Reasons to Stay Alive – by Matt Haig
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Matt Haig’s (excellent) The Comfort Book, and now it’s time for his more famous book: Reasons To Stay Alive. So, what’s this one, beyond the obvious?
It narrates the experience of anxiety, depression, and suicidality, and discovering how to find beauty and joy in the world despite it all. It’s not that the author found a magical cure—he still experiences depression and anxiety (cannot speak for suicidality) but he knows now how to manage it, and live his life.
You may be wondering: is this book instructional; is it reproducible, or is it just an autobiography? It’s centered around his own experience and learnings, but it gives a huge sense of not feeling alone, of having hope, and it gives a template for making sense of one’s own experience, even if every person will of course have some points of differences, the commonalities are nonetheless of immense value.
The writing style is similar to The Comfort Book; it’s lots of small chapters, and all very easy-reading. Well, the subject matter is sometimes rather heavy, but the language is easy-reading! In other words, just the thing for when one is feeling easily overwhelmed, or not feeling up to reading a lot.
Bottom line: whether or not you suffer with anxiety and/or depression, whether or not you sometimes feel suicidal, the contents of this book are important, valuable insights for everyone.
Click here to check out Reasons To Stay Alive, and see through the highs and lows of life.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Young Forever – by Dr. Mark Hyman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of work on the topic of aging looks at dealing with symptoms of aging, rather than the causes. And, that’s worthy too! Those symptoms often do need addressing. But this book is about treating the causes.
Dr. Hyman outlines:
- How and why we age
- The root causes of aging
- The ten hallmarks of aging
From there, we go on to learn about the foundations of longevity, and balancing our seven core biological systems:
- Nutrition, digestion, and the microbiome
- Immune and inflammatory system
- Cellular energy
- Biotransformation and elimination/detoxification*
- Hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signalling molecules
- Circulation and lymphatic flow
- Structural health, from muscle and bones to cells and tissues
*This isn’t about celery juice fasts and the like; this talking about the work your kidneys, liver, and other organs do
The book goes on to detail how, precisely, with practical actionable advices, to optimize and take care of each of those systems.
All in all: if you want a great foundational understanding of aging and how to slow it to increase your healthy lifespan, this is a very respectable option.
Click here to get your copy of “Young Forever” from Amazon today!
Share This Post
-
What’s Your Vascular Dementia Risk?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We often say that “what’s good for your heart is good for your brain”, and this is because the former feeds the latter, with oxygen and nutrients, and also clears away detritus like beta-amyloid (associated with Alzheimer’s) and alpha-synuclein (associated with Parkinson’s).
For more on those, see: How To Clean Your Brain (Glymphatic Health Primer)
For this reason, there are many risk factors that apply equally cardiovascular disease (CVD), and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and other vascular dementias, as well as stroke risk.
The link between the two has also been studied; recently a team of scienists led by Dr. Anisa Dhana asked the question:
❝What is the association between cardiovascular health (CVH) and biomarkers of neurodegeneration, including neurofilament light chain and total tau?❞
To answer this, they looked at data from more than 10,000 Americans aged 65+; of these, they were able to get serum samples from 5,470 of them, and tested those samples for the biomarkers of neurodegeneration mentioned above.
They then tabulated the results with cardiovascular health scores based on the American Heart Association (AHA)’s “Life’s Simple 7” tool, and found, amongst other things:
- 34.6% of participants carried the APOE e4 allele, a genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s.
- Higher CVH scores were associated with lower NfL levels, but not with t-tau concentrations.
- APOE e4 carriers with high CVH had significantly lower NfL levels.
- Race did not influence the CVH-NfL relationship.
- Higher CVH was linked to a slower annual increase in NfL levels but did not affect t-tau changes.
- Over 10 years, participants with the lowest CVH scores saw a 7.1% annual increase in NfL levels, while those with the highest CVH scores had a 5.2% annual increase.
- Better CVH is linked to lower serum NfL levels, regardless of age, sex, or race.
- CVH is particularly crucial for APOE e4 carriers
In other words: higher cardiovascular health meant lower markers of neurodegeneration, and this not only still held true for APOE e4 carriers, but also, the benefits actually even more pronounced in those participants.
You may be wondering: “but it said it helped with NfL levels, not t-tau concentrations?” And, indeed, it is so. But this means that the overall neurodegeneration risk is still inversely proportional to cardiovascular health; it just means it’s not a magical panacea and we must still do other things too.
See also: How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
And as for the study, you can read the paper itself in full here:
Cardiovascular Health and Biomarkers of Neurodegenerative Disease in Older Adults
Life’s Simple 7
We mentioned that they used the AHA’s “Life’s Simple 7” tool to assess cardiovascular health; it is indeed simple, but important. Here it is:
Metric Poor Intermediate Ideal Current smoking Yes Former ≤12 mo Never or quit >12 mo BMI, kg/m2 ≥30 25–29.9 <25 Physical activity None 1–149 min/wk of moderate activity or 1–74 min/wk of vigorous activity or 1–149 min/wk of moderate and vigorous activity ≥150 min/wk of moderate activity or ≥75 min/wk of vigorous activity or ≥150 min/wk of moderate and vigorous activity Diet pattern score* 0–1 2–3 4–5 Total cholesterol, mg/dL ≥240 200–239 or treated to goal <200 Blood pressure, mm Hg SBP ≥140 or DBP ≥90 SBP 120–139 or DBP 80–89 or treated to goal <120/<80 Fasting plasma glucose, mg/dL ≥126 100–125 or treated to goal <100 *Each of the following 5 diet elements is given a score of 1: (1) ≥4.5 cups/day of fruits and vegetables; (2) ≥2 servings/week of fish; (3) ≥3 servings/day of whole grains; (4) no more than 36 oz/wk of sugar‐sweetened beverages; and (5) no more than 1500 mg/d of sodium.
As the AHA notes,
❝Unfortunately, 99% of the U.S. adult population has at least one of seven cardiovascular health risks: tobacco use,
poor diet, physical inactivity, unhealthy weight, high blood pressure, high cholesterol or high blood glucose.❞It then goes on to talk about the financial burden of this on employers, but this was taken from a workplace health resource, and we recognize the rest of it won’t be of pressing concern for most of our readers. In case you are interested though, here it is:
American Heart Association | Life’s Simple 7® Journey to Health™
For a more practical (if you’re just a private individual and employee healthcare is not your main concern) overview, see:
Want to know more?
Here are some very good starting points for improving each of those 7 metrics, as necessary:
- Which Addiction-Quitting Methods Work Best?
- How To Lose Weight (Healthily!)
- The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, & Move More
- Which Diet? Top Diets Ranked By Experts
- Lower Cholesterol Naturally, Without Statins
- 10 Ways To Lower Blood Pressure Naturally
- 10 Ways To Balance Your Blood Sugars
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How an Idaho vaccine advocacy org plans its annual goals
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The start of a new year means many nonprofits and community health workers are busy setting goals and reflecting on what’s worked and what hasn’t. For those engaged in vaccine outreach, it also means reflecting on the tools and tactics that help them communicate better with their communities about why vaccines matter.
Across the country, childhood vaccination rates have declined since the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in a resurgence of preventable diseases like pertussis.
Also known as whooping cough, pertussis has surged in states like Idaho, said Karen Jachimowski Sharpnack, executive director of the Idaho Immunization Coalition, in a conversation with PGN about the organization’s 2025 priorities.
Sharpnack shared how spikes in infectious respiratory illnesses can create opportunities to listen better and understand the nuances of the communities they serve.
Here’s more of what Sharpnack said.
[Editor’s note: The contents of this interview have been edited for length and clarity.]
PGN: Whooping cough cases are up in your state. Can you share an example of how your organization is responding?
Karen Jachimowski Sharpnack: If you look at Treasure Valley and Northern Idaho, the majority of those cases have been reported, and it’s like five times as much as we had the previous year.
So, two things that the Coalition is doing in response: First, we put out radio public service announcements throughout those particular areas about what whooping cough is, how contagious it is, and what you should do if you think your child or anyone you know has it.
Second, we are contacting every school superintendent, principal, school nurse, with a letter from us at the Coalition [to warn about] the whooping cough outbreaks in schools right now. Here’s what the symptoms are, here’s what you can do, and then here’s how you can protect yourself and your families.
It doesn’t mean the health district wouldn’t do it, or the Department of Health and Welfare can’t do it. But from our standpoint, at least we are bringing an awareness to the schools that this is happening.
PGN: How does your organization decide when outreach is needed? How do you take a pulse of your communities’ vaccine attitudes?
K.J.S.: We consistently hold listening sessions. We do them in English and Spanish if we need to, and we go around—and I’m talking about the southern part of the state—and bring people together.
We’ve done adults, we’ve done teenagers, we’ve done college students, we’ve done seniors, we’ve done all age groups.
So, we’ll bring eight or 10 people together, and we’ll spend a couple of hours with them. We feed them and we also pay them to be there. We say, ‘We want to hear from you about what you’re hearing about vaccines, what your views are if you’re vaccinated.’ Anytime, by the way, they can get up and leave and still get paid.
We want to hear what they’re hearing on the ground. And these sessions are extremely informational. For one, we learn about the misinformation that goes out there, like immediately. And two, we’re able to then focus [on how to respond]. If we’re hearing this, what kind of media campaign do we need to get together?
PGN: How do these listening sessions inform your work?
K.J.S.: So, a couple times a year we also pay a professional poller to do a poll. And when we get those results we check them against our listening sessions. We want to see: Are we on target? Are we ahead?
We just finished putting a one-pager together for legislators, so we’re ready to go with the new [legislative] session. We do this poll every year in August-September to know how Idahoans are feeling about vaccines. We get the results in October, because we’re getting ready for the next year.
We actually poll 19-to-64-year-olds, really honing in on questions like, ‘Do you believe vaccines are safe and effective?’ ‘Do you believe that school vaccination rules should still be in place?’
And what’s pretty cool is that two-thirds of Idahoans still believe vaccines are safe and effective, want to keep school rules in place, and believe that the infrastructure systems that we have in place for our vaccine registry should remain the same. Those are important to hear, so this is really good information that we can pull out and do something with.
PGN: Like what?
K.J.S.: Here’s the bottom line. It takes money to do this work, so you have to be able to say what you are going to do with the results.
Doing a poll costs anywhere from $15,000 to $35,000. This is an expensive investment, but we know that the polling is so important to us, along with the time that I have my staff go out and do the listening sessions and get feedback.
We take those results to educate, to talk to our legislators, and advocate for vaccines. We actually do these high-level media campaigns around the state. So, we are actually doing something with the polling. We’re not just sharing the results out.
And then we actually ask, what can we do to make a change? What are we hearing that we need to focus on?
That’s why it’s really important, because we are actually pushing this out for 2025. We know where we’re going in 2025 programmatically with marketing, and we know where we’re going with advocacy work.
We’re not guessing. We’re actually listening to people. And then we’re making really concrete decisions on how we’re going to move the organization forward to be able to help our communities.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Is there anything good about menopause? Yep, here are 4 things to look forward to
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Menopause is having a bit of a moment, with less stigma and more awareness about the changes it can bring.
A recent senate inquiry recommended public education about perimenopause and menopause, more affordable treatments and flexible work arrangements.
But like many things in life the experiences of menopause are on a continuum. While some women find it challenging and require support, others experience some physical and emotional benefits. These are rarely reported – but we can learn from the research available and, importantly, from people’s lived experiences.
Here are four changes to look forward to once you reach menopause.
Insta_Photos/Shutterstock 1. No more periods or related issues
Menopause is considered “complete” 12 months after the final period of a woman (or person assigned female at birth) who previously menstruated.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, the benefit at the top of the list is no more periods (unless you are taking hormone therapy and still have your womb). This can be particularly beneficial for women who have had to manage erratic, unpredictable and heavy bleeding.
At last, you don’t need to keep sanitary protection in every bag “just in case”. No more planning where the bathroom is or having to take extra clothes. And you’ll save money by not purchasing sanitary products.
There is also good news for women who have had heavy bleeding due to uterine fibroids – common benign gynaecological tumours that affect up to 80% of women. The evidence suggests hormonal changes (for women not taking hormone therapy) can lead to a reduction in the size of fibroids and relieve symptoms.
Women who suffer from menstrual migraine may experience an improvement in migraines post-menopause as their hormonal fluctuations begin to settle – but the timeframe for this remains unclear.
For some women, no more periods also means more participation in social activities from which they may have been excluded due to periods. For example, religious activities or food preparation in some cultures.
2. Getting your body and your groove back
Throughout their reproductive lives, women in heterosexual relationships are usually the ones expected to be proactive about preventing pregnancy.
Some post-menopausal women describe a re-emergence of their sexuality and a sense of sexual freedom that they had not previously experienced (despite contraceptive availability) as there is no longer a risk of pregnancy.
A participant in my research into women’s experiences of menopause described the joy of no longer being child-bearing age:
I’ve got a body back for me, you know, coz I can’t get pregnant, not that I haven’t enjoyed having [children] and things like that and it was a decision to get pregnant but I feel like, ooh my body isn’t for anybody now but me, people, you know?
For women who have chosen to be child-free there may also be a sense of freedom from social expectations. People will likely stop asking them when they are planning to have children.
3. A new chapter and a time to focus on yourself
Another participant described menopause as an unexpected “acceleration point” for change.
Women told us they were more accepting of themselves and their needs rather than being focused on the needs of other people. Researchers have previously tracked this shift from “living for others” to “a life of one’s own”.
Some women find the strength of emotions at this time a challenge, whereas others find their potency can facilitate liberation – enabling them to speak their minds or be more assertive than at any other time in their lives.
4. Increased self-confidence
A new sense of liberation can fuel increased self-confidence at menopause. This has been reported in studies based on in-depth interviews with women.
Confidence boosts can coincide with changes in career and sometimes in relationships as priorities and self-advocacy transform.
Life on the other side
It can be hard to think about what is good about menopause, particularly if you are having challenges during perimenopause – but these can get better with time.
In cultures where women are valued as they become older, women describe themselves as positively contributing to the community. They find they gain power and respect as they age.
We need to work towards more positive societal attitudes on this front. Our bodies change across the lifespan and are remarkable at every stage, including menopause.
Yvonne Middlewick, Nurse, Lecturer & Director of Post-graduate Studies in the School of Nursing and Midwifery, Edith Cowan University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Yes, blue light from your phone can harm your skin. A dermatologist explains
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Social media is full of claims that everyday habits can harm your skin. It’s also full of recommendations or advertisements for products that can protect you.
Now social media has blue light from our devices in its sights.
So can scrolling on our phones really damage your skin? And will applying creams or lotions help?
Here’s what the evidence says and what we should really be focusing on.
Max kegfire/Shutterstock Remind me, what actually is blue light?
Blue light is part of the visible light spectrum. Sunlight is the strongest source. But our electronic devices – such as our phones, laptops and TVs – also emit it, albeit at levels 100-1,000 times lower.
Seeing as we spend so much time using these devices, there has been some concern about the impact of blue light on our health, including on our eyes and sleep.
Now, we’re learning more about the impact of blue light on our skin.
How does blue light affect the skin?
The evidence for blue light’s impact on skin is still emerging. But there are some interesting findings.
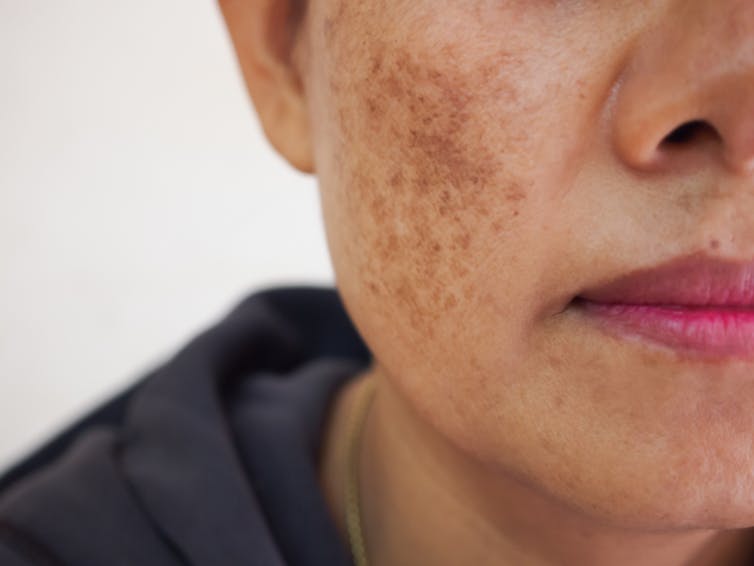
1. Blue light can increase pigmentation
Studies suggest exposure to blue light can stimulate production of melanin, the natural skin pigment that gives skin its colour.
So too much blue light can potentially worsen hyperpigmentation – overproduction of melanin leading to dark spots on the skin – especially in people with darker skin.
Blue light can worsen dark spots on the skin caused by overproduction of melanin. DUANGJAN J/Shutterstock 2. Blue light can give you wrinkles
Some research suggests blue light might damage collagen, a protein essential for skin structure, potentially accelerating the formation of wrinkles.
A laboratory study suggests this can happen if you hold your device one centimetre from your skin for as little as an hour.
However, for most people, if you hold your device more than 10cm away from your skin, that would reduce your exposure 100-fold. So this is much less likely to be significant.
3. Blue light can disrupt your sleep, affecting your skin
If the skin around your eyes looks dull or puffy, it’s easy to blame this directly on blue light. But as we know blue light affects sleep, what you’re probably seeing are some of the visible signs of sleep deprivation.
We know blue light is particularly good at suppressing production of melatonin. This natural hormone normally signals to our bodies when it’s time for sleep and helps regulate our sleep-wake cycle.
By suppressing melatonin, blue light exposure before bed disrupts this natural process, making it harder to fall asleep and potentially reducing the quality of your sleep.
The stimulating nature of screen content further disrupts sleep. Social media feeds, news articles, video games, or even work emails can keep our brains active and alert, hindering the transition into a sleep state.
Long-term sleep problems can also worsen existing skin conditions, such as acne, eczema and rosacea.
Sleep deprivation can elevate cortisol levels, a stress hormone that breaks down collagen, the protein responsible for skin’s firmness. Lack of sleep can also weaken the skin’s natural barrier, making it more susceptible to environmental damage and dryness.
Can skincare protect me?
The beauty industry has capitalised on concerns about blue light and offers a range of protective products such as mists, serums and lip glosses.
From a practical perspective, probably only those with the more troublesome hyperpigmentation known as melasma need to be concerned about blue light from devices.
This condition requires the skin to be well protected from all visible light at all times. The only products that are totally effective are those that block all light, namely mineral-based suncreens or some cosmetics. If you can’t see the skin through them they are going to be effective.
But there is a lack of rigorous testing for non-opaque products outside laboratories. This makes it difficult to assess if they work and if it’s worth adding them to your skincare routine.
What can I do to minimise blue light then?
Here are some simple steps you can take to minimise your exposure to blue light, especially at night when it can disrupt your sleep:
- use the “night mode” setting on your device or use a blue-light filter app to reduce your exposure to blue light in the evening
- minimise screen time before bed and create a relaxing bedtime routine to avoid the types of sleep disturbances that can affect the health of your skin
- hold your phone or device away from your skin to minimise exposure to blue light
- use sunscreen. Mineral and physical sunscreens containing titanium dioxide and iron oxides offer broad protection, including from blue light.
In a nutshell
Blue light exposure has been linked with some skin concerns, particularly pigmentation for people with darker skin. However, research is ongoing.
While skincare to protect against blue light shows promise, more testing is needed to determine if it works.
For now, prioritise good sun protection with a broad-spectrum sunscreen, which not only protects against UV, but also light.
Michael Freeman, Associate Professor of Dermatology, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
It Didn’t Start with You – by Mark Wolynn
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There is a trend in psychology to “blame the parents” for “childhood trauma” that can result in problems later in life. Sometimes fairly, sometimes not. This book’s mostly not about that.
It does touch on our own childhood trauma, if applicable. But mostly, it’s about epigenetic trauma inheritance. In other words, not just trauma that’s passed on in terms of “the cycle of abuse”, but trauma that’s passed on in terms of “this generation experienced trauma x, developed trauma response y, encoded it epigenetically, and passed it on to their offspring”.
So, how does one heal from a trauma one never directly experienced, and just inherited the response to it? That’s what most of this book is about, after establishing how epigenetic trauma inheritance works.
The author, a therapist, provides practical advice for how to do the things that can be done to rewrite the epigenetic code we inherited. Better late than never!
Bottom line: it is well-established that trauma is inheritable. But unlike one’s eye color or the ability to smell asparagus metabolites in urine, we can rewrite epigenetic things, to a degree. This book explains how.
Click here to check out It Didn’t Start With You, and put things to rest!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: