Healthy Chocolate Fudge Energy Bites
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
While these are quite high-calorie, they’re also high in protein, and the fiber and healthy fats flatten the blood sugar curve:
You will need
- 1 cup peanut butter
- 4 oz dark chocolate, melted (try to get dark chocolate with >80% cocoa, if you can; 85% is very respectable and 90% is perfect)
- ⅓ cup maple syrup (you can safely reduce this, or even omit it, if you prefer less sweetness)
- ¼ cup hazelnuts
- ¼ cup almond milk (or your preferred milk, but we recommend almond for taste and health)
- 1 tsp vanilla extract
- Topping: ¼ cup hazelnuts, roughly chopped
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine all the ingredients (except the topping) in a food processor, and blend until smooth.
2) Line a container (5″x7″ is a good size) with baking paper and spread the mixture evenly into it, pressing down gently.
3) Sprinkle the topping onto it, press that even more gently into it.
4) Refrigerate overnight (or chill it for 2hrs in the freezer).
5) Cut into cubes to serve; they can be served frozen or thawed, per your preference:
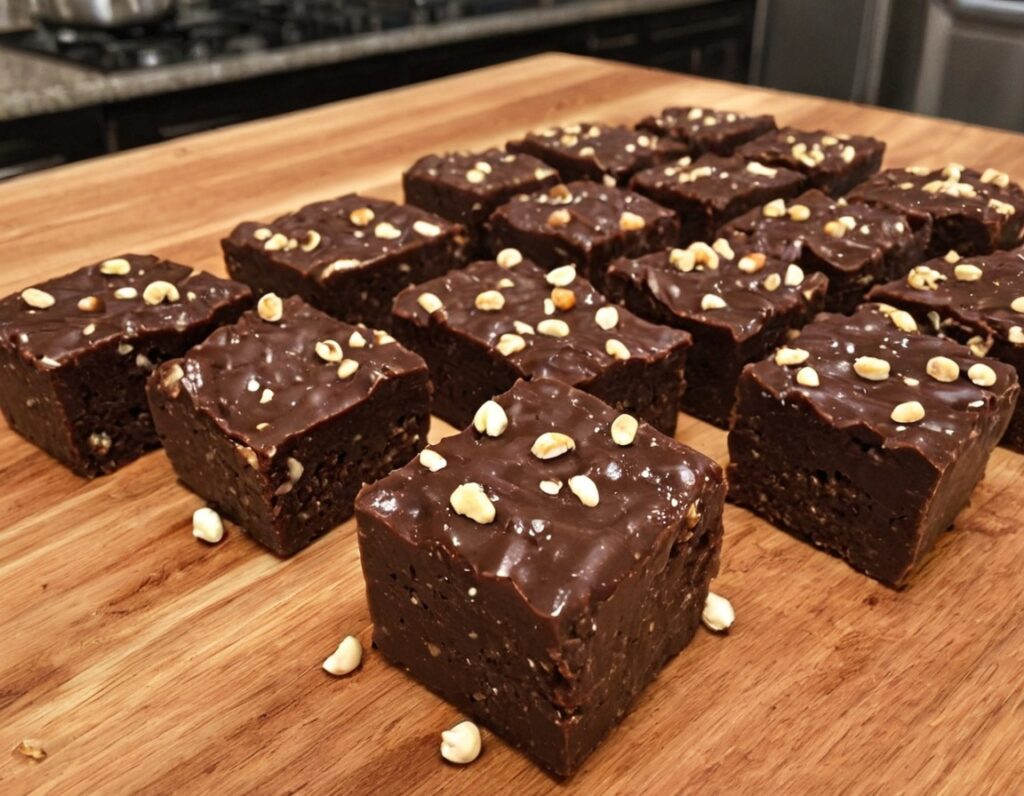

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Eating For Energy (In Ways That Actually Work)
- “Let Them Eat Cake”, She Said…
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Plant-Based Milks—What’s Best?
- Chocolate & Health: Fact or Fiction?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Daily, Weekly, Monthly: Habits Against Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Anil Rajani has advice on restoring/retaining youthfulness. Two out of three of the sections are on skincare specifically, which may seem a vanity, but it’s also worth remembering that our skin is a very large and significant organ, and makes a big difference for the rest of our physical health, as well as our mental health. So, it’s worthwhile to look after it:
The recommendations
Daily: meditation practice
Meditation reduces stress, which reduction in turn protects telomere length, slowing the overall aging process in every living cell of the body.
Weekly: skincare basics
Dr. Rajani recommends a combination of retinol and glycolic acid. The former to accelerate cell turnover, stimulate collagen production, and reduce wrinkles; the latter, to exfoliate dead cells, allowing the retinol to do its job more effectively.
We at 10almonds would like to add: wearing sunscreen with SPF50 is a very good thing to do on any day that your phone’s weather app says the UV index is “moderate” or higher.
Monthly: skincare extras
Here are the real luxuries; spa visits, microneedling (stimulates collagen production), and non-ablative laser therapy. He recommends creating a home spa if possible for monthly skincare treatments, investing in high-quality devices for long-term benefits.
For more on all of these things, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
- No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
- The Evidence-Based Skincare That Beats Product-Specific Hype
Take care!
Share This Post
-
What are ‘collarium’ sunbeds? Here’s why you should stay away
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Reports have recently emerged that solariums, or sunbeds – largely banned in Australia because they increase the risk of skin cancer – are being rebranded as “collarium” sunbeds (“coll” being short for collagen).
Commercial tanning and beauty salons in Queensland, New South Wales and Victoria are marketing collariums, with manufacturers and operators claiming they provide a longer lasting tan and stimulate collagen production, among other purported benefits.
A collarium sunbed emits both UV radiation and a mix of visible wavelength colours to produce a pink or red light. Like an old-school sunbed, the user lies in it for ten to 20 minute sessions to quickly develop a tan.
But as several experts have argued, the providers’ claims about safety and effectiveness don’t stack up.
Why were sunbeds banned?
Commercial sunbeds have been illegal across Australia since 2016 (except for in the Northern Territory) under state-based radiation safety laws. It’s still legal to sell and own a sunbed for private use.
Their dangers were highlighted by young Australians including Clare Oliver who developed melanoma after using sunbeds. Oliver featured in the No Tan Is Worth Dying For campaign and died from her melanoma at age 26 in 2007.
Sunbeds lead to tanning by emitting UV radiation – as much as six times the amount of UV we’re exposed to from the summer sun. When the skin detects enough DNA damage, it boosts the production of melanin, the brown pigment that gives you the tanned look, to try to filter some UV out before it hits the DNA. This is only partially successful, providing the equivalent of two to four SPF.
Essentially, if your body is producing a tan, it has detected a significant amount of DNA damage in your skin.
Research shows people who have used sunbeds at least once have a 41% increased risk of developing melanoma, while ten or more sunbed sessions led to a 100% increased risk.
In 2008, Australian researchers estimated that each year, sunbeds caused 281 cases of melanoma, 2,572 cases of squamous cell carcinoma (another common type of skin cancer), and $3 million in heath-care costs, mostly to Medicare.
How are collarium sunbeds supposed to be different?
Australian sellers of collarium sunbeds imply they are safe, but their machine descriptions note the use of UV radiation, particularly UVA.
UVA is one part of the spectrum of UV radiation. It penetrates deeper into the skin than UVB. While UVB promotes cancer-causing mutations by discharging energy straight into the DNA strand, UVA sets off damage by creating reactive oxygen species, which are unstable compounds that react easily with many types of cell structures and molecules. These damage cell membranes, protein structures and DNA.
Evidence shows all types of sunbeds increase the risk of melanoma, including those that use only UVA.
Some manufacturers and clinics suggest the machine’s light spectrum increases UV compatibility, but it’s not clear what this means. Adding red or pink light to the mix won’t negate the harm from the UV. If you’re getting a tan, you have a significant amount of DNA damage.
Collagen claims
One particularly odd claim about collarium sunbeds is that they stimulate collagen.
Collagen is the main supportive tissue in our skin. It provides elasticity and strength, and a youthful appearance. Collagen is constantly synthesised and broken down, and when the balance between production and recycling is lost, the skin loses strength and develops wrinkles. The collagen bundles become thin and fragmented. This is a natural part of ageing, but is accelerated by UV exposure.
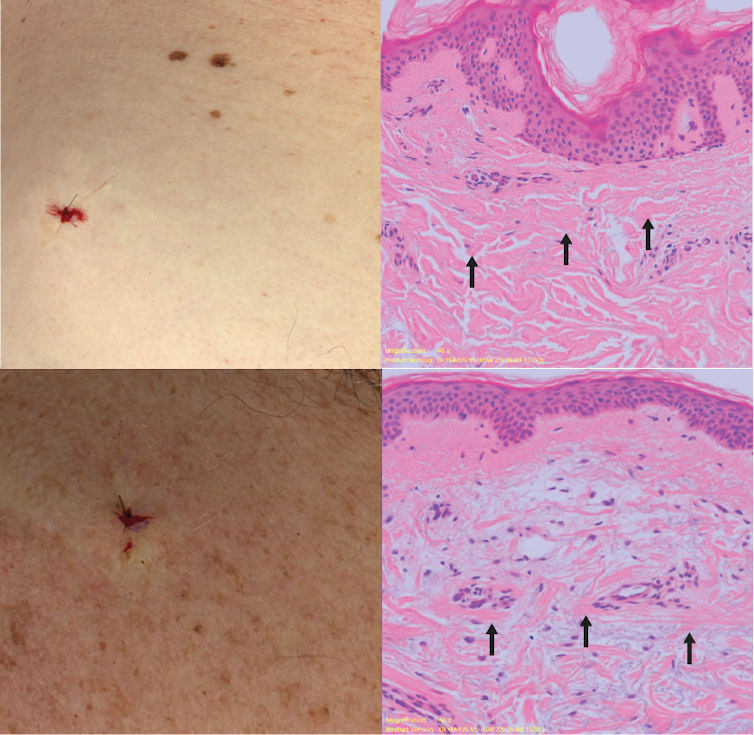
Sun-protected skin (top) has thick bands of pink collagen (arrows) in the dermis, as seen on microscopic examination. Chronically sun-damaged skin (bottom) has much thinner collagen bands.
Katie Lee/UQThe reactive oxygen species generated by UVA light damage existing collagen structures and kick off a molecular chain of events that downgrades collagen-producing enzymes and increases collagen-destroying enzymes. Over time, a build-up of degraded collagen fragments in the skin promotes even more destruction.
While there is growing evidence red light therapy alone could be useful in wound healing and skin rejuvenation, the UV radiation in collarium sunbeds is likely to undo any benefit from the red light.
What about phototherapy?
There are medical treatments that use controlled UV radiation doses to treat chronic inflammatory skin diseases like psoriasis.
The anti-collagen effects of UVA can also be used to treat thickened scars and keloids. Side-effects of UV phototherapy include tanning, itchiness, dryness, cold sore virus reactivation and, notably, premature skin ageing.
These treatments use the minimum exposure necessary to treat the condition, and are usually restricted to the affected body part to minimise risks of future cancer. They are administered under medical supervision and are not recommended for people already at high risk of skin cancer, such as people with atypical moles.
So what happens now?
It looks like many collariums are just sunbeds rebranded with red light. Queensland Health is currently investigating whether these salons are breaching the state’s Radiation Safety Act, and operators could face large fines.
As the 2024 Australians of the Year – melanoma treatment pioneers Georgina Long and Richard Scolyer – highlighted in their acceptance speech, “there is nothing healthy about a tan”, and we need to stop glamorising tanning.
However, if you’re desperate for the tanned look, there is a safer and easy way to get one – out of a bottle or by visiting a salon for a spray tan.
Katie Lee, PhD Candidate, Dermatology Research Centre, The University of Queensland and Anne Cust, Professor of Cancer Epidemiology, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Radishes vs Endives – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing radishes to endives, we picked the endives.
Why?
These are both great, but there’s a clear winner here in every category!
In terms of macros, radishes have more carbs while endives have more fiber and protein.
In the category of vitamins, radishes have more of vitamins B6 and C, while endives have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B4, B5, B7, B9, E, K, and choline.
When it comes to minerals, things are not less one-sided: radishes have more selenium, while endives have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc.
You may be thinking: but what about radishes’ shiny red bit? Doesn’t that usually mean more of something important, like carotenoids or anthocyanins or something? And the answer is that the red pigment in radishes is so thinly-distributed on the exterior that it’s barely there and if we’re looking at values per 100g, it’s a tiny fraction of a tiny fraction.
In both cases, their bitter taste comes mostly from flavonols, of which mostly kaempferol, of which endives have about 20x what radishes have, on average.
All in all, an overwhelming win for endives.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Beetroot vs Tomato – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing beetroot to tomato, we picked the beetroot.
Why?
Both are great! But we say beetroot comes out on top:
In terms of macros, beetroot has more protein, carbs, and fiber, making it the more nutritionally dense option. It has a slightly higher glycemic index, but also has specific phytochemicals that lower blood sugars and increase insulin sensitivity, more than cancelling that out. So, a clear win for beetroot in this regard.
In the category of vitamins, beetroot has more of vitamins B2, B5, B7, and B9, while tomato has more of vitamins A, C, E, and K. We’d call that a 4:4 tie, but tomato’s margins of difference are greater, so we say tomato wins this round.
When it comes to minerals, beetroot has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while tomatoes are not higher in any mineral. An easy win for beetroot here.
Looking at polyphenols and other remaining phytochemicals, beetroot has most, and especially its betalain content goes a long way. Tomatoes, meanwhile, have a famously high lycopene content (a highly beneficial carotenoid). All in all, it could swing either way based on subjective factors, so we’re saying it’s a tie this time.
Adding up the sections makes for an overall win for beetroot, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
- Beetroot For More Than Just Your Blood Pressure
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eating on the Wild Side: – by Jo Robinson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author is an investigative journalist, and it shows here, as she leaves no stone unturned in her quest for the truth in the face of many food myths.
She covers a lot of “popular wisdom” things that are varyingly true or false, or sometimes even both—in the case of food lore that’s a good rule of thumb, but has notable exceptions (e.g. “more colorful and/or darker-colored fruits/vegetables contain more nutrients”, which is a very good rule of thumb until one meets a cauliflower, for example).
She also covers food preparation myths, and how, to give one example, in spite of the popularity of “less cooked is better”, in some cases certain cooking methods will indeed destroy nutrients; in others, certain cooking methods will improve nutritional availability. Either by destroying an adjacent antinutrient (e.g. phytates), or by breaking something down into a more manageable form that our body can absorb. Knowing which is which, is important.
The book is organized by kinds of food, and does exclusively cover plants, but there’s more than enough material for any omnivore to enjoy.
The style is… Journalistic, it would be fair to say. Which is not surprising, given the author. But it means that it is written in a fairly narrative way, to draw the reader in and make it an enjoyable read while still being informative in all parts (there is no padding). In terms of science, the in-the-prose science is as minimal as possible to still convey what needs to be conveyed, while 25 pages of bibliography stack up at the end to show that indeed, this journalist cites sources.
Bottom line: this is a really enjoyable book, packed with a wealth of knowledge, and is perfect to uplift your cooking by knowing your ingredients a little more intimately!
Click here to check out Eating On The Wild Side, and, enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can you die from long COVID? The answer is not so simple
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Nearly five years into the pandemic, COVID is feeling less central to our daily lives.
But the virus, SARS-CoV-2, is still around, and for many people the effects of an infection can be long-lasting. When symptoms persist for more than three months after the initial COVID infection, this is generally referred to as long COVID.
In September, Grammy-winning Brazilian musician Sérgio Mendes died aged 83 after reportedly having long COVID.
Australian data show 196 deaths were due to the long-term effects of COVID from the beginning of the pandemic up to the end of July 2023.
In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported 3,544 long-COVID-related deaths from the start of the pandemic up to the end of June 2022.
The symptoms of long COVID – such as fatigue, shortness of breath and “brain fog” – can be debilitating. But can you die from long COVID? The answer is not so simple.
Jan Krava/Shutterstock How could long COVID lead to death?
There’s still a lot we don’t understand about what causes long COVID. A popular theory is that “zombie” virus fragments may linger in the body and cause inflammation even after the virus has gone, resulting in long-term health problems. Recent research suggests a reservoir of SARS-CoV-2 proteins in the blood might explain why some people experience ongoing symptoms.
We know a serious COVID infection can damage multiple organs. For example, severe COVID can lead to permanent lung dysfunction, persistent heart inflammation, neurological damage and long-term kidney disease.
These issues can in some cases lead to death, either immediately or months or years down the track. But is death beyond the acute phase of infection from one of these causes the direct result of COVID, long COVID, or something else? Whether long COVID can directly cause death continues to be a topic of debate.
Of the 3,544 deaths related to long COVID in the US up to June 2022, the most commonly recorded underlying cause was COVID itself (67.5%). This could mean they died as a result of one of the long-term effects of a COVID infection, such as those mentioned above.
COVID infection was followed by heart disease (8.6%), cancer (2.9%), Alzheimer’s disease (2.7%), lung disease (2.5%), diabetes (2%) and stroke (1.8%). Adults aged 75–84 had the highest rate of death related to long COVID (28.8%).
These findings suggest many of these people died “with” long COVID, rather than from the condition. In other words, long COVID may not be a direct driver of death, but rather a contributor, likely exacerbating existing conditions.
The symptoms of long COVID can be debilitating. Lysenko Andrii/Shutterstock ‘Cause of death’ is difficult to define
Long COVID is a relatively recent phenomenon, so mortality data for people with this condition are limited.
However, we can draw some insights from the experiences of people with post-viral conditions that have been studied for longer, such as myalgic encephalomyelitis or chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS).
Like long COVID, ME/CFS is a complex condition which can have significant and varied effects on a person’s physical fitness, nutritional status, social engagement, mental health and quality of life.
Some research indicates people with ME/CFS are at increased risk of dying from causes including heart conditions, infections and suicide, that may be triggered or compounded by the debilitating nature of the syndrome.
So what is the emerging data on long COVID telling us about the potential increased risk of death?
Research from 2023 has suggested adults in the US with long COVID were at greater risk of developing heart disease, stroke, lung disease and asthma.
Research has also found long COVID is associated with a higher risk of suicidal ideation (thinking about or planning suicide). This may reflect common symptoms and consequences of long COVID such as sleep problems, fatigue, chronic pain and emotional distress.
But long COVID is more likely to occur in people who have existing health conditions. This makes it challenging to accurately determine how much long COVID contributes to a person’s death.
Research has long revealed reliability issues in cause-of-death reporting, particularly for people with chronic illness.
Determining the exact cause of someone’s death is not always easy. Pixabay/Pexels So what can we conclude?
Ultimately, long COVID is a chronic condition that can significantly affect quality of life, mental wellbeing and overall health.
While long COVID is not usually immediately or directly life-threatening, it’s possible it could exacerbate existing conditions, and play a role in a person’s death in this way.
Importantly, many people with long COVID around the world lack access to appropriate support. We need to develop models of care for the optimal management of people with long COVID with a focus on multidisciplinary care.
Dr Natalie Jovanovski, Vice Chancellor’s Senior Research Fellow in the School of Health and Biomedical Sciences at RMIT University, contributed to this article.
Rose (Shiqi) Luo, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, School of Health and Biomedical Sciences, RMIT University; Catherine Itsiopoulos, Professor and Dean, School of Health and Biomedical Sciences, RMIT University; Kate Anderson, Vice Chancellor’s Senior Research Fellow, RMIT University; Magdalena Plebanski, Professor of Immunology, RMIT University, and Zhen Zheng, Associate Professor, STEM | Health and Biomedical Sciences, RMIT University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: