Celery vs Radish – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing celery to radish, we picked the celery.
Why?
It was very close! And yes, surprising, we know. Generally speaking, the more colorful/pigmented an edible plant is, the healthier it is. Celery is just one of those weird exceptions (as is cauliflower, by the way).
Macros-wise, these two are pretty much the same—95% water, with just enough other stuff to hold them together. The proportions of “other stuff” are also pretty much equal.
In the category of vitamins, celery has more vitamin K while radish has more vitamin C; the other vitamins are pretty close to equal. We’ll call this one a minor win for celery, as vitamin K is found in fewer foods than vitamin C.
When it comes to minerals, celery has more calcium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium, while radish has more copper, iron, selenium, and zinc. We’ll call this a minor win for radish, as the margins are a little wider for its minerals.
So, that makes the score 1–1 so far.
Both plants have an assortment of polyphenols, of which, when we add up the averages, celery comes out on top by some way. Celery also comes out on top when we do a head-to-head of the top flavonoid of each; celery has 5.15mg/100g of apigenin to radish’s 0.63mg/100g kaempferol.
Which means, both are great healthy foods, but celery wins the day.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Celery vs Cucumber – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Things Many People Forget When It Comes To Hydration
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Good hydration is about more than just “drink lots of water”, and in fact it’s quite possible for a person to drink too much water, and at the same time, be dehydrated. Here’s how and why and what to do about it:
Water, water, everywhere
Factors that people forget:
- Electrolyte balance: without it, we can technically have lots of water while either retaining it (in the case of too high salt levels) or peeing it out (in the case of too low salt levels), neither of which are as helpful as getting it right and actually being able to use the water.
- Gastrointestinal health: conditions like IBS, Crohn’s, or celiac disease can impair water and nutrient absorption, affecting hydration
- Genetic factors: some people simply have a predisposition to need more or less water for proper hydration
- Dietary factors: high salt, caffeine, and alcohol intake (amongst other diuretics) can increase water loss, while water-rich foods (assuming they aren’t also diuretics) increase hydration.
Strategies to do better:
- Drink small amounts of water consistently throughout the day rather than large quantities at once—healthy kidneys can process about 1 liter (about 1 quart) of water per hour, so drinking more than that will not help, no matter how dehydrated you are when you start. If your kidneys aren’t in peak health, the amount processable per hour will be lower for you.
- Increase fiber intake (e.g., fruit and vegetables) to retain water in the intestines and improve hydration
- Consume water-rich foods (e.g., watermelon, cucumbers, grapes) to enhance overall hydration and support cellular function (the body can use this a lot more efficiently than if you just drink water).
- Counteract the diuretic effects of caffeine and alcohol by drinking an additional 12 oz of water for every 8 oz of these beverages. Best yet, don’t drink alcohol and keep caffeine to a low level (or quit entirely, if you prefer, but for most people that’s not necessary).
- If you are sweating (be it because of weather, exercise, or any other reasons), include electrolyte fluids to improve cellular hydration, as they contain essential minerals like magnesium, potassium, and in moderation yes even sodium which you will have lost in your sweat too, supporting fluid regulation.
For more details on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Water’s Counterintuitive Properties
- Hydration Mythbusting
- When To Take Electrolytes (And When We Shouldn’t!)
- Keeping Your Kidneys Healthy (Especially After 60)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Dopamine Myth
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Dopamine Myth
There’s a popular misconception that, since dopamine is heavily involved in addictions, it’s the cause.
We see this most often in the context of non-chemical addictions, such as:
- gambling
- videogames
- social media
And yes, those things will promote dopamine production, and yes, that will feel good. But dopamine isn’t the problem.
Myth: The Dopamine Detox
There’s a trend we’ve mentioned before (it got a video segment a few Fridays back) about the idea of a “dopamine detox“, and how unscientific the idea is.
For a start…
- You cannot detox from dopamine, because dopamine is not a toxin
- You cannot abstain from dopamine, because your brain regulates your dopamine levels to keep them correct*
- If you could abstain from dopamine (and did), you would die, horribly.
*unless you have a serious mental illness, for example:
- forms of schizophrenia and/or psychosis that involve too much dopamine, or
- forms of depression and/or neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s (and several kinds of dementia) in which you have too little dopamine
- bipolar disorder in which dopamine levels can swing too far each way
See also: Dopamine fasting: misunderstanding science spawns a maladaptive fad
Myth: Dopamine is all about pleasure
Dopamine is a pleasure-giving neurotransmitter, but it serves more purposes than that! It also plays a central role in many neurological processes, including:
- Motivation
- Learning and memory
- Motor functions
- Language faculties
- Linear task processing
Note for example how someone taking dopaminergic drugs (prescription or otherwise; could be anything from modafinil to cocaine) is not blissed out… They’re probably in a good mood, sure, but they’re focused, organized, quick-thinking, and so forth! This is not an ad for cocaine; cocaine is very bad for the health. But you see the features? So, what if we could have a little more dopamine… healthily?
Dopamine—à la carte
Let’s look at the examples we gave earlier of non-chemical addictions that are dopaminergic in nature:
- gambling
- videogames
- social media
They’re not actually that rewarding, are they?
- Gamblers lose more than they win
- Gamers cease to care about a game once they have won
- Social media more often results in “doomscrolling”
This is because what prompts the most dopamine is actually the anticipation of reward… not the thing itself, whose reward-pleasure is very fleeting. Nobody looks back at an hour of doomscrolling and thinks “well, that was fun; I’m glad I did that”.
See the science: Liking, Wanting and the Incentive-Sensitization Theory of Addiction
But what if we anticipated a reward from things that are not deleterious to health and productivity? Things that are neutral, or even good for us?
Examples of this include:
- Sex! (remember though, it’s not a race to the finish-line)
- Good, nourishing food (bonus: some foods boost dopamine production nutritionally)
- Exercise/sport (also prompts release of endorphins, win/win!)
- Gamified learning apps (e.g. Duolingo)
- Gamified health/productivity apps (anything with bells and whistles and things that go “ding” and measure streaks etc)
Want to know more?
That’s all we have time for today, but you might want to check out:
10 Best Ways to Increase Dopamine Levels Naturally ← Science-based and well-sourced article!
Share This Post
-
Why do some people’s hair and nails grow quicker than mine?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Throughout recorded history, our hair and nails played an important role in signifying who we are and our social status. You could say, they separate the caveman from businessman.
It was no surprise then that many of us found a new level of appreciation for our hairdressers and nail artists during the COVID lockdowns. Even Taylor Swift reported she cut her own hair during lockdown.
So, what would happen if all this hair and nail grooming got too much for us and we decided to give it all up. Would our hair and nails just keep on growing?
The answer is yes. The hair on our head grows, on average, 1 centimeter per month, while our fingernails grow an average of just over 3 millimetres.
When left unchecked, our hair and nails can grow to impressive lengths. Aliia Nasyrova, known as the Ukrainian Rapunzel, holds the world record for the longest locks on a living woman, which measure an impressive 257.33 cm.
When it comes to record-breaking fingernails, Diana Armstrong from the United States holds that record at 1,306.58 cm.
Most of us, however, get regular haircuts and trim our nails – some with greater frequency than others. So why do some people’s hair and nails grow more quickly?
Jari Lobo/Pexels Remind me, what are they made out of?
Hair and nails are made mostly from keratin. Both grow from matrix cells below the skin and grow through different patterns of cell division.
Nails grow steadily from the matrix cells, which sit under the skin at the base of the nail. These cells divide, pushing the older cells forward. As they grow, the new cells slide along the nail bed – the flat area under the fingernail which looks pink because of its rich blood supply.
Nails, like hair, are made mostly of keratin. Scott Gruber/Unsplash A hair also starts growing from the matrix cells, eventually forming the visible part of the hair – the shaft. The hair shaft grows from a root that sits under the skin and is wrapped in a sac known as the hair follicle.
This sac has a nerve supply (which is why it hurts to pull out a hair), oil-producing glands that lubricate the hair and a tiny muscle that makes your hair stand up when it’s cold.
At the follicle’s base is the hair bulb, which contains the all-important hair papilla that supplies blood to the follicle.
Matrix cells near the papilla divide to produce new hair cells, which then harden and form the hair shaft. As the new hair cells are made, the hair is pushed up above the skin and the hair grows.
But the papilla also plays an integral part in regulating hair growth cycles, as it sends signals to the stem cells to move to the base of the follicle and form a hair matrix. Matrix cells then get signals to divide and start a new growth phase.
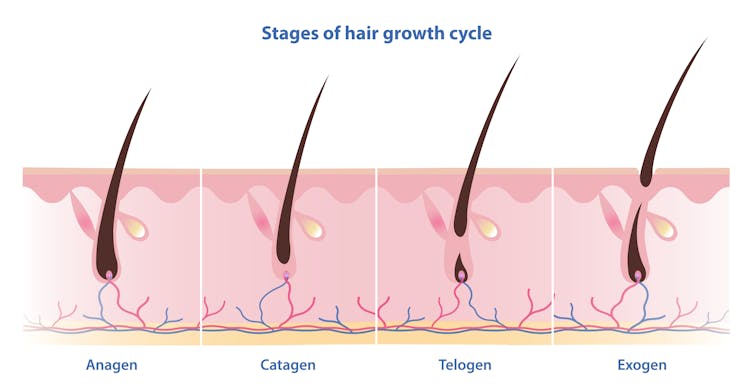
Unlike nails, our hair grows in cycles
Scientists have identified four phases of hair growth, the:
- anagen or growth phase, which lasts between two and eight years
- catagen or transition phase, when growth slows down, lasting around two weeks
- telogen or resting phase, when there is no growth at all. This usually lasts two to three months
- exogen or shedding phase, when the hair falls out and is replaced by the new hair growing from the same follicle. This starts the process all over again.
Hair follicles enter these phases at different times so we’re not left bald. Mosterpiece/Shutterstock Each follicle goes through this cycle 10–30 times in its lifespan.
If all of our hair follicles grew at the same rate and entered the same phases simultaneously, there would be times when we would all be bald. That doesn’t usually happen: at any given time, only one in ten hairs is in the resting phase.
While we lose about 100–150 hairs daily, the average person has 100,000 hairs on their head, so we barely notice this natural shedding.
So what affects the speed of growth?
Genetics is the most significant factor. While hair growth rates vary between individuals, they tend to be consistent among family members.
Nails are also influenced by genetics, as siblings, especially identical twins, tend to have similar nail growth rates.
Genetics have the biggest impact on growth speed. Cottonbro Studio/Pexels But there are also other influences.
Age makes a difference to hair and nail growth, even in healthy people. Younger people generally have faster growth rates because of the slowing metabolism and cell division that comes with ageing.
Hormonal changes can have an impact. Pregnancy often accelerates hair and nail growth rates, while menopause and high levels of the stress hormone cortisol can slow growth rates.
Nutrition also changes hair and nail strength and growth rate. While hair and nails are made mostly of keratin, they also contain water, fats and various minerals. As hair and nails keep growing, these minerals need to be replaced.
That’s why a balanced diet that includes sufficient nutrients to support your hair and nails is essential for maintaining their health.
Nutrition can impact hair and nail growth. Cottonbro Studio/Pexels Nutrient deficiencies may contribute to hair loss and nail breakage by disrupting their growth cycle or weakening their structure. Iron and zinc deficiencies, for example, have both been linked to hair loss and brittle nails.
This may explain why thick hair and strong, well-groomed nails have long been associated with perception of good health and high status.
However, not all perceptions are true.
No, hair and nails don’t grow after death
A persistent myth that may relate to the legends of vampires is that hair and nails continue to grow after we die.
In reality, they only appear to do so. As the body dehydrates after death, the skin shrinks, making hair and nails seem longer.
Morticians are well aware of this phenomenon and some inject tissue filler into the deceased’s fingertips to minimise this effect.
So, it seems that living or dead, there is no escape from the never-ending task of caring for our hair and nails.
Michelle Moscova, Adjunct Associate Professor, Anatomy, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Farmed Fish vs Wild Caught
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Is it good to eat farm raised fish?❞
We’ll answer this as a purely health-related question (and thus not considering economy, ecology, ethics, or taste).
It’s certainly not as good as wild-caught fish, for several reasons, some more serious than others:
Farmed fish can have quite a different nutritional profile to wild-caught fish, and also contain more contaminants, including heavy metals.
For example, farmed fish tend to have much higher fat content for the same amount of protein, but lower levels of minerals and other nutrients. Here are two side-by-side:
Wild-caught salmon | Farmed salmon
See also:
Quantitative analysis of the benefits and risks of consuming farmed and wild salmon
Additionally, because fish in fish farms tend to be very susceptible to diseases (because of the artificially cramped and overcrowded environment), fish farms tend to make heavy use of antibiotics, which can cause all sorts of problems down the line:
So definitely, “let the buyer beware”!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The BAT-pause!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When Cold Weather & The Menopause Battle It Out
You may know that (moderate, safe) exposure to the cold allows our body to convert our white and yellow fat into the much healthier brown fat—also called brown adipose tissue, or “BAT” to its friends.
If you didn’t already know that, then well, neither did scientists until about 15 years ago:
The Changed Metabolic World with Human Brown Adipose Tissue: Therapeutic Visions
You can read more about it here:
Cool Temperature Alters Human Fat and Metabolism
This is important, especially because the white fat that gets converted is the kind that makes up most visceral fat—the kind most associated with all-cause mortality:
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It ← this is not the same as your subcutaneous fat, the kind that sits directly under your skin and keeps you warm; this is the fat that goes between your organs and of which we should only have a small amount!
The BAT-pause
It’s been known (since before the above discovery) that BAT production slows considerably as we get older. Not too shocking—after all, many metabolic functions slow as we get older, so why should fat regulation be any different?
But! Rodent studies found that this was tied less to age, but to ovarian function: rats who underwent ovariectomies suffered reduced BAT production, regardless of their age.
Naturally, it’s been difficult to recreate such studies in humans, because it’s difficult to find a large sample of young adults willing to have their ovaries whipped out (or even suppressed chemically) to see how badly their metabolism suffers as a result.
Nor can an observational study (for example, of people who incidentally have ovaries removed due to ovarian cancer) usefully be undertaken, because then the cancer itself and any additional cancer treatments would be confounding factors.
Perimenopausal study to the rescue!
A recent (published last month, at time of writing!) study looked at women around the age of menopause, but specifically in cohorts before and after, measuring BAT metabolism.
By dividing the participants into groups based on age and menopausal status, and dividing the post-menopausal group into “takes HRT” and “no HRT” groups, and dividing the pre-menopausal group into “normal ovarian function” and “ovarian production of estrogen suppressed to mimic slightly early menopause” groups (there’s a drug for that), and then having groups exposed to warm and cold temperatures, and measuring BAT metabolism in all cases, they were able to find…
It is about estrogen, not age!
You can read more about the study here:
“Good” fat metabolism changes tied to estrogen loss, not necessarily to aging, shows study
…and the study itself, here:
Brown adipose tissue metabolism in women is dependent on ovarian status
What does this mean for men?
This means nothing directly for (cis) men, sorry.
But to satisfy your likely curiosity: yes, testosterone does at least moderately suppress BAT metabolism—based on rodent studies, anyway, because again it’s difficult to find enough human volunteers willing to have their testicles removed for science (without there being other confounding variables in play, anyway):
Testosterone reduces metabolic brown fat activity in male mice
So, that’s bad per se, but there isn’t much to be done about it, since the rest of your (addressing our male readers here) metabolism runs on testosterone, as do many of your bodily functions, and you would suffer many unwanted effects without it.
However, as men do typically have notably less body fat in general than women (this is regulated by hormones), the effects of changes in BAT metabolism are rather less pronounced in men (per testosterone level changes) than in women (per estrogen level changes), because there’s less overall fat to convert.
In summary…
While menopausal HRT is not necessarily a silver bullet to all metabolic problems, its BAT-maintaining ability is certainly one more thing in its favor.
See also:
Dr. Jen Gunter | What You Should Have Been Told About The Menopause Beforehand
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Pine Nuts vs Pecans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pine nuts to pecans, we picked the pine nuts.
Why?
Both have their merits!
In terms of macros, pine nuts have more protein while pecans have more fiber. They’re about equal on fats, although pine nuts have more polyunsaturated fat and pecans have more monounsaturated fat, of which, both are healthy. They’re also about equal on carbs. So really it comes down to the subjective choice between prioritizing protein and prioritizing fiber. On principle, we pick fiber, which gives the win to pecans, but your preference in this regard may differ; prioritizing the protein would give the win to pine nuts.
In the category of vitamins, pine nuts have more of vitamins B2, B3, B9, E, K, and choline, while pecans have more of vitamins A, B1, B5, B6, and C. Thus, a 6:5 marginal win for pine nuts.
Looking at the minerals, pine nuts have more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while pecans have more calcium and selenium. An easy win for pine nuts this time.
Adding up the sections makes for a win for pine nuts, but of course, enjoy either or (preferably) both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: