Calm Your Inflammation – by Dr. Brenda Tidwell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The book starts with an overview of inflammation, both acute and chronic, before diving into how to reduce the latter kind (acute inflammation being usually necessary and helpful, usually fighting disease rather than creating it).
The advice in the book is not just dietary, and covers lifestyle interventions too, including exercise etc—and how to strike the right balance, since the wrong kind of exercise or too much of it can sabotage our efforts. Similarly, Dr. Tidwell doesn’t just say such things as “manage stress” but also provides 10 ways of doing so, and so forth for other vectors of inflammation-control. She does cover dietary things as well though, including supplements where applicable, and the role of gut health, sleep, and other factors.
The style of the book is quite entry-level pop-science, designed to be readable and comprehensible to all, without unduly dumbing-down. In terms of hard science or jargon, there are 6 pages of bibliography and 3 pages of glossary, so it’s neither devoid of such nor overwhelmed by it.
Bottom line: if fighting inflammation is a priority for you, then this book is an excellent primer.
Click here to check out Calm Your Inflammation, and indeed calm your inflammation!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Food and exercise can treat depression as well as a psychologist, our study found. And it’s cheaper
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Around 3.2 million Australians live with depression.
At the same time, few Australians meet recommended dietary or physical activity guidelines. What has one got to do with the other?
Our world-first trial, published this week, shows improving diet and doing more physical activity can be as effective as therapy with a psychologist for treating low-grade depression.
Previous studies (including our own) have found “lifestyle” therapies are effective for depression. But they have never been directly compared with psychological therapies – until now.
Amid a nation-wide shortage of mental health professionals, our research points to a potential solution. As we found lifestyle counselling was as effective as psychological therapy, our findings suggest dietitians and exercise physiologists may one day play a role in managing depression.
Alexander Raths/shutterstock What did our study measure?
During the prolonged COVID lockdowns, Victorians’ distress levels were high and widespread. Face-to-face mental health services were limited.
Our trial targeted people living in Victoria with elevated distress, meaning at least mild depression but not necessarily a diagnosed mental disorder. Typical symptoms included feeling down, hopeless, irritable or tearful.
We partnered with our local mental health service to recruit 182 adults and provided group-based sessions on Zoom. All participants took part in up to six sessions over eight weeks, facilitated by health professionals.
Half were randomly assigned to participate in a program co-facilitated by an accredited practising dietitian and an exercise physiologist. That group – called the lifestyle program – developed nutrition and movement goals:
Lifestyle therapy aims to improve diet. Jonathan Borba/Pexels - eating a wide variety of foods
- choosing high-fibre plant foods
- including high quality fats
- limiting discretionary foods, such as those high in saturated fats and added sugars
- doing enjoyable physical activity.
The second group took part in psychotherapy sessions convened by two psychologists. The psychotherapy program used cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT), the gold standard for treating depression in groups and when delivered remotely.
In both groups, participants could continue existing treatments (such as taking antidepressant medication). We gave both groups workbooks and hampers. The lifestyle group received a food hamper, while the psychotherapy group received items such as a colouring book, stress ball and head massager.
Lifestyle therapies just as effective
We found similar results in each program.
At the trial’s beginning we gave each participant a score based on their self-reported mental health. We measured them again at the end of the program.
Over eight weeks, those scores showed symptoms of depression reduced for participants in the lifestyle program (42%) and the psychotherapy program (37%). That difference was not statistically or clinically meaningful so we could conclude both treatments were as good as each other.
There were some differences between groups. People in the lifestyle program improved their diet, while those in the psychotherapy program felt they had increased their social support – meaning how connected they felt to other people – compared to at the start of the treatment.
Participants in both programs increased their physical activity. While this was expected for those in the lifestyle program, it was less expected for those in the psychotherapy program. It may be because they knew they were enrolled in a research study about lifestyle and subconsciously changed their activity patterns, or it could be a positive by-product of doing psychotherapy.
People in both groups reported doing more physical activity. fongbeerredhot/Shutterstock There was also not much difference in cost. The lifestyle program was slightly cheaper to deliver: A$482 per participant, versus $503 for psychotherapy. That’s because hourly rates differ between dietitians and exercise physiologists, and psychologists.
What does this mean for mental health workforce shortages?
Demand for mental health services is increasing in Australia, while at the same time the workforce faces worsening nation-wide shortages.
Psychologists, who provide about half of all mental health services, can have long wait times. Our results suggest that, with the appropriate training and guidelines, allied health professionals who specialise in diet and exercise could help address this gap.
Lifestyle therapies can be combined with psychology sessions for multi-disciplinary care. But diet and exercise therapies could prove particularly effective for those on waitlists to see a psychologists, who may be receiving no other professional support while they wait.
Many dietitians and exercise physiologists already have advanced skills and expertise in motivating behaviour change. Most accredited practising dietitians are trained in managing eating disorders or gastrointestinal conditions, which commonly overlap with depression.
There is also a cost argument. It is overall cheaper to train a dietitian ($153,039) than a psychologist ($189,063) – and it takes less time.
Potential barriers
Australians with chronic conditions (such as diabetes) can access subsidised dietitian and exercise physiologist appointments under various Medicare treatment plans. Those with eating disorders can also access subsidised dietitian appointments. But mental health care plans for people with depression do not support subsidised sessions with dietitians or exercise physiologists, despite peak bodies urging them to do so.
Increased training, upskilling and Medicare subsidies would be needed to support dietitians and exercise physiologists to be involved in treating mental health issues.
Our training and clinical guidelines are intended to help clinicians practising lifestyle-based mental health care within their scope of practice (activities a health care provider can undertake).
Future directions
Our trial took place during COVID lockdowns and examined people with at least mild symptoms of depression who did not necessarily have a mental disorder. We are seeking to replicate these findings and are now running a study open to Australians with mental health conditions such as major depression or bipolar disorder.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14.
Adrienne O’Neil, Professor, Food & Mood Centre, Deakin University and Sophie Mahoney, Associate Research Fellow, Food and Mood Centre, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
You can train your nose – and 4 other surprising facts about your sense of smell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Would you give up your sense of smell to keep your hair? What about your phone?
A 2022 US study compared smell to other senses (sight and hearing) and personally prized commodities (including money, a pet or hair) to see what people valued more.
The researchers found smell was viewed as much less important than sight and hearing, and valued less than many commodities. For example, half the women surveyed said they’d choose to keep their hair over sense of smell.
Smell often goes under the radar as one of the least valued senses. But it is one of the first sensory systems vertebrates developed and is linked to your mental health, memory and more.
Here are five fascinating facts about your olfactory system.
DimaBerlin/Shutterstock 1. Smell is linked to memory and emotion
Why can the waft of fresh baking trigger joyful childhood memories? And why might a certain perfume jolt you back to a painful breakup?
Smell is directly linked to both your memory and emotions. This connection was first established by American psychologist Donald Laird in 1935 (although French novelist Marcel Proust had already made it famous in his reverie about the scent of madeleines baking.)
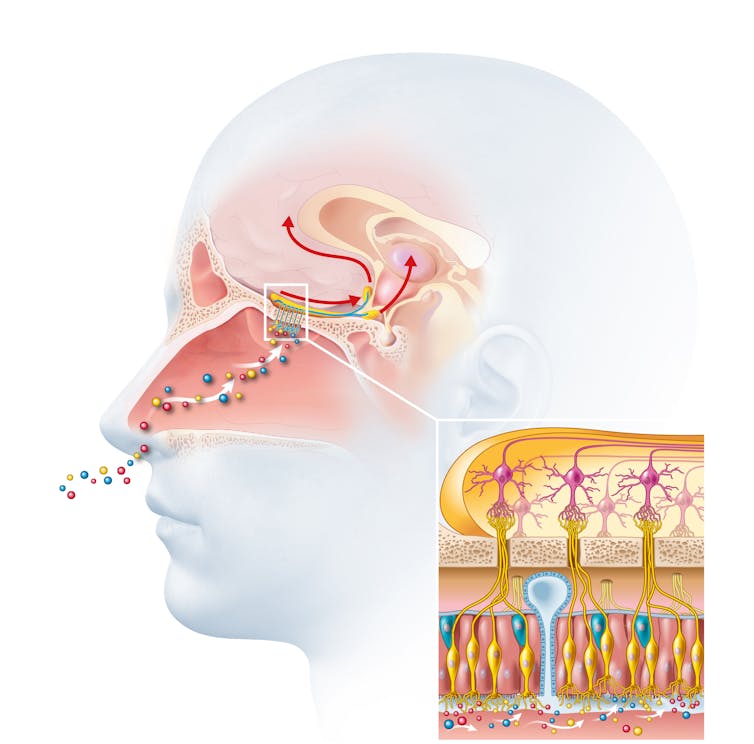
Odours are first captured by special olfactory nerve cells inside your nose. These cells extend upwards from the roof of your nose towards the smell-processing centre of your brain, called the olfactory bulb.
Smells are first detected by nerve cells in the nose. Axel_Kock/Shutterstock From the olfactory bulb they form direct connection with the brain’s limbic system. This includes the amygdala, where emotions are generated, and the hippocampus, where memories are created.
Other senses – such as sight and hearing – aren’t directly connected to the lymbic system.
One 2004 study used functional magnetic resonance imaging to demonstrate odours trigger a much stronger emotional and memory response in the brain than a visual cue.
2. Your sense of smell constantly regenerates
You can lose your ability to smell due to injury or infection – for example during and after a COVID infection. This is known as olfactory dysfunction. In most cases it’s temporary, returning to normal within a few weeks.
This is because every few months your olfactory nerve cells die and are replaced by new cells.
We’re not entirely sure how this occurs, but it likely involves your nose’s stem cells, the olfactory bulb and other cells in the olfactory nerves.
Other areas of your nervous system – including your brain and spinal cord – cannot regenerate and repair after an injury.
Constant regeneration may be a protective mechanism, as the olfactory nerves are vulnerable to damage caused by the external environment, including toxins (such as cigarette smoke), chemicals and pathogens (such as the flu virus).
But following a COVID infection some people might continue to experience a loss of smell. Studies suggest the virus and a long-term immune response damages the cells that allow the olfactory system to regenerate.
3. Smell is linked to mental health
Around 5% of the global population suffer from anosmia – total loss of smell. An estimated 15-20% suffer partial loss, known as hyposmia.
Given smell loss is often a primary and long-term symptom of COVID, these numbers are likely to be higher since the pandemic.
Yet in Australia, the prevalence of olfactory dysfunction remains surprisingly understudied.
Losing your sense of smell is shown to impact your personal and social relationships. For example, it can mean you miss out on shared eating experiences, or cause changes in sexual desire and behaviour.
In older people, declining ability to smell is associated with a higher risk of depression and even death, although we still don’t know why.
Losing your sense of smell can have a major impact on mental health. Halfpoint/Shutterstock 4. Loss of smell can help identify neurodegenerative diseases
Partial or full loss of smell is often an early indicator for a range of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
Patients frequently report losing their sense of smell years before any symptoms show in body or brain function. However many people are not aware they are losing their sense of smell.
There are ways you can determine if you have smell loss and to what extent. You may be able to visit a formal smell testing centre or do a self-test at home, which assesses your ability to identify household items like coffee, wine or soap.
5. You can train your nose back into smelling
“Smell training” is emerging as a promising experimental treatment option for olfactory dysfunction. For people experiencing smell loss after COVID, it’s been show to improve the ability to detect and differentiate odours.
Smell training (or “olfactory training”) was first tested in 2009 in a German psychology study. It involves sniffing robust odours — such as floral, citrus, aromatic or fruity scents — at least twice a day for 10—20 seconds at a time, usually over a 3—6 month period.
Participants are asked to focus on the memory of the smell while sniffing and recall information about the odour and its intensity. This is believed to help reorganise the nerve connections in the brain, although the exact mechanism behind it is unclear.
Some studies recommend using a single set of scents, while others recommend switching to a new set of odours after a certain amount of time. However both methods show significant improvement in smelling.
This training has also been shown to alleviate depressive symptoms and improve cognitive decline both in older adults and those suffering from dementia.
Just like physiotherapy after a physical injury, olfactory training is thought to act like rehabilitation for your sense of smell. It retrains the nerves in your nose and the connections it forms within the brain, allowing you to correctly detect, process and interpret odours.
Lynn Nazareth, Research Scientist in Olfactory Biology, CSIRO
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
The Silent Struggle – by L. William Ross-Child, MLC
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The vast majority of literature out there about ADHD is about children. And fair enough, there are enough popular misunderstandings of ADHD in children so it’s good those works exist… but what about adults?
Adults face different challenges than children, and have different responsibilities. People have different expectations. And even if you say you have ADHD… If you’re not behaving like a squirrel, they will often not accept this, much less understand it, because half the actual symptoms are not what most people think they are.
Ross-Child first lays out the neurobiological underpinnings of ADHD. This is a good place to start, because the physiology of it explains a lot of the other parts of it that can otherwise seem quite mystifying.
Thereafter, he looks one-by-one at the various cognitive and behavioral aspects of ADHD in adults, which will surely help the reader to better understand themself (or perhaps a loved one).
The next part of the book is given over to an exploration of ADHD and the differences it can make in the workplace, relationships (incl. ADHD and sex), as well as parenting, and how these things can all be navigated better by all concerned.
The style throughout is light and very readable, peppered with science made comprehensible. If there’s any flaw, it’s that there are only two pages of references in the bibliography—we’d have liked to have seen more.
All in all though, a really useful guide if you or a loved one has ADHD and you’d like strategies for working with (or around) this condition in a world not made to be kind to such.
Order your copy of “The Silent Struggle: Taking Charge of ADHD in Adults” from Amazon today!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Smart Hearing – by Katherine Bouton
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author’s hearing loss began in her 30s, and now she’s in her 70s with even less hearing, and/but much more experience. Having worked at the Hearing Loss Association of America for much of that time, she has a lot to share.
This book is a practical guide to adult-onset hearing loss, and aims to help the reader navigate not just the difficulties inherent to the condition, but also the complexities around it that are largely societal, administrative, financial, and so forth.
She advocates for early intervention where possible, and that most people in the early stages of hearing loss don’t realize what’s happening. They will tend to just blame the noisy environment, or the speaker, for example. And beyond just hearing tests, she recommends specifics that you might not have heard of, such as the speech-in-noise test.
With regard to technology, she covers the various options,and also ways to pay for them (because Medicare won’t)—which latter is specific to the US, so if you’re from somewhere else, then probably a) this advice won’t help, but b) you probably won’t need it, as most places have more comprehensive healthcare coverage.
The style is quite personal while remaining professional; she often uses her own story as an illustration, but covers experiences other than hers just as thoroughly, so that no major variant of hearing loss gets overlooked.
Bottom line: if you and/or a loved one aren’t hearing/understanding auditory things so well as you used to, this book can help guide you into a position of more practical empowerment, without the need for quite so much trial and error as you might otherwise find alone.
Click here to check out Smart Hearing, and live better with hearing loss!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is TikTok right? Can adding a teaspoon of cinnamon to your coffee help you burn fat?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cinnamon has been long used around the world in both sweet and savoury dishes and drinks.
But a new TikTok trend claims adding a teaspoon of cinnamon to your daily coffee (and some cocoa to make it more palatable) for one week can help you burn fat. Is there any truth to this?
Evannovostro/Shutterstock Not all cinnamon is the same
There are two types of cinnamon, both of which come from grinding the bark of the cinnamomum tree and may include several naturally occurring active ingredients.
Cassia cinnamon is the most common type available in grocery stores. It has a bitter taste and contains higher levels of one of the active ingredient cinnamaldehyde, a compound that gives cinnamon its flavour and odour. About 95% of cassia cinnamon is cinnamaldehyde.
The other is Ceylon cinnamon, which tastes sweeter. It contains about 50-60% cinnamaldehyde.
Does cinnamon burn fat? What does the research say?
A review of 35 studies examined whether consuming cinnamon could affect waist circumference, which is linked to increased body fat levels. It found cinnamon doses below 1.5 grams per day (around half a teaspoon) decreased waist circumference by 1.68cm. However, consuming more than 1.5g/day did not have a significant effect.
A meta-analysis of 21 clinical trials with 1,480 total participants found cinnamon also reduced body mass index (BMI) by 0.40kg/m² and body weight by 0.92kg. But it did not change the participants’ composition of fat or lean mass.
Another umbrella review, which included all the meta-analyses, found a small effect of cinnamon on weight loss. Participants lost an average of 0.67kg and reduced their BMI by 0.45kg/m².
The effect appears small. Radu Sebastian/Shutterstock So overall, the weight loss we see from these high-quality studies is very small, ranging anywhere from two to six months and mostly with no change in body composition.
The studies included people with different diseases, and most were from the Middle East and/or the Indian subcontinent. So we can’t be certain we would see this effect in people with other health profiles and in other countries. They were also conducted over different lengths of time from two to six months.
The supplements were different, depending on the study. Some had the active ingredient extracted from cinnamon, others used cinnamon powder. Doses varied from 0.36g to 10g per day.
They also used the two different types of cinnamon – but none of the studies used cinnamon from the grocery store.
How could cinnamon result in small amounts of weight loss?
There are several possible mechanisms.
It appears to allow blood glucose (sugar) to enter the body’s cells more quickly. This lowers blood glucose levels and can make insulin work more effectively.
It also seems to improve the way we break down fat when we need it for energy.
Finally, it may make us feel fuller for longer by slowing down how quickly the food is released from our stomach into the small intestine.
What are the risks?
Cinnamon is generally regarded as safe when used as a spice in cooking and food.
However, in recent months the United States and Australia have issued health alerts about the level of lead and other heavy metals in some cinnamon preparations.
Lead enters as a contaminant during growth (from the environment) and in harvesting. In some cases, it has been suggested there may have been intentional contamination.
Some people can have side effects from cinnamon, including gastrointestinal pain and allergic reactions.
One of the active ingredients, coumarin, can be toxic for some people’s livers. This has prompted the European Food Authority to set a limit of 0.1mg/kg of body weight.
Cassia cinnamon contains up to 1% of coumarin, and the Ceylon variety contains much less, 0.004%. So for people weighing above 60kg, 2 teaspoons (6g) of cassia cinnamon would bring them over the safe limit.
What about the coffee and cocoa?
Many people may think coffee can also help us lose weight. However there isn’t good evidence to support this yet.
An observational study found drinking one cup of regular coffee was linked to a reduction in weight that is gained over four years, but by a very small amount: an average of 0.12kg.
Good-quality cocoa and dark chocolate have also been shown to reduce weight. But again, the weight loss was small (between 0.2 and 0.4kg) and only after consuming it for four to eight weeks.
So what does this all mean?
Using cinnamon may have a very small effect on weight, but it’s unlikely to deliver meaningful weight loss without other lifestyle adjustments.
We also need to remember these trials used products that differ from the cinnamon we buy in the shops. How we store and how long we keep cinnamon might also impact or degrade the active ingredients.
And consuming more isn’t going to provide additional benefit. In fact, it could increase your risk of side effects.
So if you enjoy the taste of cinnamon in your coffee, continue to add it, but given its strong taste, you’re likely to only want to add a little.
And no matter how much we’d like this to be true, we certainly won’t gain any fat-loss benefits by consuming cinnamon on doughnuts or in buns, due to their high kilojoule count.
If you want to lose weight, there are evidence-backed approaches that won’t spoil your morning coffee.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Is Earwax & Should You Get Rid Of It?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Earwax (cerumen) forms in the outer ear canal when dead skin cells mix with oily sweat (a specialty of the apocrine glands) and sebum, a fatty substance mostly associated with facial oiliness. But, does it have a purpose, or is it just a waste product?
Nature is (mostly) best in this case
Earwax plays an important role in ear health, acting as a natural lubricant that prevents dryness and itchiness, trapping debris and microbes, and forming a protective barrier for the ear canal. It even contains proteins that help fight bacterial infections.
As for removal: the body has a natural mechanism for removing excess earwax: as skin cells grow, they migrate outward, carrying earwax with them.
In contrast, manual removal of earwax can do more harm than good. Using swabs or other items often pushes wax deeper, risks damaging the ear canal, and disrupts its protective barrier, potentially leading to infection.
Ear candling, which claims to extract earwax, not only does not work (its main premise has been actively disproven and clinical evidence shows unequivocally that it doesn’t work by any mysterious method either; it just plain doesn’t work), but also can cause injuries and will tend to leave more harmful debris behind than was there originally.
For those prone to earwax buildup, over-the-counter eardrops can help soften wax for natural removal, and medical professionals have safe methods to clear blockages if necessary.
To maintain ear health, it’s best to clean only the outer ear with a damp cloth, limit the use of earplugs or earbuds, and generally leave earwax alone unless it causes discomfort or hearing issues.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Ear Candling: Is It Safe & Does It Work? ← the answer is “no and no”, but the science may interest you
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: