The Book of Lymph – by Lisa Levitt Gainsely
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The book starts with an overview of what lymph is and why it matters, before getting into the main meat of the book, which is lymphatic massage techniques to improve lymphatic flow/drainage throughout different parts of the body, and in the context of an assortment of common maladies that may merit particular attention.
There’s an element of aesthetic medicine here, and improving beauty, but there’s also a whole section devoted to such things as breast care and the like (bearing in mind, the lymphatic system is one of our main defenses against cancer). There’s also a lot about managing lymph in the context of chronic health conditions.
The style is light pop-science; the science is explained clearly throughout, but without academic citations every few lines as some books might have. The author is, after all, a practitioner (CLT) and/but not an academic.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your lymphatic health, whether for beauty or health maintenance or recovery, this book will walk you through it.
Click here to check out The Book of Lymph, and give yours some love!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sweet Spot for Brain Health – by Dr. Sui Wong
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
At 10almonds we often mention that “what’s good for the heart is good for the brain”, but at least in part, it’s because (as this book makes very clear), “what’s good for the blood is good for the brain”. After all, our brain uses about 25% of our energy, and that energy is delivered there by the blood. And if it doesn’t get enough nutrients, oxygen, etc, and detritus isn’t taken away, then problems happen.
Dr. Wong discusses Alzheimer’s as heavily driven by metabolic problems such as diabetes and even pre-diabetes, and sets out to put in our hands the guidebook to not only not doing that, but also, actually making sure our brain gets proper nourishment without delivering that as intermittent sugar spikes because we opted for a something with very fast-acting carbs to perk us up energetically.
More than most books on the topic, she talks a lot about the neurobiology of glucose metabolism, so that’s something that really sets this book apart from many of its genre.
The style is narrative, explaining the body’s processes in a clear fashion, without skimping on science. There are definitely words that your average layperson might not know, but they’re explained as we go, and there are frequent recaps of what we learned previously, making for ultimately easy reading.
After all the information is given, there’s also a guided “12-week challenge” with a theme-of-the-week for each week, to integrate a new lifestyle adjustment each week in a progressive fashion so that without needing to drastically change many things at once, we get where we need to be in terms of healthy habits.
Bottom line: if you’d like to do right by your brain and while you’re at it say goodbye to blood sugar highs and lows, then this book is an excellent guide for that.
Click here to check out Sweet Spot For Brain Health, and enjoy a consistently-energized brain!
Share This Post
-
We Hope This Email Blows Your Tits Clean Off
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Right Kind Of “Email Hacks”!
Are you a Gmailer or an Outlookista? Whatever your preference, you’re probably facing many of the same challenges that most of us face in our work and personal lives:
Email’s greatest strength (its ease of accessibility) brings about its greatest problem (our inboxes are cluttered and chaotic), not to mention that each of us are usually managing a whole flock of email addresses.
Sometimes we put productivity resources up against each other; that’s not what we’re going to do today! Each of these can play a role alongside each other; grab as many as will make your life easier:
ProtonMail: this is an email client; it’s the nicest, simplest, easiest, free email client that doesn’t track, let alone share, everything you do.
Bonus: there also exists ProtonCalendar (it’s a calendar that doesn’t share your data), ProtonDrive (it’s a cloud storage provider that doesn’t share your data) and, because they’re indeed serious about your privacy, ProtonVPN (it’s a VPN that, of course, doesn’t share your data).
Clean Email: maybe you’re stuck with the email provider you have. It happens. But it doesn’t have to be a chaotic mess. This tool will make tidying your email (and keeping it tidy!) a simplified dream.
See How Clean Your Email Can Get With Just A Few Clicks!
Right Inbox: a Gmail extension with many useful features, including read receipts, emails scheduled for later (e.g: time your email to send at 7am to look like a morning lark when in fact you’re peacefully snoozing), add unforwardable “For Your Eyes Only” notes to emails, and more.
Power Up Your Gmail With The Right Inbox Extension!
Email Finder: find the verified work email address of any person, so long as you know what company you’re looking for them in! No more “I thought it was lastname.firstname@ and it was firstname.lastname@”, no more “the wrong John Smith”, no more “undelivered” bounceback notices. Just: your email delivered.
Never Hear From The Mailer Daemon Again, With Email Finder!
Unroll.me: love your subscriptions, but hate the clutter? Unroll.me aggregates them for you in a virtual roll-up, with an “unroll” button to read them.
Get What You Really Want From Your Subscriptions, With Unroll.Me!
On which note, anything you’d like to hear more of from us? Let us know! You can always just hit reply, or use the feedback widget at the bottom of this email
Share This Post
-
Metabolical – by Dr. Robert Lustig
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The premise of this book itself is not novel: processed food is bad, food giants lie to us, and eating better makes us less prone to disease (especially metabolic disease).
What this book does offer that’s less commonly found is a comprehensive guide, a walkthrough of each relevant what and why and how, with plenty of good science and practical real-world examples.
In terms of unique selling points, perhaps the greatest strength of this book is its focus on two things in particular that affect many aspects of health: looking after our liver, and looking after our gut.
The style is… A little dramatic perhaps, but that’s just the style; there’s no hyperbole, he is stating well-established scientific facts.
Bottom line: very much of chronic disease would be a lot less diseasey if we all ate with these aspects of our health in mind. This book’s a comprehensive guide to that.
Click here to check out Metabolical, and let food be thy medicine!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
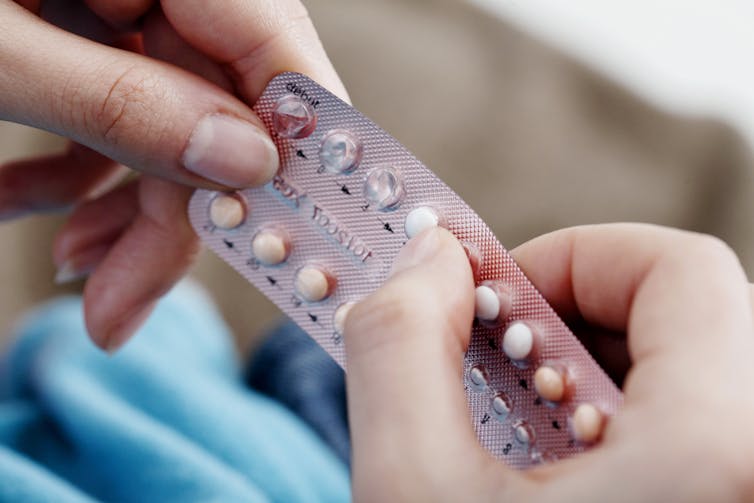
Long-acting contraceptives seem to be as safe as the pill when it comes to cancer risk
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many women worry hormonal contraceptives have dangerous side-effects including increased cancer risk. But this perception is often out of proportion with the actual risks.
So, what does the research actually say about cancer risk for contraceptive users?
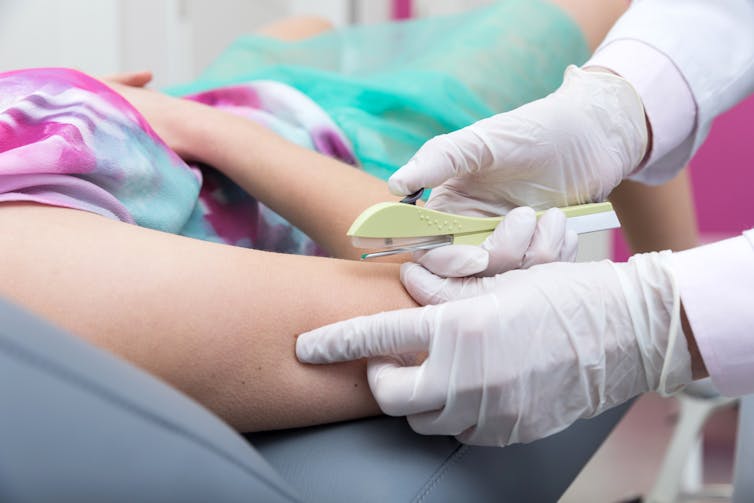
And is your cancer risk different if, instead of the pill, you use long-acting reversible contraceptives? These include intrauterine devices or IUDs (such as Mirena), implants under the skin (such as Implanon), and injections (such as Depo Provera).
Our new study, conducted by the University of Queensland and QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute and published by the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, looked at this question.
We found long-acting contraceptives seem to be as safe as the pill when it comes to cancer risk (which is good news) but not necessarily any safer than the pill.
Peakstock/Shutterstock Some hormonal contraceptives take the form of implants under the skin. WiP-Studio/Shutterstock How does the contraceptive pill affect cancer risk?
The International Agency for Research on Cancer, which compiles evidence on cancer causes, has concluded that oral contraceptives have mixed effects on cancer risk.
Using the oral contraceptive pill:
- slightly increases your risk of breast and cervical cancer in the short term, but
- substantially reduces your risk of cancers of the uterus and ovaries in the longer term.
Our earlier work showed the pill was responsible for preventing far more cancers overall than it contributed to.
In previous research we estimated that in 2010, oral contraceptive pill use prevented over 1,300 cases of endometrial and ovarian cancers in Australian women.
It also prevented almost 500 deaths from these cancers in 2013. This is a reduction of around 25% in the deaths that could have occurred that year if women hadn’t taken the pill.
In contrast, we calculated the pill may have contributed to around 15 deaths from breast cancer in 2013, which is less than 0.5% of all breast cancer deaths in that year.
Previous work showed the pill was responsible for preventing far more cancers overall than it contributed to. Image Point Fr What about long-acting reversible contraceptives and cancer risk?
Long-acting reversible contraceptives – which include intrauterine devices or IUDs, implants under the skin, and injections – release progesterone-like hormones.
These are very effective contraceptives that can last from a few months (injections) up to seven years (intrauterine devices).
Notably, they don’t contain the hormone oestrogen, which may be responsible for some of the side-effects of the pill (including perhaps contributing to a higher risk of breast cancer).
Use of these long-acting contraceptives has doubled over the past decade, while the use of the pill has declined. So it’s important to know whether this change could affect cancer risk for Australian women.
Our new study of more than 1 million Australian women investigated whether long-acting, reversible contraceptives affect risk of invasive cancers. We compared the results to the oral contraceptive pill.
We used de-identified health records for Australian women aged 55 and under in 2002.
Among this group, about 176,000 were diagnosed with cancer between 2004 and 2013 when the oldest women were aged 67. We compared hormonal contraceptive use among these women who got cancer to women without cancer.
We found that long-term users of all types of hormonal contraception had around a 70% lower risk of developing endometrial cancer in the years after use. In other words, the risk of developing endometrial cancer is substantially lower among women who took hormonal contraception compared to those who didn’t.
For ovarian cancer, we saw a 50% reduced risk (compared to those who took no hormonal contraception) for women who were long-term users of the hormone-containing IUD.
The risk reduction was not as marked for the implants or injections, however few long-term users of these products developed these cancers in our study.
As the risk of endometrial and ovarian cancers increases with age, it will be important to look at cancer risk in these women as they get older.
What about breast cancer risk?
Our findings suggest that the risk of breast cancer for current users of long-acting contraceptives is similar to users of the pill.
However, the contraceptive injection was only associated with an increase in breast cancer risk after five years of use and there was no longer a higher risk once women stopped using them.
Our results suggested that the risk of breast cancer also reduces after stopping use of the contraceptive implants.
We will need to follow-up the women for longer to determine whether this is also the case for the IUD.
It is worth emphasising that the breast cancer risk associated with all hormonal contraceptives is very small.
About 30 in every 100,000 women aged 20 to 39 years develop breast cancer each year, and any hormonal contraceptive use would only increase this to around 36 cases per 100,000.
What about other cancers?
Our study did not show any consistent relationships between contraceptive use and other cancers types. However, we only at looked at invasive cancers (meaning those that start at a primary site but have the potential to spread to other parts of the body).
A recent French study found that prolonged use of the contraceptive injection increased the risk of meningioma (a type of benign brain tumour).
However, meningiomas are rare, especially in young women. There are around two cases in every 100,000 in women aged 20–39, so the extra number of cases linked to contraceptive injection use was small.
The French study found the hormonal IUD did not increase meningioma risk (and they did not investigate contraceptive implants).
Benefits and side-effects
There are benefits and side-effects for all medicines, including contraceptives, but it is important to know most very serious side-effects are rare.
A conversation with your doctor about the balance of benefits and side-effects for you is always a good place to start.
Susan Jordan, Professor of Epidemiology, The University of Queensland; Karen Tuesley, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, School of Public Health, The University of Queensland, and Penny Webb, Distinguished Scientist, Gynaecological Cancers Group, QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Caffeine Blues – by Stephen Cherniske
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Caffeine use is an interesting and often-underexamined factor in health. Beyond the most superficial of sleep hygiene advice (à la “if you aren’t sleeping well, consider skipping your triple espresso martini at bedtime”), it’s often considered a “everybody has this” drug.
In this book, Cherniske explores a lot of the lesser-known effects of caffeine, and the book certainly is a litany against caffeine dependence, ultimately arguing strongly against caffeine use itself. The goal is certainly to persuade the reader to desist in caffeine use, and while the book’s selling point is “learn about caffeine” not “how to quit caffeine”, a program for quitting caffeine is nevertheless included.
You may notice the title and cover design are strongly reminiscent of “Sugar Blues”, which came decades before it, and that’s clearly not accidental. The style is similar—very sensationalist, and with a lot of strong claims. In this case, however, there is actually a more robust bibliography, albeit somewhat dated now as science has continued to progress since this book was published.
Bottom line: in this reviewer’s opinion, the book overstates its case a little, and is prone to undue sensationalism, but there is a lot of genuinely very good information in here too, making it definitely worth reading.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Accidentally Overweight – by Dr. Libby Weaver
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book’s main premise is that for most people who become overweight especially in midlife or later, if there wasn’t an obvious lifestyle change to precipitate this (e.g. started living on fast food for some reason), then in most cases, what’s needed is not drastic action, so much as some metabolic tweaks to correct things that have gone off-piste a little in our physiology.
The book covers nine factors that make an impact, and how each can be managed. They are:
- Insulin
- Stress hormones
- Calories
- Thyroid function
- Nervous system
- Emotions
- Sex hormones
- Liver function
- Gut bacteria
Some will be obvious, but as Dr. Weaver explains, are relative trivial compared to the others; “calories” in one such example of this “yes, it’s a factor, but very overrated” category.
Others are things that most people don’t think too much about, like liver function. And yet, it is indeed very much critical, and a major player in metabolism and adiposity.
The style is on the very light end of pop-science, but she does bring her professional knowledge to bear on topic (her doctorate is a PhD in biochemistry, so a lot of explanations come from that angle).
Bottom line: if you’ve found yourself “accidentally overweight”, and would like to tip the scales back in the other direction without doing anything extreme, then this book provides the tweaks that no amount of cardio or restrictive dieting will.
Click here to check out Accidentally Overweight, and re-adjust it back the other way!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: