Cranberries vs Goji Berries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cranberries to goji berries, we picked the cranberries.
Why?
Both are great! And your priorities may differ. Here’s how they stack up:
In terms of macros, goji berries have more protein, carbs, and fiber. This is consistent with them generally being eaten very dried, whereas cranberries are more often eaten fresh or from frozen, or partially rehydrated. In any case, goji berries are the “more food per food” option, so it wins this category. The glycemic indices are both low, by the way, though goji berries are the lower.
When it comes to vitamins, cranberries have more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, E, K, and choline, while goji berries have more of vitamins A and C. Admittedly it’s a lot more, but still, on strength of overall vitamin coverage, the clear winner here is cranberries.
We see a similar story when it comes to minerals: cranberries have more copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while goji berries have (a lot) more calcium and iron. Again, by strength of overall mineral coverage, the clear winner here is cranberries.
Cranberries do also have some extra phytochemical benefits, including their prevention/cure status when it comes to UTIs—see our link below for more on that.
At any rate, enjoy either or both, but those are the strengths and weaknesses of these two berries!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Health Benefits Of Cranberries (But: You’d Better Watch Out)
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- The Sugary Food That Lowers Blood Sugars ← this is also about goji berries
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Pasteurization: What It Does And Doesn’t Do
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pasteurization’s Effect On Risks & Nutrients
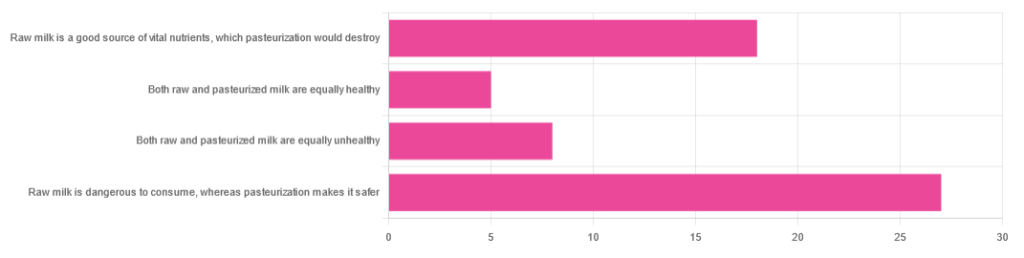
In Wednesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your health-related opinions of raw (cow’s) milk, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 47% said “raw milk is dangerous to consume, whereas pasteurization makes it safer”
- About 31% said “raw milk is a good source of vital nutrients which pasteurization would destroy”
- About 14% said “both raw milk and pasteurized milk are equally unhealthy”
- About 9% said “both raw milk and pasteurized milk are equally healthy”
Quite polarizing! So, what does the science say?
“Raw milk is dangerous to consume, whereas pasteurization makes it safer: True or False?”
True! Coincidentally, the 47% who voted for this are mirrored by the 47% of the general US population in a similar poll, deciding between the options of whether raw milk is less safe to drink (47%), just as safe to drink (15%), safer to drink (9%), or not sure (30%):
Public Fails to Appreciate Risk of Consuming Raw Milk, Survey Finds
As for what those risks are, by the way, unpasteurized dairy products are estimated to cause 840x more illness and 45x more hospitalizations than pasteurized products.
This is because unpasteurized milk can (and often does) contain E. coli, Listeria, Salmonella, Cryptosporidium, and other such unpleasantries, which pasteurization kills.
Source for both of the above claims:
(we know the title sounds vague, but all this information is easily visible in the abstract, specifically, the first two paragraphs)
Raw milk is a good source of vital nutrients which pasteurization would destroy: True or False?
False! Whether it’s a “good” source can be debated depending on other factors (e.g., if we considered milk’s inflammatory qualities against its positive nutritional content), but it’s undeniably a rich source. However, pasteurization doesn’t destroy or damage those nutrients.
Incidentally, in the same survey we linked up top, 16% of the general US public believed that pasteurization destroys nutrients, while 41% were not sure (and 43% knew that it doesn’t).
Note: for our confidence here, we are skipping over studies published by, for example, dairy farming lobbies and so forth. Those do agree, by the way, but nevertheless we like sources to be as unbiased as possible. The FDA, which is not completely unbiased, has produced a good list of references for this, about half of which we would consider biased, and half unbiased; the clue is generally in the journal names. For example, Food Chemistry and the Journal of Food Science and Journal of Nutrition are probably less biased than the International Dairy Association and the Journal of Dairy Science:
FDA | Raw Milk Misconceptions and the Danger of Raw Milk Consumption
this page covers a lot of other myths too, more than we have room to “bust” here, but it’s very interesting reading and we recommend to check it out!
Notably, we also weren’t able to find any refutation by counterexample on PubMed, with the very slight exception that some studies sometimes found that in the case of milks that were of low quality, pasteurization can reduce the vitamin E content while increasing the vitamin A content. For most milks however, no significant change was found, and in all cases we looked at, B-vitamins were comparable and vitamin D, popularly touted as a benefit of cow’s milk, is actually added later in any case. And, importantly, because this is a common argument, no change in lipid profiles appears to be findable either.
In science, when something has been well-studied and there aren’t clear refutations by counterexample, and the weight of evidence is clearly very much tipped into one camp, that usually means that camp has it right.
Milk generally is good/bad for the health: True or False?
True or False, depending on what we want to look at. It’s definitely not good for inflammation, but the whole it seems to be cancer-neutral and only increases heart disease risk very slightly:
- Keep Inflammation At Bay ← short version is milk is bad, fermented milk products are fine in moderation
- Is Dairy Scary? ← short version is that milk is neither good nor terrible; fermented dairy products however are health-positive in numerous ways when consumed in moderation
You may be wondering…
…how this goes for the safety of dairy products when it comes to the bird flu currently affecting dairy cows, so:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Blind Spots – by Dr. Marty Makary
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From the time the US recommended not giving peanuts to infants for the first three years of life “in order to avoid peanut allergies” (whereupon non-exposure to peanuts early in life led to, instead, an increase in peanut allergies and anaphylactic incidents), to the time the US recommended not taking HRT on the strength of the claim that “HRT causes breast cancer” (whereupon the reduced popularity of HRT led to, instead, an increase in breast cancer incidence and mortality), to many other such incidents of very bad public advice being given on the strength of a single badly-misrepresented study (for each respective thing), Dr. Makary puts the spotlight on what went wrong.
This is important, because this is not just a book of outrage, exclaiming “how could this happen?!”, but rather instead, is a book of inquisition, asking “how did this happen?”, in such a way that we the reader can spot similar patterns going forwards.
Oftentimes, this is a simple matter of having a basic understanding of statistics, and checking sources to see if the dataset really supports what the headlines are claiming—and indeed, whether sometimes it suggests rather the opposite.
The style is a little on the sensationalist side, but it’s well-supported with sound arguments, good science, and clear mathematics.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your scientific literacy, this book is an excellent illustrative guide.
Share This Post
-
Stop Checking Your Likes – by Susie Moore
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You might think this one’s advice is summed up sufficiently by the title, that there’s no need for a book! But…
There’s a lot more to this than “stop comparing the worst out-takes of your life to someone else’s highlight reel”, and there’s a lot more to this than “just unplug”.
Instead, Susie Moore discusses the serious underlying real emotional considerations of the need for approval (and even just acceptance) by our community, as well the fear of missing out.
It’s not just about how social media is designed to hijack various parts of our brain, or how The Alogorithm™ is out to personally drag your soul through Hell for a few more clicks; it’s also about the human element that would exist even without that. Who remembers MySpace? No algorithm in those days, but oh the drama potential for those “top 8 friends” places. And if you think that kind of problem is just for young people 20 years ago, you have mercifully missed the drama that older generations can get into on Facebook.
Along with the litany of evil, though, Moore also gives practical advice on how to overcome those things, how to “see the world through comedy-colored glasses”, how to ask “what’s missing, really?”, and how to make your social media experience work for you, rather than it merely using you as fuel. ← link is to our own related article!
Bottom line: if social media sucks a lot of your time, there may be more to it than just “social media sucks in general”, and there are ways to meet your emotional needs without playing by corporations’ rules to do so.
Click here to check out Stop Checking Your Likes, and breathe easy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Indistractable – by Nir Eyal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Have you ever felt that you could accomplish anything you wanted/needed, if only you didn’t get distracted?
This book lays out a series of psychological interventions for precisely that aim, and it goes a lot beyond the usual “download/delete these apps to help you stop checking social media every 47 seconds”.
Some you’ll have heard of before, some you won’t have, and if even one method works for you, it’ll have been well worth your while reading this book. This reviewer, for example, enjoyed the call to identity-based strength, e.g. adopting an “I am indistractable*” perspective going into tasks. This is akin to the strength of, for example, “I don’t drink” over “I am a recovering alcoholic”.
*the usual spelling of this, by the way, is “undistractable”, but we use the author’s version here for consistency. It’s a great marketing gimmick, as all searches for the word “indistractable” will bring up his book.
Nor is the book just about maximizing productivity to the detriment of everything else; this is not about having a 25 hours per day “grindset”. Rather, it even makes sure to cover such things as focusing on one’s loved ones, for instance.
Bottom line: if you’ve tried blocking out the distractions but still find you can’t focus, this book offers next-level solutions
Click here to check out Indistractible, and become indeed indistractable!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Mastering Gut Health for Women – by Karín Feltman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author, a registered nurse, has a focus on holistic health, and in this book it’s all about wellness from the inside out.
To effect this, she lays out a 12-week program of transformations:
- Week 1: transform your knowledge
- Week 2: transform your brain
- Week 3: transform your digestion
- Week 4: transform your immunity
- Week 5: transform your emotions
- Week 6: transform your sleep
- Week 7: transform your energy/vitality
- Week 8: transform your activity
- Week 9: transform your hormones
- Week 10: transform your diet
- Week 11: transform your weight
- Week 12: transform your habits
Which all adds up to quite a comprehensive overall transformation!
Of course, it’s possible you might want to implement everything at once; an exciting prospect for sure, but oftentimes it really is best to just change one thing at once before moving on; that way it’s a lot more likely to stick, and that’s why she presents it in this format.
On the other hand, maybe you might want to take longer than the 12 weeks, if for example it takes you more than a week to do a certain part. That’s fine too, though for most people without serious constraints (or suffering some unexpected major interruption to your usual life), the 12-week program should be quite doable as-is.
The style is personable and friendly, albeit with frequent references to science and appropriate citations.
Bottom line: the title centers gut health, and so does the book itself, but this is truly a holistic approach that goes far beyond the gut, which makes it even more worthwhile.
Click here to check out Mastering Gut Health For Women, and master gut health for yourself!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Walk Like You’re 20 Years Younger Again
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How fit, healthy, strong, and mobile were you 20 years ago? For most people, the answer is “better than now”. Physiotherapist Dr. Doug Weiss has advice on turning back the clock:
The exercises
If you already have no problems walking, this one is probably not for you. However, if you’re not so able to comfortably walk as you used to be, then Dr. Weiss recommends:
- Pillow squat: putting pillow on a chair, crossing hands on chest, standing up and sitting down. Similar to the very important “getting up off the floor without using your hands” exercise, but easier.
- Wall leaning: standing against a wall with heels 4″ away from it, crossing arms over chest again, and pulling the body off the wall using the muscles in the front of the shin. Note, this means not cheating by using other muscles, leveraging the upper body, pushing off with the buttocks, or anything else like that.
- Stepping forward: well, this certainly is making good on the promise of walking like we did 20 years ago; there sure was a lot of stepping forward involved. More seriously, this is actually about stepping over some object, first with support, and then without.
- Heel raise: is what it sounds like, raising up on toes and back down again; first with support, then without.
- Side stepping: step sideways 2–3 steps in each direction. First with support, then without. Bonus: if your support is your partner, then congratulations, you are now dancing bachata.
For more details (and visual demonstration) of these exercises and more, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
4 Tips To Stand Without Using Hands
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: