Peas vs Green Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing peas to green beans, we picked the peas.
Why?
Looking at macros first, peas have nearly 6x the protein, nearly 2x the fiber, and nearly 2x the carbs, making them the “more food per food” choice.
In terms of vitamins, peas have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, and choline, while green beans have more of vitamins E and K. An easy win for peas.
In the category of minerals, peas have more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while green beans have more calcium. Another overwhelming win for peas.
In short, enjoy both (diversity is good), but there’s a clear winner here and it’s peas.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Peas vs Broad Beans – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
“Skinny Fat” Explained (& How To Fix It)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Skinny fat” is a term you may have seen floating around social media. It describes people who have a low body weight but a high body fat percentage, often resulting in flabby appearance despite being within a weight range considered healthy. Many try dieting and exercising, only to find that neither work.
This video explains what’s going wrong, and how to fix it:
Diet & exercise won’t work if it’s not right
This problem occurs because common weight-loss approaches, such as restrictive dieting and excessive cardio, fail to improve body composition:
- Restrictive dieting reduces both fat and lean mass, keeping the body fat percentage unchanged
- Cardio burns some calories but the underlying metabolic issue hasn’t meaningfully changed, so any loss will be temporary (and most of any immediate loss will be water weight, anyway)
The key to overcoming skinny fat is resistance training. Lifting weights or doing bodyweight exercises helps build muscle, which not only lowers body fat percentage (by simple mathematics; add more muscle and the percentages of other things must go down even if the total amount is the same) and improves overall definition, which is something most people consider nice. However, the real value here is that it actually addresses the underlying metabolic issue—because muscle costs calories to maintain, one’s basal metabolic rate will now be faster, even when you’re sleeping.
This then becomes… Not quite a self-sustaining system, because you do have to still eat well and continue to do resistance training, but your body will be doing most of the work for you, and you’ll find it’s a lot easier to maintain a healthy body composition than to get one in the first place, for exactly the metabolic reason we described.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It ← this is a different, but adjacent issue (and very important for avoiding metabolic disease risks)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
What Do The Different Kinds Of Fiber Do? 30 Foods That Rank Highest
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve talked before about how important fiber is:
Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
And even how it’s arguably the most important dietary factor when it comes to avoiding heart disease:
What Matters Most For Your Heart? Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure ← Spoiler: it’s fiber
And yes, that’s even when considered alongside other (also laudable) dietary interventions such as lowering intake of sodium, various kinds of saturated fat, and red meat.
So, what should we know about fiber, aside from “aim to get nearer 40g/day instead of the US average 16g/day”?
Soluble vs Insoluble
The first main way that dietary fibers can be categorized is soluble vs insoluble. Part of the difference is obvious, but bear with us, because there’s more to know about each:
- Soluble fiber dissolves (what a surprise) in water and, which part is important, forms a gel. This slows down things going through your intestines, which is important for proper digestion and absorption of nutrients (as well as avoiding diarrhea). Yes, you heard right: getting enough of the right kind of fiber helps you avoid diarrhea.
- Insoluble fiber does not dissolve (how shocking) in water and thus mostly passes through undigested by us (some will actually be digested by gut microbes who subsist on this, and in return for us feeding them daily, they make useful chemicals for us). This kind of fiber is also critical for healthy bowel movements, because without it, constipation can ensue.
Both kinds of fiber improve just about every metric related to blood, including improving triglycerides and improving insulin sensitivity and blood glucose levels. Thus, they help guard against various kinds of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and metabolic disease in general. Do note that because whatever’s good for your heart/blood is good for your brain (which requires a healthy heart and bloodstream to nourish it and take away waste), likely this also has a knock-on effect against cognitive decline, but we don’t have hard science for that claim so we’re going to leave that last item as a “likely”.
However, one thing’s for sure: if you want a healthy gut, heart, and brain, you need a good balance of soluble and insoluble fibers.
10 of the best for soluble fiber
Food Soluble Fiber Type(s) Soluble Fiber (g per serving) Insoluble Fiber Type(s) Insoluble Fiber (g per serving) Total Fiber (g per serving) Kidney beans (1 cup cooked) Pectin, Resistant Starch 1.5–2 Hemicellulose, Cellulose 6 8 Lentils (1 cup cooked) Pectin, Resistant Starch 1.5–2 Cellulose 6 7.5 Barley (1 cup cooked) Beta-glucan 3–4 Hemicellulose 2 6 Brussels sprouts (1 cup cooked) Pectin 1–1.5 Cellulose, Hemicellulose 2 3.5 Oats (1 cup cooked) Beta-glucan 2–3 Cellulose 1 3 Apples (1 medium) Pectin 1–2 Cellulose, Hemicellulose 2 3 Carrots (1 cup raw) Pectin 1–1.5 Cellulose, Hemicellulose 2 3 Citrus fruits (orange, 1 medium) Pectin 1–1.5 Cellulose 1 2.5 Flaxseeds (2 tbsp) Mucilage, Lignin 1–1.5 Cellulose 1 2.5 Psyllium husk (1 tbsp) Mucilage 3–4 Trace amounts 0 3–4 10 of the best for insoluble fiber
Food Soluble Fiber Type(s) Soluble Fiber (g per serving) Insoluble Fiber Type(s) Insoluble Fiber (g per serving) Total Fiber (g per serving) Wheat bran (1 cup) Trace amounts 0 Cellulose, Lignin 6–8 6–8 Black beans (1 cup cooked) Pectin, Resistant Starch 1.5 Cellulose 6 7.5 Brown rice (1 cup cooked) Trace amounts 0.5 Hemicellulose, Lignin 2–3 2.5–3.5 Popcorn (3 cups popped) Trace amounts 0.5 Hemicellulose 3 3.5 Broccoli (1 cup cooked) Pectin 1 Cellulose, Hemicellulose 4 5 Green beans (1 cup cooked) Trace amounts 0.5 Cellulose, Hemicellulose 3 3.5 Sweet potatoes (1 cup cooked) Pectin 1–1.5 Cellulose 3 4.5 Whole wheat bread (1 slice) Trace amounts 0.5 Cellulose, Hemicellulose 1 1.5 Pears (1 medium) Pectin 1 Cellulose, Hemicellulose 4 5 Almonds (1 oz) Trace amounts 0.5 Cellulose, Hemicellulose 2 2.5 10 of the best for a balance of both
Food Soluble Fiber Type(s) Soluble Fiber (g per serving) Insoluble Fiber Type(s) Insoluble Fiber (g per serving) Total Fiber (g per serving) Raspberries (1 cup) Pectin 1 Cellulose 5 6 Edamame (1 cup cooked) Pectin 1 Cellulose 5 6 Chia seeds (2 tbsp) Mucilage, Pectin 2–3 Lignin, Cellulose 3 5.5 Artichokes (1 medium) Inulin 1 Cellulose, Hemicellulose 5 6 Avocado (1 medium) Pectin ~2 Cellulose 4 6 Black beans (1 cup cooked) Pectin, Resistant Starch 1.5 Cellulose 6 7.5 Quinoa (1 cup cooked) Pectin, Saponins 1 Cellulose, Hemicellulose 3 4 Spinach (1 cup cooked) Pectin 0.5 Cellulose, Lignin 3 3.5 Prunes (1/2 cup) Pectin, Sorbitol 2 Cellulose 4 6 Figs (3 medium) Pectin 1 Cellulose 2 3 You’ll notice that the above “balance” is not equal; that’s ok; we need greater quantities of insoluble than soluble anyway, so it is as well that nature provides such.
This is the same kind of balance when we talk about “balanced hormones” (does not mean all hormones are in equal amounts; means they are in the right proportions) or “balanced microbiome” (does not mean that pathogens and friendly bacteria are in equal numbers), etc.
Some notes on the above:
About those fiber types, some of the most important soluble ones to aim for are:
- Beta-glucan: found in oats and barley, it supports heart health.
- Pectin: found in fruits like apples, citrus, and pears, it helps with cholesterol control.
- Inulin: a type of prebiotic fiber found in artichokes.
- Lignin: found in seeds and wheat bran, it has antioxidant properties.
- Resistant starch: found in beans and lentils, it acts as a prebiotic for gut health.
See also: When Is A Fiber Not A Fiber? The Food Additive You Do Want
One fiber to rule them all
Well, not entirely (we still need the others) but there is a best all-rounder:
The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health?
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
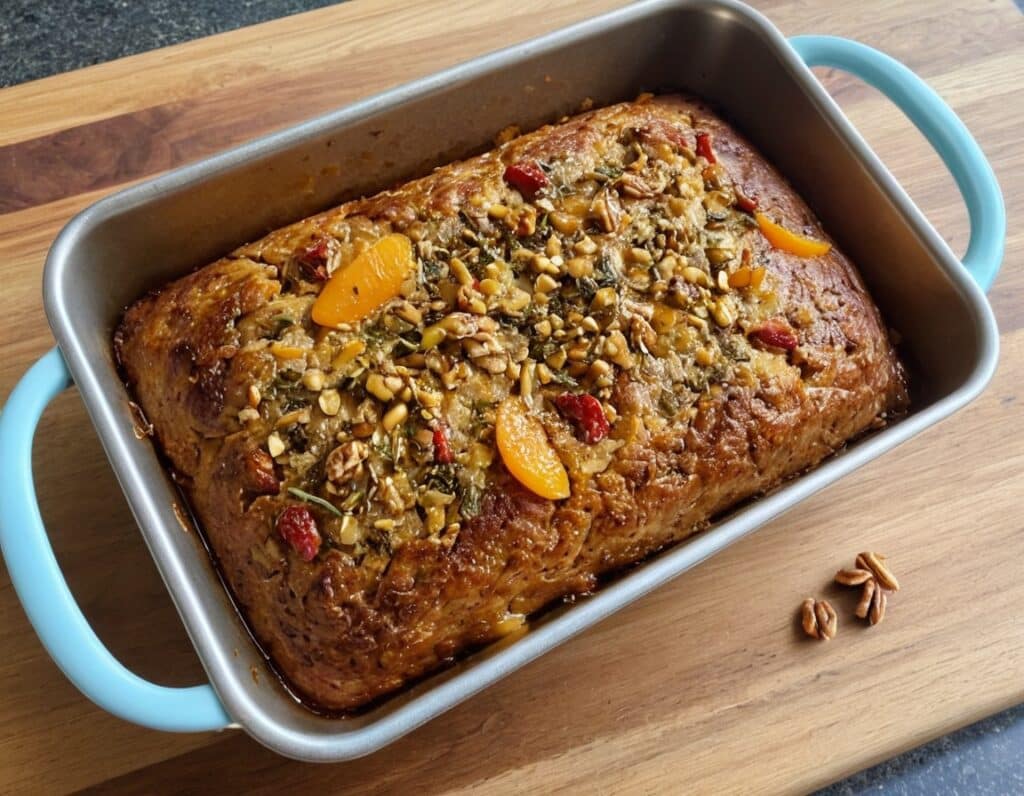
Walnut, Apricot, & Sage Nut Roast
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s important to have at least one good nut roast recipe in your repertoire. It’s something that’s very good for making a good dish out of odds and ends that are in your house, and done well, it’s not only filling and nutritious, but a tasty treat too. Done badly, everyone knows the results can be unfortunate… Making this the perfect way to show off your skills!
You will need
- 1 cup walnuts
- ½ cup almonds
- ¼ cup whole mixed seeds (chia, pumpkin, & poppy are great)
- ¼ cup ground flax (also called flax meal)
- 1 medium onion, finely chopped
- 1 large carrot, grated
- 4 oz dried apricots, chopped
- 3 oz mushrooms, chopped
- 1 oz dried goji berries
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 2 tbsp fresh sage, chopped
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp dried rosemary
- 2 tsp dried thyme
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp yeast extract (even if you don’t like it; trust us; it will work) dissolved in ¼ cup hot water
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 350℉ / 180℃, and line a 2 lb loaf tin with baking paper.
2) Heat some oil in a skillet over a moderate heat, and fry the onion for a few minutes until translucent. Add the garlic, carrot, and mushrooms, cooking for another 5 minutes, stirring well. Set aside to cool a little once done.
3) Process the nuts in a food processor, pulsing until they are well-chopped but not so much that they turn into flour.
4) Combine the nuts, vegetables, and all the other ingredients in a big bowl, and mix thoroughly. If it doesn’t have enough structural integrity to be thick and sticky and somewhat standing up by itself if you shape it, add more ground flax. If it is too dry, add a little water but be sparing.
5) Spoon the mixture into the loaf tin, press down well (or else it will break upon removal), cover with foil and bake for 30 minutes. Remove the foil, and bake for a further 15 minutes, until firm and golden. When done, allow it to rest in the tin for a further 15 minutes, before turning it out.
6) Serve, as part of a roast dinner (roast potatoes, vegetables, gravy, etc).
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Chia Seeds vs Pumpkin Seeds – Which is Healthier?
- Apricots vs Peaches – Which is Healthier?
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- Ergothioneine: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Can I take antihistamines everyday? More than the recommended dose? What if I’m pregnant? Here’s what the research says
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Allergies happen when your immune system overreacts to a normally harmless substance like dust or pollen. Hay fever, hives and anaphylaxis are all types of allergic reactions.
Many of those affected reach quickly for antihistamines to treat mild to moderate allergies (though adrenaline, not antihistamines, should always be used to treat anaphylaxis).
If you’re using oral antihistamines very often, you might have wondered if it’s OK to keep relying on antihistamines to control symptoms of allergies. The good news is there’s no research evidence to suggest regular, long-term use of modern antihistamines is a problem.
But while they’re good at targeting the early symptoms of a mild to moderate allergic reaction (sneezing, for example), oral antihistamines aren’t as effective as steroid nose sprays for managing hay fever. This is because nasal steroid sprays target the underlying inflammation of hay fever, not just the symptoms.
Here are the top six antihistamines myths – busted.
Andrea Piacquadio/Pexels Myth 1. Oral antihistamines are the best way to control hay fever symptoms
Wrong. In fact, the recommended first line medical treatment for most patients with moderate to severe hay fever is intranasal steroids. This might include steroid nose sprays (ask your doctor or pharmacist if you’d like to know more).
Studies have shown intranasal steroids relieve hay fever symptoms better than antihistamine tablets or syrups.
To be effective, nasal steroids need to be used regularly, and importantly, with the correct technique.
In Australia, you can buy intranasal steroids without a doctor’s script at your pharmacy. They work well to relieve a blocked nose and itchy, watery eyes, as well as improve chronic nasal blockage (however, antihistamine tablets or syrups do not improve chronic nasal blockage).
Some newer nose sprays contain both steroids and antihistamines. These can provide more rapid and comprehensive relief from hay fever symptoms than just oral antihistamines or intranasal steroids alone. But patients need to keep using them regularly for between two and four weeks to yield the maximum effect.
For people with seasonal allergic rhinitis (hayfever), it may be best to start using intranasal steroids a few weeks before the pollen season in your regions hits. Taking an antihistamine tablet as well can help.
Antihistamine eye drops work better than oral antihistamines to relieve acutely itchy eyes (allergic conjunctivitis).
Myth 2. My body will ‘get used to’ antihistamines
Some believe this myth so strongly they may switch antihistamines. But there’s no scientific reason to swap antihistamines if the one you’re using is working for you. Studies show antihistamines continue to work even after six months of sustained use.
Myth 3. Long-term antihistamine use is dangerous
There are two main types of antihistamines – first-generation and second-generation.
First-generation antihistamines, such as chlorphenamine or promethazine, are short-acting. Side effects include drowsiness, dry mouth and blurred vision. You shouldn’t drive or operate machinery if you are taking them, or mix them with alcohol or other medications.
Most doctors no longer recommend first-generation antihistamines. The risks outweigh the benefits.
The newer second-generation antihistamines, such as cetirizine, fexofenadine, or loratadine, have been extensively studied in clinical trials. They are generally non-sedating and have very few side effects. Interactions with other medications appear to be uncommon and they don’t interact badly with alcohol. They are longer acting, so can be taken once a day.
Although rare, some side effects (such as photosensitivity or stomach upset) can happen. At higher doses, cetirizine can make some people feel drowsy. However, research conducted over a period of six months showed taking second-generation antihistamines is safe and effective. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you’re concerned.
Allergies can make it hard to focus. Pexels/Edward Jenner Myth 4. Antihistamines aren’t safe for children or pregnant people
As long as it’s the second-generation antihistamine, it’s fine. You can buy child versions of second-generation antihistamines as syrups for kids under 12.
Though still used, some studies have shown certain first-generation antihistamines can impair childrens’ ability to learn and retain information.
Studies on second-generation antihistamines for children have found them to be safer and better than the first-generation drugs. They may even improve academic performance (perhaps by allowing kids who would otherwise be distracted by their allergy symptoms to focus). There’s no good evidence they stop working in children, even after long-term use.
For all these reasons, doctors say it’s better for children to use second-generation than first-generation antihistimines.
What about using antihistimines while you’re pregnant? One meta analysis of combined study data including over 200,000 women found no increase in fetal abnormalities.
Many doctors recommend the second-generation antihistamines loratadine or cetirizine for pregnant people. They have not been associated with any adverse pregnancy outcomes. Both can be used during breastfeeding, too.
Myth 5. It is unsafe to use higher than the recommended dose of antihistamines
Higher than standard doses of antihistamines can be safely used over extended periods of time for adults, if required.
But speak to your doctor first. These higher doses are generally recommended for a skin condition called chronic urticaria (a kind of chronic hives).
Myth 6. You can use antihistamines instead of adrenaline for anaphylaxis
No. Adrenaline (delivered via an epipen, for example) is always the first choice. Antihistamines don’t work fast enough, nor address all the problems caused by anaphylaxis.
Antihistamines may be used later on to calm any hives and itching, once the very serious and acute phase of anaphylaxis has been resolved.
In general, oral antihistamines are not the best treatment to control hay fever – you’re better off with steroid nose sprays. That said, second-generation oral antihistamines can be used to treat mild to moderate allergy symptoms safely on a regular basis over the long term.
Janet Davies, Respiratory Allergy Stream Co-chair, National Allergy Centre of Excellence; Professor and Head, Allergy Research Group, Queensland University of Technology; Connie Katelaris, Professor of Immunology and Allergy, Western Sydney University, and Joy Lee, Respiratory Allergy Stream member, National Allergy Centre of Excellence; Associate Professor, School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What’s Lurking In Your Household Air?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As individuals, we can’t do much about the outside air. We can try to spend more time in green spaces* and away from traffic, and we can wear face-masks—as was popular in Tokyo and other such large cities long before the pandemic struck.
*The well-known mental health benefits aside (and contrary to British politician Amber Rudd’s famous assertion in a televised political debate that “clean air doesn’t grow on trees”), clean air comes mostly from trees—their natural process of respiration scrubs not only carbon dioxide, but also pollutants, from the air before releasing oxygen without the pollutants. Neat!
See also this study: Site new care homes near trees and away from busy roads to protect residents’ lungs
We are fortunate to be living in a world where most of us in industrialized countries can exercise a great degree of control over our home’s climate. But, what to do with all that power?
Temperature
Let’s start with the basics. Outside temperature may vary, but you probably have heating and air conditioning. There’s a simple answer here; the optimal temperature for human comfort and wellbeing is 20℃ / 68℉:
Scientists Identify a Universal Optimal Temperature For Life on Earth
Note: this does not mean that that is the ideal global average temperature, because that would mean the polar caps are completely gone, the methane stored there released, many large cities underwater, currently hot places will be too hot for human life (e.g. outside temperatures above human body temperature), there will be mass extinctions of many kinds of animals and plants, including those we humans require for survival, and a great proliferation of many bugs that will kill us. Basically we need diversity for the planet to survive, arctic through to tropical and yes, even deserts (deserts are important carbon sinks!). The ideal global average temperature is about 14℃ (we currently have about 15℃ and rising).
But, for setting the thermostat in your home, 20℃ / 68℉ is perfect for most people, though down as far as 17℃ / 61℉ is fine too, provided other things such as humidity are in order. In fact, for sleeping, 18℃ / 62℉ is ideal. This is because the cooler temperature is one of the several things that tell our brain it is nighttime now, and thus trigger secretion of melatonin.
If you’re wondering about temperatures and respiratory viruses, by the way, check out:
The Cold Truth About Respiratory Infections: The Pathogens That Came In From The Cold
Humidity
Most people pay more attention to the temperature in their home than the humidity, and the latter is just as important:
❝Conditions that fall outside of the optimal range of 40–60% can have significant impacts on health, including facilitating infectious transmission and exacerbating respiratory diseases.
When humidity is too low, it can cause dryness and irritation of the respiratory tract and skin, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
When humidity is too high, it can create a damp environment that encourages the growth of harmful microorganisms like mould, bacteria, and viruses.❞
~ Dr. Gabriella Guarnieri et al.
So, if your average indoor humidity falls outside of that range, consider getting a humidifier or dehumidifier, to correct it. Example items on Amazon, for your convenience:
Humidity monitor | Humidifier | Dehumidifier
See also, about a seriously underestimated killer:
Pneumonia: Prevention Is Better Than Cure
Now, one last component to deal with, for perfect indoor air:
Pollution
We tend to think of pollution as an outdoors thing, and indeed, the pollution in your home will (hopefully!) be lower than that of a busy traffic intersection. However…
- The air you have inside comes from outside, and that matters if you’re in an urban area
- Even in suburban and rural areas, general atmospheric pollutants will reach you, and if you’ve ever been subject to wildfire smoke, you’ll know that’s no fun either.
- Gas appliances in the home cause indoor pollution, even when carbon monoxide is within levels considered acceptable. This polluting effect is much stronger for open gas flames (such as on gas cookers/stoves, or gas fires), than for closed gas heating systems (such as a gas-powered boiler for central heating).
- Wood stoves/fireplaces are not an improvement, in fact they are worse, and don’t get us started on coal. You should not be breathing these things, and definitely should not be burning them in an enclosed space.
- That air conditioning, humidifier, dehumidifier? They may be great for temperature and humidity, but please clean/change the filter more often than you think is necessary, or things will grow there and then your device will be adding pathogens to the air as it goes.
- Plug-in air-freshening devices? They may smell clean, but they are effectively spraying cleaning fluids into your lungs. So please don’t.
So, what of air purifiers? They can definitely be of benefit. for example:
But watch out! Because if you don’t clean/change the filter regularly, guess what happens! That’s right, it’ll be colonized with bacteria/fungus and then be blowing those at you.
And no, not all of them will be visible to the naked eye:
Is Unnoticed Environmental Mold Harming Your Health?
Taking a holistic approach
The air is a very important factor for the health of your lungs (and thus, for the health of everything that’s fed oxygen by your lungs), but there are more things we can do as well:
Seven Things To Do For Good Lung Health!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Driving under the influence of marijuana: An explainer and research roundup
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Update 1: On May 16, 2024, the U.S. Department of Justice sent a proposed rule to the Federal Register to downgrade marijuana from a Schedule I to a Schedule III drug. This is the first step in a lengthy approval process that starts with a 60-day comment period.
Update 2: Two recent research studies were added to the “Studies on marijuana and driving” section of this piece on July 18, 2024.
As marijuana use continues to rise and state-level marijuana legalization sweeps the U.S., researchers and policymakers are grappling with a growing public safety concern: marijuana-impaired driving.
As of April 2023, 38 U.S. states had legalized medical marijuana and 23 had legalized its recreational use, according to the National Conference of State Legislatures. Recreational or medical marijuana measures are on the ballot in seven states this year.
The issue of marijuana-impaired driving has not been an easy one to tackle because, unlike alcohol, which has well-established thresholds of impairment, the metrics for marijuana’s effects on driving remain rather elusive.
“We don’t have that kind of deep knowledge right now and it’s not because of lack of trying,” says Dr. Guohua Li, professor of epidemiology and the founding director of the Center for Injury Science and Prevention at Columbia University.
“Marijuana is very different from alcohol in important ways,” says Li, who has published several studies on marijuana and driving. “And one of them is that the effect of marijuana on cognitive functions and behaviors is much more unpredictable than alcohol. In general, alcohol is a depressant drug. But marijuana could act on the central nervous system as a depressant, a stimulant, and a hallucinogenic substance.”
Efforts to create a breathalyzer to measure the level of THC, the main psychoactive compound found in the marijuana plant, have largely failed, because “the THC molecule is much bigger than ethanol and its behavior after ingestion is very different from alcohol,” Li says.
Currently, the two most common methods used to measure THC concentration to identify impaired drivers are blood and saliva tests, although there’s ongoing debate about their reliability.
Marijuana, a term interchangeably used with cannabis, is the most commonly used federally illegal drug in the U.S.: 48.2 million people, or about 18% of Americans reported using it at least once in 2019, according to the latest available data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Worldwide, 2.5% of the population consumes marijuana, according to the World Health Organization.
Marijuana is legal in several countries, including Canada, where it was legalized in 2018. Despite state laws legalizing cannabis, it remains illegal at the federal level in the U.S.
As states grapple with the contentious issue of marijuana legalization, the debate is not just about public health, potential tax revenues and economic interests. At the heart of the discussion is also the U.S. criminal justice system.
Marijuana is shown to have medicinal qualities and, compared with substances like alcohol, tobacco, and opioids, it has relatively milder health risks. However, it’s not risk-free, a large body of research has shown.
Marijuana consumption can lead to immediate effects such as impaired muscle coordination and paranoia, as well as longer-term effects on mental health and cognitive functions — and addiction. As its use becomes more widespread, researchers are trying to better understand the potential hazards of marijuana, particularly for younger users whose brains are in critical stages of development.
Marijuana and driving
The use of marijuana among drivers, passengers and pedestrians has increased steadily over the past two decades, Li says.
Compared with the year 2000, the proportion of U.S. drivers on the road who are under the influence of marijuana has increased by several folds, between five to 10 times, based on toxicology testing of people who died in car crashes, Li says.
A 2022 report from the National Transportation Safety Board finds alcohol and cannabis are the two most commonly detected drugs among drivers arrested for impaired driving and fatally injured drivers. Most drivers who tested positive for cannabis also tested positive for another potentially impairing drug.
“Although cannabis and many other drugs have been shown to impair driving performance and are associated with increased crash risk, there is evidence that, relative to alcohol, awareness about the potential dangers of driving after using other drugs is lower,” according to the report.
Indeed, many U.S. adults perceive daily marijuana use or exposure to its smoke safer than tobacco, even though research finds otherwise.
Several studies have demonstrated marijuana’s impact on driving.
Marijuana use can reduce the drivers’ ability to pay attention, particularly when they are performing multiple tasks, research finds. It also slows reaction time and can impair coordination.
“The combination is that you potentially have people who are noticing hazards later, braking slower and potentially not even noticing hazards because of their inability to focus on competing things on the road,” says Dr. Daniel Myran, an assistant professor at the Department of Family Medicine and health services researcher at the University of Ottawa.
In a study published in September in JAMA Network Open, Myran and colleagues find that from 2010 to 2021 the rate of cannabis-involved traffic injuries that led to emergency department visits in Ontario, Canada, increased by 475%, from 0.18 per 1,000 traffic injury emergency department visits in 2010 to 1.01 visits in 2021.
To be sure, cannabis-involved traffic injuries made up a small fraction of all traffic injury-related visits to hospital emergency departments. Out of 947,604 traffic injury emergency department visits, 426 had documented cannabis involvement.
Myran cautions the increase shouldn’t be solely attributed to marijuana legalization. It captures changing societal attitudes toward marijuana and acceptance of cannabis use over time in the lead-up to legalization. In addition, it may reflect an increasing awareness among health care providers about cannabis-impaired driving, and they may be more likely to ask about cannabis use and document it in medical charts, he says.
“When you look at the 475% increase in cannabis involvement in traffic injuries, rather than saying legalizing cannabis has caused the roads to be unsafe and is a public health disaster, it’s that cannabis use appears to be growing as a risk for road traffic injuries and that there seem to be more cannabis impaired drivers on the road,” Myran says. “Legalization may have accelerated this trend. Faced with this increase, we need to think about what are public health measures and different policy interventions to reduce harms from cannabis-impaired driving.”
Setting a legal limit for marijuana-impaired driving
Setting a legal limit for marijuana-impaired driving has not been easy. Countries like Canada and some U.S. states have agreed upon a certain level of THC in blood, usually between 1 to 5 nanograms per milliliter. Still, some studies have found those limits to be weak indicators of cannabis-impaired driving.
When Canada legalized recreational marijuana in 2018, it also passed a law that made it illegal to drive with blood THC levels of more than 2 nanograms. The penalties are more severe for blood THC levels above 5 nanograms. The blood test is done at the police station for people who are pulled over and are deemed to be drug impaired.
In the U.S., five states — Ohio, Illinois, Montana, Washington and Nevada — have “per se laws,” which set a specific amount of THC in the driver’s blood as evidence of impaired driving, according to the National Conference of State Legislatures. That limit ranges between 2 and 5 nanograms of THC per milliliter of blood.
Colorado, meanwhile, has a “permissible inference law,” which states that it’s permissible to assume the driver was under the influence if their blood THC level is 5 nanograms per milliliter or higher, according to NCSL.
Twelve states, most which have legalized some form of marijuana of use, have zero tolerance laws for any amount of certain drugs, including THC, in the body.
The remaining states have “driving under the influence of drugs” laws. Among those states, Alabama and Michigan, have oral fluid roadside testing program to screen drivers for marijuana and other drugs, according to NCSL.
In May this year, the U.S. Department of Transportation published a final rule that allows employers to use saliva testing for commercially licensed drivers, including truck drivers. The rule, which went into effect in June, sets the THC limit in saliva at 4 nanograms.
Saliva tests can detect THC for 8 to 24 hours after use, but the tests are not perfect and can results in false positives, leading some scientists to argue against using them in randomly-selected drivers.
In a 2021 report, the U.S. National Institute of Justice, the research and development arm of the Department of Justice, concluded that THC levels in bodily fluids, including blood and saliva “were not reliable indicators of marijuana intoxication.”
Studies on marijuana and driving
Over the past two decades, many studies have shown marijuana use can impair driving. However, discussions about what’s the best way to measure the level of THC in blood or saliva are ongoing. Below, we highlight and summarize several recent studies that address the issue. The studies are listed in order of publication date. We also include a list of related studies and resources to inform your audiences.
State Driving Under the Influence of Drugs Laws
Alexandra N. Origenes, Sarah A. White, Emma E. McGinty and Jon S. Vernick. Journal of Law, Medicine & Ethics, July 2024.Summary: As of January 2023, 33 states and D.C. had a driving under the influence of drugs law for at least one drug other than cannabis. Of those, 29 states and D.C. had a law specifically for driving under the influence of cannabis, in addition to a law for driving under the influence of other drugs. Four states had a driving under the influence of drug laws, excluding cannabis. Meanwhile, 17 states had no law for driving under the influence of drugs, including cannabis. “The 17 states lacking a DUID law that names specific drugs should consider enacting such a law. These states already have expressed their concern — through legislation — with drug-impaired driving. However, failure to name specific drugs is likely to make the laws more difficult to enforce. These laws may force courts and/or law enforcement to rely on potentially subjective indicators of impairment,” the authors write.
Associations between Adolescent Marijuana Use, Driving After Marijuana Use and Recreational Retail Sale in Colorado, USA
Lucas M. Neuroth, et al. Substance Use & Misuse, October 2023.Summary: Researchers use data from four waves (2013, 2015, 2017 and 2019) of the Healthy Kids Colorado Survey, including 47,518 students 15 and older who indicated that they drove. They find 20.3% of students said that they had used marijuana in the past month and 10.5% said they had driven under the influence of marijuana. They find that the availability of recreational marijuana in stores was associated with an increased prevalence of using marijuana one to two times in the past month and driving under the influence of marijuana at least once. “Over the study period, one in ten high school age drivers engaged in [driving after marijuana use], which is concerning given the high risk of motor vehicle-related injury and death arising from impaired driving among adolescents,” the authors write.
Are Blood and Oral Fluid Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Metabolite Concentrations Related to Impairment? A Meta-Regression Analysis
Danielle McCartney, et al. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, March 2022.Summary: Commonly used THC measurements may not be strong indicators of driving impairment. While there is a relationship between certain biomarkers like blood THC concentrations and impaired driving, this correlation is often weak. The study underscores the need for more nuanced and comprehensive research on this topic, especially as cannabis usage becomes more widespread and legally accepted.
The Effects of Cannabis and Alcohol on Driving Performance and Driver Behaviour: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sarah M. Simmons, Jeff K. Caird, Frances Sterzer and Mark Asbridge. Addiction, January 2022.Summary: This meta-analysis of experimental driving studies, including driving simulations, confirms that cannabis impairs driving performance, contrary to some beliefs that it might enhance driving abilities. Cannabis affects lateral control and speed — typically increasing lane excursions while reducing speed. The combination of alcohol and marijuana appears worse than either alone, challenging the idea that they cancel each other out.
Cannabis Legalization and Detection of Tetrahydrocannabinol in Injured Drivers
Jeffrey R. Brubacher, et al. The New England Journal of Medicine, January 2022.Summary: Following the legalization of recreational marijuana in Canada, there was a notable increase in injured drivers testing positive for THC, especially among those 50 years of age or older. This rise in cannabis-related driving incidents occurred even with new traffic laws aiming to deter cannabis-impaired driving. This uptick began before legalization became official, possibly due to perceptions that cannabis use was soon-to-be legal or illegal but not enforced. The data suggests that while legalization has broad societal impacts, more comprehensive strategies are needed to deter driving under the influence of cannabis and raise public awareness about its risks.
Cannabis and Driving
Godfrey D. Pearlson, Michael C. Stevens and Deepak Cyril D’Souza. Frontiers in Psychiatry, September 2021.Summary: Cannabis-impaired driving is a growing public health concern, and studies show that such drivers are more likely to be involved in car crashes, according to this review paper. Drivers are less affected by cannabis than they are by alcohol or cocaine, but the problem is expected to escalate with increasing cannabis legalization and use. Unlike alcohol, THC’s properties make it challenging to determine direct impairment levels from testing results. Current roadside tests lack precision in detecting genuine cannabis-impaired drivers, leading to potential wrongful convictions. Moreover, there is a pressing need for research on the combined effects of alcohol and cannabis on driving, as well as the impact of emerging popular forms of cannabis, like concentrates and edibles. The authors recommend public awareness campaigns about the dangers of driving under the influence of cannabis, similar to those against drunk driving, to address misconceptions. Policymakers should prioritize science-based decisions and encourage further research in this domain.
Demographic And Policy-Based Differences in Behaviors And Attitudes Towards Driving After Marijuana Use: An Analysis of the 2013–2017 Traffic Safety Culture Index
Marco H. Benedetti, et al. BMC Research Notes, June 2021.Summary: The study, based on a U.S. survey, finds younger, low-income, low-education and male participants were more tolerant of driving after marijuana consumption. Notably, those in states that legalized medical marijuana reported driving after use more frequently, aligning with studies indicating a higher prevalence of THC detection in drivers from these states. Overall, while the majority perceive driving after marijuana use as dangerous, not all research agrees on its impairment effects. Existing studies highlight that marijuana impacts motor skills and executive functions, yet its direct correlation with crash risk remains debated, given the variations in individual tolerance and how long THC remains in the system.
Driving Under the Influence of Cannabis: A Framework for Future Policy
Robert M. Chow, et al.Anesthesia & Analgesia, June 2019.Summary: The study presents a conceptual framework focusing on four main domains: legalization, driving under the influence of cannabis, driver impairment, and motor vehicle accidents. With the growing legalization of cannabis, there’s an anticipated rise in cannabis-impaired driving cases. The authors group marijuana users into infrequent users who show significant impairment with increased THC blood levels, chronic users with minimal impairment despite high THC levels, and those with consistent psychomotor deficits. Current challenges lie in the lack of standardized regulation for drivers influenced by cannabis, primarily because of state-to-state variability and the absence of a federal statutory limit for blood THC levels. European nations, however, have established thresholds for blood THC levels, ranging from 0.5 to 50.0 micrograms per liter depending on whether blood or blood serum are tested. The authors suggest the combined use of alcohol and THC blood tests with a psychomotor evaluation by a trained professional to determine impairment levels. The paper stresses the importance of creating a structured policy framework, given the rising acceptance and use of marijuana in society.
Additional research
Cannabis-Involved Traffic Injury Emergency Department Visits After Cannabis Legalization and Commercialization
Daniel T. Myran, et al. JAMA Network Open, September 2023.Driving Performance and Cannabis Users’ Perception of Safety: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Thomas D. Marcotte, et al. JAMA Psychiatry, January 2022.Medicinal Cannabis and Driving: The Intersection of Health and Road Safety Policy
Daniel Perkins, et al. International Journal of Drug Policy, November 2021.Prevalence of Marijuana Use Among Trauma Patients Before and After Legalization of Medical Marijuana: The Arizona Experience
Michael Levine, et al. Substance Abuse, July 2021.Self-Reported Driving After Marijuana Use in Association With Medical And Recreational Marijuana Policies
Marco H. Benedetti, et al. International Journal of Drug Policy, June 2021.Cannabis and Driving Ability
Eric L. Sevigny. Current Opinion in Psychology, April 2021.The Failings of per se Limits to Detect Cannabis-Induced Driving Impairment: Results from a Simulated Driving Study
Thomas R. Arkell, et al. Traffic Injury Prevention, February 2021.Risky Driving Behaviors of Drivers Who Use Alcohol and Cannabis
Tara Kelley-Baker, et al. Transportation Research Record, January 2021.Direct and Indirect Effects of Marijuana Use on the Risk of Fatal 2-Vehicle Crash Initiation
Stanford Chihuri and Guohua Li. Injury Epidemiology, September 2020Cannabis-Impaired Driving: Evidence and the Role of Toxicology Testing
Edward C. Wood and Robert L. Dupont. Cannabis in Medicine, July 2020.Association of Recreational Cannabis Laws in Colorado and Washington State With Changes in Traffic Fatalities, 2005-2017
Julian Santaella-Tenorio, et al. JAMA Internal Medicine, June 2020.Marijuana Decriminalization, Medical Marijuana Laws, and Fatal Traffic Crashes in US Cities, 2010–2017
Amanda Cook, Gregory Leung and Rhet A. Smith. American Journal of Public Health, February 2020.Cannabis Use in Older Drivers in Colorado: The LongROAD Study
Carolyn G. DiGuiseppi, et al. Accident Analysis & Prevention, November 2019.Crash Fatality Rates After Recreational Marijuana Legalization in Washington and Colorado
Jayson D. Aydelotte, et al. American Journal of Public Health, August 2017.Marijuana-Impaired Driving: A Report to Congress
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, July 2017Interaction of Marijuana And Alcohol on Fatal Motor Vehicle Crash Risk: A Case–Control Study
Stanford Chihuri, Guohua Li and Qixuan Chen. Injury Epidemiology, March 2017.US Traffic Fatalities, 1985–2014, and Their Relationship to Medical Marijuana Laws
Julian Santaella-Tenorio, et al. American Journal of Public Health, February 2017.Delays in DUI Blood Testing: Impact on Cannabis DUI Assessments
Ed Wood, Ashley Brooks-Russell and Phillip Drum. Traffic Injury Prevention, June 2015.Establishing Legal Limits for Driving Under the Influence of Marijuana
Kristin Wong, Joanne E. Brady and Guohua Li. Injury Epidemiology, October 2014.Cannabis Effects on Driving Skills
Rebecca L. Hartman and Marilyn A. Huestis. Clinical Chemistry, March 2014.Acute Cannabis Consumption And Motor Vehicle Collision Risk: Systematic Review of Observational Studies and Meta-Analysis
Mark Asbridge, Jill A. Hayden and Jennifer L. Cartwright. The BMJ, February 2012.Resources for your audiences
The following resources include explainers from federal agencies and national organizations. You’re free to use images and graphics from federal agencies.
- CDC’s main marijuana page.
- CDC’s marijuana data and statistics.
- Marijuana Drug Facts from the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
- Health Effects of Marijuana from the CDC.
- Learn About Marijuana Risks from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.
- Marijuana and Lung Health from the American Lung Association.
- Substance Use Disorder 101 from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
- What You Need To Know About Marijuana Use and Driving from the CDC.
- Does marijuana use affect driving? from the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
- Drug-Impaired Driving from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration.
This article first appeared on The Journalist’s Resource and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: