The Problem With Active Listening
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The problem with active listening
Listening is an important skill to keep well-trained at any age. It’s important in romantic relationships, parent-child relationships, friendships, and more.
First, for any unfamiliar or hazy-of-memory: active listening is the practice of listening, actively. The “active” side of this comes in several parts:
- Asking helpful questions
- Giving feedback to indicate that the answer has been understood
- Prompting further information-giving
This can look like:
- A: How did you feel when that happened?
- B: My heart was racing and I felt panicked, it really shocked me
- A: It really shocked you?
- B: Yes, because it was so unexpected; I’d never imagined something like this happening
- A: You’d never expect something like that
- B: No, I mean, I had no reason to
And… As a superficial listening technique, it’s not terrible, and it has its place
But unfortunately, if it’s one’s only listening technique, one will very quickly start sounding like a Furby—that children’s toy from the 90s that allegedly randomly parroted fragments of things that had been said to it. In fact this was a trick of programming, but that’s beyond the scope of this article.
The point is: the above technique, if used indiscriminately and/or too often, starts to feel like talking to a very basic simulacrum.
Which is the opposite of feeling like being listened to!
A better way to listen
Start off similarly, but better.
Ask open questions, or otherwise invite sharing of information.
People can be resistant to stock phrases like “How did that make you feel?”, but this can be got around by simply changing it up, e.g.:
- “What was your reaction?” ← oblique but often elicits the same information
- “I’m not sure how I’d feel about that, in your shoes” ← not even a question, but shows active attention much better than the “mmhmm” noises of traditional active listening, and again prompts the same information
Express understanding… But better
People have been told “I understand” a lot, and often it’s code for “Stop talking”. So, avoid “I understand”. Instead, try:
- “I can understand that”
- “Understandable”
- “That makes sense”
Ask clarifying questions… Better
Sometimes, a clarifying question doesn’t have to have its own point, beyond prompting more sharing, and sometimes, an “open question” can be truly wide open, meaning that vaguer is better, such as:
- “Oh?”
- “How so?” ← this is the heavy artillery that can open up a lot
Know when to STFU
Something that good therapists (and also military interrogators) know: when to STFU
If someone is talking, don’t interrupt them. If you do, they might not start again, or might skip what they were going to say.
Interruption says “I think you’ve said all that needs to be said there”, or else, if the interruption was to ask one of the above questions, it says “you’re not doing a good enough job of talking”, and neither of those sentiments encourage people to share, nor do they make someone feel listened-to!
Instead, just listen. Passive listening has its place too! When there’s a break, then you can go to one of the above questions/prompts/expressions of understanding, as appropriate.
Judge not, lest they feel judged
Reserve judgement until the conversation is over, at the earliest. If asked for your judgement of some aspect, be as reassuring as you can. People feel listened-to when they don’t feel judged.
If they feel judged, conversely, they can often feel you didn’t listen properly, or else you’d be in agreement with them. So instead, just sit on it for as long as you can.
Note: that goes for positive judgements too! Sit on it. Expressing a positive judgement too soon can seem that you were simply eager to please, and can suggest insincerity.
If this seems simple, that’s because it is. But, try it, and see the difference.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Anise vs Diabetes & Menopause
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What A Daily Gram Of Anise Can Do
Anise, specifically the seed of the plant, also called aniseed, is enjoyed for its licorice taste—as well as its medicinal properties.
Let’s see how well the science lives up to the folk medicine…
What medicinal properties does it claim?
The main contenders are:
- Reduces menopause symptoms
- Reduces blood sugar levels
- Reduces inflammation
Does it reduce menopause symptoms?
At least some of them! Including hot flashes and bone density loss. This seems to be due to the estrogenic-like activity of anethole, the active compound in anise that gives it these effects:
Estrogenic activity of isolated compounds and essential oils of Pimpinella species
1g of anise/day yielded a huge reduction in frequency and severity of hot flashes, compared to placebo*:
*you may be wondering what the placebo is for 1g of a substance that has a very distinctive taste. The researchers used capsules, with 3x330g as the dose, either anise seed or potato starch.
❝In the experimental group, the frequency and severity of hot flashes before the treatment were 4.21% and 56.21% and, after that, were 1.06% and 14.44% at the end of the fourth week respectively. No change was found in the frequency and severity of hot flashes in the control group. The frequency and severity of hot flashes was decreased during 4 weeks of follow up period. P. anisum is effective on the frequency and severity of hot flashes in postmenopausal women. ❞
See for yourself: The Study on the Effects of Pimpinella anisum on Relief and Recurrence of Menopausal Hot Flashes
As for bone mineral density, we couldn’t find a good study for anise, but we did find this one for fennel, which is a plant of the same family and also with the primary active compound anethole:
The Prophylactic Effect of Fennel Essential Oil on Experimental Osteoporosis
That was a rat study, though, so we’d like to see studies done with humans.
Summary on this one: it clearly helps against hot flashes (per the very convincing human study we listed above); it probably helps against bone mineral density loss.
Does it reduce blood sugar levels?
This one got a flurry of attention all so recently, on account of this research review:
Review on Anti-diabetic Research on Two Important Spices: Trachyspermum ammi and Pimpinella anisum
If you read this (and we do recommend reading it! It has a lot more information than we can squeeze in here!) one of the most interesting things about the in vivo anti-diabetic activity of anise was that while it did lower the fasting blood glucose levels, that wasn’t the only effect:
❝Over a course of 60 days, study participants were administered seed powders (5 g/d), which resulted in significant antioxidant, anti-diabetic, and hypolipidemic effects.
Notably, significant reductions in fasting blood glucose levels were observed. This intervention also elicited alterations in the lipid profile, LPO, lipoprotein levels, and the high-density lipoprotein (HDL) level.
Moreover, the serum levels of essential antioxidants, such as beta carotene, vitamin C, vitamin A, and vitamin E, which are typically decreased in diabetic patients, underwent a reversal.❞
That’s just one of the studies cited in that review (the comments lightly edited here for brevity), but it stands out, and you can read that study in its entirety (it’s well worth reading).
Rajeshwari et al, bless them, added a “tl;dr” at the top of their already concise abstract; their “tl;dr” reads:
❝Both the seeds significantly influenced almost all the parameters without any detrimental effects by virtue of a number of phytochemicals, vitamins and minerals present in the seeds having therapeutic effects.❞
Shortest answer: yes, yes it does
Does it fight inflammation?
This one’s quick and simple enough: yes it does; it’s full of antioxidants which thus also have an anti-inflammatory effect:
Review of Pharmacological Properties and Chemical Constituents of Pimpinella anisum
…which can also be used an essential oil, applied topically, to fight both pain and the inflammation that causes it—at least in rats and mice:
❝Indomethacin and etodolac were treated reference drugs for the anti-inflammatory activity. Aspirin and morphine hydrochloride were treated reference drugs for the analgesic activity. The results showed that fixed oil of P. anisum has an anti-inflammatory action more than etodolac and this effect was as strong as indomethacin. P. anisum induces analgesic effect comparable to that of 100 mg/kg Aspirin and 10 mg/kg morphine at 30 th min. of the study❞
Summary of this section:
- Aniseeds are a potent source of antioxidants, which fight inflammation.
- Anise essential oil is probably also useful as a topical anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent, but we’d like to see human tests to know for sure.
Is it safe?
For most people, enjoyed in moderation (e.g., within the dosage parameters described in the above studies), anise is safe. However:
- If you’re allergic to it, it won’t be safe
- Its estrogen-mimicking effects could cause problems if you have (or have a higher risk factor for) breast cancer, ovarian cancer, or endometriosis.
- For most men, the main concern is that it may lower sperm count.
Where to get it?
As ever, we don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience, you can buy the seeds in bulk on Amazon, or in case you prefer it, here’s an example of it available as an essential oil.
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Mushrooms vs Eggplant – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing mushrooms to eggplant, we picked the mushrooms.
Why?
First, you may be wondering: which mushrooms? Button mushrooms? White mushrooms? Chestnut mushrooms? Portobello mushrooms? And the answer is yes. Those (and more; it represents most mushrooms that are commonly sold fresh in western supermarkets) are all the same species at different ages; namely, Agaricus bisporus—not to be mistaken for fly agaric, which despite the name, is not even a member of the Agaricus genus, and is in fact Amanita muscari. This is an important distinction, because fly agaric is poisonous, though fatality is rare, and it’s commonly enjoyed recreationally (after some preparation, which reduces its toxicity) for its psychoactive effects. It’s the famous red one with white spots. Anyway, today we will be talking instead about Agaricus bisporus, which is most popular western varieties of “edible mushroom”.
With that in mind, let’s get down to it:
In terms of macros, mushrooms contain more than 3x the protein, while eggplant contains nearly 2x the carbs and 3x the fiber. We’ll call this a tie for macros.
As for vitamins, mushrooms contain more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12, D, and choline, while eggplant contains more of vitamins A, E, and K. Most notably for vegans, mushrooms are a good non-animal source of vitamins B12 and D, which nutrients are not generally found in plants. Mushrooms, of course, are not technically plants. In any case, the vitamins category is an easy win for mushrooms.
When it comes to minerals, mushrooms have more copper, iron, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while eggplant has more calcium, magnesium, and manganese. Another easy win for mushrooms.
One final thing worth noting is that mushrooms are a rich source of the amino acid ergothioneine, which has been called a “longevity vitamin” for its healthspan-increasing effects (see our article below).
Meanwhile, in the category of mushrooms vs eggplant, mushrooms don’t leave much room for doubt and are the clear winner here.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
The Magic of Mushrooms: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Metabolical – by Dr. Robert Lustig
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The premise of this book itself is not novel: processed food is bad, food giants lie to us, and eating better makes us less prone to disease (especially metabolic disease).
What this book does offer that’s less commonly found is a comprehensive guide, a walkthrough of each relevant what and why and how, with plenty of good science and practical real-world examples.
In terms of unique selling points, perhaps the greatest strength of this book is its focus on two things in particular that affect many aspects of health: looking after our liver, and looking after our gut.
The style is… A little dramatic perhaps, but that’s just the style; there’s no hyperbole, he is stating well-established scientific facts.
Bottom line: very much of chronic disease would be a lot less diseasey if we all ate with these aspects of our health in mind. This book’s a comprehensive guide to that.
Click here to check out Metabolical, and let food be thy medicine!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Power Foods Diet – by Dr. Neal Barnard
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this is not: it’s not a cookbook. There are recipes, more than a hundred if we consider such things as “barbecue sauce” as a standalone recipe, and if we overlook such things as how “perfect hot oatmeal” is followed on the next page by a recipe for “perfect hot oatmeal with berries”.
However, as we say, it’s not a cookbook; it’s first and foremost an educational text on the topic of nutrition.
Here we will learn about good eating for general health, which foods are natural appetite-suppressants, which foods reduce our body’s absorption of sugars from foods (not merely slowing, but flushing them away so they cannot be absorbed at all), and which foods actually boost metabolism for a few hours after the meal.
Dr. Barnard also talks about some foods that are more healthy, or less healthy, than popularly believed, and how to use all this information to craft a good, optimized, dietary plan for you.
Bottom line: there’s a lot of good information here, and the recipes are simply a bonus.
Click here to check out The Power Foods Diet, and optimize yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Homeopathy: Evidence So Tiny That It’s Not there?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Homeopathy: Evidence So Tiny That It’s Not There?
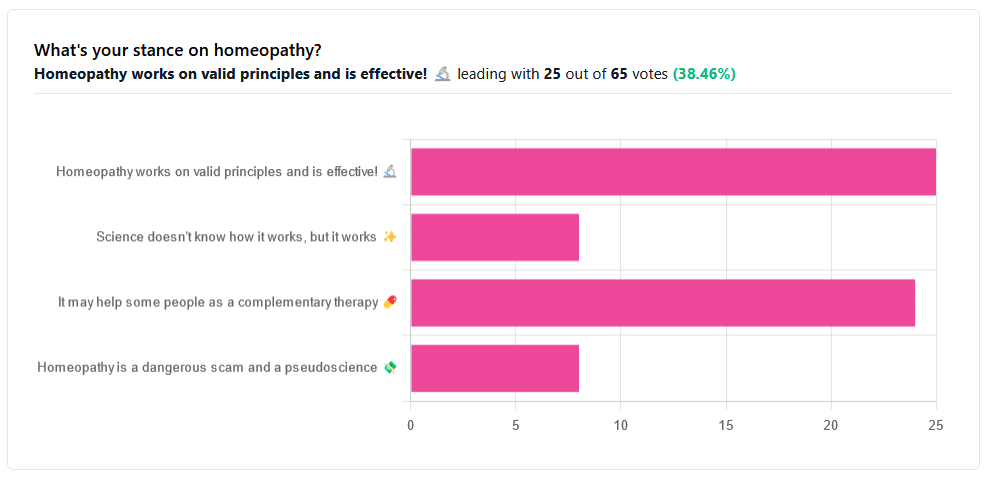
Yesterday, we asked you your opinions on homeopathy. The sample size of responses was a little lower than we usually get, but of those who did reply, there was a clear trend:
- A lot of enthusiasm for “Homeopathy works on valid principles and is effective”
- Near equal support for “It may help some people as a complementary therapy”
- Very few people voted for “Science doesn’t know how it works, but it works”; this is probably because people who considered voting for this, voted for the more flexible “It may help some people as a complementary therapy” instead.
- Very few people considered it a dangerous scam and a pseudoscience.
So, what does the science say?
Well, let us start our investigation by checking out the position of the UK’s National Health Service, an organization with a strong focus on providing the least expensive treatments that are effective.
Since homeopathy is very inexpensive to arrange, they will surely want to put it atop their list of treatments, right?
❝Homeopathy is a “treatment” based on the use of highly diluted substances, which practitioners claim can cause the body to heal itself.
There’s been extensive investigation of the effectiveness of homeopathy. There’s no good-quality evidence that homeopathy is effective as a treatment for any health condition.❞
The NHS actually has a lot more to say about that, and you can read their full statement here.
But that’s just one institution. Here’s what Australia’s National Health and Medical Research Council had to say:
❝There was no reliable evidence from research in humans that homeopathy was effective for treating the range of health conditions considered: no good-quality, well-designed studies with enough participants for a meaningful result reported either that homeopathy caused greater health improvements than placebo, or caused health improvements equal to those of another treatment❞
You can read their full statement here.
The American FDA, meanwhile, have a stronger statement:
❝Homeopathic drug products are made from a wide range of substances, including ingredients derived from plants, healthy or diseased animal or human sources, minerals and chemicals, including known poisons. These products have the potential to cause significant and even permanent harm if they are poorly manufactured, since that could lead to contaminated products or products that have potentially toxic ingredients at higher levels than are labeled and/or safe, or if they are marketed as substitute treatments for serious or life-threatening diseases and conditions, or to vulnerable populations.❞
You can read their full statement here.
Homeopathy is a dangerous scam and a pseudoscience: True or False?
False and True, respectively, mostly.
That may be a confusing answer, so let’s elaborate:
- Is it dangerous? Mostly not; it’s mostly just water. However, two possibilities for harm exist:
- Careless preparation could result in a harmful ingredient still being present in the water—and because of the “like cures like” principle, many of the ingredients used in homeopathy are harmful, ranging from heavy metals to plant-based neurotoxins. However, the process of “ultra-dilution” usually removes these so thoroughly that they are absent or otherwise scientifically undetectable.
- Placebo treatment has its place, but could result in “real” treatment going undelivered. This can cause harm if the “real” treatment was critically needed, especially if it was needed on a short timescale.
- Is it a scam? Probably mostly not; to be a scam requires malintent. Most practitioners probably believe in what they are practising.
- Is it a pseudoscience? With the exception that placebo effect has been highly studied and is a very valid complementary therapy… Yes, aside from that it is a pseudoscience. There is no scientific evidence to support homeopathy’s “like cures like” principle, and there is no scientific evidence to support homeopathy’s “water memory” idea. On the contrary, they go against the commonly understood physics of our world.
It may help some people as a complementary therapy: True or False?
True! Not only is placebo effect very well-studied, but best of all, it can still work as a placebo even if you know that you’re taking a placebo… Provided you also believe that!
Science doesn’t know how it works, but it works: True or False?
False, simply. At best, it performs as a placebo.
Placebo is most effective when it’s a remedy against subjective symptoms, like pain.
However, psychosomatic effect (the effect that our brain has on the rest of our body, to which it is very well-connected) can mean that placebo can also help against objective symptoms, like inflammation.
After all, our body, directed primarily by the brain, can “decide” what immunological defenses to deploy or hold back, for example. This is why placebo can help with conditions as diverse as arthritis (an inflammatory condition) or diabetes (an autoimmune condition, and/or a metabolic condition, depending on type).
Here’s how homeopathy measures up, for those conditions:
(the short answer is “no better than placebo”)
Homeopathy works on valid principles and is effective: True or False?
False, except insofar as placebo is a valid principle and can be effective.
The stated principles of homeopathy—”like cures like” and “water memory”—have no scientific basis.
We’d love to show the science for this, but we cannot prove a negative.
However, the ideas were conceived in 1796, and are tantamount to alchemy. A good scientific attitude means being open-minded to new ideas and testing them. In homeopathy’s case, this has been done, extensively, and more than 200 years of testing later, homeopathy has consistently performed equal to placebo.
In summary…
- If you’re enjoying homeopathic treatment and that’s working for you, great, keep at it.
- If you’re open-minded to enjoying a placebo treatment that may benefit you, be careful, but don’t let us stop you.
- If your condition is serious, please do not delay seeking evidence-based medical treatment.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Doctor’s Kitchen – by Dr. Rupy Aujla
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve featured Dr. Aujla before as an expert-of-the-week, and now it’s time to review a book by him. What’s his deal, and what should you expect?
Dr. Aujla first outlines the case for food as medicine. Not just “eat nutritionally balanced meals”, but literally, “here are the medicinal properties of these plants”. Think of some of the herbs and spices we’ve featured in our Monday Research Reviews, and add in medicinal properties of cancer-fighting cruciferous vegetables, bananas with dopamine and dopamine precursors, berries full of polyphenols, hemp seeds that fight cognitive decline, and so forth.
Most of the book is given over to recipes. They’re plant-centric, but mostly not vegan. They’re consistent with the Mediterranean diet, but mostly Indian. They’re economically mindful (favoring cheap ingredients where reasonable) while giving a nod to where an extra dollar will elevate the meal. They don’t give calorie values etc—this is a feature not a bug, as Dr. Aujla is of the “positive dieting” camp that advocates for us to “count colors, not calories”. Which, we have to admit, makes for very stress-free cooking, too.
Dr. Aujla is himself an Indian Brit, by the way, which gives him two intersecting factors for having a taste for spices. If you don’t share that taste, just go easier on the pepper etc.
As for the medicinal properties we mentioned up top? Four pages of references at the back, for any who are curious to look up the science of them. We at 10almonds do love references!
Bottom line: if you like tasty food and you’re looking for a one-stop, well-rounded, food-as-medicine cookbook, this one is a top-tier choice.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: