Solitary Fitness – by Charles Bronson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sometimes it can seem that every new diet and/or exercise regime you want to try will change your life, if just you first max out your credit card on restocking your kitchen and refurbishing your home gym, not to mention buying all the best supplements, enjoying the latest medical gadgets, and so on and so forth.
And often… Most of those things genuinely are good! And it’s great that such things are becoming more accessible and available.
But… Wouldn’t it be nice to know how to have excellent strength and fitness without any of that, even if just as a “bare bones” protocol to fall back on? That’s what Manson provides in this book.
The writing style is casual and friendly; Manson is not exactly an academic, but he knows his stuff when it comes to what works. And a good general rule of thumb is: if it’s something that he can do in his jail cell, we can surely do it in the comfort of our homes.
Bottom line: if you want functional strength and fitness with zero gimmicks, this is the book for you (as an aside, it’s also simply an interesting and recommendable read, sociologically speaking, but that’s another matter entirely).
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Which Magnesium? (And: When?)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Good morning! I have been waiting for this day to ask: the magnesium in my calcium supplement is neither of the two versions you mentioned in a recent email newsletter. Is this a good type of magnesium and is it efficiently bioavailable in this composition? I also take magnesium that says it is elemental (oxide, gluconate, and lactate). Are these absorbable and useful in these sources? I am not interested in taking things if they aren’t helping me or making me healthier. Thank you for your wonderful, informative newsletter. It’s so nice to get non-biased information❞
Thank you for the kind words! We certainly do our best.
For reference: the attached image showed a supplement containing “Magnesium (as Magnesium Oxide & AlgaeCal® l.superpositum)”
Also for reference: the two versions we compared head-to-head were these very good options:
Magnesium Glycinate vs Magnesium Citrate – Which is Healthier?
Let’s first borrow from the above, where we mentioned: magnesium oxide is probably the most widely-sold magnesium supplement because it’s cheapest to make. It also has woeful bioavailability, to the point that there seems to be negligible benefit to taking it. So we don’t recommend that.
As for magnesium gluconate and magnesium lactate:
- Magnesium lactate has very good bioavailability and in cases where people have problems with other types (e.g. gastrointestinal side effects), this will probably not trigger those.
- Magnesium gluconate has excellent bioavailability, probably coming second only to magnesium glycinate.
The “AlgaeCal® l.superpositum” supplement is a little opaque (and we did ntoice they didn’t specify what percentage of the magnesium is magnesium oxide, and what percentage is from the algae, meaning it could be a 99:1 ratio split, just so that they can claim it’s in there), but we can say Lithothamnion superpositum is indeed an algae and magnesium from green things is usually good.
Except…
It’s generally best not to take magnesium and calcium together (as that supplement contains). While they do work synergistically once absorbed, they compete for absorption first so it’s best to take them separately. Because of magnesium’s sleep-improving qualities, many people take calcium in the morning, and magnesium in the evening, for this reason.
Some previous articles you might enjoy meanwhile:
- Pinpointing The Usefulness Of Acupuncture
- Science-Based Alternative Pain Relief
- Peripheral Neuropathy: How To Avoid It, Manage It, Treat It
- What Does Lion’s Mane Actually Do, Anyway?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Recipe For Empowered Leadership – by Doug Meyer-Cuno
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is not a “here’s how to become a leader, you young would-be Machiavelli”; it’s more a “so you’re in a leadership role; now what?” book. The book’s subtitle describes well its contents: “25 Ingredients For Creating Value & Empowering Others”
The book is written with the voice of experience, but without the ego-driven padding that accompanies many such books. Especially: any anecdotal illustrations are short and to-the-point, no chapter-long diversions here.
Which we love!
Equally helpful is where the author does spend a little more time and energy: on the “down to brass tacks” of how exactly to do various things.
In short: if instead of a lofty-minded book of vague idealized notions selling a pipedream, you’d rather have a manual of how to actually be a good leader when it comes down to it, this is the book for you.
Pick Up The Recipe For Empowered Leadership On Amazon Today!
Share This Post
-
Paulina Porizkova (Former Supermodel) Talks Menopause, Aging, & Appearances
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are supermodels destined to all eventually become “Grizabella the Glamor Cat”, a washed-up shell of their former glory? Is it true that “men grow cold as girls grow old, and we all lose our charms in the end”? And what—if anything—can we do about it?
Insights from a retired professional
Paulina Porizkova is 56, and she looks like she’s… 56, maybe? Perhaps a little younger or a bit older depending on the camera and lighting and such.
It’s usually the case, on glossy magazine covers and YouTube thumbnails, that there’s a 20-year difference between appearance and reality, but not here. Why’s that?
Porizkova noted that many celebrities of a similar age look younger, and felt bad. But then she noted that they’d all had various cosmetic work done, and looked for images of “real” women in their mid-50s, and didn’t find them.
Note: we at 10almonds do disagree with one thing here: we say that someone who has had cosmetic work done is no less real for it; it’s a simple matter of personal choice and bodily autonomy. She is, in our opinion, making the same mistake as people make when they say such things as “real people, rather than models”, as though models are not also real people.
Porizkova found modelling highly lucrative but dehumanizing, and did not enjoy the objectification involved—and she enjoyed even less, when she reached a certain age, negative comments about aging, and people being visibly wrong-footed when meeting her, as they had misconceptions based on past images.
As a child and younger adult through her modelling career, she felt very much “seen and not heard”, and these days, she realizes she’s more interesting now but feels less seen. Menopause coincided with her marriage ending, and she felt unattractive and ignored by her husband; she questioned her self-worth, and felt very bad about it. Then her husband (they had separated, but had not divorced) died, and she felt even more isolated—but it heightened her sensitivity to life.
In her pain and longing for recognition, she reached out through her Instagram, crying, and received positive feedback—but still she struggles with expressing needs and feeling worthy.
And yet, when it comes to looks, she embraces her wrinkles as a form of expression, and values her natural appearance over cosmetic alterations.
She describes herself as a work in progress—still broken, still needing cleansing and healing, but proud of how far she’s come so far, and optimistic with regard to the future.
For all this and more in her own words, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Many Faces Of Cosmetic Surgery
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What to Eat When – by Drs. Michael Roizen and Michael Crupain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Here at 10almonds, we cover a lot of the “what to eat”, but tend to only sometimes touch on the “when”—and indeed, this is a reflection of a popular focus. But what if we were to pay a little more attention to that “when”; what would it get us?
According to Drs. Roizen and Crupain… Quite a bit!
In this work, they take into account the various factors affecting the benefit (or harm!) of what we eat when:
- in the context of our circadian rhythm
- in the context of our insulin responses
- in the context of intermittent fasting
The style throughout is very focused on practical actionable advice. For example, amongst other lifestyle-adjustment suggestions, the authors make the case for front-loading various kinds of food earlier in the day, and eating more attentively and mindfully when we do eat.
They also offer a lot of “quick tips” of the kind we love here at 10almonds! Ranging from “how about this breakfast idea” to “roasting chickpeas like this makes a great snack” to “this dessert is three healthy foods disguised as a sundae”
All in all, if you’d like a stack of small tweaks that can add up to a big difference in your overall health, this is a book for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
More Things Dopamine Does For Us
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In this week’s news roundup, we have two dopamine items and one other for variety:
The real “dopamine switch”
Dopamine is well-known as “the reward chemical”, and indeed it is that, but it also plays a central role in many neurological processes, including:
- Linear task processing
- Motivation
- Learning and memory
- Motor functions
- Language faculties
Recent research has now shown its importance in cognitive flexibility, i.e. the ability to adapt to circumstances, and switch approaches appropriately to such, and generally not get stuck in a cognitive rut:
Read in full: Scientists confirm neurobiochemical link between dopamine and cognitive flexibility
Related: The Dopamine Myth
You may like the sound of this
It’s been known for a while that dopamine is involved in learning and memory (as mentioned above), but this has been established largely by associative studies, e.g. “people with lower dopamine levels learn less easily”. But scientists have now mapped out more of how it actually does that.
One more reason to ensure we have and maintain healthy dopamine levels!
Read in full: Songbirds highlight dopamine’s role in learning
Related: 10 Ways To Naturally Boost Dopamine
Resist Or Run!
When it comes to protecting against bone loss, resistance exercise remains key, but impact-laden activities such as running (but not lower-level everyday activity) can help too. There have been studies on the extent to which walking (a load-bearing activity) may be protective against bone loss, and the results of those studies have mostly been inconclusive.
This study looked into the incidence (or not, as the case may be) of bone-loading impacts in everyday movements, using accelerometers, and measured bone mineral density before and after testing periods. Those that had higher-intensity bone-loading movements (so, resistance training or running, for example) retained the best measures of bone density through menopause into postmenopause:
Read in full: Everyday physical activity does not slow bone loss during menopause, finds study
Related: The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
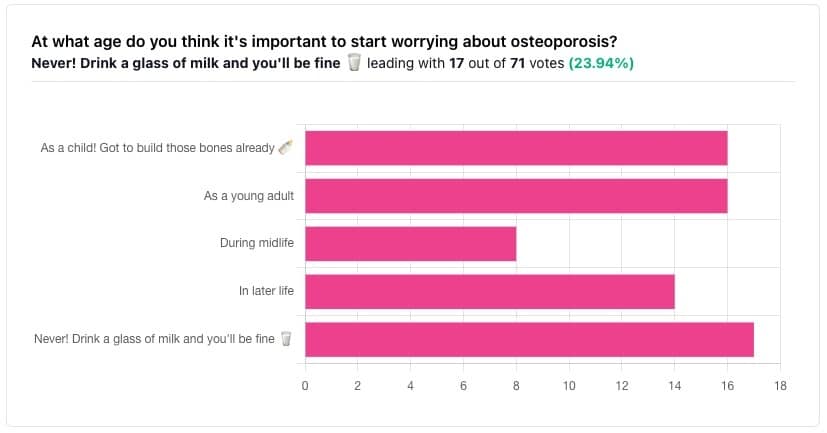
In yesterday’s issue of 10almonds, we asked you “at what age do you think it’s important to start worrying about osteoporosis?”, and here’s the spread of answers you gave us:
The Bare-bones Truth About Osteoporosis
In yesterday’s issue of 10almonds, we asked you “at what age do you think it’s important to start worrying about osteoporosis?”, and here’s the spread of answers you gave us:
At first glance it may seem shocking that a majority of respondents to a poll in a health-focused newsletter think it’ll never be an issue worth worrying about, but in fact this is partly a statistical quirk, because the vote of the strongest “early prevention” crowd was divided between “as a child” and “as a young adult”.
This poll also gave you the option to add a comment with your vote. Many subscribers chose to do so, explaining your choices… But, interestingly, not one single person who voted for “never” had any additional thoughts to add.
We loved reading your replies, by the way, and wish we had room to include them here, because they were very interesting and thought-provoking.
Let’s get to the myths and facts:
Top myth: “you will never need to worry about it; drink a glass of milk and you’ll be fine!”
The body is constantly repairing itself. Its ability to do that declines with age. Until about 35 on average, we can replace bone mineral as quickly as it is lost. After that, we lose it by up to 1% per year, and that rate climbs after 50, and climbs even more steeply for those who go through (untreated) menopause.
Losing 1% per year might not seem like a lot, but if you want to live to 100, there are some unfortunate implications!
About that menopause, by the way… Because declining estrogen levels late in life contribute significantly to osteoporosis, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be of value to many for the sake of bone health, never mind the more obvious and commonly-sought benefits.
On the topic of that glass of milk…
- Milk is a great source of calcium, which is useless to the body if you don’t also have good levels of vitamin D and magnesium.
- People’s vitamin D levels tend to directly correlate to the level of sun where they live, if supplementation isn’t undertaken.
- Plant-based milks are usually fortified with vitamin D (and calcium), by the way.
- Most people are deficient in magnesium, because green leafy things don’t form as big a part of most people’s diets as they should.
See also: An update on magnesium and bone health
Next most common myth: “bone health is all about calcium”
We spoke a little above about the importance of vitamin D and magnesium for being able to properly use that. But potassium is also critical:
Read more: The effects of potassium on bone health
While we’re on the topic…
People think of collagen as being for skin health. And it is important for that, but collagen’s benefits (and the negative effects of its absence) go much deeper, to include bone health. We’ve written about this before, so rather than take more space today, we’ll just drop the link:
We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
Want to really maximize your bone health?
You might want to check out this well-sourced LiveStrong article:
Bone Health: Best and Worst Foods
(Teaser: leafy greens are in 2nd place, topped by sardines at #1—where do you think milk ranks?)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: