Thinking of using an activity tracker to achieve your exercise goals? Here’s where it can help – and where it probably won’t
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s that time of year when many people are getting started on their resolutions for the year ahead. Doing more physical activity is a popular and worthwhile goal.
If you’re hoping to be more active in 2024, perhaps you’ve invested in an activity tracker, or you’re considering buying one.
But what are the benefits of activity trackers? And will a basic tracker do the trick, or do you need a fancy one with lots of features? Let’s take a look.
Why use an activity tracker?
One of the most powerful predictors for being active is whether or not you are monitoring how active you are.
Most people have a vague idea of how active they are, but this is inaccurate a lot of the time. Once people consciously start to keep track of how much activity they do, they often realise it’s less than what they thought, and this motivates them to be more active.
You can self-monitor without an activity tracker (just by writing down what you do), but this method is hard to keep up in the long run and it’s also a lot less accurate compared to devices that track your every move 24/7.
By tracking steps or “activity minutes” you can ascertain whether or not you are meeting the physical activity guidelines (150 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity per week).
It also allows you to track how you’re progressing with any personal activity goals, and view your progress over time. All this would be difficult without an activity tracker.
Research has shown the most popular brands of activity trackers are generally reliable when it comes to tracking basic measures such as steps and activity minutes.
But wait, there’s more
Many activity trackers on the market nowadays track a range of other measures which their manufacturers promote as important in monitoring health and fitness. But is this really the case? Let’s look at some of these.
Resting heart rate
This is your heart rate at rest, which is normally somewhere between 60 and 100 beats per minute. Your resting heart rate will gradually go down as you become fitter, especially if you’re doing a lot of high-intensity exercise. Your risk of dying of any cause (all-cause mortality) is much lower when you have a low resting heart rate.
So, it is useful to keep an eye on your resting heart rate. Activity trackers are pretty good at tracking it, but you can also easily measure your heart rate by monitoring your pulse and using a stopwatch.
Heart rate during exercise
Activity trackers will also measure your heart rate when you’re active. To improve fitness efficiently, professional athletes focus on having their heart rate in certain “zones” when they’re exercising – so knowing their heart rate during exercise is important.
But if you just want to be more active and healthier, without a specific training goal in mind, you can exercise at a level that feels good to you and not worry about your heart rate during activity. The most important thing is that you’re being active.
Also, a dedicated heart rate monitor with a strap around your chest will do a much better job at measuring your actual heart rate compared to an activity tracker worn around your wrist.
Maximal heart rate
This is the hardest your heart could beat when you’re active, not something you could sustain very long. Your maximal heart rate is not influenced by how much exercise you do, or your fitness level.
Most activity trackers don’t measure it accurately anyway, so you might as well forget about this one.
VO₂max
Your muscles need oxygen to work. The more oxygen your body can process, the harder you can work, and therefore the fitter you are.
VO₂max is the volume (V) of oxygen (O₂) we could breathe maximally (max) over a one minute interval, expressed as millilitres of oxygen per kilogram of body weight per minute (ml/kg/min). Inactive women and men would have a VO₂max lower than 30 and 40 ml/kg/min, respectively. A reasonably good VO₂max would be mid thirties and higher for women and mid forties and higher for men.
VO₂max is another measure of fitness that correlates well with all-cause mortality: the higher it is, the lower your risk of dying.
For athletes, VO₂max is usually measured in a lab on a treadmill while wearing a mask that measures oxygen consumption. Activity trackers instead look at your running speed (using a GPS chip) and your heart rate and compare these measures to values from other people.
If you can run fast with a low heart rate your tracker will assume you are relatively fit, resulting in a higher VO₂max. These estimates are not very accurate as they are based on lots of assumptions. However, the error of the measurement is reasonably consistent. This means if your VO₂max is gradually increasing, you are likely to be getting fitter.
So what’s the take-home message? Focus on how many steps you take every day or the number of activity minutes you achieve. Even a basic activity tracker will measure these factors relatively accurately. There is no real need to track other measures and pay more for an activity tracker that records them, unless you are getting really serious about exercise.
Corneel Vandelanotte, Professorial Research Fellow: Physical Activity and Health, CQUniversity Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.

Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Reflexology: What The Science Says
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How Does Reflexology Work, Really?
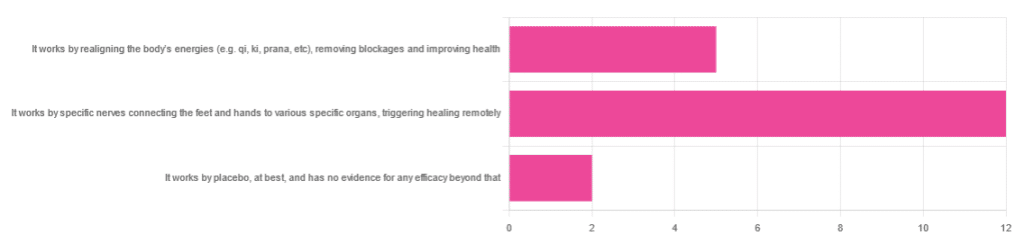
In Wednesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion of reflexology, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- About 63% said “It works by specific nerves connecting the feet and hands to various specific organs, triggering healing remotely”
- About 26% said “It works by realigning the body’s energies (e.g. qi, ki, prana, etc), removing blockages and improving health“
- About 11% said “It works by placebo, at best, and has no evidence for any efficacy beyond that”
So, what does the science say?
It works by realigning the body’s energies (e.g. qi, ki, prana, etc), removing blockages and improving health: True or False?
False, or since we can’t prove a negative: there is no reliable scientific evidence for this.
Further, there is no reliable scientific evidence for the existence of qi, ki, prana, soma, mana, or whatever we want to call it.
To save doubling up, we did discuss this in some more detail, exploring the notion of qi as bioelectrical energy, including a look at some unreliable clinical evidence for it (a study that used shoddy methodology, but it’s important to understand what they did wrong, to watch out for such), when we looked at [the legitimately very healthful practice of] qigong, a couple of weeks ago:
Qigong: A Breath Of Fresh Air?
As for reflexology specifically: in terms of blockages of qi causing disease (and thus being a putative therapeutic mechanism of action for attenuating disease), it’s an interesting hypothesis but in terms of scientific merit, it was pre-emptively supplanted by germ theory and other similarly observable-and-measurable phenomena.
We say “pre-emptively”, because despite orientalist marketing, unless we want to count some ancient pictures of people getting a foot massage and say it is reflexology, there is no record of reflexology being a thing before 1913 (and that was in the US, by a laryngologist working with a spiritualist to produce a book that they published in 1917).
It works by specific nerves connecting the feet and hands to various specific organs, triggering healing remotely: True or False?
False, or since we can’t prove a negative: there is no reliable scientific evidence for this.
A very large independent review of available scientific literature found the current medical consensus on reflexology is that:
- Reflexology is effective for: anxiety (but short lasting), edema, mild insomnia, quality of sleep, and relieving pain (short term: 2–3 hours)
- Reflexology is not effective for: inflammatory bowel disease, fertility treatment, neuropathy and polyneuropathy, acute low back pain, sub acute low back pain, chronic low back pain, radicular pain syndromes (including sciatica), post-operative low back pain, spinal stenosis, spinal fractures, sacroiliitis, spondylolisthesis, complex regional pain syndrome, trigger points / myofascial pain, chronic persistent pain, chronic low back pain, depression, work related injuries of the hip and pelvis
Source: Reflexology – a scientific literary review compilation
(the above is a fascinating read, by the way, and its 50 pages go into a lot more detail than we have room to here)
Now, those items that they found it effective for, looks suspiciously like a short list of things that placebo is often good for, and/or any relaxing activity.
Another review was not so generous:
❝The best evidence available to date does not demonstrate convincingly that reflexology is an effective treatment for any medical condition❞
~ Dr. Edzard Ernst (MD, PhD, FMedSci)
Source: Is reflexology an effective intervention? A systematic review of randomised controlled trials
In short, from the available scientific literature, we can surmise:
- Some researchers have found it to have some usefulness against chiefly psychosomatic conditions
- Other researchers have found the evidence for even that much to be uncompelling
It works by placebo, at best, and has no evidence for any efficacy beyond that: True or False?
Mostly True; of course reflexology runs into similar problems as acupuncture when it comes to testing against placebo:
How Does One Test Acupuncture Against Placebo Anyway?
…but not quite as bad, since it is easier to give a random foot massage while pretending it is a clinical treatment, than to fake putting needles into key locations.
However, as the paper we cited just above (in answer to the previous True/False question) shows, reflexology does not appear to meaningfully outperform placebo—which points to the possibility that it does work by placebo, and is just a placebo treatment on the high end of placebo (because the placebo effect is real, does work, isn’t “nothing”, and some placebos work better than others).
For more on the fascinating science and useful (applicable in daily life!) practicalities of how placebo does work, check out:
How To Leverage Placebo Effect For Yourself
Take care!
Share This Post
-
5 Stretches To Relieve The Pain From Sitting & Poor Posture
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sitting is not good for the health, yes often it’s a necessity of modern life, especially if driving. To make things worse, it can often be difficult to remember to maintain good posture the rest of the time, if it’s not a habit. So, while reducing sitting and improving posture are both very good things to do, here are 5 stretches to mitigate the damage meanwhile:
Daily doses:
These are best done at a rate of 2–3 sets daily:
Cat-Cow Stretch:
- Benefits: eases spinal tension, boosts flexibility, improves posture.
- How to: start on all fours, alternate between arching and rounding your back while syncing with your breath (10-15 times).
Butterfly Stretch:
- Benefits: loosens tight hips, improves lower back flexibility, and enhances mobility for activities like squats.
- How to: sit with soles of feet together, let knees fall toward the floor, lean forward slightly, and hold for 30 seconds to 1 minute.
Supine Twist:
- Benefits: unlocks the spine, relieves post-workout tension, and relaxes the shoulders and hips.
- How to: lie on your back, bend knees, twist to one side while keeping shoulders grounded, and hold for 30 seconds to 1 minute per side.
Calf Stretch:
- Benefits: improves ankle mobility, loosens tight calves, and prevents injuries like Achilles tendinitis.
- How to: stand facing a wall, extend one leg back with the heel on the ground, lean into the stretch, or use a step for deeper stretches. Hold for 30 seconds to 1 minute per leg.
Child’s Pose:
- Benefits: decompresses the spine, relaxes hips, and relieves tension in back and thighs.
- How to: start on hands and knees, sit back onto your heels, stretch arms forward, and rest forehead on the mat. Hold for 30 seconds to 1 minute.
For more on each of these, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
10 Tips To Reduce Morning Pain & Stiffness With Arthritis
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Menopause: 50 Things You Need to Know – by Dr. Felice Gersh
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Can you list 50 important facts about the menopause? If not, you’ll surely find things to learn in here.
The book is divided into three main sections:
- What to expect in perimenopause
- What to expect in early menopause
- What to expect in late menopause
Each section comes with an alarming array of symptoms, ranging from perimenopause fatigue and acne to late menopause tooth loss and vaginal prolapse. This is not to say that everyone will experience everything (fortunately), but rather, that these are the things that can happen and should not arrive unexpected.
Helpfully, of course, Dr. Gersh also gives advice on how to improve your energy and skin health, as well as keep your teeth and vagina in place. And similar professional insights for the rest of the “50 things you need to know”.
The style is like one big (182 pages) patient information leaflet—thus, very clear, explaining everything, and offering reassurance where possible and also what things are reasonable cause for seeking personalized medical attention.
Bottom line: if menopause is in your future, present, or very near past, this is an excellent book for you.
Click here to check out Menopause: 50 Things You Need To Know, and know them!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Vagus Nerve (And How You Can Make Use Of It)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Vagus Nerve: The Brain-Gut Highway
The longest cranial nerve is the vagus nerve; it runs all the way from your brain to your colon. It’s very important, and (amongst other tasks) it largely regulates your parasympathetic nervous system, and autonomous functions like:
- Breathing
- Heart rate
- Vasodilation & vasoconstriction
- Blood pressure
- Reflex actions (e.g. coughing, sneezing, swallowing, vomiting, hiccuping)
That’s great, but how does knowing about it help us?
Because of vagal maneuvers! This means taking an action to stimulate the vagus nerve, and prompt it to calm down various bodily functions that need calming down. This can take the form of:
- Massage
- Electrostimulation
- Diaphragmatic breathing
Massage is perhaps the simplest; “vagus” means “wandering”, and the nerve is accessible in various places, including behind the ears. That’s the kind of thing that’ easier to show than tell, though, so we’ll include a video at the end.
Electrostimulation is the fanciest, and has been used to treat migraines and cluster headaches. Check out, for example:
Update on noninvasive neuromodulation for migraine treatment-Vagus nerve stimulation
Diaphragmatic breathing means breathing from the diaphragm—the big muscular tissue that sits under your lungs. You might know it as “abdominal breathing”, and refers to breathing “to the abdomen” rather than merely to the chest.
Even though your lungs are obviously in your chest not your abdomen, breathing with a focus on expanding the abdomen (rather than the chest) when breathing in, will result in much deeper breathing as the diaphragm allows the lungs to fill downwards as well as outwards.
Why this helps when it comes to the vagus nerve is simply that the vagus nerve passes by the diaphragm, such that diaphragmatic breathing will massage the vagus nerve deep inside your body.
More than just treating migraines
Vagus nerve stimulation has also been researched and found potentially helpful for managing:
- Depression, inflammation, and heart disease
- Diabetes and glycemic issues in general
- Multiple sclerosis and autoimmune disease in general
- Alzheimer’s disease and dementia in general
- Rheumatoid arthritis (we already mentioned inflammation and autoimmune diseases, but this is an interesting paper so we included it)
All this is particularly important as we get older, because vagal response reduces with age, and vagus nerve stimulation, which improves vagal tone, makes it easier not just to manage the aforementioned maladies, but also simply to relax more easily and more deeply.
See: Influence of age and gender on autonomic regulation of heart
We promised a video for the massage, so here it is:
! Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
13 Things Mentally Strong Couples Don’t Do – by Dr. Amy Morin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The saying “happy wife; happy life” indeed goes regardless of gender. One can have every other happiness, but if there’s relational trouble, it brings everything else down.
This book is not intended, however, only for people whose relationships are one couple’s therapy session away from divorce. Rather, it’s intended as a preventative. Because, in this as in every other aspect of health, prevention is better than cure!
It is the sign of a strong couple to be proactive about the health of the relationship, and work together to build and reinforce things along the way.
The style of this book is very accessible pop-science, but the author speaks from a strong professional background in social work, psychology, and psychotherapy, and it shows.
Bottom line: if you’d like to strengthen your relationship skills, this book gives 13 great ways to do that.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Support For Long COVID & Chronic Fatigue
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Long COVID and Chronic Fatigue
Getting COVID-19 can be very physically draining, so it’s no surprise that getting Long COVID can (and usually does) result in chronic fatigue.
But, what does this mean and what can we do about it?
What makes Long COVID “long”
Long COVID is generally defined as COVID-19 whose symptoms last longer than 28 days, but in reality the symptoms not only tend to last for much longer than that, but also, they can be quite distinct.
Here’s a large (3,762 participants) study of Long COVID, which looked at 203 symptoms:
Characterizing long COVID in an international cohort: 7 months of symptoms and their impact
Three symptoms stood at out as most prevalent:
- Chronic fatigue (CFS)
- Cognitive dysfunction
- Post-exertional malaise (PEM)
The latter means “the symptoms get worse following physical or mental exertion”.
CFS, Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, is also called Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (ME).
What can be done about it?
The main “thing that people do about it” is to reduce their workload to what they can do, but this is not viable for everyone. Note that work doesn’t just mean “one’s profession”, but anything that requires physical or mental energy, including:
- Childcare
- Housework
- Errand-running
- Personal hygiene/maintenance
For many, this means having to get someone else to do the things—either with support of family and friends, or by hiring help. For many who don’t have those safety nets available, this means things simply not getting done.
That seems bleak; isn’t there anything more we can do?
Doctors’ recommendations are chiefly “wait it out and hope for the best”, which is not encouraging. Some people do recover from Long COVID; for others, it so far appears it might be lifelong. We just don’t know yet.
Doctors also recommend to journal, not for the usual mental health benefits, but because that is data collection. Patients who journal about their symptoms and then discuss those symptoms with their doctors, are contributing to the “big picture” of what Long COVID and its associated ME/CFS look like.
You may notice that that’s not so much saying what doctors can do for you, so much as what you can do for doctors (and in the big picture, eventually help them help people, which might include you).
So, is there any support for individuals with Long COVID ME/CFS?
Medically, no. Not that we could find.
However! Socially, there are grassroots support networks, that may be able to offer direct assistance, or at least point individuals to useful local resources.
Grassroots initiatives include Long COVID SOS and the Patient-Led Research Collaborative.
The patient-led organization Body Politic also used to have such a group, until it shut down due to lack of funding, but they do still have a good resource list:
Click here to check out the Body Politic resource list (it has eight more specific resources)
Stay strong!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: