Gut Feelings – by Dr Will Cole
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
More and more, science is uncovering links between our gut health and the rest of our health—including our mental health! We all know “get some fiber and consider probiotics”, but what else is there that we can do?
Quite a lot, actually. And part of it, which Dr. Cole also explores, is the fact that the gut-brain highway is a two-way street!
The book looks a lot especially at the particular relationship between shame and eating. The shame need not initially be about eating, though it can certainly end up that way too. But any kind of shame—be it relating to one’s body, work, relationship, or anything else, can not only have a direct effect on the gut, but indirect too:
Once our “eating our feelings” instinct kicks in, things can spiral from there, after all.
So, Dr. Cole walks us through tackling this from both sides—nutrition and psychology. With chapters full of tips and tricks, plus a 21-day plan (not a diet plan, a habit integration plan), this book hits shame (and inflammation, incidentally) hard and leads us into much healthier habits and cycles.
In short: if you’d like to have a better relationship with your food, improve your gut health, and/or reduce inflammation, this is definitely a book for you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
True Age – by Dr. Morgan Levine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Yesterday’s book review (Counterclockwise) was about psychological factors affecting physical aging (progression or reversal thereof); today we have a book about the physiological factors affecting physical aging (progression or reversal thereof).
Dr. Levine is first and foremost a gerontological epigeneticist, and a lot of this book touches on her research in that field and that of her colleagues.
She does also discuss direct environmental factors also though, and—as you might well expect—lifestyle factors.
Regular readers of 10almonds are unlikely to gain anything new in the category of lifestyle matters, but a lot of the other material will be enlightening, especially with regard to the things that might at first glance seem set in stone, but we can in fact modify, and thus “choose our own adventure” when it comes to how the rest of our life plays out, healthwise (so: choose wisely!).
The book is mostly an overview on the (at time of writing: 2022) current state of affairs in the world of longevity research, and although it’s not a “how to” manual, there is plenty in the category of practical takeaways to be gleaned too.
The style is is mostly light pop science, but with a lot of hard science woven in—she is a good explainer, and has clearly made a notable effort to explain complex concepts in simple ways, while still delivering the complex concepts too (i.e. not overly “dumbing down”).
Bottom line: if you’d like to know about what can be done to increase your healthspan and general longevity, this book has a lot of answers!
Click here to check out True Age, and shift yours in the direction you prefer!
Share This Post
-
Triple Life Threat – by Donald R. Lyman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book takes a similar approach to “How Not To Die” (which we featured previously), but focussed specifically on three things, per the title: chronic pulmonary obstructive disease (CPOD), diabetes (type 2), and Alzheimer’s disease.
Lyman strikes a great balance of being both information-dense and accessible; there’s a lot of reference material in here, and the reader is not assumed to have a lot of medical knowledge—but we’re not patronized either, and this is an informative manual, not a sensationalized scaremongering piece.
All in all… if you have known risk factors for one or more of three diseases this book covers, the information within could well be a lifesaver.
Share This Post
-
Robert F. Kennedy Jr says vitamin A protects you from deadly measles. Here’s what the study he cites actually says
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Robert F. Kennedy Jr, who oversees the health of more than 340 million Americans, says vitamin A can prevent the worst effects of measles rather than urging more people to get vaccinated.
In an opinion piece for Fox News, the US health secretary said he was “deeply concerned” about the current measles outbreak in Texas. However, he said the decision to vaccinate was a “personal one” and something for parents to discuss with their health-care provider.
Kennedy mentioned updated advice from the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) to treat measles with vitamin A. He also cited a study he said shows vitamin A can reduce the risk of dying from measles.
Here’s what the vitamin A study actually says and why public health officials are so concerned about Kennedy’s latest statement.
RobsPhoto/Shutterstock Why is a measles outbreak so worrying?
Measles is a highly contagious disease caused by a virus. It spreads easily including when an infected person breathes, coughs or sneezes.
Measles initially infects the respiratory tract and then the virus spreads throughout the body. Symptoms include a high fever, cough, red eyes, runny nose and a rash all over the body.
Measles can also be severe, can cause complications including blindness and swelling of the brain, and can be fatal. Measles can affect anyone but is most common in children.
The Texan health department has confirmed 150-plus cases of measles and one death of an unvaccinated child during the current outbreak. While this is by far the largest measles outbreak in the US in 2025, the CDC has reported smaller outbreaks in several other states so far this year.
Why vitamin A?
Vitamin A is essential for our overall health. It has many roles in the body, from supporting our growth and reproduction, to making sure we have healthy vision, skin and immune function.
Foods rich in vitamin A or related molecules include orange, yellow and red coloured fruits and vegetables, green leafy vegetables, as well as dairy, egg, fish and meat. You can take it as a supplement.
Vitamin A can also be used therapeutically. In other words, doctors may prescribe vitamin A to treat a deficiency. Vitamin A deficiency has long been associated with more severe cases of infectious disease, including measles. Vitamin A boosts immune cells and strengthens the respiratory tract lining, which is the body’s first defence against infections.
Because of this, the CDC has recently said vitamin A can also be prescribed as part of treatment for children with severe measles – such as those in hospital – under doctor supervision.
One key message from the CDC’s advice is that people are already sick enough with measles to be in hospital. They’re not taking vitamin A to prevent catching measles in the first place.
The other key message is vitamin A is taken under medical supervision, under specific circumstances, where patients can be closely monitored to prevent toxicity from high doses.
Vitamin A toxicity can cause birth defects and increase the risk of fractures in elderly people. Vitamin A and beta-carotene (which the body turns into vitamin A) from supplements may also increase your risk of cancer, especially if you smoke.
Taking too much vitamin A can lead to toxicity and cause birth defects. ChameleonsEye/Shutterstock How about the study Kennedy cites?
Kennedy cites and links to a 2010 study, a type known as a systematic review and meta-analysis. Researchers reviewed and analysed existing studies, which included ones that looked at the effectiveness of vitamin A in preventing measles deaths.
They found three studies that looked at vitamin A treatment by specific dose. There were different doses depending on the age of the children, measured in IU (international units). Having two doses of vitamin A (200,000IU for children over one year of age or 100,000IU for infants below one year) reduced mortality by 62% compared to children who did not have vitamin A.
The 2010 study did not show vitamin A reduced your risk of getting measles from another infected person. To my knowledge no study has shown this.
To be fair, Kennedy did not say that vitamin A stops you from catching measles from another infected person. Instead, he used the following vague statement:
Studies have found that vitamin A can dramatically reduce measles mortality.
It’s easy to see how a reader could misinterpret this as “take vitamin A if you want to avoid dying from measles”.
We know what works – vaccines
The World Health Organization recommends all children receive two doses of measles vaccine.
The CDC states two doses of the measles vaccine (measles-mumps-rubella or MMR vaccine) is 97% effective against getting measles. This means out of every 100 people who are vaccinated only three will get it, and this will be a milder form.
But these facts were missing from Kennedy’s statement. Should we be surprised? Kennedy is well known for his vaccine sceptism and for undermining vaccination efforts, including for the measles vaccine.
As Sue Kressly, president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, told the Washington Post:
relying on vitamin A instead of the vaccine is not only dangerous and ineffective […] it puts children at serious risk.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How Regularity Of Sleep Can Be Even More Important Than Duration
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A recent, large (n=72,269) 8-year prospective* observational study of adults aged 40-79 has found an association between irregular sleep and major cardiovascular events.
*this means they started the study at a given point, and measured what happened for the next eight years—as opposed to a retrospective study, which would look at what had happened during the previous 8 years.
As to what qualifies as major cardiovascular events, they counted:
- Heart attack
- Cardiac arrest
- Stroke
- Cardiovascular death (any)
Irregular sleep, meanwhile, was defined per a bell curve of participants. Based on a sleep regularity index (SRI) score, those with a score of 87 or more were on the “regular” side of the curve, and those with a score of 72 or lower were on the “irregular” side of the curve.
What they found is that irregular sleep is associated with major cardiovascular events, regardless of the actual amount of sleep that people got. So in other words, you could be sleeping 9 hours per day, but if it’s a different 9 hours each day, your cardiovascular risk will still be higher.
How much higher?
- For those in the middle of the curve (so, moderate irregularity), it was 8% higher than those on the “regular” side.
- For those on the “irregular” side of the curve, it was 26% higher than those on the “regular” side.
All of the above is after taking into account confounding variables such as age, physical activity levels, discretionary screen time, fruit, vegetable, and coffee intake, alcohol consumption, smoking, mental health issues, medication use, and shift work. Which is quite something, given that shift work is a very common reason for irregular sleep schedules in a lot of people.
Limitations
While, as noted above, they did their best to account for a lot of things, this was an observational study, not an interventional study or a randomized controlled trial, and as such, it cannot truly establish cause and effect.
For example, an observational study in the 90s found that the sport most strongly associated with longevity was polo. For any unfamiliar, it’s a game played on horseback with mallets and balls. Why was this game so much better than, say, swimming? And the answer is most likely that polo is played almost entirely by very rich people. It wasn’t the sport that enhanced longevity—it was the wealth.
So similarly here, it could be for example that people who are predisposed to heart conditions, are prone to having irregular schedules. We won’t know for sure until we have interventional studies (and we probably can’t get RCTs for this, for practical reasons).
Still, it seems likely that the association is indeed causal, in which case, having a regular sleep schedule if at all possible seems like a very good way to look after one’s health.
You can read more about the study here:
Irregular sleep may elevate risk of major cardiovascular events
Practical take-away
This study strongly suggests that sleep regularity is even more important than sleep duration.
This means that there is extra reason to not sleep in past one’s normal getting-up time, even if one had a less restful night.
That’s the end of sleep that’s the most important in practical terms, too, because we can control our getting-up time, whereas we can’t really control our going-to-sleep time, because it’s perfectly possible to just lie there awake.
So, controlling the getting-up time is really the key to the whole thing. See also:
Calculate (And Enjoy) The Perfect Night’s Sleep
And for scope, you might enjoy reading:
Morning Larks vs Night Owls: How Much Can We Control Our Sleep Schedule?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Taurine: An Anti-Aging Powerhouse? Exploring Its Unexpected Benefits
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Mark Rosenberg explains:
Not a stimulant, but…
- Its presence in energy drinks often causes people to assume it’s a stimulant, but it’s not. In fact, it’s a GABA-agonist, thus having a calming effect.
- The real reason it’s in energy drinks is because it helps increase mitochondrial ATP production (ATP = adenosine triphosphate = how cells store energy that’s ready to use; mitochondria take glucose and make ATP)
- Taurine is also anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer.
- In the category of aging, human studies are slow to give results for obvious reasons, but mouse studies show that supplementing taurine in middle-aged mice increased their lifespan by 10–12%, as well as improving various physiological markers of aging.
- Taking a closer look at aging—literally; looking at cellular aging—taurine reduces cellular senescence and protects telomeres, thus decreasing DNA mutations.
For more on the science of these, plus Dr. Rosenberg’s personal experience, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Taurine’s Benefits For Heart Health And More
- Dr. Greger’s Anti-Aging Eight
- Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Are plant-based burgers really bad for your heart? Here’s what’s behind the scary headlines
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’re hearing a lot about ultra-processed foods and the health effects of eating too many. And we know plant-based foods are popular for health or other reasons.
So it’s not surprising new research out this week including the health effects of ultra-processed, plant-based foods is going to attract global attention.
And the headlines can be scary if that research and the publicity surrounding it suggests eating these foods increases your risk of heart disease, stroke or dying early.
Here’s how some media outlets interpreted the research. The Daily Mail ran with:
Vegan fake meats are linked to increase in heart deaths, study suggests: Experts say plant-based diets can boost health – but NOT if they are ultra-processed
The New York Post’s headline was:
Vegan fake meats linked to heart disease, early death: study
But when we look at the study itself, it seems the media coverage has focused on a tiny aspect of the research, and is misleading.
So does eating supermarket plant-based burgers and other plant-based, ultra-processed foods really put you at greater risk of heart disease, stroke and premature death?
Here’s what prompted the research and what the study actually found.
Nina Firsova/Shutterstock Remind me, what are ultra-processed foods?
Ultra-processed foods undergo processing and reformulation with additives to enhance flavour, shelf-life and appeal. These include everything from packet macaroni cheese and pork sausages, to supermarket pastries and plant-based mince.
There is now strong and extensive evidence showing ultra-processed foods are linked with an increased risk of many physical and mental chronic health conditions.
Although researchers question which foods should be counted as ultra-processed, or if all of them are linked to poorer health, the consensus is that, generally, we should be eating less of them.
We also know plant-based diets are popular. These are linked with a reduced risk of chronic health conditions such as heart disease and stroke, cancer and diabetes. And supermarkets are stocking more plant-based, ultra-processed food options.
How about the new study?
The study looked for any health differences between eating plant-based, ultra-processed foods compared to eating non-plant based, ultra-processed foods. The researchers focused on the risk of cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease and stroke) and deaths from it.
Plant-based, ultra-processed foods in this study included mass-produced packaged bread, pastries, buns, cakes, biscuits, cereals and meat alternatives (fake meats). Ultra-processed foods that were not plant-based included milk-based drinks and desserts, sausages, nuggets and other reconstituted meat products.
The researchers used data from the UK Biobank. This is a large biomedical database that contains de-identified genetic, lifestyle (diet and exercise) and health information and biological samples from half a million UK participants. This databank allows researchers to determine links between this data and a wide range of diseases, including heart disease and stroke.
They used data from nearly 127,000 people who provided details of their diet between 2009 and 2012. The researchers linked this to their hospital records and death records. On average, the researchers followed each participant’s diet and health for nine years.
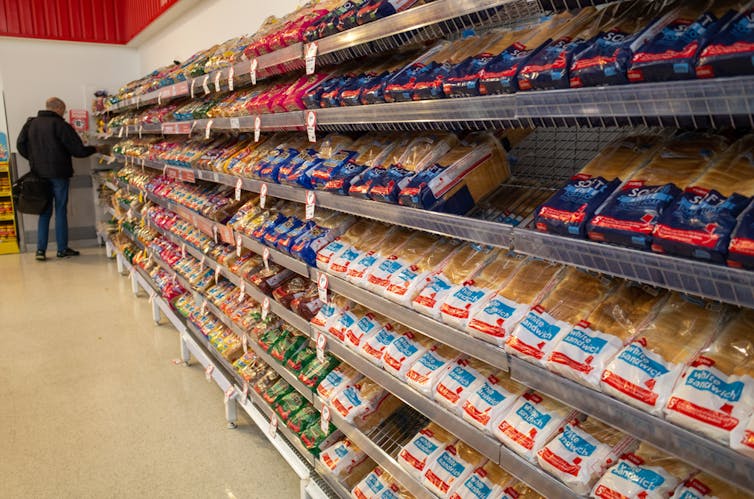
Plant-based, ultra-processed foods included in this study included packaged supermarket bread. doublelee/Shutterstock What did the study find?
With every 10% increase of total energy from plant-sourced, ultra-processed foods there was an associated 5% increased risk of cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease or stroke) and a 12% higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
But for every 10% increase in plant-sourced, non-ultra-processed foods consumed there was an associated 7% lower risk of cardiovascular disease and a 13% lower risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
The researchers found no evidence for an association between all plant-sourced foods (whether or not they were ultra-processed) and either an increased or decreased risk of cardiovascular disease or dying from it.
This was an observational study, where people recalled their diet using questionnaires. When coupled with other data, this can only tell us if someone’s diet is associated with a particular risk of a health outcome. So we cannot say that, in this case, the ultra-processed foods caused the heart disease and deaths from it.
Why has media coverage focused on fake meats?
Much of the media coverage has focused on the apparent health risks associated with eating fake meats, such as sausages, burgers, nuggets and even steaks.
These are considered ultra-processed foods. They are made by deconstructing whole plant foods such as pea, soy, wheat protein, nuts and mushrooms, and extracting the protein. They are then reformulated with additives to make the products look, taste and feel like traditional red and white meats.
However this was only one type of plant-based, ultra-processed food analysed in this study. This only accounted for an average 0.2% of the dietary energy intake of all the participants.
Compare this to bread, pastries, buns, cakes and biscuits, which are other types of plant-based, ultra-processed foods. These accounted for 20.7% of total energy intake in the study.
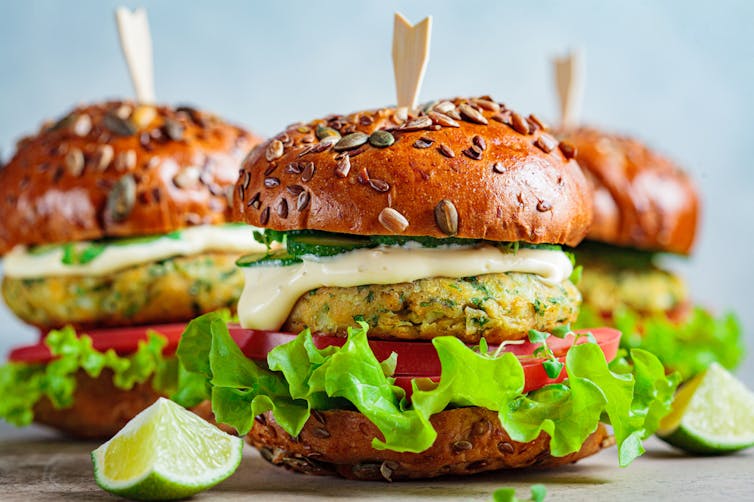
This image was at the top of the media release. Screenshot/Imperial It’s hard to say why the media focused on fake meat. But there is one clue in the media release issued to promote the research.
Although the media release did not mention the words “fake meat”, an image of plant-based burgers, sausages and meat balls or rissoles featured prominently.
The introduction of the study itself also mentions plant-sourced, ultra-processed foods, such as sausages, nuggets and burgers.
So it’s no wonder people can be confused.
Does this mean fake meats are fine?
Not necessarily. This study analysed the total intake of plant-based, ultra-processed foods, which included fake meats, albeit a very small proportion of people’s diets.
From this study alone we cannot tell if there would be a different outcome if someone ate large amounts of fake meats.
In fact, a recent review of fake meats found there was not enough evidence to determine their impact on health.
We also need more recent data to reflect current eating patterns of fake meats. This study used dietary data collected from 2009 to 2012, and fake meats have become more popular since.
What if I really like fake meat?
We have known for a while that ultra-processed foods can harm our health. This study tells us that regardless if an ultra-processed food is plant-based or not, it may still be harmful.
We know fake meat can contain large amounts of saturated fats (from coconut or palm oil), salt and sugar.
So like other ultra-processed foods, they should be eaten infrequently. The Australian Dietary Guidelines currently recommends people should only consume foods like this sometimes and in small amounts.
Are some fake meats healthier than others?
Check the labels and nutrition information panels. Look for those lowest in fat and salt. Burgers and sausages that are a “pressed cake” of minced ingredients such as nuts, beans and vegetables will be preferable to reformulated products that look identical to meat.
You can also eat whole plant-based protein foods such as legumes. These include beans, lentils, chickpeas and soy beans. As well as being high in protein and fibre, they also provide essential nutrients such as iron and zinc. Using spices and mushrooms alongside these in your recipes can replicate some of the umami taste associated with meat.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: