How Emotions Are Made – by Dr. Lisa Feldman Barrett
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Dr. Barrett’s (also good) book Seven And A Half Lessons About The Brain, and this one is very different, and of more practical use:
The main thrust of the book is: the bioessentialist model of emotions is flawed; there is also no Platonic perfect form of any given emotion, and in fact emotions are constructed by the brain as a learned adaptive response.
She argues this from the dual vectors of on the one hand hard sciences of affective neuroscience and clinical psychology, and on the other hand sociology and anthropology.
In the category of criticism: Dr. Barrett, a very well-known and well-respected cognitive neuroscientist, is not an expert on sociology and anthropology, and some of her claims there are verifiably false.
However, most of the book is given over the psychophysiology, which is entirely her thing, and she explains it clearly and simply while backing everything up with mountains of data.
The usefulness of this book is chiefly: if we understand that emotions are not innate and are instead constructed adaptive (and sometimes maladaptive) neurological responses to stimuli and associations, we can set about rewiring things a little in accord with what’s actually more beneficial to us. The book also outlines how.
Bottom line: if you’d like to be able to not merely manage emotions as they are, but also prune and/or grow them from the stem up, then this book provides a robustly scientific approach for doing that.
Click here to check out How Emotions Are Made, and get more discerning about yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The push for Medicare to cover weight-loss drugs: An explainer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The largest U.S. insurer, Medicare, does not cover weight-loss drugs, making it tougher for older people to get access to promising new medications.
If you cover stories about drug costs in the U.S., it’s important to understand why Medicare’s Part D pharmacy program, which covers people aged 65 and older and people with certain disabilities, doesn’t cover weight-loss drugs today. It’s also important to consider what would happen if Medicare did start covering weight loss drugs. This explainer will give you a brief overview of the issues and then summarize some recent publications the benefits and costs of drugs like semaglutide and tirzepatide.
First, what are these new and newsy weight loss drugs?
Semaglutide is a medication used for both the treatment of type 2 diabetes and for long-term weight management in adults with obesity. It debuted in the United States in 2017 as an injectable diabetes drug called Ozempic, manufactured by Novo Nordisk. It’s part of a class of drugs that mimics the action of glucagon, a substance that the human body makes to aid digestion.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) drugs like semaglutide help prompt the body to release insulin. But they also cause a minor delay in the pace of digestion, helping people feel sated after eating.
That second effect turned Ozempic into a widely used weight-loss drug, even before the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gave its okay for this use. Doctors in the United States can prescribe medicines for uses beyond those approved by the FDA. This is known as off-label use.
In writing about her own experience in using the medicine to help her shed 40 pounds, Washington Post columnist Ruth Marcus in June noted that Novo Nordisk mentioned the potential for weight loss in its “ubiquitous cable ads (‘Oh-oh-oh, Ozempic!’)”
The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists has reported shortages of semaglutide due to demand, leaving some people with diabetes struggling to find supply of the medicine.
Novo Nordisk won Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval in 2021 to market semaglutide as an injectable weight loss drug under the name Wegovy, but with a different dosing regimen than Ozempic. Rival Eli Lilly first won FDA approval of its similar GLP-1 diabetes drug, tirzepatide, in the United States in 2022 and sells it under the brand name Mounjaro.
In November of 2023, Eli Lilly won FDA approval to sell tirzepatide as a weight-loss drug, soon-to-be marketed under the brand name Zepbound. The company said it will set a monthly list price for a month’s supply of the drug at $1,059.87, which the company described as 20% discount to the cost of rival Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy. Wegovy has a list price of $1,349.02, according to the Novo Nordisk website.
Even when their insurance plans officially cover costs for weight loss drugs, consumers may face barriers in seeking that coverage for these drugs. Commercial health plans have in place prior authorization requirements to try to limit coverage of new weight-loss shots to those who qualify for these treatments. The Wegovy shot, for example, is intended for people whose weight reaches a certain benchmark for obesity or who are overweight and have a condition related to excess weight, such as diabetes, high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
State Medicaid programs, meanwhile, have taken approaches that vary by state. For example, the most populous U.S. state, California, provides some coverage to new weight-loss injections through its Medicaid program, but many others, including Texas, the No. 2 state in terms of population, do not, according to an online tool that Novo Nordisk created to help people check on coverage.
Medicare does cover semaglutide for treatment of diabetes, and the insurer reported $3 billion in 2021 spending on the drug under Medicare Part D. Congress last year gave Medicare new tools that might help it try to lower the cost of semaglutide.
Medicare is in the midst of implementing new authority it gained through the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022 to negotiate with companies about the cost of certain medicines.
This legislation gave Medicare, for the first time, tools to directly negotiate with pharmaceutical companies on the cost of some medicines. Congress tailored this program to spare drug makers from negotiations for the first few years they put new medicines on the market, allowing them to recoup investment in these products.
Why doesn’t Medicare cover weight-loss drugs?
Congress created the Medicare Part D pharmacy program in 2003 to address a gap in coverage that had existed since the creation of Medicare in 1965. The program long covered the costs of drugs administered by doctors and those given in hospitals, but not the kinds of medicines people took on their own, like Wegovy shots.
In 2003, there seemed to be good reasons to leave weight-loss drugs out of the benefit, write Inmaculada Hernandez of the University of California, San Diego, and coauthors in their September 2023 editorial in the Journal of General Internal Medicine, “Medicare Part D Coverage of Anti-obesity Medications: a Call for Forward-Looking Policy Reform.”
When members of Congress worked on the Part D benefit, the drugs available on the market were known to have limited effectiveness and unpleasant side effects. And those members of Congress were aware of how a drug combination called fen-phen, once touted as a weight-loss miracle medicine, turned out in rare cases to cause fatal heart valve damage. In 1997, American Home Products, which later became Wyeth, took its fen-phen product off the market.
But today GLP-1 drugs like semaglutide appear to offer significant benefits, with far less risk and milder side effects, write Hernandez and coauthors.
“Other than budget impact, it is hard to find a reason to justify the historical statutory exclusion of weight loss drugs from coverage other than the stigma of the condition itself,” they write.
What’s happening today that could lead Medicare to start covering weight loss drugs?
Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly both have hired lobbyists to try to persuade lawmakers to reverse this stance, according to Senate records. Pro tip: You can use the Senate’s lobbying disclosure database to track this and other issues. Type in the name of the company of interest and then read through the forms.
Some members of Congress already have been trying for years to strike the Medicare Part D restriction on weight-loss drugs. Over the past decade, senators Tom Carper (D-DE) and Bill Cassidy, MD, (R-LA) have repeatedly introduced bills that would do that. They introduced the current version, the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act of 2023, in July. It has the support of 10 other Republican senators and seven Democratic ones, as of Dec. 19. The companion House measure has the support of 41 Democrats and 23 Republicans in that chamber, which has 435 seats.
The influential nonprofit Institute for Clinical and Economic Review conducts in-depth analyses of drugs and medical treatments in the United States. ICER last year recommended passage of a law allowing Medicare Part D to cover weight-loss medications. ICER also called for broader coverage of weight-loss medications in state Medicaid programs. Insurers, including Medicare, consider ICER’s analyses in deciding whether to cover treatments.
While offering these calls for broader coverage as part of a broad assessment of obesity management, ICER also urged companies to reduce the costs of weight-loss medicines.
Most people with obesity can’t achieve sustained weight loss through diet and exercise alone, said David Rind, ICER’s chief medical officer in an August 2022 statement. The development of newer obesity treatments represents the achievement of a long-standing goal of medical research, but prices of these new products must be reasonable to allow broad access to them, he noted.
After an extensive process of reviewing studies, engaging in public debate and processing feedback, ICER concluded that semaglutide for weight loss should have an annual cost of $7,500 to $9,800, based on its potential benefits.
What does academic research say about the benefits and the potential costs of new obesity drugs?
Here are a couple of studies to consider when covering the ongoing story of weight-loss drug costs:
Medicare Part D Coverage of Antiobesity Medications — Challenges and Uncertainty Ahead
Khrysta Baig, Stacie B. Dusetzina, David D. Kim and Ashley A. Leech. New England Journal of Medicine, March 2023In this Perspective piece, researchers at Vanderbilt University create a series of estimates about how much Medicare may have to spend annually on weight-loss drugs if the program eventually covers these drugs.
These include a high estimate — $268 billion — based on an extreme calculation, one reflecting the potential cost if virtually all people on Medicare who have obesity used semaglutide. In an announcement of the study on the Vanderbilt website, lead author Khrysta Baig described this as a “purely hypothetical scenario,” but one that “ underscores that at current prices, these medications cannot be the only way – or even the main way – we address obesity as a society.”
In a more conservative estimate, Bhaig and coauthors consider a case where only about 10% of those eligible for obesity treatment opted for semaglutide, which would result in $27 billion in new costs.
(To put these numbers in context, consider that the federal government now spends about $145 billion a year on the entire Part D program.)
It’s likely that all people enrolled in Part D would have to pay higher monthly premiums if Medicare were to cover weight-loss injections, Baig and coauthors write.
Baig and coauthors note that the recent ICER review of weight-loss drugs focused on patients younger than the Medicare population. The balance of benefits and risks associated with weight-loss drugs may be less favorable for older people than the younger ones, making it necessary to study further how these drugs work for people aged 65 and older, they write. For example, research has shown older adults with a high blood sugar level called prediabetes are less likely to develop diabetes than younger adults with this condition.
SELECTing Treatments for Cardiovascular Disease — Obesity in the Spotlight
Amit Khera and Tiffany M. Powell-Wiley. New England Journal of Medicine, Dec. 14, 2023
Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients Without Diabetes
A Michael Lincoff, et. al. New England Journal of Medicine, Dec. 14, 2023.An editorial accompanies the publication of a semaglutide study that drew a lot of coverage in the media. The Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Obesity without Diabetes (SELECT) study was a randomized controlled trial, conducted by Novo Nordisk, which looked at rates of cardiovascular events in people who already had known heart risk and were overweight, but not diabetic. Patients were randomly assigned to receive a once-weekly dose of semaglutide (Wegovy) or a placebo.
In the study, the authors report that of the 8,803 patients who took Wegovy in the trial, 569 (6.5%)
The study also reports a mean 9.4% reduction in body weight among patients taking Wegovy, while those on placebo had a mean loss of 0.88%.
The findings suggest Wegovy may be a welcome new treatment option for many people who have coronary disease and are overweight, but are not diabetic, write Khera and Powell-Wiley in their editorial.
But the duo, both of whom focus on disease prevention in their research, also call for more focus on the prevention and root causes of obesity and on the use of proven treatment approaches other than medication.
“Socioeconomic, environmental, and psychosocial factors contribute to incident obesity, and therefore equity-focused obesity prevention and treatment efforts must target multiple levels,” they write. “For instance, public policy targeting built environment features that limit healthy behaviors can be coupled with clinical care interventions that provide for social needs and access to treatments like semaglutide.”
Additional information:
The nonprofit KFF, formerly known as the Kaiser Family Foundation, has done recent reports looking at the potential for expanded coverage of semaglutide:
Medicaid Utilization and Spending on New Drugs Used for Weight Loss, Sept. 8, 2023
What Could New Anti-Obesity Drugs Mean for Medicare? May 18, 2023
And KFF held an Aug. 4 webinar, New Weight Loss Drugs Raise Issues of Coverage, Cost, Access and Equity, for which the recording is posted here.
This article first appeared on The Journalist’s Resource and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Brain Health Action Plan – by Dr. Teryn Clarke
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author is a physician and neurologist, and she brings a lot of science with her when she sets out to Alzheimer’s-proof our brains:
- She talks about brain nourishment, and what things in contrast sabotage our brains, and how.
- She talks intermittent fasting, and optimal scheduling when it comes to food, sleep, exercise, and more.
- She talks about how the rest of our health affects our brain health, and vice versa.
The “action plan” promised by the title includes all of those elements, plus such matters as ongoing education, cognitive stimulation, stress management, dealing with depression, and other mostly-brain-based factors.
As such, it’s not just a “for your information” book, and Dr. Clarke does outline suggested goals, tasks, and habits, advises the use of a streak tracker, provides suggested recipes, and in all ways does what she can to make it easy for the reader to implement the information within.
Bottom line: if you’d like to dodge dementia, this book is quite a comprehensive guide.
Click here to check out Brain Health Action Plan, and enact yours!
Share This Post
-
I can’t afford olive oil. What else can I use?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you buy your olive oil in bulk, you’ve likely been in for a shock in recent weeks. Major supermarkets have been selling olive oil for up to A$65 for a four-litre tin, and up to $26 for a 750 millilitre bottle.
We’ve been hearing about the health benefits of olive oil for years. And many of us are adding it to salads, or baking and frying with it.
But during a cost-of-living crisis, these high prices can put olive oil out of reach.
Let’s take a look at why olive oil is in demand, why it’s so expensive right now, and what to do until prices come down.
Joyisjoyful/Shutterstock Remind me, why is olive oil so good for you?
Including olive oil in your diet can reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and improve heart health through more favourable blood pressure, inflammation and cholesterol levels.
This is largely because olive oil is high in monounsaturated fatty acids and polyphenols (antioxidants).
Some researchers have suggested you can get these benefits from consuming up to 20 grams a day. That’s equivalent to about five teaspoons of olive oil.
Why is olive oil so expensive right now?
A European heatwave and drought have limited Spanish and Italian producers’ ability to supply olive oil to international markets, including Australia.
This has been coupled with an unusually cold and short growing season for Australian olive oil suppliers.
The lower-than-usual production and supply of olive oil, together with heightened demand from shoppers, means prices have gone up.
We’ve seen unfavourable growing conditions in Europe and Australia. KaMay/Shutterstock How can I make my olive oil go further?
Many households buy olive oil in large quantities because it is cheaper per litre. So, if you have some still in stock, you can make it go further by:
- storing it correctly – make sure the lid is on tightly and it’s kept in a cool, dark place, such as a pantry or cabinet. If stored this way, olive oil can typically last 12–18 months
- using a spray – sprays distribute oil more evenly than pourers, using less olive oil overall. You could buy a spray bottle to fill from a large tin, as needed
- straining or freezing it – if you have leftover olive oil after frying, strain it and reuse it for other fried dishes. You could also freeze this used oil in an airtight container, then thaw and fry with it later, without affecting the oil’s taste and other characteristics. But for dressings, only use fresh oil.
I’ve run out of olive oil. What else can I use?
Here are some healthy and cheaper alternatives to olive oil:
- canola oil is a good alternative for frying. It’s relatively low in saturated fat so is generally considered healthy. Like olive oil, it is high in healthy monounsaturated fats. Cost? Up to $6 for a 750mL bottle (home brand is about half the price)
- sunflower oil is a great alternative to use on salads or for frying. It has a mild flavour that does not overwhelm other ingredients. Some studies suggest using sunflower oil may help reduce your risk of heart disease by lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol and raising HDL (good) cholesterol. Cost? Up to $6.50 for a 750mL bottle (again, home brand is about half the price)
- sesame oil has a nutty flavour. It’s good for Asian dressings, and frying. Light sesame oil is typically used as a neutral cooking oil, while the toasted type is used to flavour sauces. Sesame oil is high in antioxidants and has some anti-inflammatory properties. Sesame oil is generally sold in smaller bottles than canola or sunflower oil. Cost? Up to $5 for a 150mL bottle.
There are plenty of alternative oils you can use in salads or for frying. narai chal/Shutterstock How can I use less oil, generally?
Using less oil in your cooking could keep your meals healthy. Here are some alternatives and cooking techniques:
- use alternatives for baking – unless you are making an olive oil cake, if your recipe calls for a large quantity of oil, try using an alternative such as apple sauce, Greek yoghurt or mashed banana
- use non-stick cookware – using high-quality, non-stick pots and pans reduces the need for oil when cooking, or means you don’t need oil at all
- steam instead – steam vegetables, fish and poultry to retain nutrients and moisture without adding oil
- bake or roast – potatoes, vegetables or chicken can be baked or roasted rather than fried. You can still achieve crispy textures without needing excessive oil
- grill – the natural fats in meat and vegetables can help keep ingredients moist, without using oil
- use stock – instead of sautéing vegetables in oil, try using vegetable broth or stock to add flavour
- try vinegar or citrus – use vinegar or citrus juice (such as lemon or lime) to add flavour to salads, marinades and sauces without relying on oil
- use natural moisture – use the natural moisture in ingredients such as tomatoes, onions and mushrooms to cook dishes without adding extra oil. They release moisture as they cook, helping to prevent sticking.
Lauren Ball, Professor of Community Health and Wellbeing, The University of Queensland and Emily Burch, Accredited Practising Dietitian and Lecturer, Southern Cross University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Studies of Parkinson’s disease have long overlooked Pacific populations – our work shows why that must change
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A form of Parkinson’s disease caused by mutations in a gene known as PINK1 has long been labelled rare. But our research shows it’s anything but – at least for some populations.
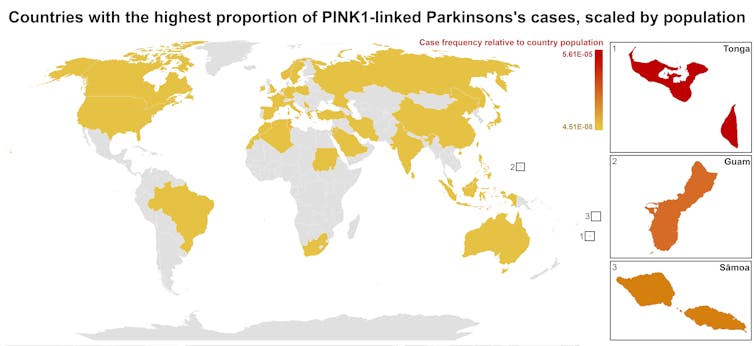
Our meta-analysis revealed that people in specific Polynesian communities have a much higher rate of PINK1-linked Parkinson’s than expected. This finding reshapes not only our understanding of who is most at risk, but also how soon symptoms may appear and what that might mean for treatment and testing.
Parkinson’s disease is often thought of as a single condition. In reality, it is better understood as a group of syndromes caused by different factors – genetic, environmental or a combination of both.
These varying causes lead to differences in disease patterns, progression and subsequent diagnosis. Recognising this distinction is crucial as it paves the way for targeted interventions and may even help prevent the disease altogether.
Shutterstock/sfam_photo Why we focus on PINK1-linked Parkinson’s
We became interested in this gene after a 2021 study highlighted five people of Samoan and Tongan descent living in New Zealand who shared the same PINK1 mutation.
Previously, this mutation had been spotted only in a few more distant places –Malaysia, Guam and the Philippines. The fact it appeared in people from Samoan and Tongan backgrounds suggested a historical connection dating back to early Polynesian migrations.
One person in 1,300 West Polynesians carries this mutation. This is a frequency well above what scientists usually classify as rare (below one in 2,200). This discovery means we may be overlooking entire communities in Parkinson’s research if we continue to assume PINK1-linked cases are uncommon.
This world map shows people in some Polynesian communities have a much higher rate of PINK1-linked Parkinson’s than the global population. Eden Yin, CC BY-SA Traditional understanding says PINK1-linked Parkinson’s is both rare and typically strikes younger people, mostly in their 30s or 40s, if they inherit two faulty copies of the gene. In other words, it’s considered a recessive condition, needing two matching puzzle pieces before the disease can unfold.
Our work challenges this view. We show that even one defective PINK1 gene can cause Parkinson’s at an average age of 43, much earlier than the typical onset after 65. That’s a significant departure from the standard belief that only people with two defective gene copies are at risk.
Why this matters for people with the disease
It’s not just genetics that challenge long-held views. Historically, PINK1-linked Parkinson’s was thought to lack some of the classic features of the disease, such as toxic clumps of alpha-synuclein protein.
In typical Parkinson’s, alpha-synuclein builds up in the brain, forming sticky clumps known as Lewy bodies. Our results, contrary to prior beliefs, show that alpha-synuclein pathology is present in 87.5% of PINK1 cases. This finding opens up a promising new avenue for future treatment development.
The biggest concern is early onset. PINK1-linked Parkinson’s can begin as early as 11 years old, although a more common starting point is around the mid-30s. This early onset means living longer with the disease, which can profoundly affect education, work opportunities and family life.
Current treatments (such as levodopa, a precursor of dopamine) help manage symptoms, but they’re not designed to address the root cause. If we know someone has a PINK1 mutation, scientists and clinicians can explore therapies for specific genetic pathways, potentially delivering relief beyond symptom management.
Sex differences add a layer of complexity
In Parkinson’s, generally, men are at higher risk and tend to develop symptoms earlier. However, our findings suggest the opposite pattern for PINK1-linked cases. Particularly, women with two defective copies of the gene experience onset earlier than men.
This highlights the need to consider sex-related factors in Parkinson’s research. Overlooking them risks missing key elements of the disease.
Genetic testing could be a game-changer for PINK1-linked Parkinson’s. Because it often appears earlier, doctors may not recognise it immediately, especially if they are more familiar with the common, later-onset form of Parkinson’s.
Early genetic testing could lead to a faster, more accurate diagnosis, allowing treatment to begin when interventions are most effective. It would help families understand how the disease is inherited, enabling relatives to get tested.
In some cases, where appropriate and culturally acceptable, embryo screening may be considered to prevent the passing of the faulty gene.
Knowing you have a PINK1 mutation could also make finding the right treatment more efficient. Instead of a lengthy trial-and-error process with different medications, doctors could use emerging therapies designed to target the underlying PINK1 mutation rather than relying on general Parkinson’s treatments meant for the broader population.
Addressing research gaps
These findings underscore how crucial it is to include diverse populations in health research.
Many communities, such as those in Samoa, Tonga and other Pacific nations, have had little to no involvement in global Parkinson’s genetics studies. This has created gaps in knowledge and real-world consequences for people who may not receive timely or accurate diagnoses.
Researchers, funding bodies and policymakers must prioritise projects beyond the usual focus on European or industrialised countries to ensure research findings and treatments are relevant to all affected populations.
To better diagnose and treat Parkinson’s, we need a more inclusive approach. Recognising that PINK1-linked Parkinson’s is not as rare as previously thought – and that genetics, sex differences and cultural factors all play a role – allows us to improve care for everyone.
By expanding genetic testing, refining treatments and ensuring research reflects the full spectrum of Parkinson’s, we can move closer to more precise diagnoses, targeted therapies and better support systems for all.
Victor Dieriks, Research Fellow in Health Sciences, University of Auckland, Waipapa Taumata Rau and Eden Paige Yin, PhD candidate in Health Sciences, University of Auckland, Waipapa Taumata Rau
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The “Five Tibetan Rites” & Why To Do Them!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Spinning Around
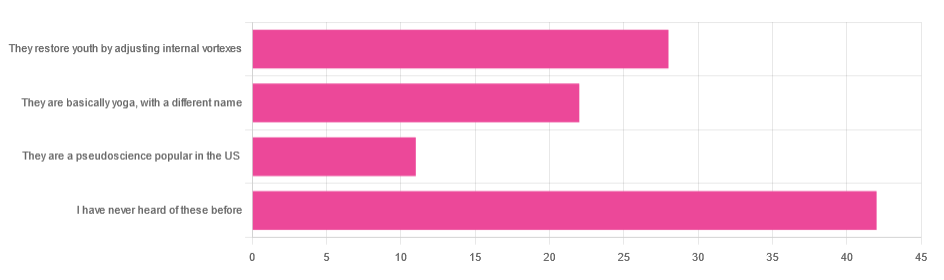
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion of the “Five Tibetan Rites”, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 41% said “I have never heard of these before”
- About 27% said “they restore youth by adjusting internal vortexes”
- About 22% said “they are basically yoga, by a different name”
- About 11% said “they are a pseudoscience popular in the US”
So what does the science say?
The Five Tibetan Rites are five Tibetan rites: True or False?
False, though this is more question of social science than of health science, so we’ll not count it against them for having a misleading name.
The first known mentioning of the “Five Tibetan Rites” is by an American named Peter Kelder, who in 1939 published, through a small LA occult-specialized publishing house, a booklet called “The Eye of Revelation”. This work was then varyingly republished, repackaged, and occasionally expanded upon by Kelder or other American authors, including Chris Kilham’s popular 1994 book “The Five Tibetans”.
The “Five Tibetan Rites” are unknown as such in Tibet, except for what awareness of them has been raised by people asking about them in the context of the American phenomenon.
Here’s a good history book, for those interested:
The author didn’t originally set out to “debunk” anything, and is himself a keen spiritualist (and practitioner of the five rites), but he was curious about the origins of the rites, and ultimately found them—as a collection of five rites, and the other assorted advices given by Kelder—to be an American synthesis in the whole, each part inspired by various different physical practices (some of them hatha yoga, some from the then-popular German gymnastics movement, some purely American spiritualism, all available in books that were popular in California in the early 1900s).
You may be wondering: why didn’t Kelder just say that, then, instead of telling stories of an ancient Tibetan tradition that empirically does not exist? The answer to this lies again in social science not health science, but it’s been argued that it’s common for Westerners to “pick ‘n’ mix” ideas from the East, champion them as inscrutably mystical, and (since they are inscrutable) then simply decide how to interpret and represent them. Here’s an excellent book on this, if you’re interested:
(in Kelder’s case, this meant that “there’s a Tibetan tradition, trust me” was thus more marketable in the West than “I read these books in LA”)
They are at least five rites: True or False?
True! If we use the broad definition of “rite” as “something done repeatedly in a solemn fashion”. And there are indeed five of them:
- Spinning around (good for balance)
- Leg raises (this one’s from German gymnastics)
- Kneeling back bend (various possible sources)
- Tabletop (hatha yoga, amongst others)
- Pendulum (hatha yoga, amongst others) ← you may recognize this one from the Sun Salutation
You can see them demonstrated here:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
Kelder also advocated for what was basically the Hay Diet (named not for the substance but for William Hay; it involved separating foods into acid and alkali, not necessarily according to the actual pH of the foods, and combining only “acid” foods or only “alkali” foods at a time), which was popular at the time, but has since been rejected as without scientific merit. Kelder referred to this as “the sixth rite”.
The Five Rites restore youth by adjusting internal vortexes: True or False?
False, in any scientific sense of that statement. Scientifically speaking, the body does not have vortexes to adjust, therefore that is not the mechanism of action.
Spiritually speaking, who knows? Not us, a humble health science publication.
The Five Rites are a pseudoscience popular in the US: True or False?
True, if 27% of those who responded of our mostly North American readership can be considered as representative of what is popular.
However…
“Pseudoscience” gets thrown around a lot as a bad word; it’s often used as a criticism, but it doesn’t have to be. Consider:
A small child who hears about “eating the rainbow” and mistakenly understands that we are all fuelled by internal rainbows that need powering-up by eating fruits and vegetables of different colors, and then does so…
…does not hold a remotely scientific view of how things are happening, but is nevertheless doing the correct thing as recommended by our best current science.
It’s thus a little similar with the five rites. Because…
The Five Rites are at least good for our health: True or False?
True! They are great for the health.
The first one (spinning around) is good for balance. Science would recommend doing it both ways rather than just one way, but one is not bad. It trains balance, trains our stabilizing muscles, and confuses our heart a bit (in a good way).
See also: Fall Special (How To Not Fall, And Not Get Injured If You Do)
The second one (leg raises) is excellent for core strength, which in turn helps keep our organs where they are supposed to be (this is a bigger health issue than most people realise, because “out of sight, out of mind”), which is beneficial for many aspects of our health!
See also: Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It ← visceral fat is the fat that surrounds your internal organs; too much there becomes a problem!
The third, fourth, and fifth ones stretch our spine (healthily), strengthen our back, and in the cases of the fourth and fifth ones, are good full-body exercises for building strength, and maintaining muscle mass and mobility.
See also: Building & Maintaining Mobility
So in short…
If you’ve been enjoying the Five Rites, by all means keep on doing them; they might not be Tibetan (or an ancient practice, as presented), and any mystical aspect is beyond the scope of our health science publication, but they are great for the health in science-based ways!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Build Muscle (Healthily!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Do You Have To Gain?
We have previously promised a three-part series about changing one’s weight:
- Losing weight (specifically, losing fat)
- Gaining weight (specifically, gaining muscle)
- Gaining weight (specifically, gaining fat)
And yes, that last one is also something that some people want/need to do (healthily!), and want/need help with that.
There will be, however, no need for a “losing muscle” article, because (even though sometimes a person might have some reason to want to do this), it’s really just a case of “those things we said for gaining muscle? Don’t do those and the muscle will atrophy naturally”.
Here’s the first part: How To Lose Weight (Healthily!)
While some people will want to lose fat, please do be aware that the association between weight loss and good health is not nearly so strong as the weight loss industry would have you believe:
And, while BMI is not a useful measure of health in general, it’s worth noting that over the age of 65, a BMI of 27 (which is in the high end of “overweight”, without being obese) is associated with the lowest all-cause mortality:
BMI and all-cause mortality in older adults: a meta-analysis
Body weight, muscle mass, and protein:
That BMI of 27, or whatever weight you might wish to be, ignores body composition. You’re probably aware that volume-for-volume, muscle weighs more than fat.
You’re also probably aware that if we’re not careful, we tend to lose muscle as we get older. This is known as age-related sarcopenia:
Protein, & Fighting Sarcopenia
Dr. Gabrielle Lyon, our featured expert in the above article, recommends getting at least 1.6g of protein per kg of body weight per day (Americans, divide your weight in pounds by 2.2 to get your weight in kg).
So for example, if you weigh 165lb, that’s 75kg, that’s 1.6×75=120g of protein per day.
There is an upper limit to how much protein per day is healthy, and that limit is probably around 2g of protein per kg of body weight per day:
Protein: How Much Do We Need, Really?
You may be wondering: should we go for animal or plant protein? In which case, the short version is:
- If you only care about muscle growth, any complete sources of protein are fine
- If you care about your general health too, then avoiding red meat is best, but other common protein sources are all fine
- Unprocessed is (unsurprisingly) better than processed in either case
Longer version: Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
What exercises are best for muscle-building?
Of course, different muscles require different exercises, but for all of them, resistance training is what builds muscle the most, and it’s pretty much impossible to build a lot of muscle otherwise.
Check out: Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
Prepare to fail!
No, really, prepare to fail. Because while resistance training in general is good for maintaining strong muscles and bones, you will only gain muscle if your current muscle is not enough to do the exercise:
- If you do a heavy resistance exercise without undue difficulty, your muscles will say to each other “Good job, team! That was hard, but luckily we were strong enough; no changes necessary”.
- If you do a heavy resistance exercise to the point where you can no longer do it (called: training to failure), then your muscles will say to each other “Oof, what a task! What we’ve got here is clearly not enough, so we’ll have to add more muscle for next time”.
Safety note: training to failure comes with safety risks. If using free weights or weight machines, please do so under well-trained supervision. If doing it with bodyweight (e.g. press-ups until you can press no more) or resistance bands, please check with your doctor first to ensure this is safe for you.
You can also increase the effectiveness of your resistance training by doing it in a way that “confuses” your muscles, making it harder for them to adapt in the moment, and thus forcing them to adapt more in the long term (e.g. get bigger and stronger):
HIIT, But Make It HIRT: High Intensity Resistance Training
Make time for recovery
While many kinds of exercise can be done daily, exercise to build muscle(s) means at the very least resting that muscle (or muscle group) the next day.
For this reason, a lot of bodybuilders have for example a week’s schedule that might look like:
- Monday: Upper body training
- Wednesday: Lower body training
- Friday: Core strength training
…and rest on other days. This gives most muscles a full week of recovery, and every muscle at least 48 hours of recovery.
Note: bodybuilders, like children (who are also doing a lot of body-building, in their own way) need more sleep in order to allow for this recovery and growth to occur. Serious bodybuilders often aim for 12 hours sleep per day. This might be impractical, undesirable, or even impossible for some people, but it’s a factor to be borne in mind and not forgotten.
See also:
Overdone It? How To Speed Up Recovery After Exercise (According To Actual Science)
Anything else that can (safely and healthily) be done to promote muscle growth?
There are a lot of supplements on the market; some are healthy and helpful, other not so much. Here are some we’ve written about:
- What To Eat, Take, And Do Before A Workout
- Creatine: Very Different For Young & Old People
- Ginseng: Exercising With Less Soreness!
- Taurine’s Benefits For Heart Health And More
- Topping Up Testosterone? What To Consider
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: