In Vermont, Where Almost Everyone Has Insurance, Many Can’t Find or Afford Care
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
RICHMOND, Vt. — On a warm autumn morning, Roger Brown walked through a grove of towering trees whose sap fuels his maple syrup business. He was checking for damage after recent flooding. But these days, his workers’ health worries him more than his trees’.
The cost of Slopeside Syrup’s employee health insurance premiums spiked 24% this year. Next year it will rise 14%.
The jumps mean less money to pay workers, and expensive insurance coverage that doesn’t ensure employees can get care, Brown said. “Vermont is seen as the most progressive state, so how is health care here so screwed up?”
Vermont consistently ranks among the healthiest states, and its unemployment and uninsured rates are among the lowest. Yet Vermonters pay the highest prices nationwide for individual health coverage, and state reports show its providers and insurers are in financial trouble. Nine of the state’s 14 hospitals are losing money, and the state’s largest insurer is struggling to remain solvent. Long waits for care have become increasingly common, according to state reports and interviews with residents and industry officials.
Rising health costs are a problem across the country, but Vermont’s situation surprises health experts because virtually all its residents have insurance and the state regulates care and coverage prices.
For more than 15 years, federal and state policymakers have focused on increasing the number of people insured, which they expected would shore up hospital finances and make care more available and affordable.
“Vermont’s struggles are a wake-up call that insurance is only one piece of the puzzle to ensuring access to care,” said Keith Mueller, a rural health expert at the University of Iowa.
Regulators and consultants say the state’s small, aging population of about 650,000 makes spreading insurance risk difficult. That demographic challenge is compounded by geography, as many Vermonters live in rural areas, where it’s difficult to attract more health workers to address shortages.
At least part of the cost spike can be attributed to patients crossing state lines for quicker care in New York and Massachusetts. Those visits can be more expensive for both insurers and patients because of long ambulance rides and charges from out-of-network providers.
Patients who stay, like Lynne Drevik, face long waits. Drevik said her doctor told her in April that she needed knee replacement surgeries — but the earliest appointment would be in January for one knee and the following April for the other.
Drevik, 59, said it hurts to climb the stairs in the 19th-century farmhouse in Montgomery Center she and her husband operate as an inn and a spa. “My life is on hold here, and it’s hard to make any plans,” she said. “It’s terrible.”
Health experts say some of the state’s health system troubles are self-inflicted.
Unlike most states, Vermont regulates hospital and insurance prices through an independent agency, the Green Mountain Care Board. Until recently, the board typically approved whatever price changes companies wanted, said Julie Wasserman, a health consultant in Vermont.
The board allowed one health system — the University of Vermont Health Network — to control about two-thirds of the state’s hospital market and allowed its main facility, the University of Vermont Medical Center in Burlington, to raise its prices until it ranked among the nation’s most expensive, she said, citing data the board presented in September.
Hospital officials contend their prices are no higher than industry averages.
But for 2025, the board required the University of Vermont Medical Center to cut the prices it bills private insurers by 1%.
The nonprofit system says it is navigating its own challenges. Top officials say a severe lack of housing makes it hard to recruit workers, while too few mental health providers, nursing homes, and long-term care services often create delays in discharging patients, adding to costs.
Two-thirds of the system’s patients are covered by Medicare or Medicaid, said CEO Sunny Eappen. Both government programs pay providers lower rates than private insurance, which Eappen said makes it difficult to afford rising prices for drugs, medical devices, and labor.
Officials at the University of Vermont Medical Center point to several ways they are trying to adapt. They cited, for example, $9 million the hospital system has contributed to the construction of two large apartment buildings to house new workers, at a subsidized price for lower-income employees.
The hospital also has worked with community partners to open a mental health urgent care center, providing an alternative to the emergency room.
In the ER, curtains separate areas in the hallway where patients can lie on beds or gurneys for hours waiting for a room. The hospital also uses what was a storage closet as an overflow room to provide care.
“It’s good to get patients into a hallway, as it’s better than a chair,” said Mariah McNamara, an ER doctor and associate chief medical officer with the hospital.
For the about 250 days a year when the hospital is full, doctors face pressure to discharge patients without the ideal home or community care setup, she said. “We have to go in the direction of letting you go home without patient services and giving that a try, because otherwise the hospital is going to be full of people, and that includes people that don’t need to be here,” McNamara said.
Searching for solutions, the Green Mountain Care Board hired a consultant who recommended a number of changes, including converting four rural hospitals into outpatient facilities, in a worst-case scenario, and consolidating specialty services at several others.
The consultant, Bruce Hamory, said in a call with reporters that his report provides a road map for Vermont, where “the health care system is no match for demographic, workforce, and housing challenges.”
But he cautioned that any fix would require sacrifice from everyone, including patients, employers, and health providers. “There is no simple single policy solution,” he said.
One place Hamory recommended converting to an outpatient center only was North Country Hospital in Newport, a village in Vermont’s least populated region, known as the Northeast Kingdom.
The 25-bed hospital has lost money for years, partly because of an electronic health record system that has made it difficult to bill patients. But the hospital also has struggled to attract providers and make enough money to pay them.
Officials said they would fight any plans to close the hospital, which recently dropped several specialty services, including pulmonology, neurology, urology, and orthopedics. It doesn’t have the cash to upgrade patient rooms to include bathroom doors wide enough for wheelchairs.
On a recent morning, CEO Tom Frank walked the halls of his hospital. The facility was quiet, with just 14 admitted patients and only a couple of people in the ER. “This place used to be bustling,” he said of the former pulmonology clinic.
Frank said the hospital breaks even treating Medicare patients, loses money treating Medicaid patients, and makes money from a dwindling number of privately insured patients.
The state’s strict regulations have earned it an antihousing, antibusiness reputation, he said. “The cost of health care is a symptom of a larger problem.”
About 30 miles south of Newport, Andy Kehler often worries about the cost of providing health insurance to the 85 workers at Jasper Hill Farm, the cheesemaking business he co-owns.
“It’s an issue every year for us, and it looks like there is no end in sight,” he said.
Jasper Hill pays half the cost of its workers’ health insurance premiums because that’s all it can afford, Kehler said. Employees pay $1,700 a month for a family, with a $5,000 deductible.
“The coverage we provide is inadequate for what you pay,” he said.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Passion Fruit vs Pomegranate – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing passion fruit to pomegranate, we picked the passion fruit.
Why?
Both of these fruits have beaten a lot of other contenders, so it’s time to pit them against each other:
In terms of macros, passion fruit has more protein, carbs, and fiber, the ratio of which meaning also that passion fruit has the lower glycemic index. So, we say passion fruit wins on macros.
In the category of vitamins, things are more even; passion fruit has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B6, and C, while pomegranate has more of vitamins B1, B5, B9, E, and K. In light of this 5:5 tie, and since passion fruit’s overall vitamin coverage is better (in terms of meeting RDA needs) but pomegranate’s vitamins are often in shorter supply in diet, we’re calling it a tie on vitamins.
When it comes to minerals, passion fruit has more calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while pomegranate has more copper, manganese, and zinc. That’s already an easy 6:3 win for passion fruit, before we even consider the fact that passion fruit’s minerals’ margin of difference is greater too.
Adding it up makes for a clear win for passion fruit. As ever when it comes to plants, enjoy both if you can, though!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
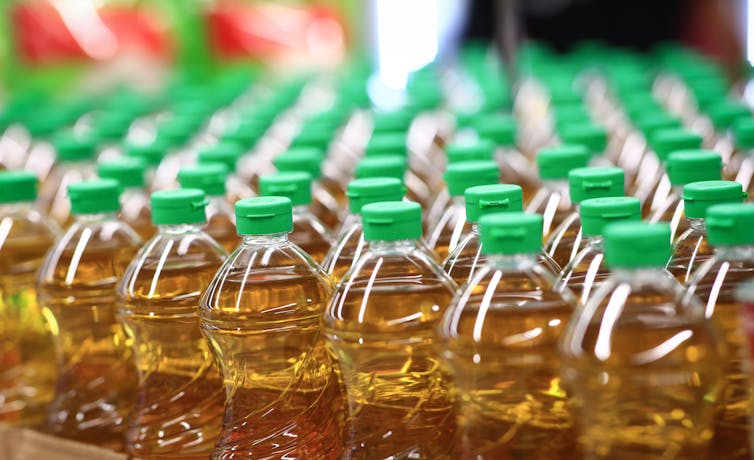
I can’t afford olive oil. What else can I use?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you buy your olive oil in bulk, you’ve likely been in for a shock in recent weeks. Major supermarkets have been selling olive oil for up to A$65 for a four-litre tin, and up to $26 for a 750 millilitre bottle.
We’ve been hearing about the health benefits of olive oil for years. And many of us are adding it to salads, or baking and frying with it.
But during a cost-of-living crisis, these high prices can put olive oil out of reach.
Let’s take a look at why olive oil is in demand, why it’s so expensive right now, and what to do until prices come down.
Joyisjoyful/Shutterstock Remind me, why is olive oil so good for you?
Including olive oil in your diet can reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and improve heart health through more favourable blood pressure, inflammation and cholesterol levels.
This is largely because olive oil is high in monounsaturated fatty acids and polyphenols (antioxidants).
Some researchers have suggested you can get these benefits from consuming up to 20 grams a day. That’s equivalent to about five teaspoons of olive oil.
Why is olive oil so expensive right now?
A European heatwave and drought have limited Spanish and Italian producers’ ability to supply olive oil to international markets, including Australia.
This has been coupled with an unusually cold and short growing season for Australian olive oil suppliers.
The lower-than-usual production and supply of olive oil, together with heightened demand from shoppers, means prices have gone up.
We’ve seen unfavourable growing conditions in Europe and Australia. KaMay/Shutterstock How can I make my olive oil go further?
Many households buy olive oil in large quantities because it is cheaper per litre. So, if you have some still in stock, you can make it go further by:
- storing it correctly – make sure the lid is on tightly and it’s kept in a cool, dark place, such as a pantry or cabinet. If stored this way, olive oil can typically last 12–18 months
- using a spray – sprays distribute oil more evenly than pourers, using less olive oil overall. You could buy a spray bottle to fill from a large tin, as needed
- straining or freezing it – if you have leftover olive oil after frying, strain it and reuse it for other fried dishes. You could also freeze this used oil in an airtight container, then thaw and fry with it later, without affecting the oil’s taste and other characteristics. But for dressings, only use fresh oil.
I’ve run out of olive oil. What else can I use?
Here are some healthy and cheaper alternatives to olive oil:
- canola oil is a good alternative for frying. It’s relatively low in saturated fat so is generally considered healthy. Like olive oil, it is high in healthy monounsaturated fats. Cost? Up to $6 for a 750mL bottle (home brand is about half the price)
- sunflower oil is a great alternative to use on salads or for frying. It has a mild flavour that does not overwhelm other ingredients. Some studies suggest using sunflower oil may help reduce your risk of heart disease by lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol and raising HDL (good) cholesterol. Cost? Up to $6.50 for a 750mL bottle (again, home brand is about half the price)
- sesame oil has a nutty flavour. It’s good for Asian dressings, and frying. Light sesame oil is typically used as a neutral cooking oil, while the toasted type is used to flavour sauces. Sesame oil is high in antioxidants and has some anti-inflammatory properties. Sesame oil is generally sold in smaller bottles than canola or sunflower oil. Cost? Up to $5 for a 150mL bottle.
There are plenty of alternative oils you can use in salads or for frying. narai chal/Shutterstock How can I use less oil, generally?
Using less oil in your cooking could keep your meals healthy. Here are some alternatives and cooking techniques:
- use alternatives for baking – unless you are making an olive oil cake, if your recipe calls for a large quantity of oil, try using an alternative such as apple sauce, Greek yoghurt or mashed banana
- use non-stick cookware – using high-quality, non-stick pots and pans reduces the need for oil when cooking, or means you don’t need oil at all
- steam instead – steam vegetables, fish and poultry to retain nutrients and moisture without adding oil
- bake or roast – potatoes, vegetables or chicken can be baked or roasted rather than fried. You can still achieve crispy textures without needing excessive oil
- grill – the natural fats in meat and vegetables can help keep ingredients moist, without using oil
- use stock – instead of sautéing vegetables in oil, try using vegetable broth or stock to add flavour
- try vinegar or citrus – use vinegar or citrus juice (such as lemon or lime) to add flavour to salads, marinades and sauces without relying on oil
- use natural moisture – use the natural moisture in ingredients such as tomatoes, onions and mushrooms to cook dishes without adding extra oil. They release moisture as they cook, helping to prevent sticking.
Lauren Ball, Professor of Community Health and Wellbeing, The University of Queensland and Emily Burch, Accredited Practising Dietitian and Lecturer, Southern Cross University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Celery vs Radish – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing celery to radish, we picked the celery.
Why?
It was very close! And yes, surprising, we know. Generally speaking, the more colorful/pigmented an edible plant is, the healthier it is. Celery is just one of those weird exceptions (as is cauliflower, by the way).
Macros-wise, these two are pretty much the same—95% water, with just enough other stuff to hold them together. The proportions of “other stuff” are also pretty much equal.
In the category of vitamins, celery has more vitamin K while radish has more vitamin C; the other vitamins are pretty close to equal. We’ll call this one a minor win for celery, as vitamin K is found in fewer foods than vitamin C.
When it comes to minerals, celery has more calcium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium, while radish has more copper, iron, selenium, and zinc. We’ll call this a minor win for radish, as the margins are a little wider for its minerals.
So, that makes the score 1–1 so far.
Both plants have an assortment of polyphenols, of which, when we add up the averages, celery comes out on top by some way. Celery also comes out on top when we do a head-to-head of the top flavonoid of each; celery has 5.15mg/100g of apigenin to radish’s 0.63mg/100g kaempferol.
Which means, both are great healthy foods, but celery wins the day.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Celery vs Cucumber – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Egg Whites vs Whole Eggs – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing egg whites to whole eggs, we picked the whole eggs.
Why?
Egg whites are mostly protein. Egg yolks are mostly fat, with some protein.
However, fat ≠ bad, and the yolk is also where the choline is stored, which itself (as well as its benefits for your brain) will tend to reduce fat storage in the body.
Furthermore, the yolk contains an assortment of vitamins, minerals, and essential amino acids. After all, the yolk is there specifically to contain everything needed to turn a cluster of cells into a small bird.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
New California Laws Target Medical Debt, AI Care Decisions, Detention Centers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
SACRAMENTO, Calif. — As the nation braces for potential policy shifts under President-elect Donald Trump’s “Make America Healthy Again” mantra, the nation’s most populous state and largest health care market is preparing for a few changes of its own.
With supermajorities in both houses, Democrats in the California Legislature passed — and Democratic Gov. Gavin Newsom signed — laws taking effect this year that will erase medical debt from credit reports, allow public health officials to inspect immigrant detention centers, and require health insurance companies to cover fertility services such as in vitro fertilization.
Still, industry experts say it was a relatively quiet year for health policy in the Golden State, with more attention on a divisive presidential election and with several state legislators seeking to avoid controversial issues as they ran for Congress in competitive swing districts.
Newsom shot down some of legislators’ most ambitious health care policies, including proposals that would have regulated pharmaceutical industry middlemen and given the state more power to stop private equity deals in health care.
Health policy experts say advocates and legislators are now focused on how to defend progressive California policies such as sweeping abortion access in the state and health coverage for immigrants living in the U.S. without authorization.
“I think everyone’s just thinking about how we’re going to enter 2025,” said Rachel Linn Gish, a spokesperson with the consumer health advocacy group Health Access California. “We’re figuring out what is vulnerable, what we are exposed to on the federal side, and what do budget changes mean for our work. That’s kind of putting a cloud over everything.”
Here are some of the biggest new health care laws Californians should know about:
Medical debt
California becomes the eighth state in which medical debt will no longer affect patients’ credit reports or credit scores. SB 1061 bars health care providers and debt collectors from reporting unpaid medical bills to credit bureaus, a practice that supporters of the law say penalizes people for seeking critical care and can make it harder for patients to get a job, buy a car, or secure a mortgage.
Critics including the California Association of Collectors called the measure from Sen. Monique Limón (D-Santa Barbara) a “tremendous overreach” and successfully lobbied for amendments that limited the scope of the bill, including an exemption for any medical debt incurred on credit cards.
The Biden administration has finalized federal rules that would stop unpaid medical bills from affecting patients’ credit scores, but the fate of those changes remains unclear as Trump takes office.
Psychiatric hospital stays for violent offenders
Violent offenders with severe mental illness can now be held longer after a judge orders them released from a state mental hospital.
State officials and local law enforcement will now have 30 days to coordinate housing, medication, and behavioral health treatment for those parolees, giving them far more time than the five-day deadline previously in effect.
The bill drew overwhelming bipartisan support after a high-profile case in San Francisco in which a 61-year-old man was charged in the repeated stabbing of a bakery employee just days after his release from a state mental hospital. The bill’s author, Assembly member Matt Haney (D-San Francisco), called the previous five-day timeline “dangerously short.”
Cosmetics and ‘forever chemicals’
California was the first state to ban PFAS chemicals, also known as “forever chemicals,” in all cosmetics sold and manufactured within its borders. The synthetic compounds, found in everyday products including rain jackets, food packaging, lipstick, and shaving cream, have been linked to cancer, birth defects, and diminished immune function and have been increasingly detected in drinking water.
Industry representatives have argued that use of PFAS — perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances — is critical in some products and that some can be safely used at certain levels.
Immigration detention facilities
After covid-19 outbreaks, contaminated water, and moldy food became the subjects of detainee complaints and lawsuits, state legislators gave local county health officials the authority to enter and inspect privately run immigrant detention centers. SB 1132, from Sen. María Elena Durazo (D-Los Angeles), gives public health officials the ability to evaluate whether privately run facilities are complying with state and local public health regulations regarding proper ventilation, basic mental and physical health care, and food safety.
Although the federal government regulates immigration, six federal detention centers in California are operated by the GEO Group. One of the country’s largest private prison contractors, GEO has faced a litany of complaints related to health and safety. Unlike public prisons and jails, which are inspected annually, these facilities would be inspected only as deemed necessary.
The contractor filed suit in October to stop implementation of the law, saying it unconstitutionally oversteps the federal government’s authority to regulate immigration detention centers. A hearing in the case is set for March 3, said Bethany Lesser, a spokesperson for California Attorney General Rob Bonta. The law took effect Jan. 1.
Doctors vs. insurance companies using AI
As major insurance companies increasingly use artificial intelligence as a tool to analyze patient claims and authorize some treatment, trade groups representing doctors are concerned that AI algorithms are driving an increase in denials for necessary care. Legislators unanimously agreed.
SB 1120 states that decisions about whether a treatment is medically necessary can be made only by licensed, qualified physicians or other health care providers who review a patient’s medical history and other records.
Sick leave and protected time off
Two new laws expand the circumstances under which California workers may use sick days and other leave. SB 1105 entitles farmworkers who work outdoors to take paid sick leave to avoid heat, smoke, or flooding when local or state officials declare an emergency.
AB 2499 expands the list of reasons employees may take paid sick days or use protected unpaid leave to include assisting a family member who is experiencing domestic violence or other violent crimes.
Prescription labels for the visually impaired
Starting this year, pharmacies will be required to provide drug labels and use instructions in Braille, large print, or audio for blind patients.
Advocates of the move said state law, which already required translated instructions in five languages for non-English speakers, has overlooked blind patients, making it difficult for them to monitor prescriptions and take the correct dosage.
Maternal mental health screenings
Health insurers will be required to bolster maternal mental health programs by mandating additional screenings to better detect perinatal depression, which affects 1 in 5 people who give birth in California, according to state data. Pregnant people will now undergo screenings at least once during pregnancy and then six weeks postpartum, with further screenings as providers deem necessary.
Penalties for threatening health care workers (abortion clinics)
With abortion care at the center of national policy fights, California is cracking down on those who threaten, post personal information about, or otherwise target providers or patients at clinics that perform abortions. Penalties for such behavior will increase under AB 2099, and offenders can face felony charges, up to three years in jail, and $50,000 in fines for repeat or violent offenses. Previously, state law classified many of those offenses as misdemeanors.
Insurance coverage for IVF
Starting in July, state-regulated health plans covering 50 employees or more would be required to cover fertility services under SB 729, passed and signed last year. Advocates have long fought for this benefit, which they say is essential care for many families who have trouble getting pregnant and would ensure LGBTQ+ couples aren’t required to pay more out-of-pocket costs than straight couples when starting a family.
In a signing statement, Newsom asked legislators to delay implementation of the law until 2026 as state officials consider whether to add infertility treatments to the list of benefits that insurance plans are required to cover.
It’s unclear whether legislators intend to address that this session, but a spokesperson for the governor said that Newsom “clearly stated his position on the need for an extension” and that he “will continue to work with the legislature” on the matter.
Plans under CalPERS, the California Public Employees’ Retirement System, would have to comply by July 2027.
This article was produced by KFF Health News, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
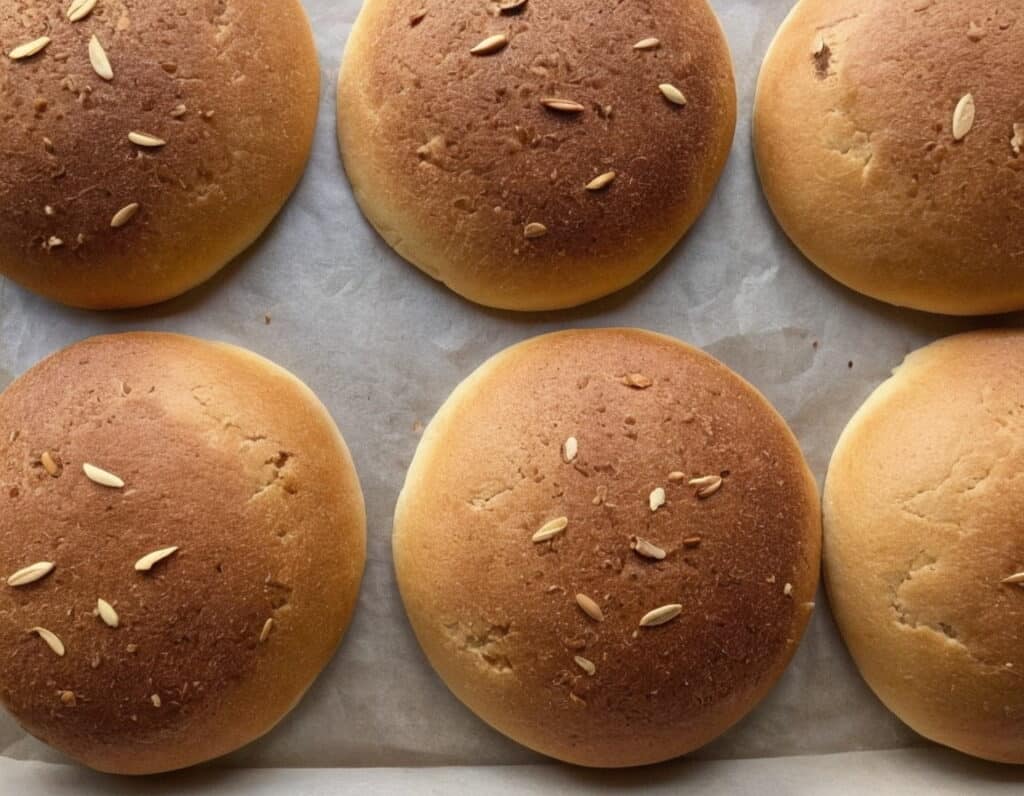
Delicious Quinoa Avocado Bread
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
They’re gluten-free, full of protein and healthy fats, generous with the fiber, easy to make, and tasty too! What’s not to love? Keep this recipe (and its ingredients) handy for next time you want healthy burger buns or similar:
You will need
- 2½ cups quinoa flour
- 2 cups almond flour (if allergic, just substitute more quinoa flour)
- 1 avocado, peeled, pitted, and mashed
- zest and juice of 1 lime
- 2 tbsp ground flaxseed
- 1 tsp baking powder
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Optional: seeds, oats, or similar for topping the buns
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 350℉/175℃.
2) Mix the flaxseed with ⅓ cup warm water and set aside.
3) Mix, in a large bowl, the quinoa flour and almond flour with the baking powder and the MSG or salt.
4) Mix, in a separate smaller bowl, the avocado and lime.
5) Add the wet ingredients to the dry, slowly, adding an extra ½ cup water as you do, and knead into a dough.
6) Divide the dough into 4 equal portions, each shaped into a ball and then slightly flattened, to create a burger bun shape. If you’re going to add any seeds or similar as a topping, add those now.
7) Bake them in the oven (on a baking sheet lined with baking paper) for 20–25 minutes. You can check whether they’re done the same way you would a cake, by piercing them to the center with a toothpick and seeing whether it comes out clean.
8) Serve when sufficiently cooled.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Gluten: What’s The Truth?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: