The Physical Exercises That Build Your Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Jim Kwik: from broken brain to brain coach

This is Jim Kwik. He suffered a traumatic brain injury as a small child, and later taught himself to read and write by reading comic books. He became fascinated with the process of learning, and in his late 20s he set up Kwik Learning, to teach accelerated learning in classrooms and companies, which he continued until 2009 when he launched his online learning platform. His courses have now been enjoyed by people in 195 countries.
So, since accelerated learning is his thing, you might wonder…
What does he have to share that we can benefit from in the next five minutes?
Three brain exercises to improve memory and concentration
A lot of problems we have with working memory are a case of executive dysfunction, but there are tricks we can use to get our brains into gear and make them cumulatively stronger:
First exercise
You can strengthen your corpus callosum (the little bridge between the two hemispheres of the brain) by performing a simple kinesiological exercise, such as alternating touching your left elbow to your right knee, and touching your right elbow to your left knee.
Do it for about a minute, but the goal here is not a cardio exercise, it’s accuracy!
You want to touch your elbow and opposite knee to each other as precisely as possible each time. Not missing slightly off to the side, not falling slightly short, not hitting it too hard.
Second exercise
Put your hands out in front of you, as though you’re about to type at a keyboard. Now, turn your hands palm-upwards. Now back to where they were. Now palm-upwards again. Got it? Good.
That’s not the exercise, the exercise is:
You’re now going to do the same thing, but do it twice as quickly with one hand than the other. So they’ll still be flipping to the same basic “beat”, put it in musical terms, the tempo on one hand will now be twice that of the other. When you get the hang of that, switch hands and do the other side.
This is again about the corpus callosum, but it’s now adding an extra level of challenge because of holding the two rhythms separately, which is also working the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex.
The pre-frontal cortex in particular is incredibly important to executive function, self-discipline, and being able to “do” delayed gratification. So this exercise is really important!
Third exercise
This one works the same features of the brain, but most people find it harder. So, consider it a level-up on the previous:
Imagine there’s a bicycle wheel in front of you (as though the bike is facing you at chest-height). Turn the wheel towards you with your hands, one on each side.
Now, do the same thing, but each of your hands is going in the opposite direction. So one is turning the wheel towards you; the other is turning it away from you.
Now, do the same thing, but one hand goes twice as quickly as the other.
Switch sides.
Why is this harder for most people than the previous? Because the previous involved processing discrete (distinct from each other) movements while this one involves analog continuous movements.
It’s like reading an analog clock vs a digital clock, but while using both halves of your brain, your corpus callosum, your pre-frontal cortex, and the motor cortex too.
Want to learn more?
You might enjoy his book, which as well as offering exercises like the above, also offers a lot about learning strategies, memory processes, and generally building a quicker more efficient brain:
Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Water Water Everywhere, But Which Is Best To Drink?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Well Well Well…
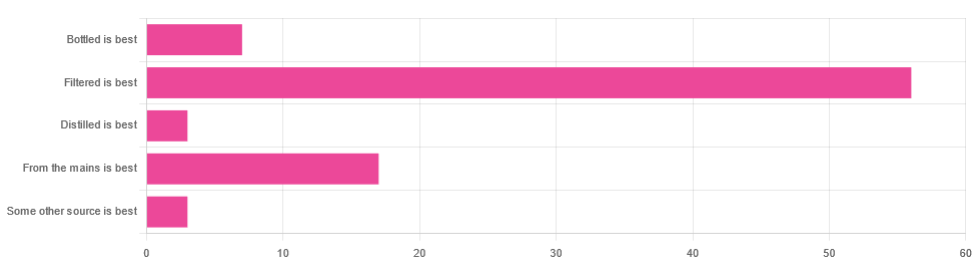
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your (health-related) opinion on drinking water—with the understanding that this may vary from place to place. We got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 65% said “Filtered is best”
- About 20% said “From the mains is best”
- About 8% said “Bottled is best”
- About 3% said “Distilled is best”
- About 3% said “Some other source is best”
Of those who said “some other source is best”, one clarified that their preferred source was well water.
So what does the science say?
Fluoridated water is bad for you: True or False?
False, assuming a normal level of consumption. Rather than take up more space today though, we’ll link to what we previously wrote on this topic:
You may be wondering: but what if my level of consumption is higher than normal?
Let’s quickly look at some stats:
- The maximum permitted safety level varies from place to place, but is (for example) 2mg/l in the US, 1.5mg/l in Canada & the UK.
- The minimum recommended amount also varies from place to place, but is (for example) 0.7mg/l in Canada and the US, and 1mg/l in the UK.
It doesn’t take grabbing a calculator to realize that if you drink twice as much water as someone else, then depending on where you are, water fluoridated to the minimum may give you more than the recommended maximum.
However… Those safety margins are set so much lower than the actual toxicity levels of fluoride, that it doesn’t make a difference.
For example: your writer here takes a medication that has the side effect of causing dryness of the mouth, and consequently she drinks at least 3l of water per day in a climate that could not be described as hot (except perhaps for about 2 weeks of the year). She weighs 72kg (that’s about 158 pounds), and the toxicity of fluoride (for ill symptoms, not death) is 0.2mg/kg. So, she’d need 14.4mg of fluoride, which even if the water fluoridation here were 2mg/l (it’s not; it’s lower here, but let’s go with the highest figure to make a point), would require drinking more than 7l of water faster than the body can process it.
For more about the numbers, check out:
Acute Fluoride Poisoning from a Public Water System
Bottled water is the best: True or False?
False, if we consider “best” to be “healthiest”, which in turn we consider to be “most nutrients, with highest safety”.
Bottled water generally does have higher levels of minerals than most local mains supply water does. That’s good!
But you know what else is generally has? Microplastics and nanoplastics. That’s bad!
We don’t like to be alarmist in tone; it’s not what we’re about here, but the stats on bottled water are simply not good; see:
We Are Such Stuff As Bottles Are Made Of
You may be wondering: “but what about bottled water that comes in glass bottles?”
Indeed, water that comes in glass bottles can be expected to have lower levels of plastic than water that comes in plastic bottles, for obvious reasons.
However, we invite you to consider how likely you believe it to be that the water wasn’t stored in plastic while being processed, shipped and stored, before being portioned into its final store-ready glass bottles for end-consumer use.
Distilled water is the best: True or False?
False, generally, with caveats:
Distilled water is surely the safest water anywhere, because you know that you’ve removed any nasties.
However, it’s also devoid of nutrients, because you also removed any minerals it contained. Indeed, if you use a still, you’ll be accustomed to the build-up of these minerals (generally simplified and referenced as “limescale”, but it’s a whole collection of minerals).
Furthermore, that loss of nutrients can be more than just a “something good is missing”, because having removed certain ions, that water could now potentially strip minerals from your teeth. In practice, however, you’d probably have to swill it excessively to cause this damage.
Nevertheless, if you have the misfortune of living somewhere like Flint, Michigan, then a water still may be a fair necessity of life. In other places, it can simply be useful to have in case of emergency, of course.
Here’s an example product on Amazon if you’d like to invest in a water still for such cases.
PS: distilled water is also tasteless, and is generally considered bad, tastewise, for making tea and coffee. So we really don’t recommend distilling your water unless you have a good reason to do so.
Filtered water is the best: True or False?
True for most people in most places.
Let’s put it this way: it can’t logically be worse than whatever source of water you put into it…
Provided you change the filter regularly, of course.
Otherwise, after overusing a filter, at best it won’t be working, and at worst it’ll be adding in bacteria that have multiplied in the filter over however long you left it there.
You may be wondering: can water filters remove microplastics, and can they remove minerals?
The answer in both cases is: sometimes.
- For microplastics it depends on the filter size and the microplastic size (see our previous article for details on that).
- For minerals, it depends on the filter type. Check out:
The H2O Chronicles | 5 Water Filters That Remove Minerals
One other thing to think about: while most water filtration jugs are made of PFAS-free BPA-free plastics for obvious reasons, for greater peace of mind, you might consider investing in a glass filtration jug, like this one ← this is just one example product on Amazon; by all means shop around and find one you like
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Corn Chips vs Potato Chips: Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing corn chips to potato chips, we picked the corn chips.
Why?
First, let it be said, this was definitely a case of “lesser evil voting” as there was no healthy choice here. But as for which is relatively least unhealthy…
Most of the macronutrient and micronutrient profile is quite similar. Both foods are high carb, moderately high fat, negligible protein, and contain some trace minerals and even some tiny amounts of vitamins. Both are unhealthily salty.
Exact numbers will of course vary from one brand’s product to another, but you can see some indicative aggregate scores here in the USDA’s “FoodData Central” database:
The biggest health-related difference that doesn’t have something to balance it out is that the glycemic index of corn chips averages around 63, whereas the glycemic index of potato chips averages around 70 (that is worse).
That’s enough to just about tip the scales in favor of corn chips.
The decision thus having been made in favor of corn chips (and the next information not having been part of that decision), we’ll mention one circumstantial extra benefit to corn chips:
Corn chips are usually eaten with some kind of dip (e.g. guacamole, sour cream, tomato salsa, etc) which can thus deliver actual nutrients. Potato chips meanwhile are generally eaten with no additional nutrients. So while we can’t claim the dip as being part of the nutritional make-up of the corn chips, we can say:
If you’re going to have a habit of eating one or the other, then corn chips are probably the least unhealthy of the two.
And yes, getting vegetables (e.g. in the dips) in ways that are not typically associated with “healthy eating” is still better than not getting vegetables at all!
Check out: Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Share This Post
-
In Defense of Food – by Michael Pollan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Eat more like the French. Or the Italians. Or the Japanese. Or…
Somehow, whatever we eat is not good enough, and we should always be doing it differently!
Michael Pollan takes a more down-to-Earth approach.
He kicks off by questioning the wisdom of thinking of our food only in terms of nutritional profiles, and overthinking healthy-eating. He concludes, as many do, that a “common-sense, moderate” approach is needed.
And yet, most people who believe they are taking a “common-sense, moderate” approach to health are in fact over-fed yet under-nourished.
So, how to fix this?
He offers us a reframe: to think of food as a relationship, and health being a product of it:
- If we are constantly stressing about a relationship, it’s probably not good.
- On the other hand, if we are completely thoughtless about it, it’s probably not good either.
- But if we can outline some good, basic principles and celebrate it with a whole heart? It’s probably at the very least decent.
The style is very casual and readable throughout. His conclusions, by the way, can be summed up as “Eat real food, make it mostly plants, and make it not too much”.
However, to summarize it thusly undercuts a lot of the actual value of the book, which is the principles for discerning what is “real food” and what is “not too much”.
Bottom line: if you’re tired of complicated eating plans, this book can help produce something very simple, attainable, and really quite good.
Click here to check out In Defense of Food, for some good, hearty eating.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
10 Great Exercises to Improve Your Eyesight
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If your eyesight has been declining a bit, all is not lost. Just like many other muscles in the body, the muscles of the eye—including those responsible for changing the focal length of your vision—can atrophy without exercise. So, without further ado, here are the exercises recommended:
The eyes (still) have it
- Blink for a minute: blink rapidly for 30–60 seconds to regulate blood circulation, lubricate your eyes, and prevent dryness.
- Rotate your head while staring ahead: turn your head in a circular motion while keeping your gaze straight ahead. This improves blood circulation to your eyes.
- Look to your right and left: slowly move your gaze from right to left while breathing. This one relaxes and stretches the eye muscles.
- Close your eyes and relax: close your eyes for at least 30 seconds to relax and strengthen your photoreceptor cells.
- Move your gaze in different directions: shift your gaze right-left, up-down, in circular motions, and trace a figure 8 with your eyes. This improves visual perception for both near- and far-sightedness.
- Close and open your eyes: tighten your eyes shut for 3–5 seconds, then open them. Repeat seven times to improve blood circulation and relax your eye muscles. ← 10almonds note: the duration makes this different from #4, so do try both!
- Push against your temples with your fingers: gently press your temples with your fingers for two seconds, then release. Repeat 4–5 times to improve fluid circulation in your eyes.
- Draw geometric figures with your gaze: use your eyes to trace shapes such as triangles, squares, and circles to enhance your eye coordination and muscle strength.
- Move your eyeballs up and down: close your eyes and slowly move your eyeballs up and down five times to stretch and relax the muscles ← 10almonds note: this seems to be the same as part of #5 and has a considerable overlap with #8, but we’re listing it anyway, or else everyone will wonder where #9 went!
- Strengthen near and far focusing: focus on your thumb 10 inches away for 10–15 seconds, then switch focus to an object 10–20 feet away. Repeat five times to improve focus adjustment ability.
By practicing these exercises daily, we are told that you can improve eye health and vision within a week.
For more on all these, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Vision for Life, Revised Edition – by Dr. Meir Schneider
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
3 Appetite Suppressants Better Than Ozempic
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Annette Bosworth gives her recommendations, and explains why:
What and how
We’ll get straight to it; the recommendations are:
- Coffee, black, unsweetened: not only suppresses the appetite but also boosts the metabolism, increasing fat burn.
- Salt: especially for when fasting (as under such circumstances we may lose salts without replenishing them), a small taste of this can help satisfy taste buds while replenishing sodium and—depending on the salt—other minerals. For example, if you buy “low-sodium salt” in the supermarket, this is generally sodium chloride cut with potassium chloride and/or occasionally magnesium sulfate.
- Ketones (MCT oil): ketones can suppress hunger, particularly when fasting causes blood sugar levels to drop. Supplementing with MCT oil promotes ketone production in the liver, training the body to produce more ketones naturally, thus curbing appetite.
For more on these including the science of them, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Ozempic vs Five Natural Supplements
- Some Surprising Truths About Hunger And Satiety
- The Fruit That Can Specifically Reduce Belly Fat
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Be A Plant-Based Woman Warrior – by Jane Esselstyn & Ann Esselstyn
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Notwithstanding the title, this book is not about being a woman or a warrior, but let us share what one reviewer on Amazon wrote:
❝I don’t want to become a plant based woman warrior. The sex change would be traumatic for me. However, as a man who proudly takes ballet classes and Pilates, I am old enough not to worry about stereotypes. When I see a good thing, I am going to use it❞
The authors, a mother-and-daughter team in their 80s and 50s respectively, do give a focus on things that disproportionally affect women, and rectifying those things with diet, especially in one of the opening chapters.
Most the book, however, is about preventing/reversing things that can affect everyone, such as heart disease, diabetes, inflammation and the autoimmune diseases associated with such, and cancer in general, hence the dietary advice being good for most people (unless you have an unusually restrictive diet).
We get an overview of the pantry we should cultivate and curate, as well as some basic kitchen skills that will see us well for the rest of the book, such as how to make oat flour and other similar mini-recipes, before getting into the main recipes themselves.
About the recipes: they are mostly quite simple, though often rely on having pre-prepared items from the mini-recipes we mentioned earlier. They’re all vegan, mostly but not all gluten-free, whole foods, no added sugar, and as for oil… Well, it seems to be not necessarily oil-free, but rather oil-taboo. You see, they just don’t mention it. For example, when they say to caramelize onions, they say to heat a skillet, and when it is hot, add the onions, and stir until browned. They don’t mention any oil in the ingredients or in the steps. It is a mystery. 10almonds note: we recommend olive oil, or avocado oil if you prefer a milder taste and/or need a higher smoke point.
Bottom line: the odd oil taboo aside, this is a good book of simple recipes that teaches some good plant-based kitchen skills while working with a healthy, whole food pantry.
Click here to check out Be A Plant-Based Woman Warrior, and be a plant-based woman warrior!
Or at the very least: be a plant-based cook regardless of gender, hopefully without war, and enjoy the additions to your culinary repertoire
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: