Kiwi vs Grapefruit – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing kiwi to grapefruit, we picked the kiwi.
Why?
In terms of macros, kiwi has nearly 2x the protein, slightly more carbs, and 2x the fiber; both fruits are low glycemic index foods, however.
When it comes to vitamins, kiwi has more of vitamins B3, B6, B7, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while grapefruit has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, and B5. An easy win for kiwi.
In the category of minerals, kiwi is higher in calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while grapefruit is not higher in any minerals. So, no surprises for guessing which wins this category.
One thing that grapefruit is a rich source of: furanocoumarin, which can inhibit cytochrome P-450 3A4 isoenzyme and P-glycoptrotein transporters in the intestine and liver—slowing down their drug metabolism capabilities, thus effectively increasing the bioavailability of many drugs manifold.
This may sound superficially like a good thing (improving bioavailability of things we want), but in practice it means that in the case of many drugs, if you take them with (or near in time to) grapefruit or grapefruit juice, then congratulations, you just took an overdose. This happens with a lot of meds for blood pressure, cholesterol (including statins), calcium channel-blockers, anti-depressants, benzo-family drugs, beta-blockers, and more. Oh, and Viagra, too. Which latter might sound funny, but remember, Viagra’s mechanism of action is blood pressure modulation, and that is not something you want to mess around with unduly. So, do check with your pharmacist to know if you’re on any meds that would be affected by grapefruit or grapefruit juice!
All in all, adding up the categories makes for an overwhelming total win for kiwis.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← kiwi is top of the list!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hope Not Nope – by Dr. Dillon Caswell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author a Doctor of Physical Therapy, writes from both professional expertise and personal experience, when it comes to the treatment of long term injury / disability / chronic illness.
His position here is that while suffering is unavoidable, we don’t have to suffer as much or as long as many might tell us. We can do things to crawl and claw our way to a better position, and we do not have to settle for any outcome we don’t want. That doesn’t mean there’s always a miracle cure—we don’t get to decide that—but we do get to decide whether we keep trying.
Dr. Caswell’s advice is based mostly in psychology—a lot of it in sports psychology, which is no surprise given his long history as an athlete as well as his medical career.
The style is very easy-reading, and a combination of explanation, illustrative (often funny) anecdotes, and a backbone of actual research to keep everything within the realms of science rather than mere wishful thinking—he strikes a good balance.
Bottom line: if your current health outlook is more of an uphill marathon, then this book can give you the tools to carry yourself through the healthcare system that’s been made for numbers, not people.
Share This Post
-
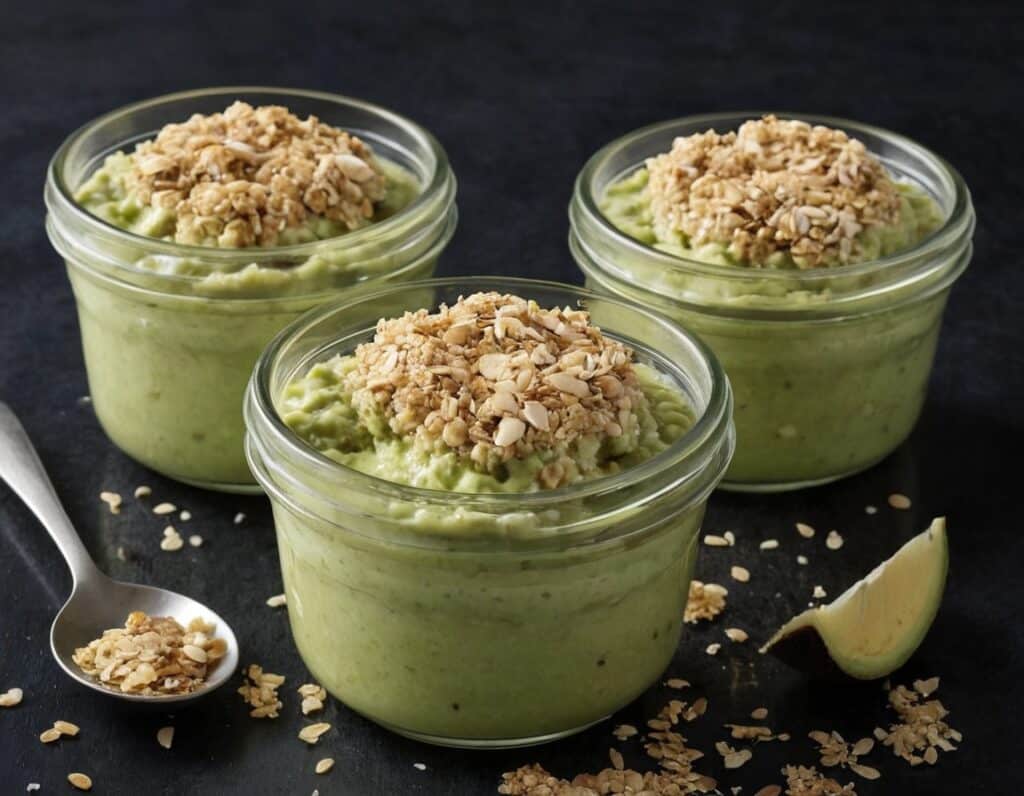
Avocado, Coconut & Lime Crumble Pots
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This one’s a refreshing snack or dessert, whose ingredients come together to make a very good essential fatty acid supplement. Coconut is a good source of MCTs, avocados are rich in omega 3, 6, and 9, while chia seeds are a great ALA omega 3 food, topping up the healthy balance.
You will need
- flesh of 2 large ripe avocados
- grated zest and juice of 2 limes
- 3 tbsp coconut oil
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 2 tsp honey (omit if you prefer a less sweet dish)
- 1 tsp desiccated coconut
- 4 low-sugar oat biscuits
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the avocado, lime juice, coconut oil, honey, and half the desiccated coconut, in a food processor.
2) Scoop the mixture into 4 ramekins (or equivalent-sized glasses), making sure to leave a ½” gap at the top. Refrigerate for at least 2–4 hours (longer is fine if you’re not ready to serve yet).
3) Assemble, by crumbling the oat biscuits and sprinkling on top of each serving, along with the other half of the desiccated coconut, the lime zest, and the chia seeds.
4) Serve immediately:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Uses of Delusion – by Dr. Stuart Vyse
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most of us try to live rational lives. We try to make the best decisions we can based on the information we have… And if we’re thoughtful, we even try to be aware of common logical fallacies, and overcome our personal biases too. But is self-delusion ever useful?
Dr. Stuart Vyse, psychologist and Fellow for the Committee for Skeptical Inquiry, argues that it can be.
From self-fulfilling prophecies of optimism and pessimism, to the role of delusion in love and loss, Dr. Vyse explores what separates useful delusion from dangerous irrationality.
We also read about such questions as (and proposed answers to):
- Why is placebo effect stronger if we attach a ritual to it?
- Why are negative superstitions harder to shake than positive ones?
- Why do we tend to hold to the notion of free will, despite so much evidence for determinism?
The style of the book is conversational, and captivating from the start; a highly compelling read.
Bottom line: if you’ve ever felt yourself wondering if you are deluding yourself and if so, whether that’s useful or counterproductive, this is the book for you!
Click here to check out The Uses of Delusion, and optimize yours!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
5 Ways To Make Your Smoothie Blood Sugar Friendly (Avoid the Spike!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
At 10almonds, we are often saying “eat whole fruit; don’t drink your calories”. Whole fruit is great for blood sugars; fruit juices and many smoothies on the other hand, not so much. Especially juices, being near-completely or perhaps even completely stripped of fiber, but even smoothies have had a lot of the fiber broken down and are still a liquid, meaning they are very quickly and easily digestible, and thus their sugars (whatever carbs are in there) can just zip straight into your veins.
However, there are ways to mitigate this…
Slow it down
The theme here is “give the digestive process something else to do”; some things are more quickly and easily digestible than others, and if it’s working on breaking down some of the slower things, it’s not waving sugars straight on through; they have to wait their turn.
To that end, recommendations include:
- Full-fat Greek yogurt which provides both protein and fat, helping to slow down the absorption of sugar. Always choose unsweetened versions to avoid added sugars, though!
- Coconut milk (canned) which is low in sugar and carbs, high in fat. This helps reduce blood sugar spikes, as she found through personal experimentation too.
- Avocado which is rich in healthy fats that help stabilize blood sugar. As a bonus, it blends well into smoothies without affecting the taste much.
- Coconut oil which contains medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) that are quickly absorbed for energy without involving glucose, promoting fat-burning and reducing blood sugar spikes.
- Collagen powder which is a protein that helps lower blood sugar spikes while also supporting muscle growth, skin, and joints.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eat To Beat Chronic Fatigue!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Eat To Beat Chronic Fatigue
Chronic fatigue is on the rise, and it can make life a living Hell. Days blur into one, and you try to take each day as it comes, but sometimes several days gang up on you at once.
You probably know some lifestyle changes that might help—if only you had the energy to implement them.
You’d like to eat well, but you need to…
- Buy the fresh produce (and take a little rest after)
- Put the groceries away (and take a little rest after)
- Wash the vegetables (and take a little rest after)
- Chop the things as necessary (and take a little rest after)
- Cook dinner (and take a little rest after)
…and now you’re too exhausted to eat it.
So, what can be done?
First, avoid things that cause inflammation, as this is a major contributor to chronic fatigue. You might like our previous main feature:
Next up, really do stay hydrated. It’s less about quantity, and more about ubiquity. Hydrate often.
Best is if you always have some (hydrating) drink on the go.
Do experiment with your diet, and/but keep a food journal of what you eat and how you feel 30–60 minutes after eating it. Only make one change at a time, otherwise you won’t know which change made the difference.
Notice what patterns emerge over time, and adjust your ingredients accordingly.
Limit your caffeine intake. We know that sometimes it seems like the only way to get through the day, but you will always crash later, because it was only ever taxing your adrenal system (thus: making you more tired in the long run) and pulling the wool over the eyes of your adenosine receptors (blocking you from feeling how tired you are, but not actually reducing your body’s tiredness).
Put simply, caffeine is the “payday loan” of energy.
Eat more non-starchy vegetables, and enjoy healthy fats. Those healthy fats can come from nuts and seeds, avocado, or fish (not fried, though!).
The non-starchy vegetables will boost your vitamins and fiber while being easy on your beleaguered metabolism, while the healthy fats will perk up your energy levels without spiking insulin like sugars would.
Pay the fatigue tax up front. What this means is… Instead of throwing away vegetables that didn’t get used because it would take too much effort and you just need an easier dinner today, buy ready-chopped vegetables, for example.
And if you buy vegetables frozen, they’re also often not only cheaper, but also (counterintuitively) contain more nutrients.
A note of distinction:
Many more people have chronic fatigue (the symptom: being exhausted all the time) than have chronic fatigue syndrome (the illness: myalgic encephalomyelitis).
This is because fatigue can be a symptom of many, many other conditions, and can be heavily influenced by lifestyle factors too.
A lot of the advice for dealing with chronic fatigue is often the same in both cases, but some will be different, because for example:
- If your fatigue is from some other condition, that condition probably impacts what lifestyle factors you are (and are not) able to change, too
- If your fatigue is from lifestyle factors, that hopefully means you can change those and enjoy less fatigue…
- But if it’s not from lifestyle factors, as in ME/CFS, then advice to “exercise more” etc is not going to help so much.
There are ways to know the difference though:
Check out: Do You Have Chronic Fatigue Syndrome?
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Six Ways To Eat For Healthier Skin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sadia Badiei, the nutritionist-chef of “Pick Up Limes” fame, has advice:
More than skin-deep:
We’ll not keep them a mystery; here are the six points of focus:
1. Collagen and skin elasticity
Collagen is the structural protein that provides firmness and elasticity to the skin, but its production decreases with age, resulting in about a 1% annual loss starting at age 20. To support collagen, a diet rich in protein is essential, including foods like beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, nuts, and seeds. They can’t do their work alone though; vitamins C and E play a critical role in collagen production and repair, protecting against damage from sun exposure, pollution, and free radicals. Vitamin E can be found in almonds, sunflower seeds, leafy greens, peanuts, and avocados, while vitamin C is abundant in citrus fruits, bell peppers, and broccoli.
2. Skin healing and zinc
Zinc is critical for wound healing and reducing inflammation, making it particularly helpful in managing skin conditions such as acne, eczema, psoriasis, and rosacea. Great dietary sources of zinc include nutritional yeast, pumpkin, sesame, and hemp seeds, as well as legumes and whole grains. However, zinc absorption can be hindered by phytate levels in some foods. Soaking, sprouting, or fermenting foods where possible can correct for that and improve zinc absorption.
3. Dry skin and hydration
Dry skin can result from many things, including dry air, hot water, abrasive soaps, and certain medications. While moisturizers provide external hydration, dietary omega-3 fats are essential for improving the skin’s barrier function, helping it retain moisture. Plant-based sources of omega-3s include walnuts, hemp seeds, chia seeds, flax seeds, and algae-based supplements. Staying adequately hydrated also supports overall health of course (everything runs on water in one way or another, after all), which indirectly benefits skin hydration, although drinking additional water only helps if dehydration is present.
4. Sebum regulation
Sebum, an oily substance that lubricates the skin, can cause issues like acne and blackheads when overproduced. Hormonal fluctuations and diet both influence sebum levels (in either direction). High glycemic index foods, such as sweetened beverages, refined grains, and sugary snacks, can lead to spikes in insulin, which in turn stimulates excess sebum production. In contrast, low glycemic index foods like vegetables, whole grains, tofu, nuts, and seeds regulate blood sugar and help manage sebum production, promoting clearer skin without an excess or a shortage of sebum.
5. Gut health and skin
The gut-skin connection means that imbalances in gut bacteria can contribute to skin issues like acne, eczema, and psoriasis. Supporting gut health involves increasing the diversity of beneficial bacteria through probiotic-rich foods. Fermented options like plant-based yogurts, kimchi, miso, sauerkraut, and kombucha not only improve gut microbiome health but also positively impact skin health by reducing inflammation and improving overall skin conditions.
6. Inflammation and skin health
Chronic inflammation is associated with so many health issues, and when it comes to skin, that includes acne, rosacea, and even wrinkles. Anti-inflammatory foods, especially those rich in antioxidants, can mitigate these effects and improve skin elasticity, smoothness, and color. Diets centered around fruits, vegetables, and other plant-based foods provide the necessary nutrients to combat inflammation, showcasing the significant role of nutrition in promoting radiant, healthy skin.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Undo The Sun’s Damage To Your Skin
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: