweight exercises like lunges, squats or push-ups) can help you live independently for longer, make your bones stronger, reduce your risk of diseases such as diabetes, and may even improve your sleep and mental health.
But not everyone loves the gym. Perhaps you feel you’re not a “gym person” and never will be, or you’re too old to start. Being a gym-goer can be expensive and time-consuming, and some people report feeling unwelcome or awkward at the gym.
The good news is you don’t need the gym, or lots of free time, to get the health benefits resistance training can offer.
You can try “exercise snacking” instead.
Pressmaster/Shutterstock What is exercise snacking?
Exercise snacking involves doing multiple shorter bouts (as little as 20 seconds) of exercise throughout the day – often with minimal or no equipment. It’s OK to have several hours of rest between.
You could do simple bodyweight exercises such as:
- chair sit-to-stand (squats)
- lunges
- box step-ups
- calf raises
- push-ups.
Exercise snacking like this can help improve muscle mass, strength and physical function.
It’s OK to hold onto a nearby object for balance, if you need. And doing these exercises regularly will also improve your balance. That, in turn, reduces your risk of falls and fractures.
OK I have done all those, now what?
Great! You can also try using resistance bands or dumbbells to do the previously mentioned five exercises as well as some of the following exercises:
When using resistance bands, make sure you hold them tightly and that they’re securely attached to an immovable object.
Exercise snacking works well when you pair it with an activity you do often throughout the day. Perhaps you could:
- do a few extra squats every time you get up from a bed or chair
- do some lunges during a TV ad break
- chuck in a few half squats while you’re waiting for your kettle to boil
- do a couple of elevated push-ups (where you support your body with your hands on a chair or a bench while doing the push-up) before tucking into lunch
- sneak in a couple of calf raises while you’re brushing your teeth.
Exercise snacking involves doing multiple shorter bouts (as little as 20 seconds) of exercise throughout the day. Cavan-Images/Shutterstock What does the evidence say about exercise snacking?
One study had older adults without a history of resistance training do exercise snacks at home twice per day for four weeks.
Each session involved five simple bodyweight exercises (chair sit-to-stand, seated knee extension, standing knee bends, marching on the spot, and standing calf raises). The participants did each exercise continuously for one minute, with a one-minute break between exercises.
These short and simple exercise sessions, which lasted just nine minutes, were enough to improve a person’s ability to stand up from a chair by 31% after four weeks (compared to a control group who didn’t exercise). Leg power and thigh muscle size improved, too.
Research involving one of us (Jackson Fyfe) has also shown older adults found “exercise snacking” feasible and enjoyable when done at home either once, twice, or three times per day for four weeks.
Exercise snacking may be a more sustainable approach to improve muscle health in those who don’t want to – or can’t – lift heavier weights in a gym.
A little can yield a lot
We know from other research that the more you exercise, the more likely it is you will keep exercising in future.
Very brief resistance training, albeit with heavier weights, may be more enjoyable than traditional approaches where people aim to do many, many sets.
We also know brief-and-frequent exercise sessions can break up periods of sedentary behaviour (which usually means sitting too much). Too much sitting increases your risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, whereas exercise snacking can help keep your blood sugar levels steady.
Of course, longer-term studies are needed. But the evidence we do have suggests exercise snacking really helps.
Just a few short exercise sessions can do you a world of good. eggeegg/Shutterstock Why does any of this matter?
As you age, you lose strength and mass in the muscles you use to walk, or stand up. Everyday tasks can become a struggle.
All this contributes to disability, hospitalisation, chronic disease, and reliance on community and residential aged care support.
By preserving your muscle mass and strength, you can:
- reduce joint pain
- get on with activities you enjoy
- live independently in your own home
- delay or even eliminate the need for expensive health care or residential aged care.
What if I walk a lot – is that enough?
Walking may maintain some level of lower body muscle mass, but it won’t preserve your upper body muscles.
If you find it difficult to get out of a chair, or can only walk short distances without getting out of breath, resistance training is the best way to regain some of the independence and function you’ve lost.
It’s even more important for women, as muscle mass and strength are typically lower in older women than men. And if you’ve been diagnosed with osteoporosis, which is more common in older women than men, resistance exercise snacking at home can improve your balance, strength, and bone mineral density. All of this reduces the risk of falls and fractures.
You don’t need heavy weights or fancy equipment to benefit from resistance training.
So, will you start exercise snacking today?
Justin Keogh, Associate Dean of Research, Faculty of Health Sciences and Medicine, Bond University and Jackson Fyfe, Senior Lecturer, Strength and Conditioning Sciences, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What’s the difference between shyness and social anxiety?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s the difference? is a new editorial product that explains the similarities and differences between commonly confused health and medical terms, and why they matter.
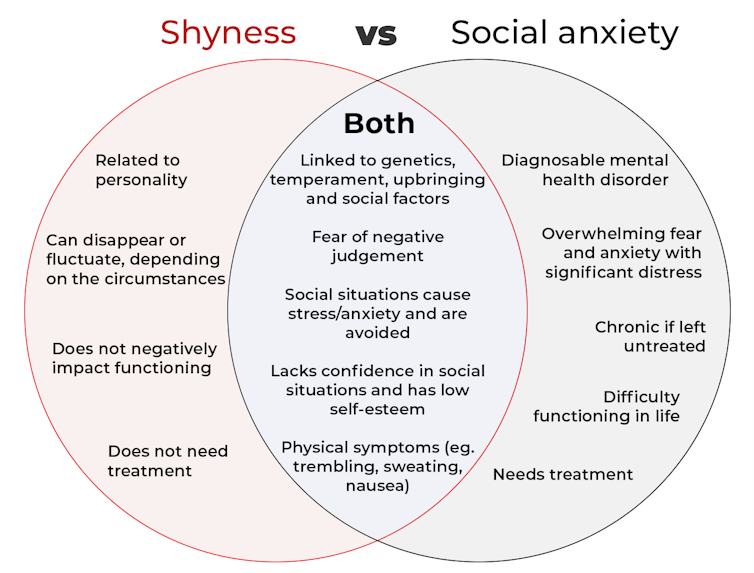
The terms “shyness” and “social anxiety” are often used interchangeably because they both involve feeling uncomfortable in social situations.
However, feeling shy, or having a shy personality, is not the same as experiencing social anxiety (short for “social anxiety disorder”).
Here are some of the similarities and differences, and what the distinction means.
pathdoc/Shutterstock How are they similar?
It can be normal to feel nervous or even stressed in new social situations or when interacting with new people. And everyone differs in how comfortable they feel when interacting with others.
For people who are shy or socially anxious, social situations can be very uncomfortable, stressful or even threatening. There can be a strong desire to avoid these situations.
People who are shy or socially anxious may respond with “flight” (by withdrawing from the situation or avoiding it entirely), “freeze” (by detaching themselves or feeling disconnected from their body), or “fawn” (by trying to appease or placate others).
A complex interaction of biological and environmental factors is also thought to influence the development of shyness and social anxiety.
For example, both shy children and adults with social anxiety have neural circuits that respond strongly to stressful social situations, such as being excluded or left out.
People who are shy or socially anxious commonly report physical symptoms of stress in certain situations, or even when anticipating them. These include sweating, blushing, trembling, an increased heart rate or hyperventilation.
How are they different?
Social anxiety is a diagnosable mental health condition and is an example of an anxiety disorder.
For people who struggle with social anxiety, social situations – including social interactions, being observed and performing in front of others – trigger intense fear or anxiety about being judged, criticised or rejected.
To be diagnosed with social anxiety disorder, social anxiety needs to be persistent (lasting more than six months) and have a significant negative impact on important areas of life such as work, school, relationships, and identity or sense of self.
Many adults with social anxiety report feeling shy, timid and lacking in confidence when they were a child. However, not all shy children go on to develop social anxiety. Also, feeling shy does not necessarily mean a person meets the criteria for social anxiety disorder.
People vary in how shy or outgoing they are, depending on where they are, who they are with and how comfortable they feel in the situation. This is particularly true for children, who sometimes appear reserved and shy with strangers and peers, and outgoing with known and trusted adults.
Individual differences in temperament, personality traits, early childhood experiences, family upbringing and environment, and parenting style, can also influence the extent to which people feel shy across social situations.
Not all shy children go on to develop social anxiety. 249 Anurak/Shutterstock However, people with social anxiety have overwhelming fears about embarrassing themselves or being negatively judged by others; they experience these fears consistently and across multiple social situations.
The intensity of this fear or anxiety often leads people to avoid situations. If avoiding a situation is not possible, they may engage in safety behaviours, such as looking at their phone, wearing sunglasses or rehearsing conversation topics.
The effect social anxiety can have on a person’s life can be far-reaching. It may include low self-esteem, breakdown of friendships or romantic relationships, difficulties pursuing and progressing in a career, and dropping out of study.
The impact this has on a person’s ability to lead a meaningful and fulfilling life, and the distress this causes, differentiates social anxiety from shyness.
Children can show similar signs or symptoms of social anxiety to adults. But they may also feel upset and teary, irritable, have temper tantrums, cling to their parents, or refuse to speak in certain situations.
If left untreated, social anxiety can set children and young people up for a future of missed opportunities, so early intervention is key. With professional and parental support, patience and guidance, children can be taught strategies to overcome social anxiety.
Why does the distinction matter?
Social anxiety disorder is a mental health condition that persists for people who do not receive adequate support or treatment.
Without treatment, it can lead to difficulties in education and at work, and in developing meaningful relationships.
Receiving a diagnosis of social anxiety disorder can be validating for some people as it recognises the level of distress and that its impact is more intense than shyness.
A diagnosis can also be an important first step in accessing appropriate, evidence-based treatment.
Different people have different support needs. However, clinical practice guidelines recommend cognitive-behavioural therapy (a kind of psychological therapy that teaches people practical coping skills). This is often used with exposure therapy (a kind of psychological therapy that helps people face their fears by breaking them down into a series of step-by-step activities). This combination is effective in-person, online and in brief treatments.
Treatment is available online as well as in-person. ImYanis/Shutterstock For more support or further reading
Online resources about social anxiety include:
- This Way Up’s online program for managing excessive shyness and fear of social situations
- Beyond Blue’s resources on social anxiety
- a guide to looking after yourself if you have social anxiety, from the Western Australian health department
- social anxiety online program for children and teens from the University of Queensland
- inroads, a self-guided online program for young adults who drink alcohol to manage their anxiety.
We thank the Black Dog Institute Lived Experience Advisory Network members for providing feedback and input for this article and our research.
Kayla Steele, Postdoctoral research fellow and clinical psychologist, UNSW Sydney and Jill Newby, Professor, NHMRC Emerging Leader & Clinical Psychologist, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: