From Cucumbers To Kindles
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You’ve Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers!
Q: Where do I get cucumber extract?
A: You can buy it from BulkSupplements.com (who, despite their name, start at 100g packs)
Alternatively: you want it as a topical ointment (for skin health) rather than as a dietary supplement (for bone and joint health), you can extract it yourself! No, it’s not “just juice cucumbers”, but it’s also not too tricky.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Pine Nuts vs Macadamia Nuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pine nuts to macadamias, we picked the pine nuts.
Why?
In terms of macros, it’s subjective depending on what you want to prioritize; the two nuts are equal in carbs, but pine nuts have more protein and macadamias have more fiber. We’d generally prioritize the fiber, which so far would give macadamias a win in this category, but if you prefer the protein, then consider it pine nuts. Next, we must consider fats; macadamias have slightly more fat, and of which, proportionally more saturated fat, resulting in 3x the total saturated fat compared to pine nuts, gram for gram. With this in mind, we consider this category a tie or a marginal nominal win for pine nuts.
In the category of vitamins, pine nuts have more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B9, E, K, and choline, while macadamias have more of vitamins B1, B5, B6, and C. A clear win for pine nuts this time, especially with pine nuts having more than 17x the vitamin E of macadamias.
When it comes to minerals, pine nuts have more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while macadamias have more calcium and selenium. Another easy win for pine nuts.
In short, enjoy either or both (diversity is good), but pine nuts are the healthier by most metrics.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Ice Baths: To Dip Or Not To Dip?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
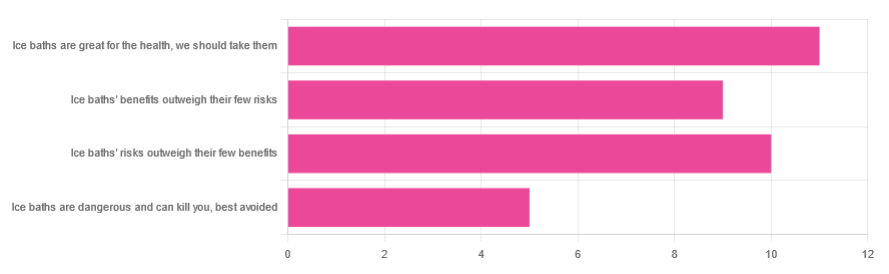
We asked you for your (health-related) view of ice baths, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 31% said “ice baths are great for the health; we should take them”
- About 29% said “ice baths’ risks outweigh their few benefits”
- About 26% said “ice baths’ benefits outweigh their few risks”
- About 14% said “ice baths are dangerous and can kill you; best avoided”
So what does the science say?
Freezing water is very dangerous: True or False?
True! Water close to freezing point is indeed very dangerous, and can most certainly kill you.
Fun fact, though: many such people are still saveable with timely medical intervention, in part because the same hypothermia that is killing them also slows down the process* of death
Source (and science) for both parts of that:
Cold water immersion: sudden death and prolonged survival
*and biologically speaking, death is a process, not an event, by the way. But we don’t have room for that today!
(unless you die in some sudden violent way, such as a powerful explosion that destroys your brain instantly; then it’s an event)
Ice baths are thus also very dangerous: True or False?
False! Assuming that they are undertaken responsibly and you have no chronic diseases that make it more dangerous for you.
What does “undertaken responsibly” mean?
Firstly, the temperature should not be near freezing. It should be 10–15℃, which for Americans is 50–59℉.
You can get a bath thermometer to check this, by the way. Here’s an example product on Amazon.
Secondly, your ice bath should last no more than 10–15 minutes. This is not a place to go to sleep.
What chronic diseases would make it dangerous?
Do check with your doctor if you have any doubts, as no list we make can be exhaustive and we don’t know your personal medical history, but the main culprits are:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Hypertension
- Diabetes (any type)
The first two are for heart attack risk; the latter is because diabetes can affect core temperature regulation.
Ice baths are good for the heart: True or False?
True or False depending on how they’re done, and your health before starting.
For most people, undertaking ice baths responsibly, repeated ice bath use causes the cardiovascular system to adapt to better maintain homeostasis when subjected to thermal shock (i.e. sudden rapid changes in temperature).
For example: Respiratory and cardiovascular responses to cold stress following repeated cold water immersion
And because that was a small study, here’s a big research review with a lot of data; just scroll to where it has the heading“Specific thermoregulative adaptations to regular exposure to cold air and/or cold water exposure“ for many examples and much discussion:
Health effects of voluntary exposure to cold water: a continuing subject of debate
Ice baths are good against inflammation: True or False?
True! Here’s one example:
Uric acid and glutathione levels (important markers of chronic inflammation) are also significantly affected:
Uric acid and glutathione levels during short-term whole body cold exposure
Want to know more?
That’s all we have room for today, but check out our previous “Expert Insights” main feature looking at Wim Hof’s work in cryotherapy:
A Cold Shower A Day Keeps The Doctor Away?
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Do Breathe – by Michael Williams
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Have you ever felt you could get everything in your life in order, if you could just get a little breathing room first?
Notwithstanding the title, this is mostly not a book about breathing exercises. It does cover that too, but there’s a lot more.
The author’s advices draw from a variety of high quality sources. Well-read readers will certainly recognise sections that are straight from David Allen’s “Getting Things Done”, and Mihaly Czikszentmihalyi’s “Flow”, for example, as well as Francesco Cirillo’s “Pomodoro Technique”, and James Clear’s “Atomic Habits”.
We also learn about how even simple yoga can help us, and good sleep, and a healthy diet.
In short, if you’ve been reading 10almonds for a while, you might not actually learn much new! But it’s very nice to have all these things in one book, for sure, and it’s a pleasant, easy read too.
Bottom line: if you’d like to streamline your life and not have to buy a whole stack of different books to do it, this book is a great composite that will enable you to get the job done efficiently.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Scarcity Brain – by Michael Easter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
After a brief overview of theevolutionary psychology underpinnings of the scarcity brain, the author grounds the rest of this book firmly in the present. He explains how the scarcity loop hooks us and why we crave more, and what factors can increase or lessen its hold over us.
As for what things we are wired to consider “potentially scarce any time now” no matter how saturated we are in them, he looks at an array of categories, each with their nuances. From the obvious such as “food” and “stuff“, to understandable “information” and “happiness“, to abstractions like “influence“, he goes to many sources—experts of various kinds from around the world—to explore how we can know “how much is enough”, and—which can be harder—act accordingly.
The key, he argues, is not in simply wanting less, but in understanding why we crave more in the first place, get rid of our worst habits, and use what we already have, better.
Bottom line: if you feel a gnawing sense of needing more “to be on the safe side”, this book can help you to be a little more strategic (and at the same time, less stressed!) about that.
Click here to check out Scarcity Brain, and manage yours more mindfully!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What’s the difference between shyness and social anxiety?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s the difference? is a new editorial product that explains the similarities and differences between commonly confused health and medical terms, and why they matter.
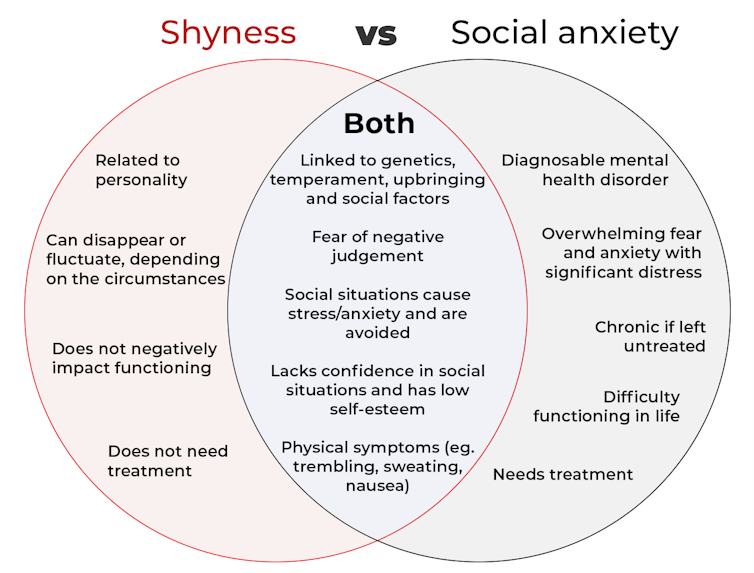
The terms “shyness” and “social anxiety” are often used interchangeably because they both involve feeling uncomfortable in social situations.
However, feeling shy, or having a shy personality, is not the same as experiencing social anxiety (short for “social anxiety disorder”).
Here are some of the similarities and differences, and what the distinction means.
pathdoc/Shutterstock How are they similar?
It can be normal to feel nervous or even stressed in new social situations or when interacting with new people. And everyone differs in how comfortable they feel when interacting with others.
For people who are shy or socially anxious, social situations can be very uncomfortable, stressful or even threatening. There can be a strong desire to avoid these situations.
People who are shy or socially anxious may respond with “flight” (by withdrawing from the situation or avoiding it entirely), “freeze” (by detaching themselves or feeling disconnected from their body), or “fawn” (by trying to appease or placate others).
A complex interaction of biological and environmental factors is also thought to influence the development of shyness and social anxiety.
For example, both shy children and adults with social anxiety have neural circuits that respond strongly to stressful social situations, such as being excluded or left out.
People who are shy or socially anxious commonly report physical symptoms of stress in certain situations, or even when anticipating them. These include sweating, blushing, trembling, an increased heart rate or hyperventilation.
How are they different?
Social anxiety is a diagnosable mental health condition and is an example of an anxiety disorder.
For people who struggle with social anxiety, social situations – including social interactions, being observed and performing in front of others – trigger intense fear or anxiety about being judged, criticised or rejected.
To be diagnosed with social anxiety disorder, social anxiety needs to be persistent (lasting more than six months) and have a significant negative impact on important areas of life such as work, school, relationships, and identity or sense of self.
Many adults with social anxiety report feeling shy, timid and lacking in confidence when they were a child. However, not all shy children go on to develop social anxiety. Also, feeling shy does not necessarily mean a person meets the criteria for social anxiety disorder.
People vary in how shy or outgoing they are, depending on where they are, who they are with and how comfortable they feel in the situation. This is particularly true for children, who sometimes appear reserved and shy with strangers and peers, and outgoing with known and trusted adults.
Individual differences in temperament, personality traits, early childhood experiences, family upbringing and environment, and parenting style, can also influence the extent to which people feel shy across social situations.
Not all shy children go on to develop social anxiety. 249 Anurak/Shutterstock However, people with social anxiety have overwhelming fears about embarrassing themselves or being negatively judged by others; they experience these fears consistently and across multiple social situations.
The intensity of this fear or anxiety often leads people to avoid situations. If avoiding a situation is not possible, they may engage in safety behaviours, such as looking at their phone, wearing sunglasses or rehearsing conversation topics.
The effect social anxiety can have on a person’s life can be far-reaching. It may include low self-esteem, breakdown of friendships or romantic relationships, difficulties pursuing and progressing in a career, and dropping out of study.
The impact this has on a person’s ability to lead a meaningful and fulfilling life, and the distress this causes, differentiates social anxiety from shyness.
Children can show similar signs or symptoms of social anxiety to adults. But they may also feel upset and teary, irritable, have temper tantrums, cling to their parents, or refuse to speak in certain situations.
If left untreated, social anxiety can set children and young people up for a future of missed opportunities, so early intervention is key. With professional and parental support, patience and guidance, children can be taught strategies to overcome social anxiety.
Why does the distinction matter?
Social anxiety disorder is a mental health condition that persists for people who do not receive adequate support or treatment.
Without treatment, it can lead to difficulties in education and at work, and in developing meaningful relationships.
Receiving a diagnosis of social anxiety disorder can be validating for some people as it recognises the level of distress and that its impact is more intense than shyness.
A diagnosis can also be an important first step in accessing appropriate, evidence-based treatment.
Different people have different support needs. However, clinical practice guidelines recommend cognitive-behavioural therapy (a kind of psychological therapy that teaches people practical coping skills). This is often used with exposure therapy (a kind of psychological therapy that helps people face their fears by breaking them down into a series of step-by-step activities). This combination is effective in-person, online and in brief treatments.
Treatment is available online as well as in-person. ImYanis/Shutterstock For more support or further reading
Online resources about social anxiety include:
- This Way Up’s online program for managing excessive shyness and fear of social situations
- Beyond Blue’s resources on social anxiety
- a guide to looking after yourself if you have social anxiety, from the Western Australian health department
- social anxiety online program for children and teens from the University of Queensland
- inroads, a self-guided online program for young adults who drink alcohol to manage their anxiety.
We thank the Black Dog Institute Lived Experience Advisory Network members for providing feedback and input for this article and our research.
Kayla Steele, Postdoctoral research fellow and clinical psychologist, UNSW Sydney and Jill Newby, Professor, NHMRC Emerging Leader & Clinical Psychologist, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Bates Method for Better Eyesight Without Glasses − by Dr. William Bates
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a very popular book and method, albeit not a very new one. It was first published in 1920; self-published by Dr. Bates, as the American Medical Association (AMA) considered it quackery.
Of course, our understanding of eyesight has improved a lot in the past 100 years, so, with the benefit of an extra century of ophthalmological research, who was on the right side of history?
As it turns out, all of Dr. Bates’ ideas have been firmly disproven, and eyes simply do not work the way he thought they do (for example, he believed that rather than adjusting the lens for focus, the muscles around the eye elongate the eyeball; this absolutely is not how focusing works, and while how much those muscles squeeze the eye does vary depending on some physiological factors, there are no known exercises that can change them).
Nevertheless, for the interested, his techniques include such things as:
- putting pressure on one’s eyes with one’s hands (which can increase glaucoma risk)
- visualization, rather than actual viewing, of an eye chart (this is ironic, because the book cover promises that an eye chart is included; it is not; perhaps it was hoped that we would visualize it more vividly and thus see it?)
- sunning, which is not only directly looking at the sun, but also using a burning glass to increase the focus of the sunlight onto one’s eye (please do not do this under any circumstances)
His primary thesis in this work, though, is that eyesight problems of all kinds (from short- and long-sightedness, to more serious things like cataracts and glaucoma) are caused by the tension produced by reading books, so relaxation exercises are his prescription for this.
The style is characteristic of its era and then some; bold claims are made with no evidence, there are no references, and the text is (ironically, given his opinions on tension being produced by reading books) quite dense. It certainly doesn’t lend itself well to skimming, for example, because something critical can easily be buried in a wall of text of what is, honestly, mostly waffle.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your eyesight and reduce your dependency on glasses, then we absolutely cannot recommend this book, and would direct you instead to Vision for Life, Revised Edition – by Dr. Meir Schneider, which is much more consistent with actual science.
Click here if you are, nonetheless, curious about Dr. Bates’ book and wish to check it out!
PS: Dr. Bates certainly was an interesting fellow; he disappeared mysteriously, but was found working as a medical assistant a few weeks later by his wife, whom he now claimed to not recognize. Then he disappeared again two days later (his wife never found him, this time, despite trying for many years), only to show up again, 13 years later, shortly after his wife’s death, whereupon he remarried (to his long-time personal assistant). None of this has anything to do with his fascinating opinions on eyesight, but it’s a story worth mentioning.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: