Why Some Friendships Last And Others Don’t
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Friendships matter a lot, playing a significant role in our wellbeing, physical as well as mental. They bring additional meaning to our lives, help us cope with setbacks, and hopefully will be at our side through the highs and lows of life. And yet, for something that’s in principle good for everyone involved, there can be problems:
Friend to the end?
Firstly, some people find it harder to make (and then further deepen) friendships with others, which can be for a whole host of reasons.
Approaching new people can feel intimidating, but it’s a common struggle. Research shows that people often underestimate how much others enjoy their company, a phenomenon known as the “liking gap.” By reminding ourselves that others are likely to appreciate our presence and expecting to be well-received (the “acceptance prophecy”), we can approach social interactions with greater confidence.
As relationships grow, they often deepen through companionship and closeness:
- Companionship arises from shared hobbies, interests, or values, and it builds rapport.
- Closeness involves sharing thoughts, feelings, and experiences, which can build intimacy together.
An important key to these is consistency, which—whether through regular chats, honoring plans, or showing support—helps strengthen bonds, even in long-distance friendships (something often considered a barrier to closeness).
Even the strongest friendships can face challenges, of course. Conflicts may arise from a lack of support during difficult moments, or worse, betrayal. Or it could all be a misunderstanding. These situations are best addressed through honest, non-judgmental conversations. Avoiding defensiveness or accusations, and instead focusing on sharing feelings and understanding the other person’s perspective, can turn these tough discussions into opportunities for growth and stronger connections.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Better Brain – by Dr. Bonnie Kaplan and Dr. Julia Rucklidge
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed books about eating for brain health before, but this is the first time we’ve reviewed one written by clinical psychologists.
What does that change? Well, it means it less focus on, say, reducing beta amyloid plaques, and more on mental health—which often has a more immediate impact in our life.
In the category of criticisms, the authors do seem to have a bit of a double-standard. For example, they criticise psychiatrists prescribing drugs that have only undergone 12-week clinical trials, but they cite a single case-study of a 10-year-old boy as evidence for a multivitamin treating his psychosis when antipsychotics didn’t work.
However, the authors’ actual dietary advice is nonetheless very respectable. Whole foods, nutrients taken in synergistic stacks, cut the sugar, etc.
Bottom line: if you’d like to learn about the impact good nutrition can have on the brain’s health, ranging from diet itself to dietary supplements, this book presents many avenues to explore.
Click here to check out “The Better Brain”, and eat for the good health of yours!
Share This Post
-
Parenting a perfectionist? Here’s how you can respond
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some children show signs of perfectionism from early on. Young children might become frustrated and rip up their drawing if it’s not quite right. Older children might avoid or refuse to do homework because they’re afraid to make a mistake.
Perfectionism can lead to children feeling overwhelmed, angry and frustrated, or sad and withdrawn.
And yet perfectionism isn’t considered all bad in our society. Being called a “perfectionist” can be a compliment – code for being a great worker or student, someone who strives to do their best and makes sure all jobs are done well.
These seemingly polarised views reflect the complex nature of perfectionism.
Annie Spratt/Unsplash What is perfectionism?
Researchers often separate perfectionism into two parts:
- perfectionistic strivings: being determined to meet goals and achieve highly
- perfectionistic concerns: worry about being able to meet high standards, and self-criticism about performance.
While perfectionistic strivings can be positive and lead to high achievement, perfectionistic concerns can lead to a higher chance of children developing eating disorders or anxiety and depression, and having lower academic achievement.
Perfectionistic concerns can result in lower academic achievement. Jessica Lewis/Unsplash Children and adolescents may experience perfectionism in relation to school work, sport, performance in art or music, or in relation to their own body.
Signs of perfectionistic concerns in children and adolescents may include:
- children being highly critical of themselves
- their reactions to mistakes seeming to be an overreaction
- intense preoccupation and worry over their standards and goals and/or procrastination
- significant change in performance, for example, lower academic results
- irritability and negative emotions, stress and feelings of worthlessness
- social problems with peers and friends, such as bullying and alienating themselves from peers.
A range of genetic, biological and environmental factors influence perfectionism in children. And as a parent, our role is important. While research evidence suggests we can’t successfully increase positive perfectionistic strivings in our children, harsh or controlling parenting can increase negative perfectionistic concerns in children.
Parents who are perfectionistic themselves can also model this to their children.
So, how can we walk the line between supporting our child’s interests and helping them to achieve their potential, without pressuring them and increasing the risk of negative outcomes?
Give them space to grow
A great metaphor is the gardener versus the carpenter described by psychology professor Alison Gopnik.
Instead of trying to build and shape our children by controlling them and their environment (like a carpenter), parents can embrace the spirit of the gardener – providing lots of space for children to grow in their own direction, and nourishing them with love, respect and trust.
Parents don’t need to control their child and their environment. Noah Silliman/Unsplash We can’t control who they become, so it’s better to sit back, enjoy the ride, and look forward to watching the person they grow into.
However, there is still plenty we can do as parents if our child is showing signs of perfectionism. We can role model to our children how to set realistic goals and be flexible when things change or go wrong, help our children manage stress and negative emotions, and create healthy balance in our family daily routine.
Set realistic goals
People with perfectionistic tendencies will often set unattainable goals. We can support the development of flexibility and realistic goal setting by asking curious questions, for example, “what would you need to do to get one small step closer to this goal?” Identifying upper and lower limits for goals is also helpful.
If your child is fixed on a high score at school, for example, set that as the “upper limit” and then support them to identify a “lower limit” they would find acceptable, even if they are less happy with the outcome.
This strategy may take time and practice to widen the gap between the two, but is useful to create flexibility over time.
If a goal is performance-based and the outcome cannot be guaranteed (for example, a sporting competition), encourage your child to set a personal goal they have more control over.
Parents can help children set goals they can achieve. liz99/Unsplash We can also have conversations about perfectionism from early on, and explain that everyone makes mistakes. In fact, it’s great to model this to our children – talking about our own mistakes and feelings, to show them that we ourselves are not perfect.
Talk aloud practices can help children to see that we “walk the walk”. For example, if you burn dinner you could reflect:
I’m disappointed because I put time and effort into that and it didn’t turn out as I expected. But we all make mistakes. I don’t get things right every time.
Manage stress and negative emotions
Some children and adolescents have a natural tendency towards perfectionism. Rather than trying to control their behaviour, we can provide gentle, loving support.
When our child or adolescent becomes frustrated, angry, sad or overwhelmed, we support them best by helping them to name, express and validate all of their emotions.
Parents may fear that acknowledging their child’s negative emotions will make the emotions worse, but the opposite is true.
Creating healthy balance
The building blocks of healthy child development are strong loving family relationships, good nutrition, creative play and plenty of physical activity, sleep and rest.
Perfectionism is associated with rigidity, and thinking that there is only one correct way to succeed. We can instead encourage flexibility and creativity in children.
Children’s brains grow through play. There is strong research evidence showing that creative, child-led play is associated with higher emotion regulation skills, and a range of cognitive skills, including problem-solving, memory, planning, flexibility and decision-making.
Play helps children’s brains grow. Mi Pham/Unsplash Play isn’t just for young children either – there’s evidence that explorative, creative play of any kind also benefits adolescents and adults.
There is also evidence that getting active outdoors in nature can promote children’s coping skills, emotion regulation and cognitive development.
Elizabeth Westrupp, Associate Professor in Psychology, Deakin University; Gabriella King, Associate Research Fellow, Deakin University, and Jade Sheen, Associate Professor, School of Psychology, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Why do I need to take some medicines with food?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
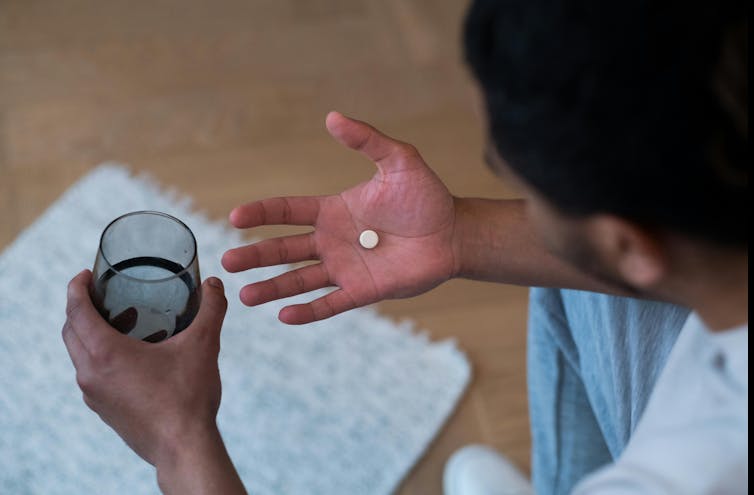
Have you ever been instructed to take your medicine with food and wondered why? Perhaps you’ve wondered if you really need to?
There are varied reasons, and sometimes complex science and chemistry, behind why you may be advised to take a medicine with food.
To complicate matters, some similar medicines need to be taken differently. The antibiotic amoxicillin with clavulanic acid (sold as Amoxil Duo Forte), for example, is recommended to be taken with food, while amoxicillin alone (sold as Amoxil), can be taken with or without food.
Different brands of the same medicine may also have different recommendations when it comes to taking it with food.
Ron Lach/Pexels Food impacts drug absorption
Food can affect how fast and how much a drug is absorbed into the body in up to 40% of medicines taken orally.
When you have food in your stomach, the makeup of the digestive juices change. This includes things like the fluid volume, thickness, pH (which becomes less acidic with food), surface tension, movement and how much salt is in your bile. These changes can impair or enhance drug absorption.
Eating a meal also delays how fast the contents of the stomach move into the small intestine – this is known as gastric emptying. The small intestine has a large surface area and rich blood supply – and this is the primary site of drug absorption.
Eating a meal with medicine will delay its onset. Farhad/Pexels Eating a larger meal, or one with lots of fibre, delays gastric emptying more than a smaller meal. Sometimes, health professionals will advise you to take a medicine with food, to help your body absorb the drug more slowly.
But if a drug can be taken with or without food – such as paracetamol – and you want it to work faster, take it on an empty stomach.
Food can make medicines more tolerable
Have you ever taken a medicine on an empty stomach and felt nauseated soon after? Some medicines can cause stomach upsets.
Metformin, for example, is a drug that reduces blood glucose and treats type 2 diabetes and polycystic ovary syndrome. It commonly causes gastrointestinal symptoms, with one in four users affected. To combat these side effects, it is generally recommended to be taken with food.
The same advice is given for corticosteroids (such as prednisolone/prednisone) and certain antibiotics (such as doxycycline).
Taking some medicines with food makes them more tolerable and improves the chance you’ll take it for the duration it’s prescribed.
Can food make medicines safer?
Ibuprofen is one of the most widely used over-the-counter medicines, with around one in five Australians reporting use within a two-week period.
While effective for pain and inflammation, ibuprofen can impact the stomach by inhibiting protective prostaglandins, increasing the risk of bleeding, ulceration and perforation with long-term use.
But there isn’t enough research to show taking ibuprofen with food reduces this risk.
Prolonged use may also affect kidney function, particularly in those with pre-existing conditions or dehydration.
The Australian Medicines Handbook, which guides prescribers about medicine usage and dosage, advises taking ibuprofen (sold as Nurofen and Advil) with a glass of water – or with a meal if it upsets your stomach.
If it doesn’t upset your stomach, ibuprofen can be taken with water. Tbel Abuseridze/Unsplash A systematic review published in 2015 found food delays the transit of ibuprofen to the small intestine and absorption, which delays therapeutic effect and the time before pain relief. It also found taking short courses of ibuprofen without food reduced the need for additional doses.
To reduce the risk of ibuprofen causing damage to your stomach or kidneys, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration, stay hydrated and avoid taking other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines at the same time.
For people who use ibuprofen for prolonged periods and are at higher risk of gastrointestinal side effects (such as people with a history of ulcers or older adults), your prescriber may start you on a proton pump inhibitor, a medicine that reduces stomach acid and protects the stomach lining.
How much food do you need?
When you need to take a medicine with food, how much is enough?
Sometimes a full glass of milk or a couple of crackers may be enough, for medicines such as prednisone/prednisolone.
However, most head-to-head studies that compare the effects of a medicine “with food” and without, usually use a heavy meal to define “with food”. So, a cracker may not be enough, particularly for those with a sensitive stomach. A more substantial meal that includes a mix of fat, protein and carbohydrates is generally advised.
Your health professional can advise you on which of your medicines need to be taken with food and how they interact with your digestive system.
Mary Bushell, Clinical Associate Professor in Pharmacy, University of Canberra
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Pajama Pilates – by Maria Mankin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If The Science Of Pilates was a bit more information than you wanted to get up and running with Pilates at home, then this book offers a much easier way in.
As the name suggests, it’s all about convenience, and making things as easy as possible while enjoying the gradual cumulative gains that come when one practises even just a little every day instead of thinking “well I would, but I have to read all this technical stuff and get changed and clear a space and…”, and thus results in meaningful improvements to mobility and strength over time.
The 40 exercises promised by the subtitle are demonstrate via cute illustrations, of which the cover art is a good representative example. There’s nothing unduly technical here, and yet everything is quite clear. There are also simple practical explanations for each, as well as an initial overview of Pilates as a whole, its principles and necessary knowledge and so forth.
Bottom line: if you’d like to get into Pilates but it has seemed sufficiently taxing that you’ve never quite got started, or if you did then it didn’t stick, then this book can make things easier.
Click here to check out Pajama Pilates, and get ready to pajama Pilates party!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Mango vs Pineapple – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing mango to pineapple, we picked the pineapple.
Why?
It was close! Both of these tropical fruits have almost identical macros, and when it comes to vitamins and minerals, mango has slightly more vitamins while pineapple has slightly more minerals, so that balances out too. Their glycemic loads are 11 and 13 respectively, so: very low, and very similar.
See also: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
In terms of what sets them apart:
Mango has a lot of vitamin A, to the point that it can interfere with blood-thinners if you take those.
Pineapple has bromelain, an enzyme with unique anti-inflammatory properties that we must devote a Research Review Monday to one of these days, because there’s a lot to say, but the short version is, it’s very powerful.
Since bromelain is found only in pineapples, whereas vitamin A is easy to find in abundance in many foods, we went with the pineapple.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
30 Days Of Weight Vest Use: Lessons Learned
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Robin, from “The Science of Self-Care”, has insights:
How to have an easier time of it
Per peer-reviewed science (linked under the video on YouTube), there are some benefits:
- Cardiovascular fitness: increases workout intensity, improving heart and lung health.
- Muscle strength & endurance: strengthens core, legs, glutes, and calves.
- Bone density: helps prevent osteoporosis through weight-bearing exercise.
- Caloric expenditure: burns more calories, aiding in weight loss.
- Balance & posture: improves balance, though posture effects were mixed.
She chose a 30 lb weighted vest, which felt much heavier than expected. Initially, this was uncomfortable but became comforting over time (much like a weighted blanket). She also found that walks became noticeably more intense, leading to increased sweating and hunger.
Over the course of the month, she found:
- Week 1: adjusting to the extra weight; walks felt significantly harder.
- Weeks 2-3: strength improvements; carrying groceries felt easier, walking without the vest felt effortless.
- Week 3: started craving the weighted vest, but also began experiencing shoulder discomfort.
- Week 4: reduced walk duration to 20 minutes due to shoulder strain.
She concluded that the vest design was flawed—all weight rested on shoulders instead of distributing across the body, which led to shoulder discomfort and posture issues. To mitigate these things, she switched to wearing the vest around the waist like a skirt. She now plans to try a weighted belt for better weight distribution, though also simply a different kind of vest would work better (the kind that looks like combat body armor distributes the weight a lot more easily)
In short, her verdict:
- Weighted walking: 10/10, highly beneficial and easy to incorporate into daily routines.
- Vest used: 2/10, poor weight distribution, causing discomfort and shoulder strain.
For more on all of this, plus links to the relevant scientific papers, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Weight Vests Against Osteoporosis: Do They Really Build Bone?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: