Widen the Window – by Dr. Elizabeth Stanley
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Firstly, about the title… That “window” that the author bids us “widen” is not a flowery metaphor, but rather, is referring to the window of exhibited resilience to stress/trauma; the “window” in question looks like an “inverted U” bell-curve on the graph.
In other words: Dr. Stanley’s main premise here is that we respond best to moderate stress (i.e: in that window, the area under the curve!), but if there is too little or too much, we don’t do so well. The key, she argues, is widening that middle part (expanding the area under the curve) in which we perform optimally. That way, we can still function in a motivated fashion without extrinsic threats, and we also don’t collapse under the weight of overwhelm, either.
The main strength of this book, however, lies in its practical exercises to accomplish that—and more.
“And more”, because the subtitle also promised recovery from trauma, and the author delivers in that regard too. In this case, it’s about widening that same window, but this time to allow one’s parasympathetic nervous system to recognize that the traumatic event is behind us, and no longer a threat; we are safe now.
Bottom line: if you would like to respond better to stress, and/or recover from trauma, this book is a very good tool.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fluoride Toothpaste vs Non-Fluoride Toothpaste – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing fluoride toothpaste to non-fluoride toothpaste, we picked the fluoride.
Why?
Fluoride is indeed toxic; that’s why it’s in toothpaste (to kill things; namely, bacteria whose waste products would harm our teeth). However, we are much bigger than those bacteria.
Given the amount of fluoride in toothpaste (usually under 1mg per strip of toothpaste to cover a toothbrush head), the amount that people swallow unintentionally (about 1/20th of that, so about 0.1mg daily if brushing teeth twice daily), and the toxicity level of fluoride (32–64mg/kg), then even if we take the most dangerous ends of all those numbers (and an average body size), to suffer ill effects from fluoride due to brushing your teeth, would require that you brush your teeth more than 23,000 times per day.
Alternatively, if you were to ravenously eat the toothpaste instead of spitting it out, you’d only need to brush your teeth a little over 1,000 times per day.
All the same, please don’t eat toothpaste; that’s not the message here.
However! In head-to-head tests, fluoride toothpaste has almost always beaten non-fluoride toothpaste.
Almost? Yes, almost: hydroxyapatite performed equally in one study, but that’s not usually an option on as many supermarket shelves.
We found some on Amazon, though, which is the one we used for today’s head-to-head. Here it is:
However, before you rush to buy it, do be aware that the toxicity of hydroxyapatite appears to be about twice that of fluoride:
Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety Opinion On Hydroxyapatite (Nano)
…which is still very safe (you’d need to brush your teeth, and eat all the toothpaste, about 500 times per day, to get to toxic levels, if we run with the same numbers we discussed before. Again, please do not do that, though).
But, since the science so far suggests it’s about twice as toxic as fluoride, then regardless of that still being very safe, the fluoride is obviously (by the same metric) twice as safe, hence picking the fluoride.
Want more options?
Check out our previous main feature:
Less Common Oral Hygiene Options
(the above article also links back to our discussion of different toothpastes and mouthwashes, by the way)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Many Faces Of Cosmetic Surgery
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cosmetic Surgery: What’s The Truth?
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your opinion on elective cosmetic surgeries, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 48% said “Everyone should be able to get what they want, assuming informed consent”
- About 28% said “It can ease discomfort to bring features more in line with normalcy”
- 15% said “They should be available in the case of extreme disfigurement only”
- 10% said “No elective cosmetic surgery should ever be performed; needless danger”
Well, there was a clear gradient of responses there! Not so polarizing as we might have expected, but still enough dissent for discussion
So what does the science say?
The risks of cosmetic surgery outweigh the benefits: True or False?
False, subjectively (but this is important).
You may be wondering: how is science subjective?
And the answer is: the science is not subjective, but people’s cost:worth calculations are. What’s worth it to one person absolutely may not be worth it to another. Which means: for those for whom it wouldn’t be worth it, they are usually the people who will not choose the elective surgery.
Let’s look at some numbers (specifically, regret rates for various surgeries, elective/cosmetic or otherwise):
- Regret rate for elective cosmetic surgery in general: 20%
- Regret rate for knee replacement (i.e., not cosmetic): 17.1%
- Regret rate for hip replacement (i.e., not cosmetic): 4.8%
- Regret rate for gender-affirming surgeries (for transgender patients): 1%
So we can see, elective surgeries have an 80–99% satisfaction rate, depending on what they are. In comparison, the two joint replacements we mentioned have a 82.9–95.2% satisfaction rate. Not too dissimilar, taken in aggregate!
In other words: if a person has studied the risks and benefits of a surgery and decides to go ahead, they’re probably going to be happy with the results, and for them, the benefits will have outweighed the risks.
Sources for the above numbers, by the way:
- What is the regret rate for plastic surgery?
- Decision regret after primary hip and knee replacement surgery
- A systematic review of patient regret after surgery—a common phenomenon in many specialties but rare within gender-affirmation surgery
But it’s just a vanity; therapy is what’s needed instead: True or False?
False, generally. True, sometimes. Whatever the reasons for why someone feels the way they do about their appearance—whether their face got burned in a fire or they just have triple-J cups that they’d like reduced, it’s generally something they’ve already done a lot of thinking about. Nevertheless, it does also sometimes happen that it’s a case of someone hoping it’ll be the magical solution, when in reality something else is also needed.
How to know the difference? One factor is whether the surgery is “type change” or “restorative”, and both have their pros and cons.
- In “type change” (e.g. rhinoplasty), more psychological adjustment is needed, but when it’s all over, the person has a new nose and, statistically speaking, is usually happy with it.
- In “restorative” (e.g. facelift), less psychological adjustment is needed (as it’s just a return to a previous state), so a person will usually be happy quickly, but ultimately it is merely “kicking the can down the road” if the underlying problem is “fear of aging”, for example. In such a case, likely talking therapy would be beneficial—whether in place of, or alongside, cosmetic surgery.
Here’s an interesting paper on that; the sample sizes are small, but the discussion about the ideas at hand is a worthwhile read:
Does cosmetic surgery improve psychosocial wellbeing?
Some people will never be happy no matter how many surgeries they get: True or False?
True! We’re going to refer to the above paper again for this one. In particular, here’s what it said about one group for whom surgeries will not usually be helpful:
❝There is a particular subgroup of people who appear to respond poorly to cosmetic procedures. These are people with the psychiatric disorder known as “body dysmorphic disorder” (BDD). BDD is characterised by a preoccupation with an objectively absent or minimal deformity that causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other areas of functioning.
For several reasons, it is important to recognise BDD in cosmetic surgery settings:
Firstly, it appears that cosmetic procedures are rarely beneficial for these people. Most patients with BDD who have had a cosmetic procedure report that it was unsatisfactory and did not diminish concerns about their appearance.
Secondly, BDD is a treatable disorder. Serotonin-reuptake inhibitors and cognitive behaviour therapy have been shown to be effective in about two-thirds of patients with BDD❞
~ Dr. David Castle et al. (lightly edited for brevity)
Which is a big difference compared to, for example, someone having triple-J breasts that need reducing, or the wrong genitals for their gender, or a face whose features are distinct outliers.
Whether that’s a reason people with BDD shouldn’t be able to get it is an ethical question rather than a scientific one, so we’ll not try to address that with science.
After all, many people (in general) will try to fix their woes with a haircut, a tattoo, or even a new sportscar, and those might sometimes be bad decisions, but they are still the person’s decision to make.
And even so, there can be protectionist laws/regulations that may provide a speed-bump, for example:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Compact Tai Chi – by Dr. Jesse Tsao
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A very frustrating thing when practicing tai chi, especially when learning, is the space typically required. We take a step this way and lunge that way and turn and now we’ve kicked a bookcase. Add a sword, and it’s goodnight to the light fixtures at the very least.
While a popular suggestion may be “do it outside”, we do not all have the luxury of living in a suitable climate. We also may prefer to practice in private, with no pressing urge to have an audience.
Tsao’s book, therefore, is very welcome. But how does he do it? The very notion of constriction is antithetical to tai chi, after all.
He takes the traditional forms, keeps the movements mostly the same, and simply changes the order of them. This way, the practitioner revolves around a central point. Occasionally, a movement will become a smaller circle than it was, but never in any way that would constrict movement.
Of course, an obvious question for any such book is “can one learn this from a book?” and the answer is complex, but we would lean towards yes, and insofar as one can learn any physical art from a book, this one does a fine job. It helps that it builds up progressively, too.
All in all, this book is a great choice for anyone who’s interested in taking up tai chi, and/but would like to do so without leaving their home.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Yoga Therapy for Arthritis – by Dr. Steffany Moonaz & Erin Byron
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Two quick notes to start with:
- One of the problems with arthritis and exercise is that arthritis can often impede exercise.
- Another of the problems with arthritis and exercise is that some kinds of exercise can exacerbate arthritis.
This book deals with both of those issues, by providing yoga specifically tailored to living with arthritis. Indeed, the first-listed author’s PhD in public health was the result of 8 years of study developing an evidence-based yoga program for people with arthritis, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
The authors take the view that arthritis is a whole-person disease (i.e. it affects all parts of you), and so addressing it requires a whole-person approach, which is what this book delivers.
As such, this is not just a book of asana (yoga postures). It does provide that, of course (as well as breathing exercises), but also its 328 pages additionally cover a lot of conscious work from the inside out, including attention to the brain, energy levels, pain, and so forth, and that the practice of yoga should not merely directly improve the joints via gentle physical exercise, but also should help to heal the whole person, including reducing stress levels, reducing physical tension, and with those two things, reducing inflammation also—and also, due to both that and the asana side of practice, better-functioning organs, which is always a bonus.
The style is interesting, as it refers to both science (8 pages of hard-science bibliography) and yogic principles (enough esoterica to put off, say, James Randi or Penn & Teller). This reviewer is very comfortable with both, and so if you, dear reader, are comfortable with both too, then you will surely enjoy this book.
Bottom line: if you or a loved one has arthritis, you’ll wish you got this book sooner.
Click here to check out Yoga Therapy For Arthritis, and live better!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Surgery is the default treatment for ACL injuries in Australia. But it’s not the only way
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
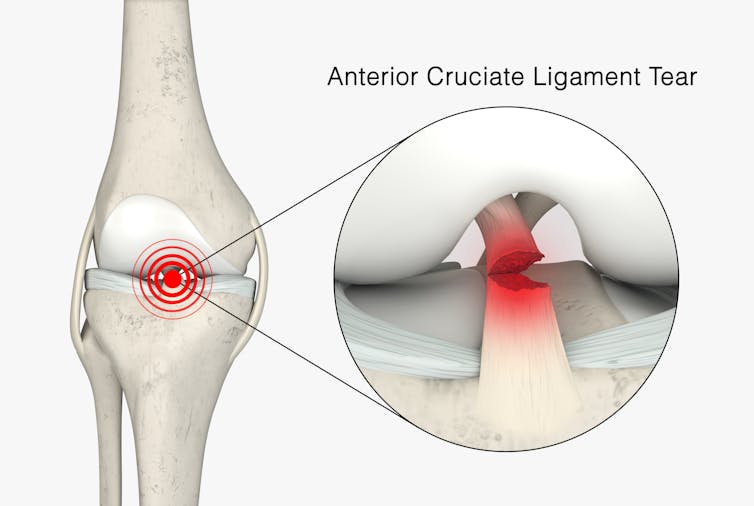
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is an important ligament in the knee. It runs from the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia) and helps stabilise the knee joint.
Injuries to the ACL, often called a “tear” or a “rupture”, are common in sport. While a ruptured ACL has just sidelined another Matildas star, people who play sport recreationally are also at risk of this injury.
For decades, surgical repair of an ACL injury, called a reconstruction, has been the primary treatment in Australia. In fact, Australia has among the highest rates of ACL surgery in the world. Reports indicate 90% of people who rupture their ACL go under the knife.
Although surgery is common – around one million are performed worldwide each year – and seems to be the default treatment for ACL injuries in Australia, it may not be required for everyone.
PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock What does the research say?
We know ACL ruptures can be treated using reconstructive surgery, but research continues to suggest they can also be treated with rehabilitation alone for many people.
Almost 15 years ago a randomised clinical trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine compared early surgery to rehabilitation with the option of delayed surgery in young active adults with an ACL injury. Over half of people in the rehabilitation group did not end up having surgery. After five years, knee function did not differ between treatment groups.
The findings of this initial trial have been supported by more research since. A review of three trials published in 2022 found delaying surgery and trialling rehabilitation leads to similar outcomes to early surgery.
A 2023 study followed up patients who received rehabilitation without surgery. It showed one in three had evidence of ACL healing on an MRI after two years. There was also evidence of improved knee-related quality of life in those with signs of ACL healing compared to those whose ACL did not show signs of healing.
Experts used to think an ACL tear couldn’t heal without surgery – now there’s evidence it can. SKYKIDKID/Shutterstock Regardless of treatment choice the rehabilitation process following ACL rupture is lengthy. It usually involves a minimum of nine months of progressive rehabilitation performed a few days per week. The length of time for rehabilitation may be slightly shorter in those not undergoing surgery, but more research is needed in this area.
Rehabilitation starts with a physiotherapist overseeing simple exercises right through to resistance exercises and dynamic movements such as jumping, hopping and agility drills.
A person can start rehabilitation with the option of having surgery later if the knee remains unstable. A common sign of instability is the knee giving way when changing direction while running or playing sports.
To rehab and wait, or to go straight under the knife?
There are a number of reasons patients and clinicians may opt for early surgical reconstruction.
For elite athletes, a key consideration is returning to sport as soon as possible. As surgery is a well established method, athletes (such as Matilda Sam Kerr) often opt for early surgical reconstruction as this gives them a more predictable timeline for recovery.
At the same time, there are risks to consider when rushing back to sport after ACL reconstruction. Re-injury of the ACL is very common. For every month return to sport is delayed until nine months after ACL reconstruction, the rate of knee re-injury is reduced by 51%.
For people who opt to try rehabilitation, the option of having surgery later is still there. PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock Historically, another reason for having early surgical reconstruction was to reduce the risk of future knee osteoarthritis, which increases following an ACL injury. But a review showed ACL reconstruction doesn’t reduce the risk of knee osteoarthritis in the long term compared with non-surgical treatment.
That said, there’s a need for more high-quality, long-term studies to give us a better understanding of how knee osteoarthritis risk is influenced by different treatments.
Rehab may not be the only non-surgical option
Last year, a study looking at 80 people fitted with a specialised knee brace for 12 weeks found 90% had evidence of ACL healing on their follow-up MRI.
People with more ACL healing on the three-month MRI reported better outcomes at 12 months, including higher rates of returning to their pre-injury level of sport and better knee function. Although promising, we now need comparative research to evaluate whether this method can achieve similar results to surgery.
What to do if you rupture your ACL
First, it’s important to seek a comprehensive medical assessment from either a sports physiotherapist, sports physician or orthopaedic surgeon. ACL injuries can also have associated injuries to surrounding ligaments and cartilage which may influence treatment decisions.
In terms of treatment, discuss with your clinician the pros and cons of management options and whether surgery is necessary. Often, patients don’t know not having surgery is an option.
Surgery appears to be necessary for some people to achieve a stable knee. But it may not be necessary in every case, so many patients may wish to try rehabilitation in the first instance where appropriate.
As always, prevention is key. Research has shown more than half of ACL injuries can be prevented by incorporating prevention strategies. This involves performing specific exercises to strengthen muscles in the legs, and improve movement control and landing technique.
Anthony Nasser, Senior Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of Technology Sydney; Joshua Pate, Senior Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of Technology Sydney, and Peter Stubbs, Senior Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of Technology Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Celery vs Lettuce – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing celery to lettuce, we picked the lettuce.
Why?
Let us consider the macros first: lettuce has 2x the protein, but of course the numbers are tiny and probably nobody is eating this for the protein. Both of these salad items are roughly comparable in terms of carbs and fiber, being both mostly water with just enough other stuff to hold their shape. Nominally this section is a slight win for lettuce on account of the protein, but in realistic practical terms, it’s a tie.
In terms of vitamins, celery has more of vitamins B5 and E, while lettuce has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, B7, B9, C, K, and choline. An easy win for lettuce here.
In the category of minerals, celery has more calcium, copper, and potassium, while lettuce has more iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. So, a fair win for lettuce.
Adding up the sections makes for an overall win for lettuce; of course, enjoy both, though!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: