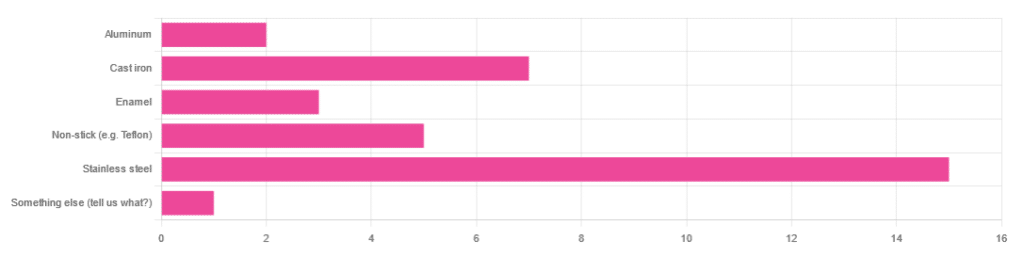
How To Gain Weight (Healthily!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Do You Have To Gain?
We have previously promised a three-part series about changing one’s weight:
- Losing weight (specifically, losing fat)
- Gaining weight (specifically, gaining muscle)
- Gaining weight (specifically, gaining fat)
There will be, however, no need for a “losing muscle” article, because (even though sometimes a person might have some reason to want to do this), it’s really just a case of “those things we said for gaining muscle? Don’t do those and the muscle will atrophy naturally”.
Here’s our first article: How To Lose Weight (Healthily!)
While some people will want to lose fat, please do be aware that the association between weight loss and good health is not nearly so strong as the weight loss industry would have you believe:
And, while BMI is not a useful measure of health in general, it’s worth noting that over the age of 65, a BMI of 27 (which is in the high end of “overweight”, without being obese) is associated with the lowest all-cause mortality:
BMI and all-cause mortality in older adults: a meta-analysis
Here was our second article: How To Build Muscle (Healthily!)
And now, it’s time for the last part, which yes, is also something that some people want/need to do (healthily!), and want/need help with that.
How to gain fat, healthily
Fat gets a bad press, but when it comes to health, we would die without it.
Even in the case of having excess fat, the fat itself is not generally the problem, so much as comorbid metabolic issues that are often caused by the same things as the excess fat.
So, how to gain fat healthily?
- Obvious but potentially dangerously misleading answer: “in moderation”
- More useful answer: “carefully”
Because, you can “in moderation” put on less than one pound per week for a few years and be in very bad health by the end of it. So how does this “carefully” work any differently to “in moderation”?
The key is in how we store the fat
Not merely where we store it (though that’ll follow from the “how”), but specifically: how we store it.
- When we consume energy from food in excess of our immediate survival needs, our body stores what it can. This is good!
- When our body is receiving energy from food faster than it can physically process it to store it healthily, it will start shoving it wherever it can instead. This is bad!
This is the physiological equivalent of the difference between tidying a room carefully, and cramming everything into one cupboard in 30 seconds just to get it out of sight.
So, you do need to consume calories yes, but you need to consume them in a way your body can take its time about storing them.
We’ve written before about the science of this, so we’ll share some links, but first, here are the practical tips:
- Do not drink your calories. Drinking calories tends to be the equivalent of injecting sugars directly into your veins, in terms of how quickly it gets received.
- See also: How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver ← this is highly relevant, because the same process that results in unhealthy weight gain, results in liver disease, by the same mechanism (the liver gets overwhelmed).
- Eat your greens. No, they won’t provide many calories, but they are critical to your body not being overwhelmed by the arrival of sugars.
- See also: 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars ← the other 9 things are also helpful for not putting on fat unhealthily, so using these alongside a calorie-dense diet can result in healthy fat gain as needed
- Get more of your calories from fats than carbs. Fats will not overwhelm your body’s glycemic response in the same way that carbs will.
- Again this is about getting calories while not getting metabolic disease. See also: How To Prevent And Reverse Type Two Diabetes as the advice is the same for that, for the same reason!
- Consider going low-carb, but even if you choose not to, go for carbs with a low glycemic index instead of a high glycemic index.
- For reference, see: Glycemic Index Chart: Glycemic index and glycemic load ratings for 500+ foods
- Need healthy fats in a snack? Enjoy nuts (unless you have an allergy); they will be your best friend in this regard. As an example, a mere 1oz portion of cashew nuts has 157 calories.
- See also: Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
- Need healthy fats for cooking? Enjoy olive oil, as it has one of the healthiest lipids profiles available, and is a great way to increase the calorific content of many meals.
Lastly…
Be patient, enjoy your food, and stick as best you can to the above considerations. All strength to you.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Macadamias vs Hazelnuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing macadamias to hazelnuts, we picked the hazelnuts.
Why?
In terms of macros first, hazelnuts have 2x the protein, and slightly more carbs and fiber. We call this a win for hazelnuts.
When it comes to vitamins, macadamias have more of vitamins B1, B2, and B3, while hazelnuts have more of vitamins A, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, and E. Notably, 28x more vitamin E, so that’s not inconsiderable. Also 10x the vitamin B9, and 5x the vitamin C, and the rest, more modest wins. In any case, clearly a strong win for hazelnuts here.
In the category of minerals, macadamias have more selenium, while hazelnuts have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. Another clear win for hazelnuts.
In short, hazelnuts win in all categories. However, by all means enjoy either or both (unless you have a nut allergy, in which case, obviously don’t).
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Mythbusting Cookware Materials
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In Wednesday’s newsletter, we asked you what kind of cookware you mostly use, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 45% said stainless steel
- About 21% said cast iron
- About 15% said non-stick (e.g. Teflon)
- About 9% said enamel
- About 6% said aluminum
- And 1 person selected “something else”, but then commented to the contrary, writing “I use all of the above”
So, what does the science say about these options?
Stainless steel cookware is safe: True or False?
True! Assuming good quality and normal use, anyway. There really isn’t a lot to say about this, because it’s very unexciting. So long as it is what it is labelled as: there’s nothing coating it, nothing comes out of it unless you go to extremes*, and it’s easy to clean.
*If you cook for long durations at very high temperatures, it can leach nickel and chromium into food. What this means in practical terms: if you are using stainless steel to do deep-frying, then maybe stop that, and also consider going easy on deep-frying in general anyway, because obviously deep-frying is unhealthy for other reasons.
Per normal use, however: pretty much the only way (good quality) stainless steel cookware will harm you is if you touch it while it’s hot, or if it falls off a shelf onto your head.
That said, do watch out for cheap stainless steel cookware that can contain a lot of impurities, including heavy metals. Since you probably don’t have a mass spectrometer and/or chemistry lab at home to check for those impurities, your best guard here is simply to buy from a reputable brand with credible certifications.
Ceramic cookware is safe: True or False?
True… Most of the time! Ceramic pans usually have metal parts and a ceramic cooking surface coated with a very thin layer of silicon. Those metal parts will be as safe as the metals used, so if that’s stainless steel, you’re just as safe as the above. As for the silicon, it is famously inert and body-safe (which is why it’s used in body implants).
However: ceramic cookware that doesn’t have an obvious metal part and is marketed as being pure ceramic, will generally be sealed with some kind of glaze that can leach heavy metals contaminants into the food; here’s an example:
Lead toxicity from glazed ceramic cookware
Copper cookware is safe: True or False?
False! This is one we forgot to mention in the poll, as one doesn’t see a lot of it nowadays. The copper from copper pans can leach into food. Now, of course copper is an important mineral that we must get from our diet, but the amount of copper that that can leach into food from copper pans is far too much, and can induce copper toxicity.
In addition, copper cookware has been found to be, on average, highly contaminated with lead:
Non-stick cookware contaminates the food with microplastics: True or False?
True! If we were to discuss all the common non-stick contaminants here, this email would no longer fit (there’s a size limit before it gets clipped by most email services).
Suffice it to say: the non-stick coating, polytetrafluoroethylene, is itself a PFAS, that is to say, part of the category of chemicals considered environmental pollutants, and associated with a long list of health issues in humans (wherein the level of PFAS in our bloodstream is associated with higher incidence of many illnesses):
You may have noticed, of course, that the “non-stick” coating doesn’t stick very well to the pan, either, and will tend to come off over time, even if used carefully.
Also, any kind of wet cooking (e.g. saucepans, skillets, rice cooker inserts) will leach PFAS into the food. In contrast, a non-stick baking tray lined with baking paper (thus: a barrier between the tray and your food) is really not such an issue.
We wrote about PFAS before, so if you’d like a more readable pop-science article than the scientific paper above, then check out:
PFAS Exposure & Cancer: The Numbers Are High
Aluminum cookware contaminates the food with aluminum: True or False?
True! But not usually in sufficient quantities to induce aluminum toxicity, unless you are aluminum pans Georg who eats half a gram of aluminum per day, who is a statistical outlier and should not be counted.
That’s a silly example, but an actual number; the dose required for aluminum toxicity in blood is 100mg/L, and you have about 5 liters of blood.
Unless you are on kidney dialysis (because 95% of aluminum is excreted by the kidneys, and kidney dialysis solution can itself contain aluminum), you will excrete aluminum a lot faster than you can possibly absorb it from cookware. On the other hand, you can get too much of it from it being a permitted additive in foods and medications, for example if you are taking antacids they often have a lot of aluminum oxide in them—but that is outside the scope of today’s article.
However, aluminum may not be the real problem in aluminum pans:
❝In addition, aluminum (3.2 ± 0.25 to 4.64 ± 0.20 g/kg) and copper cookware (2.90 ± 0.12 g/kg) were highly contaminated with lead.
The time and pH-dependent study revealed that leaching of metals (Al, Pb, Ni, Cr, Cd, Cu, and Fe, etc.) into food was predominantly from anodized and non-anodized aluminum cookware.
More metal leaching was observed from new aluminum cookware compared to old. Acidic food was found to cause more metals to leach during cooking.❞
~ the same paper we cited when talking about copper
Cast iron cookware contaminates the food with iron: True or False?
True, but unlike with the other metals discussed, this is purely a positive, and indeed, it’s even recommended as a good way to fortify one’s diet with iron:
The only notable counterpoint we could find for this is if you have hemochromatosis, a disorder in which the body is too good at absorbing iron and holding onto it.
Thinking of getting some new cookware?
Here are some example products of high-quality safe materials on Amazon, but of course feel free to shop around:
Stainless Steel | Ceramic* | Cast Iron
*it says “non-stick” in the description, but don’t worry, it’s ceramic, not Teflon etc, and is safe
Bonus: rice cooker with stainless steel inner pot
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Do You Have A Personalized Health Plan? (Here’s How)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Good health” is quite a broad umbrella, and while we all have a general idea of what “healthy” looks like, it’s easy to focus on some areas and overlook others.
Of course, how much one does this will still depend on one’s level of interest in health, which can change over the course of life, and (barring serious midlife health-related curveballs such as a cancer diagnosis or something) often looks like an inverse bell curve:
- As small kids, we probably barely thought about health
- As teenagers, we probably had a narrow view of health (often related to whatever is considered sexually attractive at the time)
- In our 20s, may have a bit of a health kick in which we learn and apply a lot… Which often then gets to later take a bit of a back seat to work responsibilities and so forth
- This is commonly followed by a few decades of just trying to make it to Friday by any means necessary (definite risk factor for substance abuse of various kinds), double if we have kids, triple if we have work, kids, and are also solely responsible for managing the household.
- Then just as suddenly as it is predictably, we are ambushed when approaching retirement age by a cluster of age-related increased health risks that we now get to do our best to mitigate—the focus here is “not dying early”. A lot of health education occurs at this time.
- Finally, upon retirement, we actually get the time to truly focus on our health again, and now it’s easier to learn about all aspects of health, even if now there’s a need to juggle many health issues all at once, most of which affect the others.
See also: How Likely Are You To Live To 100? ← in which we can also see a graph of 10almonds subscribers’ ages, consistent with the above
So, let’s recap, and personalize our health plan
There are often things we wish we could have focused on sooner, so now’s the time to figure out what future-you in your next decade (or later!) is going to thank you for having done now.
So, while 20-year-old us might have been focusing on fat levels or athletic performance, how much does that really help us now? (With apologies to any readers in their 20s, but also, with the bonus for you: now’s the perfect time to plan ahead!)
At 10almonds, while we cover very many health topics, we often especially focus on:
- Brain health
- Heart health
- Gut health
…because they affect everything else so much. We’ve listed them there in the order they appear in the body, but in fact it can be useful to view them upside down, because:
- Gut health is critical for good metabolic health (a happy efficient gut allows us to process nutrients, including energy, efficiently)
- Metabolic health is critical for good heart health (a nicely ticking metabolism will not strain our heart)
- Heart health is critical for good brain health (a strong heart will nourish the brain with well-oxygenated blood and the nutrients it also carries)
So, this isn’t a catch-22 at all! There is a clear starting point:
“How do I do the other bits, though?”
We have you covered here: Your Health Audit, From Head To Toe
“Wait, where’s the personalization?”
This comes once you’ve got those above things in order.
Hopefully you know what particular health risks you have—as in, particular to you.
First, you will have any current diagnoses, and a plan for treating those. Many chronic illnesses can be reversed or at least lessened with lifestyle changes, in particular, if we reduce chronic inflammation, which is implicated in countless chronic illnesses, and exacerbates most of the rest.
So: How to Prevent (or Reduce) Inflammation
The same goes for any heightened risks you have as a result of those current diagnoses.
Next, you will have any genetic health risks—so here’s where genetic testing is a good one-shot tool, to get a lot of information all in one go.
Learn more: The Real Benefit Of Genetic Testing
…and then, of course, take appropriate steps to avoid suffering the things of which you are at increased genetic risk.
Finally, you will have any personal concerns or goals—in other words, what do you want to still be able to do, later in life? It’s easy to say “everything”, but what’s most important?
This writer’s example: I want to remain mobile, free from pain, and sharp of mind.
That doesn’t mean I’ll neglect the rest of my health, but it does mean that I will regularly weigh my choices against whether they are consistent with those three things.
As for how to plan for that?
Check out: Train For The Event Of Your Life! ← this one is mostly about the mobility aspect; staying free from pain is in large part a matter of avoiding inflammation which we already discussed, and staying sharp of mind relies on the gut-heart-brain pipeline we also covered.
You can also, of course, personalize your diet per which areas of health are the most important for you:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean (most anti-inflammatory, gut-healthiest, heart-healthiest, brain-healthiest)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Sciatica Exercises & Home Treatment – by Dr. George Best
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Best is a doctor of chiropractic, but his work here is compelling. He starts by giving an overview of the relevant anatomy, and then the assorted possible causes of sciatica, before moving on to the treatments.
As is generally the case for chiropractic, nothing here will be “cured”, but it will give methods for ongoing management to keep you pain-free—which in the case of sciatica, is usually the single biggest thing that most people suffering from it most dearly want.
We get to read a lot about self-massage and exercises, of the (very well-evidenced; about the most well-evidenced thing there is for back pain) McKenzie technique exercises, as well as assorted acupressure-based techniques that are less well-evidenced but have good anecdotal support.
He also writes about preventing sciatica—which if you already have it, that doesn’t mean it’s too late; it just means, in that case do these things (along with the aforementioned exercises) to gradually reverse the harm done and get back to where you were pre-sciatica.
Lastly, he does also speak on when signs might point to your problems being beyond the scope of this book, and seeking professional examination if you haven’t already.
The style throughout is straight to the point, informative, and instructional. There is zero fluff or padding, and no sensationalization. There are diagrams and illustrative photos where appropriate.
Bottom line: if you have, or fear the threat of, sciatica, then this is an excellent book to have and use its exercises.
Click here to check out Sciatica Exercises & Home Treatment, and live pain-free!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Secret to Mental Health – by George Pransky
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book (and its author) have a sizeable popular following, so it definitely can be said that it has been well-received by many people. The premise in this book is that there is fundamentally nothing wrong with anybody’s brain, and rather everything can be broken down into:
- Mind (the energy and intelligence that animates all life)
- Consciousness (the capacity to be aware of one’s life and experiences)
- Thought (the ability to think, allowing individuals to create their personal experience of reality)
The author explains, over the course of 145 pages, that where anyone with any perceived mental health issue is going wrong is by either lacking self-awareness (Consciousness) or erring by creating an undesirable personal experience of reality (Thought).
In terms of the science of this, frequent references are made to “there is evidence that shows”, “new discoveries about mental health suggest…”, etc, but this claimed evidence is never actually presented, just alluded to. Where many books would have a bibliography, this one has simply a collection of what the author has titled “interesting case studies, conversations, papers, and discussions” (there are no actual case studies or papers; it is just a collection of anecdotes).
The style is… Honestly, in this reviewer’s opinion, barely readable. But, apparently lots of people love it, so your mileage may vary.
We don’t usually delve too far into claimed credentials, but because of the interesting writing style and the bold claims without evidence, we were curious as to where this PhD came from, and apparently it came from a now-shut-down diploma mill that was described by the court as “a complete scam”.
Bottom line: we can’t recommend this one, but we read it so that you don’t have to, and we hope that publishing this review will help reassure you that when we do recommend a book, we mean it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Age-Proof Brain – by Dr. Marc Milstein
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Biological aging is not truly just one thing, but rather the amalgam of many things intersecting—and most of them are modifiable. The cells of your body neither know nor care how many times you have flown around the sun; they just respond to the stimuli they’re given.
Which is what fuels this book. The idea is to have a brain that is less-assailed by the things that would make it age, and more rejuvenated by the things that can make it biologically younger.
Dr. Milstein doesn’t neglect the rest of the body, and indeed notes the brain’s connections with the immune system, the heart, the gut, and more. But everything in this book is done with the brain in mind and its good health as the top priority outcome of all the things he advises.
On which note, yes, there is plenty of practical, implementable advice here. For a book that is consistently full of study paper citations, he does take care to make everything useful to the reader, and makes everything as easy as possible for the layperson along the way.
Bottom line: if you would like your brain to age less, this is an excellent, very evidence-based, guidebook.
Click here to check out The Age-Proof Brain, and age-proof your brain!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: