Things Many People Forget When It Comes To Hydration
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Good hydration is about more than just “drink lots of water”, and in fact it’s quite possible for a person to drink too much water, and at the same time, be dehydrated. Here’s how and why and what to do about it:
Water, water, everywhere
Factors that people forget:
- Electrolyte balance: without it, we can technically have lots of water while either retaining it (in the case of too high salt levels) or peeing it out (in the case of too low salt levels), neither of which are as helpful as getting it right and actually being able to use the water.
- Gastrointestinal health: conditions like IBS, Crohn’s, or celiac disease can impair water and nutrient absorption, affecting hydration
- Genetic factors: some people simply have a predisposition to need more or less water for proper hydration
- Dietary factors: high salt, caffeine, and alcohol intake (amongst other diuretics) can increase water loss, while water-rich foods (assuming they aren’t also diuretics) increase hydration.
Strategies to do better:
- Drink small amounts of water consistently throughout the day rather than large quantities at once—healthy kidneys can process about 1 liter (about 1 quart) of water per hour, so drinking more than that will not help, no matter how dehydrated you are when you start. If your kidneys aren’t in peak health, the amount processable per hour will be lower for you.
- Increase fiber intake (e.g., fruit and vegetables) to retain water in the intestines and improve hydration
- Consume water-rich foods (e.g., watermelon, cucumbers, grapes) to enhance overall hydration and support cellular function (the body can use this a lot more efficiently than if you just drink water).
- Counteract the diuretic effects of caffeine and alcohol by drinking an additional 12 oz of water for every 8 oz of these beverages. Best yet, don’t drink alcohol and keep caffeine to a low level (or quit entirely, if you prefer, but for most people that’s not necessary).
- If you are sweating (be it because of weather, exercise, or any other reasons), include electrolyte fluids to improve cellular hydration, as they contain essential minerals like magnesium, potassium, and in moderation yes even sodium which you will have lost in your sweat too, supporting fluid regulation.
For more details on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Water’s Counterintuitive Properties
- Hydration Mythbusting
- When To Take Electrolytes (And When We Shouldn’t!)
- Keeping Your Kidneys Healthy (Especially After 60)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Peaceful Kitchen – by Catherine Perez
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author, a keen cook and Registered Dietician with a Master’s in same, covers the basics of the science of nutrition as relevant to her recipes, but first and foremost this is not a science textbook—it’s a cookbook, and its pages contain more love for the art than citations for the (perfectly respectable) science.
Mexican and Dominican cuisine are the main influences in this book, but there are dishes from around the world too.
The recipes themselves are… Comparable in difficulty to the things we often feature in our recipes section here at 10almonds. They’re probably not winning any restaurants Michelin stars, but they’re not exactly student survival recipes either. They’re made from mostly non-obscure whole foods, nutritionally-dense ingredients at that, with minimal processed foods involved.
That said, she does take a “add, don’t subtract” approach to nutrition, i.e. focussing more on adding in diversity of plants than on “don’t eat this; don’t eat that” mandates.
If there’s any criticism to be levelled at the book, it’s that in most cases we’d multiply the spices severalfold, but that’s not a big problem as readers can always judge that individually; she’s given the basic information of which spices in which proportions, which is the key knowledge.
Bottom line: if you’re looking to expand your plant-based cooking repertoire, this one is a fine choice.
Click here to check out Peaceful Kitchen, and try some new things!
Share This Post
-
Apple vs Apricot – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing apple to apricot, we picked the apricot.
Why?
In terms of macros, there’s not too much between them; apples are higher in carbs and only a little higher in fiber, which disparity makes for a slightly higher glycemic index, but it’s not a big difference and they are both low GI foods.
Micronutrients, however, set these two fruits apart:
In the category of vitamins, apple is a tiny bit higher in choline, while apricots are higher in vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, and K—in most cases, by quite large margins, too. All in all, a clear and easy win for apricots.
When it comes to minerals, apples are not higher in any minerals, while apricots are higher in calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. There’s simply no contest here.
In short, if an apple a day keeps the doctor away, then an apricot will give the doctor a nice weekend break somewhere.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Is Chiropractic All It’s Cracked Up To Be?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is Chiropractic All It’s Cracked Up To Be?
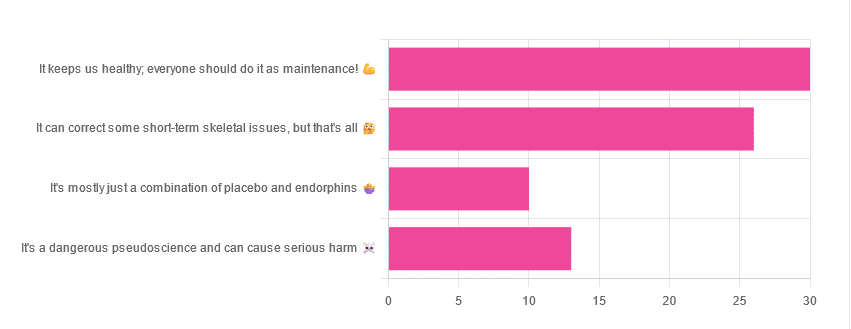
Yesterday, we asked you for your opinions on chiropractic medicine, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of results:
- 38% of respondents said it keeps us healthy, and everyone should do it as maintenance
- 33% of respondents said it can correct some short-term skeletal issues, but that’s all
- 16% of respondents said that it’s a dangerous pseudoscience and can cause serious harm
- 13% of respondents said that it’s mostly just a combination of placebo and endorphins
Respondents also shared personal horror stories of harm done, personal success stories of things cured, and personal “it didn’t seem to do anything for me” stories.
What does the science say?
It’s a dangerous pseudoscience and can cause harm: True or False?
False and True, respectively.
That is to say, chiropractic in its simplest form that makes the fewest claims, is not a pseudoscience. If somebody physically moves your bones around, your bones will be physically moved. If your bones were indeed misaligned, and the chiropractor is knowledgeable and competent, this will be for the better.
However, like any form of medicine, it can also cause harm; in chiropractic’s case, because it more often than not involves manipulation of the spine, this can be very serious:
❝Twenty six fatalities were published in the medical literature and many more might have remained unpublished.
The reported pathology usually was a vascular accident involving the dissection of a vertebral artery.
Conclusion: Numerous deaths have occurred after chiropractic manipulations. The risks of this treatment by far outweigh its benefit.❞
Source: Deaths after chiropractic: a review of published cases
From this, we might note two things:
- The abstract doesn’t note the initial sample size; we would rather have seen this information expressed as a percentage. Unfortunately, the full paper is not accessible, and nor are many of the papers it cites.
- Having a vertebral artery fatally dissected is nevertheless not an inviting prospect, and is certainly a very reasonable cause for concern.
It’s mostly just a combination of placebo and endorphins: True or False?
True or False, depending on what you went in for:
- If you went in for a regular maintenance clunk-and-click, then yes, you will get your clunk-and-click and feel better for it because you had a ritualized* experience and endorphins were released.
- If you went in for something that was actually wrong with your skeletal alignment, to get it corrected, and this correction was within your chiropractor’s competence, then yes, you will feel better because a genuine fault was corrected.
*this is not implying any mysticism, by the way. Rather it means simply that placebo effect is strongest when there is a ritual associated with it. In this case it means going to the place, sitting in a pleasant waiting room, being called in, removing your shoes and perhaps some other clothes, getting the full attention of a confident and assured person for a while, this sort of thing.
With regard to its use to combat specifically spinal pain (i.e., perhaps the most obvious thing to treat by chiropractic spinal manipulation), evidence is slightly in favor, but remains unclear:
❝Due to the low quality of evidence, the efficacy of chiropractic spinal manipulation compared with a placebo or no treatment remains uncertain. ❞
Source: Clinical Effectiveness and Efficacy of Chiropractic Spinal Manipulation for Spine Pain
It can correct some short-term skeletal issues, but that’s all: True or False?
Probably True.
Why “probably”? The effectiveness of chiropractic treatment for things other than short-term skeletal issues has barely been studied. From this, we may wish to keep an open mind, while also noting that it can hardly claim to be evidence-based—and it’s had hundreds of years to accumulate evidence. In all likelihood, publication bias has meant that studies that were conducted and found inconclusive or negative results were simply not published—but that’s just a hypothesis on our part.
In the case of using chiropractic to treat migraines, a very-related-but-not-skeletal issue, researchers found:
❝Pre-specified feasibility criteria were not met, but deficits were remediable. Preliminary data support a definitive trial of MCC+ for migraine.❞
Translating this: “it didn’t score as well as we hoped, but we can do better. We got some positive results, and would like to do another, bigger, better trial; please fund it”
Source: Multimodal chiropractic care for migraine: A pilot randomized controlled trial
Meanwhile, chiropractors’ claims for very unrelated things have been harshly criticized by the scientific community, for example:
Misinformation, chiropractic, and the COVID-19 pandemic
About that “short-term” aspect, one of our subscribers put it quite succinctly:
❝Often a skeletal correction is required for initial alignment but the surrounding fascia and muscles also need to be treated to mobilize the joint and release deep tissue damage surrounding the area. In combination with other therapies chiropractic support is beneficial.❞
This is, by the way, very consistent with what was said in the very clinically-dense book we reviewed yesterday, which has a chapter on the short-term benefits and limitations of chiropractic.
A truism that holds for many musculoskeletal healthcare matters, holds true here too:
❝In a battle between muscle and bone, muscle will always win❞
In other words…
Chiropractic can definitely help put misaligned bones back where they should be. However, once they’re there, if the cause of their misalignment is not treated, they will just re-misalign themselves shortly after you walking out of your session.
This is great for chiropractors, if it keeps you coming back for endless appointments, but it does little for your body beyond give you a brief respite.
So, by all means go to a chiropractor if you feel so inclined (and you do not fear accidental arterial dissection etc), but please also consider going to a physiotherapist, and potentially other medical professions depending on what seems to be wrong, to see about addressing the underlying cause.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Truth About Chocolate & Skin Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝What’s the science on chocolate and acne? Asking for a family member❞
The science is: these two things are broadly unrelated to each other.
There was a very illustrative study done specifically for this, though!
❝65 subjects with moderate acne ate either a bar containing ten times the amount of chocolate in a typical bar, or an identical-appearing bar which contained no chocolate. Counting of all the lesions on one side of the face before and after each ingestion period indicated no difference between the bars.
Five normal subjects ingested two enriched chocolate bars daily for one month; this represented a daily addition of the diet of 1,200 calories, of which about half was vegetable fat. This excessive intake of chocolate and fat did not alter the composition or output of sebum.
A review of studies purporting to show that diets high in carbohydrate or fat stimulate sebaceous secretion and adversely affect acne vulgaris indicates that these claims are unproved.❞
Source: Effect of Chocolate on Acne Vulgaris
As for what might help against acne more than needlessly abstaining from chocolate:
Why Do We Have Pores, And Could We Not?
…as well as:
Of Brains & Breakouts: The Neuroscience Of Your Skin
And here are some other articles that might interest you about chocolate:
- Chocolate & Health: Fact or Fiction?
- The “Love Drug”: Get PEA-Brained!
- Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Enjoy! And while we have your attention… Would you like this section to be bigger? If so, send us more questions!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
An apple cider vinegar drink a day? New study shows it might help weight loss
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Made from fermented apples and naturally high in acetic acid, apple cider vinegar has been popular in recent years for its purported health benefits – from antibacterial properties to antioxidant effects and potential for helping manage blood sugars.
Its origins as a health tonic stretch much further back. Hippocrates used it to treat wounds, fever and skin sores.
An experimental study, released today, looks into whether apple cider vinegar could be effective for weight loss, reduce blood glucose levels and reduce blood lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides).
The results suggest it could reduce all three – but it might not be as simple as downing an apple cider vinegar drink a day.
What did they do?
A group of scientists in Lebanon did a double-blinded, randomised, clinical trial in a group of overweight and obese young people aged from 12–25 years.
Researchers randomly placed 30 participants in one of four groups. The participants were instructed to consume either 5, 10 or 15ml of apple cider vinegar diluted into 250ml of water each morning before they ate anything for 12 weeks. A control group consumed an inactive drink (a placebo) made (from lactic acid added to water) to look and taste the same.
Typically this sort of study provides high quality evidence as it can show cause and effect – that is the intervention (apple cider vinegar in this case) leads to a certain outcome. The study was also double-blinded, which means neither the participants or the scientists involved with collecting the data knew who was in which group.
So, what did they find?
After a period of three months apple cider vinegar consumption was linked with significant falls in body weight and body mass index (BMI). On average, those who drank apple cider vinegar during that period lost 6–8kg in weight and reduced their BMI by 2.7–3 points, depending on the dose. They also showed significant decreases in the waist and hip circumference.
The authors also report significant decreases in levels of blood glucose, triglycerides, and cholesterol in the apple cider groups. This finding echoes previous studies. The placebo group, who were given water with lactic acid, had much smaller decreases in weight and BMI. There were also no significant decreases in blood glucose and blood lipids.
From animal studies, it is thought the acetic acid in apple cider vinegar may affect the expression of genes involved in burning fats for energy. The new study did not explore whether this mechanism was involved in any weight loss.
Is this good news?
While the study appears promising, there are also reasons for caution.
Firstly, study participants were aged from 12 to 25, so we can’t say whether the results could apply to everyone.
The statistical methods used in the study don’t allow us to confidently say the same amount of weight loss would occur again if the study was done again.
And while the researchers kept records of the participants’ diet and exercise during the study, these were not published in the paper. This makes it difficult to determine if diet or exercise may have had an impact. We don’t know whether participants changed the amount they ate or the types of food they ate, or whether they changed their exercise levels.
The study used a placebo which they tried to make identical in appearance and taste to the active treatment. But people may still be able to determine differences. Researchers may ask participants at the end of a study to guess which group they were in to test the integrity of the placebo. Unfortunately this was not done in this study, so we can’t be certain if the participants knew or not.
Finally, the authors do not report whether anyone dropped out of the study. This could be important and influence results if people who did not lose weight quit due to lack of motivation.
Is that you mother? The enzymes in apple cider vinegar might be health-giving.
ShutterstockAny other concerns?
Apple cider vinegar is acidic and there are concerns it may erode tooth enamel. This can be a problem with any acidic beverages, including fizzy drinks, lemon water and orange juice.
To minimise the risk of acid erosion some dentists recommend the following after drinking acidic drinks:
- rinsing out your mouth with tap water afterwards
- chewing sugar-free gum afterwards to stimulate saliva production
- avoiding brushing your teeth immediately after drinking because it might damage the teeth’s softened top layer
- drink with a straw to minimise contact with the teeth.
Rinsing with water could prevent acid damaging your teeth.
ShutterstockDown the hatch?
This study provides us with some evidence of a link between apple cider vinegar and weight loss. But before health professionals can recommend this as a weight loss strategy we need bigger and better conducted studies across a wider age range.
Such research would need to be done alongside a controlled background diet and exercise across all the participants. This would provide more robust evidence that apple cider vinegar could be a useful aid for weight loss.
Still, if you don’t mind the taste of apple cider vinegar then you could try drinking some for weight loss, alongside a healthy balanced and varied dietary intake. This study does not suggest people can eat whatever they like and drink apple cider vinegar as a way to control weight.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Best Salt for Neti Pots?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
❓ Q&A With 10almonds Subscribers!
Q: What kind of salt is best for neti pots?
A: Non-iodised salt is usually recommended, but really, any human-safe salt is fine. By this we mean for example:
- Sodium chloride (like most kitchen salts),
- Potassium chloride (as found in “reduced sodium” kitchen salts), or
- Magnesium sulfate (also known as epsom salts).
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: