A Guide to Rational Living – by Drs. Albert Ellis and Robert Harper
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve talked before about the evidence-based benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), and this book is indeed about CBT. In fact, it’s in many ways the book that popularized Third Wave CBT—in other words, CBT in its modern form.
Dr. Ellis’s specific branch of CBT is Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy, (REBT). What this means is using rationality to rewire emotions so that we’re not constantly sabotaging ourselves and our lives.
This is very much a “for the masses” book and doesn’t assume any prior knowledge of psychology, therapy, or psychotherapy. Or, for that matter, philosophy, since Stoic philosopher Epictetus had a lot to say that influenced Dr. Ellis’s work, too!
This book has also been described as “a self-help book for people who don’t like self-help books”… and certainly that Stoicism we mentioned does give the work a very different feel than a lot of books on the market.
The authors kick off with an initial chapter “How far can you go with self-therapy?”, and the answer is: quite far, even if it’s not a panacea. Everything has its limitations, and this book is no exception. On the other hand…
What the book does offer is a whole stack of tools, resources, and “How to…” chapters. In fact, there are so many “How to…” items in this book that, while it can be read cover-to-cover, it can also be used simply as a dip-in reference guide to refer to in times of need.
Bottom line: this book is highly recommendable to anyone and everyone, and if you don’t have it on your bookshelf, you should.
Click here to check out “A Guide To Rational Living” on Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Happens To Your Body When You Do Squats Every Day-Not Just For Legs!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Squat Every Day? Yes, Please!
It’s back to basics with this video (below). Passion for Health’s video, “What Happens To Your Body When You Do Squats Every Day-Not Just For Legs!” really brings home how squats aren’t just a one-trick pony for your legs.
The humble bodyweight squat is shown to contribute to everything from bolstering all-around lower body strength to bettering bone density and increasing metabolism.
Indeed, squats are so powerful that we reviewed a whole book that focuses just on the topic of squatting. Other, broader books on exercise also focus on the positive impacts that squatting can make.
A proper squat goes beyond your legs, engaging your core, enhancing joint health, and, some argue, can lead to improved balance and circulation.
(Plus, they’re easy to execute, given they can be done anywhere, without any equipment).
This is probably why Luigi Fontana and Dr Rangan Chatterjee have spoken about the benefits of squatting.
How Should We Start?
The video goes beyond the ‘why’ and delves into the ‘how’, offering step-by-step squatting techniques.
It answers the burning question: should you really be doing squats every day?
(Hint: the answer is most likely “yes”).
Of course, some of us may not be able to squat, and for those, we’ll feature alternatives in a future article.
For beginners, the advice is to start slow, aiming for 10 repetitions. You can gradually increase that count as you feel your muscles strengthen. Experienced gym-goers might push for 20 or more reps, adding variations like jump squats for an extra challenge.
The key takeaway is to listen to your body and ensure rest days for muscle recovery.
At the end of the day, Passion for Health’s video is a treasure trove for squat lovers, from novices to the seasoned, and insists on the importance of form, frequency, and listening to one’s body.
How did you find that video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Share This Post
-
10 Oft-Ignored Symptoms Of Diabetes
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Due in part to its prevalence and manageability, diabetes is often viewed as more of an inconvenience than an existential threat. While very few people in countries with decent healthcare die of diabetes directly (such as by diabetic ketoacidosis, which is very unpleasant, and happens disproportionately in the US where insulin is sold with a 500%–3000% markup in price compared to other countries), many more die of complications arising from comorbidities, and as for what comorbidities come with diabetes, well, it increases your risk for almost everything.
So, while for most people diabetes is by no means a death sentence, it is something that means you’ll now have to watch out for pretty much everything else too. On which note, Dr. Siobhan Deshauer is here with things to be aware of:
More than your waistline
Some of these are early symptoms (even appearing in the prediabetic stage, so can be considered an early warning for diabetes), some are later risks (it’s unlikely you’ll lose your feet from diabetic neuropathy complications before noticing that you are diabetic), but all and any of them are good reason to speak with your doctor sooner rather than later:
- Polyuria: waking up multiple times at night to urinate due to excess glucose spilling into the urine.
- Increased thirst: dehydration from frequent urination leads to excessive thirst, creating a cycle.
- Acanthosis nigricans: dark, velvety patches on areas like the neck, armpits, or groin, signalling insulin resistance.
- Skin tags: multiple skin tags in areas of friction may indicate insulin resistance.
- Recurrent Infections: high blood sugar weakens the immune system, making skin infections, UTIs, and yeast infections more common.
- Diabetic stiff hand syndrome: stiffness in hands, limited movement, or a “positive prayer sign” caused by sugar binding to skin and tendon proteins.
- Frozen shoulder and trigger finger: pain and limited movement in the shoulder or fingers, with a snapping sensation when moving inflamed tendons.
- Neuropathy: numbness, tingling, or pain in hands and feet due to nerve and blood vessel damage, often leading to foot deformities like Charcot foot.
- Diabetic foot infections: poor sensation, weakened immune response, and slow healing can result in severe infections and potential amputations.
- Gastroparesis: damage to stomach nerves causes delayed digestion, leading to bloating, nausea, and erratic blood sugar levels.
For more on all of these, plus some visuals of the things like what exactly is a “positive prayer sign”, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Cost of Insulin by Country 2024 ← after the US, the next most expensive country is Chile, at around 1/5 of the price; the cheapest listed is Turkey, at around 1/33 of the price.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Beetroot vs Carrot – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing beetroot to carrot, we picked the carrot.
Why?
It was close! And beetroot does have its advantages, but we say carrot wins on balance.
In terms of macros, these two root vegetables are close to identical, down to both having 9.57g carbs per 100g, and 2.8g fiber per 100g. Technically, beetroot has a smidgen more protein, but nobody’s eating these for their tiny protein content.
When it comes to vitamins, it’s not close and the margins are mostly huge: carrots have a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, C, E, K, and choline, while beetroot has more vitamin B9.
In the category of minerals, superficially it swings the other way, but the margins this time are small. Nevertheless, beetroot has more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while carrots have more calcium.
This would make things, on balance, a tie: equal on macros, carrots win on vitamins, beetroot wins on minerals.
But because of the relative margins of difference, carrots win the day, because they’re almost as good as beetroot on those minerals, whereas beetroot doesn’t come close to carrot on the vitamins.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
From Apples to Bees, and high-fructose C’s: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
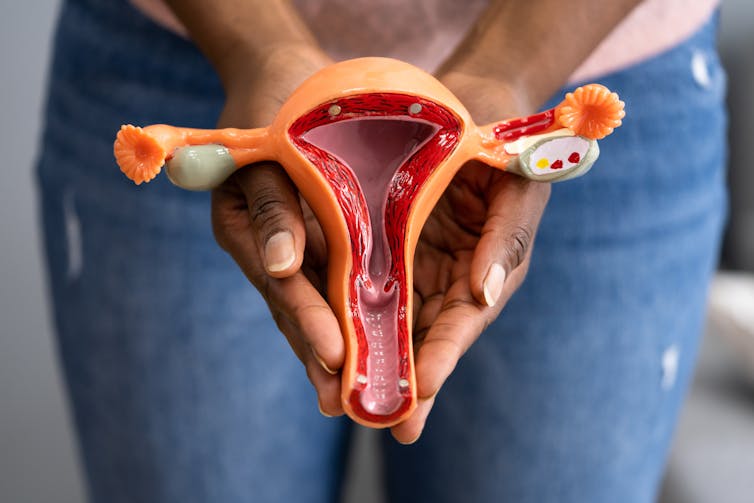
What’s the difference between period pain and endometriosis pain?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Menstruation, or a period, is the bleeding that occurs about monthly in healthy people born with a uterus, from puberty to menopause. This happens when the endometrium, the tissue that lines the inside of the uterus, is shed.
Endometriosis is a condition that occurs when endometrium-like tissue is found outside the uterus, usually within the pelvic cavity. It is often considered a major cause of pelvic pain.
Pelvic pain significantly impacts quality of life. But how can you tell the difference between period pain and endometriosis?
Polina Zimmerman/Pexels Periods and period pain
Periods involve shedding the 4-6 millimetre-thick endometrial lining from the inside of the uterus.
As the lining detaches from the wall of the uterus, the blood vessels which previously supplied the lining bleed. The uterine muscles contract, expelling the blood and crumbled endometrium.
The crumbled endometrium and blood mostly pass through the cervix and vagina. But almost everyone back-bleeds via their fallopian tubes into their pelvic cavity. This is known as “retrograde menstruation”.
Most of the lining is shed through the vagina. Andrey_Popov/Shutterstock The process of menstrual shedding is caused by inflammatory substances, which also cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, headaches, aches, pains, dizziness, feeling faint, as well as stimulating pain receptors.
These inflammatory substances are responsible for the pain and symptoms in the week before a period and the first few days.
For women with heavy periods, their worst days of pain are usually the heaviest days of their period, coinciding with more cramps to expel clots and more retrograde bleeding.
Many women also have pain when they are releasing an egg from their ovary at the time of ovulation. Ovulation or mid-cycle pain can be worse in those who bleed more, as those women are more likely to bleed into the ovulation follicle.
Around 90% of adolescents experience period pain. Among these adolescents, 20% will experience such severe period pain they need time off from school and miss activities. These symptoms are too often normalised, without validation or acknowledgement.
What about endometriosis?
Many symptoms have been attributed to endometriosis, including painful periods, pain with sex, bladder and bowel-related pain, low back pain and thigh pain.
Other pain-related conditions such migraines and chronic fatigue have also been linked to endometriosis. But these other pain-related symptoms occur equally often in people with pelvic pain who don’t have endometriosis.
One in five adolescents who menstrate experience severe symptoms. CGN089/Shutterstock Repeated, significant period and ovulation pain can eventually lead some people to develop persistent or chronic pelvic pain, which lasts longer than six months. This appears to occur through a process known as central sensitisation, where the brain becomes more sensitive to pain and other sensory stimuli.
Central sensitisation can occur in people with persistent pain, independent of the presence or absence of endometriosis.
Eventually, many people with period and/or persistent pelvic pain will have an operation called a laparoscopy, which allows surgeons to examine organs in the pelvis and abdomen, and diagnose and treat endometriosis.
Yet only 50% of those with identical pain symptoms who undergo a laparoscopy will end up having endometriosis.
Endometriosis is also found in pain-free women. So we cannot predict who does and doesn’t have endometriosis from symptoms alone.
How is this pain managed?
Endometriosis surgery usually involves removing lesions and adhesions. But at least 30% of people return to pre-surgery pain levels within six months or have more pain than before.
After surgery, emergency department presentations for pain are unchanged and 50% have repeat surgery within a few years.
Suppressing periods using hormonal therapies (such as continuous oral contraceptive pills or progesterone-only approaches) can suppress endometriosis and reduce or eliminate pain, independent of the presence or absence of endometriosis.
Not every type or dose of hormonal medications suits everyone, so medications need to be individualised.
The current gold-standard approach to manage persistent pelvic pain involves a multidisciplinary team approach, with the aim of achieving sustained remission and improving quality of life. This may include:
- physiotherapy for pelvic floor and other musculoskeletal problems
- management of bladder and bowel symptoms
- support for self-managing pain
- lifestyle changes including diet and exercise
- psychological or group therapy, as our moods, stress levels and childhood events can affect how we feel and experience pain.
Whether you have period pain, chronic pelvic pain or pain you think is associated with endometriosis, if you feel pain, it’s real. If it’s disrupting your life, you deserve to be taken seriously and treated as the whole person you are.
Sonia R. Grover, Senior Research Fellow, Murdoch Children’s Research Institute; Clinical Professor of Gynaecology, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How can I stop overthinking everything? A clinical psychologist offers solutions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As a clinical psychologist, I often have clients say they are having trouble with thoughts “on a loop” in their head, which they find difficult to manage.
While rumination and overthinking are often considered the same thing, they are slightly different (though linked). Rumination is having thoughts on repeat in our minds. This can lead to overthinking – analysing those thoughts without finding solutions or solving the problem.
It’s like a vinyl record playing the same part of the song over and over. With a record, this is usually because of a scratch. Why we overthink is a little more complicated.
We’re on the lookout for threats
Our brains are hardwired to look for threats, to make a plan to address those threats and keep us safe. Those perceived threats may be based on past experiences, or may be the “what ifs” we imagine could happen in the future.
Our “what ifs” are usually negative outcomes. These are what we call “hot thoughts” – they bring up a lot of emotion (particularly sadness, worry or anger), which means we can easily get stuck on those thoughts and keep going over them.
However, because they are about things that have either already happened or might happen in the future (but are not happening now), we cannot fix the problem, so we keep going over the same thoughts.
Who overthinks?
Most people find themselves in situations at one time or another when they overthink.
Some people are more likely to ruminate. People who have had prior challenges or experienced trauma may have come to expect threats and look for them more than people who have not had adversities.
Deep thinkers, people who are prone to anxiety or low mood, and those who are sensitive or feel emotions deeply are also more likely to ruminate and overthink.
We all overthink from time to time, but some people are more prone to rumination.
BĀBI/UnsplashAlso, when we are stressed, our emotions tend to be stronger and last longer, and our thoughts can be less accurate, which means we can get stuck on thoughts more than we would usually.
Being run down or physically unwell can also mean our thoughts are harder to tackle and manage.
Acknowledge your feelings
When thoughts go on repeat, it is helpful to use both emotion-focused and problem-focused strategies.
Being emotion-focused means figuring out how we feel about something and addressing those feelings. For example, we might feel regret, anger or sadness about something that has happened, or worry about something that might happen.
Acknowledging those emotions, using self-care techniques and accessing social support to talk about and manage your feelings will be helpful.
The second part is being problem-focused. Looking at what you would do differently (if the thoughts are about something from your past) and making a plan for dealing with future possibilities your thoughts are raising.
But it is difficult to plan for all eventualities, so this strategy has limited usefulness.
What is more helpful is to make a plan for one or two of the more likely possibilities and accept there may be things that happen you haven’t thought of.
Think about why these thoughts are showing up
Our feelings and experiences are information; it is important to ask what this information is telling you and why these thoughts are showing up now.
For example, university has just started again. Parents of high school leavers might be lying awake at night (which is when rumination and overthinking is common) worrying about their young person.
Think of what the information is telling you.
TheVisualsYouNeed/ShutterstockKnowing how you would respond to some more likely possibilities (such as they will need money, they might be lonely or homesick) might be helpful.
But overthinking is also a sign of a new stage in both your lives, and needing to accept less control over your child’s choices and lives, while wanting the best for them. Recognising this means you can also talk about those feelings with others.
Let the thoughts go
A useful way to manage rumination or overthinking is “change, accept, and let go”.
Challenge and change aspects of your thoughts where you can. For example, the chance that your young person will run out of money and have no food and starve (overthinking tends to lead to your brain coming up with catastrophic outcomes!) is not likely.
You could plan to check in with your child regularly about how they are coping financially and encourage them to access budgeting support from university services.
Your thoughts are just ideas. They are not necessarily true or accurate, but when we overthink and have them on repeat, they can start to feel true because they become familiar. Coming up with a more realistic thought can help stop the loop of the unhelpful thought.
Accepting your emotions and finding ways to manage those (good self-care, social support, communication with those close to you) will also be helpful. As will accepting that life inevitably involves a lack of complete control over outcomes and possibilities life may throw at us. What we do have control over is our reactions and behaviours.
Remember, you have a 100% success rate of getting through challenges up until this point. You might have wanted to do things differently (and can plan to do that) but nevertheless, you coped and got through.
So, the last part is letting go of the need to know exactly how things will turn out, and believing in your ability (and sometimes others’) to cope.
What else can you do?
A stressed out and tired brain will be more likely to overthink, leading to more stress and creating a cycle that can affect your wellbeing.
So it’s important to manage your stress levels by eating and sleeping well, moving your body, doing things you enjoy, seeing people you care about, and doing things that fuel your soul and spirit.
Find ways to manage your stress levels.
antoniodiaz/ShutterstockDistraction – with pleasurable activities and people who bring you joy – can also get your thoughts off repeat.
If you do find overthinking is affecting your life, and your levels of anxiety are rising or your mood is dropping (your sleep, appetite and enjoyment of life and people is being negatively affected), it might be time to talk to someone and get some strategies to manage.
When things become too difficult to manage yourself (or with the help of those close to you), a therapist can provide tools that have been proven to be helpful. Some helpful tools to manage worry and your thoughts can also be found here.
When you find yourself overthinking, think about why you are having “hot thoughts”, acknowledge your feelings and do some future-focused problem solving. But also accept life can be unpredictable and focus on having faith in your ability to cope.
Kirsty Ross, Associate Professor and Senior Clinical Psychologist, Massey University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sea salt to MSG, we picked the MSG.
Why?
Surprise! Or maybe not? The results of the poll for this one should be interesting, and will help us know whether we need to keep mentioning in every second recipe that MSG is a healthier alternative to salt.
First of all, two things:
- Don’t be fooled by their respective names, and/or with such, an appeal to naturalism. For example, hydroxybenzoic acids are a major group of beneficial phenolic compounds, whereas hemlock is a wildflower that grows in this writer’s garden and will kill you if you eat it. Actually hydroxybenzoic acids also grow here (on the apple tree), but that’s not the point. The point is: worry less about names, and more about evidence!
- Don’t be fooled by the packaging. A lot of products go for “greenwashing” of one kind or another. You’re not eating the packaging (hopefully), so don’t be swayed by a graphic designer’s implementation of a marketing team’s aesthetic choices.
If naturalism is for some reason very important to you though, do bear in mind that glutamates occur generously in many common foodstuffs (tomatoes are a fine, healthy example) and eating tomato in the presence of salt will have the same biochemical effect as eating MSG, because it’s the same chemicals.
Since there are bad rumors about MSG’s safety, especially in the US where there is often a strong distrust of anything associated with China (actually MSG was first isolated in Japan, more than 100 years ago, by Japanese biochemist Dr. Kikunae Ikeda, but that gets drowned out by the “Chinese Restaurant Syndrome” fear in the US), know that this has resulted in MSG being one of the most-studied food additives in the last 40 years or so, with many teams of scientists trying to determine its risks and not finding any (aside from the same that could be said of any substance; anything in sufficient excess will kill you, including water or oxygen).
Well, that’s all been about safety, but what makes it healthier than sea salt?
Simply, it has about ⅓ of the sodium content, that’s all. So, if you are laboring all day in a field under the hot summer sun, then probably the sea salt will be healthier, to replenish more of the sodium you lost through sweat. But for most people most of the time, having less sodium rather than more is the healthier option.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
- MSG vs. Salt: Sodium Comparison ← here be chemistry
- More Salt, Not Less? ← No
- Pink Himalayan Salt: Health Facts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: