How To Manage Your Mood With Food (8 Ways)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It is hard to be mentally healthy for long without good diet. Food can not only affect our mood directly, but also indirectly because of how our brain works (or doesn’t, if we don’t have the right nutrients, or it is being sabotaged in some other dietary fashion).
Selecting the food for setting the mood
Mind, the mental health charity, have these advices to share (with some bonus notes of our own):
- Eat regularly: blood sugar peaks and troughs can heighten feelings of tiredness, irritability, or depression. Instead, enjoy foods that are high in energy but low in glycemic index, such as nuts, seeds, and oats—that way you’ll have plenty of energy, that lasts longer.
- Choose the right fats: omega-3 fatty acids are essential for the brain. So are omega-6 fatty acids, but it is rare to have a deficiency in omega-6, and indeed, many people have the ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 far too imbalanced in omega-6’s favor. So, focussing on getting more omega-3 fatty acids is important. Nuts and seeds are again great, as are avocados, eggs, and oily fish.
- Get a healthy amount of protein: and importantly, with a good mix of amino acids—so a variety of sources of protein is best. In particular, if you are vegan, paying attention to ensure you get a full spread of amino acids is critical, as not many plants have all the ones we need (soy does, though). The reason this is important for mood is because many of those amino acids double up as the building blocks of neurotransmitters, so they’re not entirely interchangeable.
- Stay hydrated: our bodies are famously made of mostly water, and our brain will not work well if it’s dehydrated. The human body can squeeze water out of almost anything that has water in it, but water from food (such as fruit, or soups) is best. If enjoying actual drinks, then herbal teas are excellent for hydration.
- Eat a rainbow of fruits and vegetables: these have many nutrients that are important for brain health, and the point of the colors is that most of those pigments are themselves nutrients. Additionally, the fiber content of fruits and vegetables is of topmost important for your heart, and as you’ll remember (we say it often, because it’s true): what’s good for your heart is good for your brain.
- Limit caffeine intake: for many people, excess caffeine can lead to feelings of anxiety, disrupt your sleep, and for everyone who has developed an addiction to it, it will cause withdrawal symptoms if stopped abruptly. Cutting back on caffeine, or even eliminating it, may improve your mood and sleep quality. Note, however, that if you have ADHD, then your brain’s physiological relationship with caffeine is a little different, and stimulants will be more beneficial (and less deleterious) for you than for most people. If unsure, speak with your doctor about this one.
- Support your gut health: because of the gut-brain axis (via the vagal nerve), and also because nearly all of our endogenous serotonin is made in the gut (along with other neurotransmitters/hormones), getting plenty of fiber is important, and probiotics can help too.
- Consider food intolerances: if you know you have one, then keep that in mind and tailor your diet accordingly. If you suspect you have one, seek a nutritionist’s help to find out for sure. These can affect many aspects of health, including mood, so should not be dismissed as a triviality.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The 6 Pillars Of Nutritional Psychiatry
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can you get sunburnt or UV skin damage through car or home windows?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When you’re in a car, train or bus, do you choose a seat to avoid being in the sun or do you like the sunny side?
You can definitely feel the sun’s heat through a window. But can you get sunburn or skin damage when in your car or inside with the windows closed?
Let’s look at how much UV (ultraviolet) radiation passes through different types of glass, how tinting can help block UV, and whether we need sunscreen when driving or indoors.
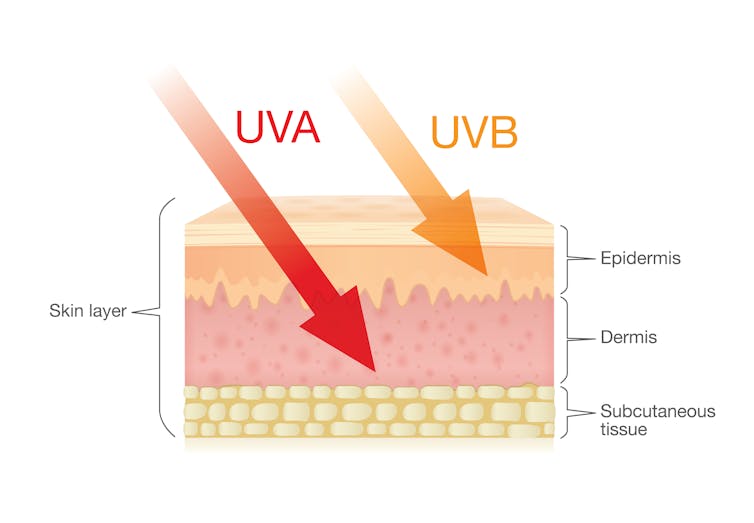
Zac Harris/Unsplash What’s the difference between UVA and UVB?
Of the total UV radiation that reaches Earth, about 95% is UVA and 5% is UVB.
UVB only reaches the upper layers of our skin but is the major cause of sunburn, cataracts and skin cancer.
UVA penetrates deeper into our skin and causes cell damage that leads to skin cancer.
UVA penetrates deeper than UVB. Shutterstock/solar22 Glass blocks UVA and UVB radiation differently
All glass used in house, office and car windows completely blocks UVB from passing through.
But only laminated glass can completely block UVA. UVA can pass through other glass used in car, house and office windows and cause skin damage, increasing the risk of cancer.
Car windscreens block UVA, but the side and rear windows don’t
A car’s front windscreen lets in lots of sunshine and light. Luckily it blocks 98% of UVA radiation because it is made of two layers of laminated glass.
But the side and rear car windows are made of tempered glass, which doesn’t completely block UVA. A study of 29 cars found a range from 4% to almost 56% of UVA passed through the side and rear windows.
The UVA protection was not related to the car’s age or cost, but to the type of glass, its colour and whether it has been tinted or coated in a protective film. Grey or bronze coloured glass, and window tinting, all increase UVA protection. Window tinting blocks around 95% of UVA radiation.
In a separate study from Saudi Arabia, researchers fitted drivers with a wearable radiation monitor. They found drivers were exposed to UV index ratings up to 3.5. (In Australia, sun protection is generally recommended when the UV index is 3 or above – at this level it takes pale skin about 20 minutes to burn.)
So if you have your windows tinted, you should not have to wear sunscreen in the car. But without tinted windows, you can accumulate skin damage.
UV exposure while driving increases skin cancer risk
Many people spend a lot of time in the car – for work, commuting, holiday travel and general transport. Repeated UVA radiation exposure through car side windows might go unnoticed, but it can affect our skin.
Indeed, skin cancer is more common on the driver’s side of the body. A study in the United States (where drivers sit on the left side) found more skin cancers on the left than the right side for the face, scalp, arm and leg, including 20 times more for the arm.
Another US study found this effect was higher in men. For melanoma in situ, an early form of melanoma, 74% of these cancers were on the on the left versus 26% on the right.
Earlier Australian studies reported more skin damage and more skin cancer on the right side.
Cataracts and other eye damage are also more common on the driver’s side of the body.
What about UV exposure through home or office windows?
We see UV damage from sunlight through our home windows in faded materials, furniture or plastics.
Most glass used in residential windows lets a lot of UVA pass through, between 45 and 75%.
Residential windows can let varied amounts of UVA through. Sherman Trotz/Pexels Single-pane glass lets through the most UVA, while thicker, tinted or coated glass blocks more UVA.
The best options are laminated glass, or double-glazed, tinted windows that allow less than 1% of UVA through.
Skylights are made from laminated glass, which completely stops UVA from passing through.
Most office and commercial window glass has better UVA protection than residential windows, allowing less than 25% of UVA transmission. These windows are usually double-glazed and tinted, with reflective properties or UV-absorbent chemicals.
Some smart windows that reduce heat using chemical treatments to darken the glass can also block UVA.
So when should you wear sunscreen and sunglasses?
The biggest risk with skin damage while driving is having the windows down or your arm out the window in direct sun. Even untinted windows will reduce UVA exposure to some extent, so it’s better to have the car window up.
For home windows, window films or tint can increase UVA protection of single pane glass. UVA blocking by glass is similar to protection by sunscreen.
When you need to use sunscreen depends on your skin type, latitude and time of the year. In a car without tinted windows, you could burn after one hour in the middle of the day in summer, and two hours in the middle of a winter’s day.
But in the middle of the day next to a home window that allows more UVA to pass through, it could take only 30 minutes to burn in summer and one hour in winter.
When the UV index is above three, it is recommended you wear protective sunglasses while driving or next to a sunny window to avoid eye damage.
Theresa Larkin, Associate Professor of Medical Sciences, University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Your Simplest Life – by Lisa Turner
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We probably know how to declutter, and perhaps even do a “unnecessary financial expenditures” audit. So, what does this offer beyond that?
A large portion of this book focuses on keeping our general life in a state of “flow”, and strategies include:
- How to make sure you’re doing the right part of the 80:20 split on a daily basis
- Knowing when to switch tasks, and when not to
- Knowing how to plan time for tasks
- No more reckless optimism, but also without falling foul of Parkinson’s Law (i.e. work expands to fill the time allotted to it)
- Decluttering your head, too!
When it comes to managing life responsibilities in general, Turner is very attuned to generational differences… Including the different challenges faced by each generation, what’s more often expected of us, what we’re used to, and how we probably initially learned to do it (or not).
To this end, a lot of strategies are tailored with variations for each age group. Not often does an author take the time to address each part of their readership like that, and it’s really helpful that she does!
All in all, a great book for simplifying your daily life.
Share This Post
-
In Defense of Food – by Michael Pollan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Eat more like the French. Or the Italians. Or the Japanese. Or…
Somehow, whatever we eat is not good enough, and we should always be doing it differently!
Michael Pollan takes a more down-to-Earth approach.
He kicks off by questioning the wisdom of thinking of our food only in terms of nutritional profiles, and overthinking healthy-eating. He concludes, as many do, that a “common-sense, moderate” approach is needed.
And yet, most people who believe they are taking a “common-sense, moderate” approach to health are in fact over-fed yet under-nourished.
So, how to fix this?
He offers us a reframe: to think of food as a relationship, and health being a product of it:
- If we are constantly stressing about a relationship, it’s probably not good.
- On the other hand, if we are completely thoughtless about it, it’s probably not good either.
- But if we can outline some good, basic principles and celebrate it with a whole heart? It’s probably at the very least decent.
The style is very casual and readable throughout. His conclusions, by the way, can be summed up as “Eat real food, make it mostly plants, and make it not too much”.
However, to summarize it thusly undercuts a lot of the actual value of the book, which is the principles for discerning what is “real food” and what is “not too much”.
Bottom line: if you’re tired of complicated eating plans, this book can help produce something very simple, attainable, and really quite good.
Click here to check out In Defense of Food, for some good, hearty eating.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Gluten: What’s The Truth?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Gluten: What’s The Truth?
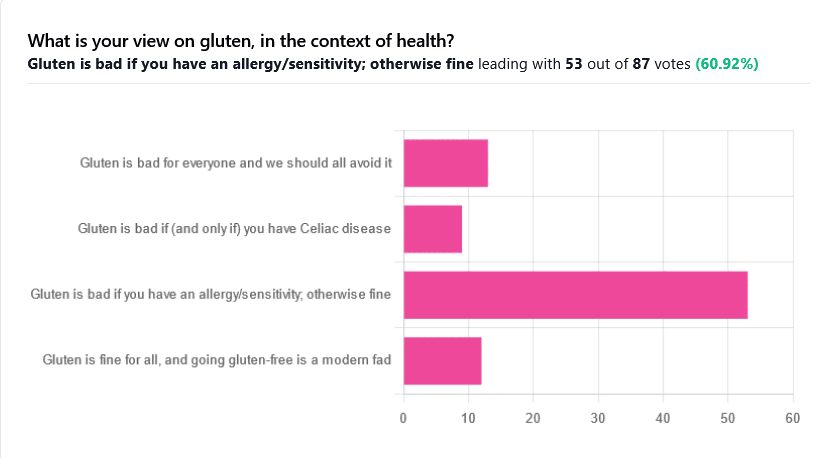
We asked you for your health-related view of gluten, and got the above spread of results. To put it simply:
Around 60% of voters voted for “Gluten is bad if you have an allergy/sensitivity; otherwise fine”
The rest of the votes were split fairly evenly between the other three options:
- Gluten is bad for everyone and we should avoid it
- Gluten is bad if (and only if) you have Celiac disease
- Gluten is fine for all, and going gluten-free is a modern fad
First, let’s define some terms so that we’re all on the same page:
What is gluten?
Gluten is a category of protein found in wheat, barley, rye, and triticale. As such, it’s not one single compound, but a little umbrella of similar compounds. However, for the sake of not making this article many times longer, we’re going to refer to “gluten” without further specification.
What is Celiac disease?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disease. Like many autoimmune diseases, we don’t know for sure how/why it occurs, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors have been strongly implicated, with the latter putatively including overexposure to gluten.
It affects about 1% of the world’s population, and people with Celiac disease will tend to respond adversely to gluten, notably by inflammation of the small intestine and destruction of enterocytes (the cells that line the wall of the small intestine). This in turn causes all sorts of other problems, beyond the scope of today’s main feature, but suffice it to say, it’s not pleasant.
What is an allergy/intolerance/sensitivity?
This may seem basic, but a lot of people conflate allergy/intolerance/sensitivity, so:
- An allergy is when the body mistakes a harmless substance for something harmful, and responds inappropriately. This can be mild (e.g. allergic rhinitis, hayfever) or severe (e.g. peanut allergy), and as such, responses can vary from “sniffly nose” to “anaphylactic shock and death”.
- In the case of a wheat allergy (for example), this is usually somewhere between the two, and can for example cause breathing problems after ingesting wheat or inhaling wheat flour.
- An intolerance is when the body fails to correctly process something it should be able to process, and just ejects it half-processed instead.
- A common and easily demonstrable example is lactose intolerance. There isn’t a well-defined analog for gluten, but gluten intolerance is nonetheless a well-reported thing.
- A sensitivity is when none of the above apply, but the body nevertheless experiences unpleasant symptoms after exposure to a substance that should normally be safe.
- In the case of gluten, this is referred to as non-Celiac gluten sensitivity
A word on scientific objectivity: at 10almonds we try to report science as objectively as possible. Sometimes people have strong feelings on a topic, especially if it is polarizing.
Sometimes people with a certain condition feel constantly disbelieved and mocked; sometimes people without a certain condition think others are imagining problems for themselves where there are none.
We can’t diagnose anyone or validate either side of that, but what we can do is report the facts as objectively as science can lay them out.
Gluten is fine for all, and going gluten-free is a modern fad: True or False?
Definitely False, Celiac disease is a real autoimmune disease that cannot be faked, and allergies are also a real thing that people can have, and again can be validated in studies. Even intolerances have scientifically measurable symptoms and can be tested against nocebo.
See for example:
- Epidemiology and clinical presentations of Celiac disease
- Severe forms of food allergy that can precipitate allergic emergencies
- Properties of gluten intolerance: gluten structure, evolution, and pathogenicity
However! It may not be a modern fad, so much as a modern genuine increase in incidence.
Widespread varieties of wheat today contain a lot more gluten than wheat of ages past, and many other molecular changes mean there are other compounds in modern grains that never even existed before.
However, the health-related impact of these (novel proteins and carbohydrates) is currently still speculative, and we are not in the business of speculating, so we’ll leave that as a “this hasn’t been studied enough to comment yet but we recognize it could potentially be a thing” factor.
Gluten is bad if (and only if) you have Celiac disease: True or False?
Definitely False; allergies for example are well-evidenced as real; same facts as we discussed/linked just above.
Gluten is bad for everyone and we should avoid it: True or False?
False, tentatively and contingently.
First, as established, there are people with clinically-evidenced Celiac disease, wheat allergy, or similar. Obviously, they should avoid triggering those diseases.
What about the rest of us, and what about those who have non-Celiac gluten sensitivity?
Clinical testing has found that of those reporting non-Celiac gluten sensitivity, nocebo-controlled studies validate that diagnosis in only a minority of cases.
In the following study, for example, only 16% of those reporting symptoms showed them in the trials, and 40% of those also showed a nocebo response (i.e., like placebo, but a bad rather than good effect):
This one, on the other hand, found that positive validations of diagnoses were found to be between 7% and 77%, depending on the trial, with an average of 30%:
Re-challenge Studies in Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
In other words: non-Celiac gluten sensitivity is a thing, and/but may be over-reported, and/but may be in some part exacerbated by psychosomatic effect.
Note: psychosomatic effect does not mean “imagining it” or “all in your head”. Indeed, the “soma” part of the word “psychosomatic” has to do with its measurable effect on the rest of the body.
For example, while pain can’t be easily objectively measured, other things, like inflammation, definitely can.
As for everyone else? If you’re enjoying your wheat (or similar) products, it’s well-established that they should be wholegrain for the best health impact (fiber, a positive for your health, rather than white flour’s super-fast metabolites padding the liver and causing metabolic problems).
Wheat itself may have other problems, for example FODMAPs, amylase trypsin inhibitors, and wheat germ agglutinins, but that’s “a wheat thing” rather than “a gluten thing”.
That’s beyond the scope of today’s main feature, but you might want to check out today’s featured book!
For a final scientific opinion on this last one, though, here’s what a respected academic journal of gastroenterology has to say:
From coeliac disease to noncoeliac gluten sensitivity; should everyone be gluten-free?
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Savoy Cabbage vs Pak Choi – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing savoy cabbage to pak choi, we picked the savoy.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, the savoy has a little more protein, just under 3x the carbs, and just over 3x the fiber. A modest yet respectable win for savoy.
In terms of vitamins, savoy has more of vitamins B1, B5, B9, E, K, and choline, while pak choi has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, and C. Thus, a 6:4 win for savoy.
When it comes to minerals, savoy has more copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while pak choi has more calcium, iron, and potassium. So this time, a 7:3 win for savoy.
On the other hand, pak choi scores higher on the polyphenols side, especially in the categories of kaempferol and quercetin.
Still, adding up the sections, we conclude this one’s an overall win for savoy cabbage. Of course, enjoy either or both, though!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Fight Inflammation & Protect Your Brain, With Quercetin
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
More research shows COVID-19 vaccines are safe for young adults
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- Myocarditis, or inflammation of the heart muscle, is most commonly caused by a viral infection like COVID-19, not by vaccination.
- In line with previous research, a recent CDC study found no association between COVID-19 vaccination and sudden cardiac death in previously healthy young people.
- A COVID-19 infection is much more likely to cause inflammation of the heart muscle than a COVID-19 vaccine, and those cases are typically more severe.
Since the approval of the first COVID-19 vaccines, anti-vaccine advocates have raised concerns about heart muscle inflammation, also called myocarditis, after vaccination to suggest that vaccines are unsafe. They’ve also used concerns about myocarditis to spread false claims that vaccines cause sudden deaths, which is not true.
Research has consistently shown that cases of myocarditis after vaccination are extremely rare and usually mild, and a new study from the CDC found no association between sudden cardiac death and COVID-19 vaccination in young adults.
Read on to learn more about myocarditis and what the latest research says about COVID-19 vaccine safety.
What is myocarditis?
Myocarditis is inflammation of the myocardium, or the middle muscular layer of the heart wall. This inflammation weakens the heart’s ability to pump blood. Symptoms may include fatigue, shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid or irregular heartbeat, and flu-like symptoms.
Myocarditis may resolve on its own. In rare cases, it may lead to stroke, heart failure, heart attack, or death.
What causes myocarditis?
Myocarditis is typically caused by a viral infection like COVID-19. Bacteria, parasites, fungi, chemicals, and certain medications can also cause myocarditis.
In very rare cases, some people develop myocarditis after receiving a COVID-19 vaccine, but these cases are usually mild and resolve on their own. In contrast, a COVID-19 infection is much more likely to cause myocarditis, and those cases are typically more severe.
Staying up to date on vaccines reduces your risk of developing myocarditis from a COVID-19 infection.
Are COVID-19 vaccines safe for young people?
Yes. COVID-19 vaccines have been rigorously tested and monitored over the past three years and have been determined to be safe for everyone 6 months and older. A recent CDC study found no association between COVID-19 vaccination and sudden cardiac death in previously healthy young adults.
The benefits of vaccination outweigh any potential risks. Staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines reduces your risk of severe illness, hospitalization, death, long COVID, and COVID-19-related complications, such as myocarditis.
The CDC recommends people 65 and older and immunocompromised people receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring—if at least four months have passed since they received a COVID-19 vaccine.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: