The Brain As A Work-In-Progress
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
And The Brain Goes Marching On!
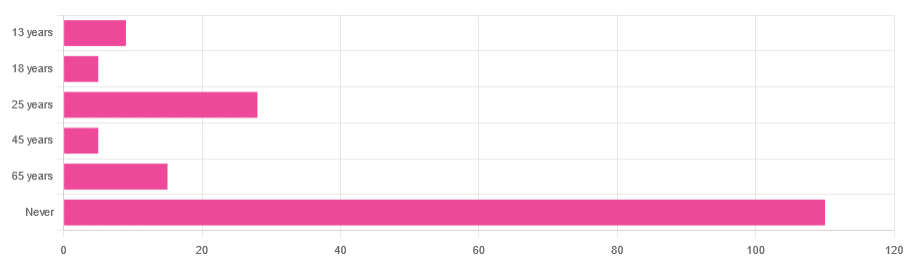
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you “when does the human brain stop developing?” and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 64% of people said “Never”
- About 16% of people said “25 years”
- About 9% of people said “65 years”
- About 5% of people said “13 years”
- About 3% of people said “18 years”
- About 3% of people said “45 years”
Some thoughts, before we get into the science:
An alternative wording for the original question was “when does the human brain finish developing”; the meaning is the same but the feeling is slightly different:
- “When does the human brain stop developing?” focuses attention on the idea of cessation, and will skew responses to later ages
- When does the human brain finish developing?” focuses on attention on a kind of “is it done yet?” and will skew responses to earlier ages
Ultimately, since we had to chose one word or another, we picked the shortest one, but it would have been interesting if we could have done an A/B test, and asked half one way, and half the other way!
Why we picked those ages
We picked those ages as poll options for reasons people might be drawn to them:
- 13 years: in English-speaking cultures, an important milestone of entering adolescence (note that the concept of a “teenager” is not precisely universal as most languages do not have “-teen” numbers in the same way; the concept of “adolescent” may thus be tied to other milestones)
- 18 years: age of legal majority in N. America and many other places
- 25 years: age popularly believed to be when the brain is finished developing, due to a study that we’ll talk about shortly (we guess that’s why there’s a spike in our results for this, too!)
- 45 years: age where many midlife hormonal changes occur, and many professionals are considered to have peaked in competence and start looking towards retirement
- 65 years: age considered “senior” in much of N. America and many other places, as well as the cut-off and/or starting point for a lot of medical research
Notice, therefore, how a lot of things are coming from places they really shouldn’t. For example, because there are many studies saying “n% of people over 65 get Alzheimer’s” or “n% of people over 65 get age-related cognitive decline”, etc, 65 becomes the age where we start expecting this—because of an arbitrary human choice of where to draw the cut-off for the study enrollment!
Similarly, we may look at common ages of legal majority, or retirement pensions, and assume “well it must be for a good reason”, and dear reader, those reasons are more often economically motivated than they are biologically reasoned.
So, what does the science say?
Our brains are never finished developing: True or False?
True! If we define “finished developing” as “we cease doing neurogenesis and neuroplasticity is no longer in effect”.
Glossary:
- Neurogenesis: the process of creating new brain cells
- Neuroplasticity: the process of the brain adapting to changes by essentially rebuilding itself to suit our perceived current needs
We say “perceived” because sometimes neuroplasticity can do very unhelpful things to us (e.g: psychological trauma, or even just bad habits), but on a biological level, it is always doing its best to serve our overall success as an organism.
For a long time it was thought that we don’t do neurogenesis at all as adults, but this was found to be untrue:
How To Grow New Brain Cells (At Any Age)
Summary of conclusions of the above: we’re all growing new brain cells at every age, even if we be in our 80s and with Alzheimer’s disease, but there are things we can do to enhance our neurogenic potential along the way.
Neuroplasticity will always be somewhat enhanced by neurogenesis (after all, new neurons get given jobs to do), and we reviewed a great book about the marvels of neuroplasticity including in older age:
Our brains are still developing up to the age of 25: True or False?
True! And then it keeps on developing after that, too. Now this is abundantly obvious considering what we just talked about, but see what a difference the phrasing makes? Now it makes it sound like it stops at 25, which this statement doesn’t claim at all—it only speaks for the time up to that age.
A lot of the popular press about “the brain isn’t fully mature until the age of 25” stems from a 2006 study that found:
❝For instance, frontal gray matter volume peaks at about age 11.0 years in girls and 12.1 years in boys, whereas temporal gray matter volume peaks at about age at 16.7 years in girls and 16.2 years in boys. The dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex, important for controlling impulses, is among the latest brain regions to mature without reaching adult dimensions until the early 20s.❞
Source: Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Adolescent Brain
There are several things to note here:
- The above statement is talking about the physical size of the brain growing
- Nowhere does he say “and stops developing at 25”
However… The study only looked at brains up to the age of 25. After that, they stopped looking, because the study was about “the adolescent brain” so there has to be a cut-off somewhere, and that was the cut-off they chose.
This is the equivalent of saying “it didn’t stop raining until four o’clock” when the reality is that four o’clock is simply when you gave up on checking.
The study didn’t misrepresent this, by the way, but the popular press did!
Another 2012 study looked at various metrics of brain development, and found:
- Synapse overproduction into the teens
- Cortex pruning into the late 20s
- Prefrontal pruning into middle age at least (they stopped looking)
- Myelination beyond middle age (they stopped looking)
Source: Experience and the developing prefrontal cortex ← check out figure 1, and make sure you’re looking at the human data not the rat data
So how’s the most recent research looking?
Here’s a 2022 study that looked at 123,984 brain scans spanning the age range from mid-gestation to 100 postnatal years, and as you can see from its own figure 1… Most (if not all) brain-things keep growing for life, even though most slow down at some point, they don’t stop:
Brain charts for the human lifespan ← check out figure 1; don’t get too excited about the ventricular volume column as that is basically “brain that isn’t being a brain”. Do get excited about the rest, though!
Want to know how not to get caught out by science being misrepresented by the popular press? Check out:
How Science News Outlets Can Lie To You (Yes, Even If They Cite Studies!)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Does intermittent fasting increase or decrease our risk of cancer?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Research over the years has suggested intermittent fasting has the potential to improve our health and reduce the likelihood of developing cancer.
So what should we make of a new study in mice suggesting fasting increases the risk of cancer?
Stock-Asso/Shutterstock What is intermittent fasting?
Intermittent fasting means switching between times of eating and not eating. Unlike traditional diets that focus on what to eat, this approach focuses on when to eat.
There are lots of commonly used intermittent fasting schedules. The 16/8 plan means you only eat within an eight-hour window, then fast for the remaining 16 hours. Another popular option is the 5:2 diet, where you eat normally for five days then restrict calories for two days.
In Australia, poor diet contributes to 7% of all cases of disease, including coronary heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and cancers of the bowel and lung. Globally, poor diet is linked to 22% of deaths in adults over the age of 25.
Intermittent fasting has gained a lot of attention in recent years for its potential health benefits. Fasting influences metabolism, which is how your body processes food and energy. It can affect how the body absorbs nutrients from food and burns energy from sugar and fat.
What did the new study find?
The new study, published in Nature, found when mice ate again after fasting, their gut stem cells, which help repair the intestine, became more active. The stem cells were better at regenerating compared with those of mice who were either totally fasting or eating normally.
This suggests the body might be better at healing itself when eating after fasting.
However, this could also have a downside. If there are genetic mutations present, the burst of stem cell-driven regeneration after eating again might make it easier for cancer to develop.
Polyamines – small molecules important for cell growth – drive this regeneration after refeeding. These polyamines can be produced by the body, influenced by diet, or come from gut bacteria.
The findings suggest that while fasting and refeeding can improve stem cell function and regeneration, there might be a tradeoff with an increased risk of cancer, especially if fasting and refeeding cycles are repeated over time.
While this has been shown in mice, the link between intermittent fasting and cancer risk in humans is more complicated and not yet fully understood.
What has other research found?
Studies in animals have found intermittent fasting can help with weight loss, improve blood pressure and blood sugar levels, and subsequently reduce the risks of diabetes and heart disease.
Research in humans suggests intermittent fasting can reduce body weight, improve metabolic health, reduce inflammation, and enhance cellular repair processes, which remove damaged cells that could potentially turn cancerous.
However, other studies warn that the benefits of intermittent fasting are the same as what can be achieved through calorie restriction, and that there isn’t enough evidence to confirm it reduces cancer risk in humans.
What about in people with cancer?
In studies of people who have cancer, fasting has been reported to protect against the side effects of chemotherapy and improve the effectiveness of cancer treatments, while decreasing damage to healthy cells.
Prolonged fasting in some patients who have cancer has been shown to be safe and may potentially be able to decrease tumour growth.
On the other hand, some experts advise caution. Studies in mice show intermittent fasting could weaken the immune system and make the body less able to fight infection, potentially leading to worse health outcomes in people who are unwell. However, there is currently no evidence that fasting increases the risk of bacterial infections in humans.
So is it OK to try intermittent fasting?
The current view on intermittent fasting is that it can be beneficial, but experts agree more research is needed. Short-term benefits such as weight loss and better overall health are well supported. But we don’t fully understand the long-term effects, especially when it comes to cancer risk and other immune-related issues.
Since there are many different methods of intermittent fasting and people react to them differently, it’s hard to give advice that works for everyone. And because most people who participated in the studies were overweight, or had diabetes or other health problems, we don’t know how the results apply to the broader population.
For healthy people, intermittent fasting is generally considered safe. But it’s not suitable for everyone, particularly those with certain medical conditions, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and people with a history of eating disorders. So consult your health-care provider before starting any fasting program.
Amali Cooray, PhD Candidate in Genetic Engineering and Cancer, WEHI (Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research)
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Vaginal Probiotics: What Does The Science Say?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Is there any merit to vaginal probiotics?❞
What a fun question! First let’s break it down, as this could mean two different things:
- Probiotics, which you consume, using your mouth, which are marketed as benefiting vaginal health
- Probiotics taken as a vaginal pessary/suppository, to act directly there
The former has limited evidence for it, but generally speaking, improving one’s gut health improves all other areas of health, so it’s not surprising if it helps this too.
See for example:
Some notes:
- candidal vaginitis means a yeast infection causing vaginal inflammation
- bacterial vaginosis means a vaginal bacterial imbalance (generally also featuring vaginal inflammation, though it can be asymptomatic)
In the latter case, the “imbalance” in question is usually a shortage of Lactobacillus sp. (that is to say, the diverse species of the Lactobacillus genus) resulting in an overgrowth of other kinds of bacteria, which in turn results in changing the vaginal microbiome to make it warmer and more acidic than it should be.
While a healthy vagina shouldn’t smell of roses, it shouldn’t smell fishy either; if it does, that’s a sign of bacterial vaginosis.
What it’s supposed to be like: slightly bitter, slightly salty, distinctly umami, along with a cocktail of personal pheromones (and if menstruating or otherwise* vaginally bleeding, then of course add: iron/”metallic”). The pheromones will also reflect any hormonal changes, but should never make anything smell bad, just different.
*e.g. due to PCOS, fibroids, etc. Note that in the case of PCOS, it may also smell a little different (if it does, then usually: a little more musky), due to often different hormone levels. Again: it still shouldn’t smell bad, though, just different.
In the above-linked study, taking more live Lactobacillus acidophilus (in yogurt, eating it, with their mouths) improved levels of L. acidophilus in the vagina. While the study authors concluded “this ingestion of yogurt may have reduced episodes of bacterial vaginosis”, which is rather a weak claim, it can be argued that it merely improving the levels of L. acidophilus in the vagina was already a win.
That was a small (n=42, and only 7 followed through to completion) and old (1996) study, and it bears mentioning that most of the studies into this seem to be small and old, but conclude similarly with weakly positive statements.
However, it does make a difference what kind of Lactobacillus is used, for example in this next study…
- L. fermentum RC-14 worked well (90% success rate)
- L. rhamnosus GR-1 worked somewhat (40% success rate)
- L. rhamnosus GG did not work (0% success rate)
So, diversity is key, and getting a wide range of Lactobacillus sp. seems to be a safe bet.
Short version: enjoying probiotics as part of your diet probably improves vaginal health, just like it improves pretty much everything else.
See also: Make Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
You would think that this would mean that taking probiotics as a vaginal pessary/suppository would be even better, but the results are weaker, as in this study, which produced temporary improvements in about half the study group, with only 3 out of 28 being free of bacterial vaginosis the next month:
Treatment of bacterial vaginosis with lactobacilli
This study got better results, with a 61% success rate:
Important note
Do note that this last category, involving topical treatments (i.e., manually introducing Lactobacillus sp. to the vagina) were all in cases of pre-existing bacterial vaginosis, not as a prophylactic and/or general health-improving thing.
If your vagina seems happy right now, then do not mess with its happy bacterial balance!
And at all times (regardless of whether it seems happy right now or not): do not douche (it does not need it and will not benefit from it; the vagina is self-cleaning*) as this will wash out many of your Lactobacilli and will do absolutely nothing against any Candida there (C. albicans being a rooted fungus, whereas Lactobacillus is a sausage-shaped bacterium with many tiny appendages but no actual ability to stay put), so Candida will flourish in the Lactobacillus’s absence.
*by the vagina, we are referring to the vaginal canal. The vulva—the outside part consisting of the two pairs of labia, the glans clitoris, and clitoral hood—are not self-cleaning, and should just be washed gently per your normal bath/shower routine; that’s perfectly fine and good.
And definitely don’t put any “cleansing” toiletries inside the vagina (or any toiletries at all, for that matter), even if they are sold and marketed for that purpose; they will not help and they will harm.
Also, due to their neighborliness, messing up the microbiome inside the vagina is a common way to also get Candida inside the urethra:
How To Avoid Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
One other option
Finally, unless you have a “very good friend” you have a pressing urge to swap germs with, you might want to leave this one to the scientists, but we share this paper just for interest:
Lastly…
Going back to oral supplementation, if you’d like to try that then check out this for further notes on what, why, how, etc:
How Much Difference Do Probiotic Supplements Make To Health?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Cancer Journey – by Dr. Chadi Nabhan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
After a brief introduction of what cancer actually is and what causes it, the layout of the rest of the book is in chronological order of patient experience, that is to say, what to expect during the journey from screening and diagnosis, to one’s first oncology visit (the author being an oncologist himself), how cancer staging works, getting second opinions, and a chapter-by-chapter review of many different treatment options, ranging from surgery and chemotherapy, to radiation and hormonal therapies, and even more modern targeted therapies, immunotherapy, cellular therapies, and yes, complementary and alternative therapies, amongst others we haven’t listed for the sake of brevity.
He doesn’t leave it there though; he also talks managing side effects, monitoring for recurrence, and even caring for the caregiver(s), along with eventual survivorship and that emotional journey, or if it comes down to it, palliative and hospice care.
Finishing on a hopeful note, he also brings attention to novel approaches that are being trialled presently, and the prospects for the near future of cancer care.
The style is very human and readable, notwithstanding that the author has hundreds of peer-reviewed publications to his name, the content here is presented in a much more approachable, less clinical way, while still conveying all the information that needs to be conveyed.
Bottom line: if you or a loved one is facing cancer, this book will be an invaluable resource.
Click here to check out The Cancer Journey, and understand each part of it!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Is Cutting Calories The Key To Healthy Long Life?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Caloric Restriction with Optimal Nutrition
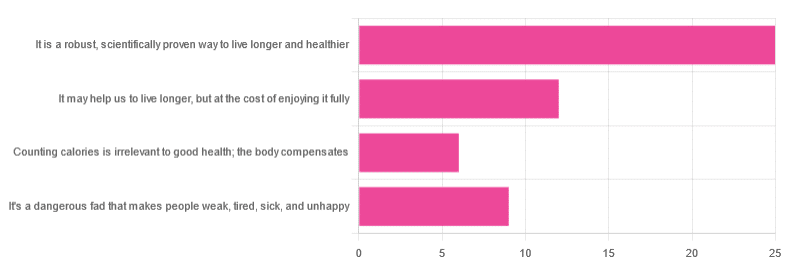
Yesterday, we asked you “What is your opinion of caloric restriction as a health practice?” and got the above-depicted, below-described spread of responses:
- 48% said “It is a robust, scientifically proven way to live longer and healthier”
- 23% said “It may help us to live longer, but at the cost of enjoying it fully”
- 17% said “It’s a dangerous fad that makes people weak, tired, sick, and unhealthy”
- 12% said “Counting calories is irrelevant to good health; the body compensates”
So… What does the science say?
A note on terms, first
“Caloric restriction” (henceforth: CR), as a term, sees scientific use to mean anything from a 25% reduction to a 50% reduction, compared to metabolic base rate.
This can also be expressed the other way around, “dropping to 60% of the metabolic base rate” (i.e., a 40% reduction).
Here we don’t have the space to go into much depth, so our policy will be: if research papers consider it CR, then so will we.
A quick spoiler, first
The above statements about CR are all to at least some degree True in one way or another.
However, there are very important distinctions, so let’s press on…
CR is a robust, scientifically proven way to live longer and healthier: True or False?
True! This has been well-studied and well-documented. There’s more science for this than we could possibly list here, but here’s a good starting point:
❝Calorie restriction (CR), a nutritional intervention of reduced energy intake but with adequate nutrition, has been shown to extend healthspan and lifespan in rodent and primate models.
Accumulating data from observational and randomized clinical trials indicate that CR in humans results in some of the same metabolic and molecular adaptations that have been shown to improve health and retard the accumulation of molecular damage in animal models of longevity.
In particular, moderate CR in humans ameliorates multiple metabolic and hormonal factors that are implicated in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer, the leading causes of morbidity, disability and mortality❞
Source: Ageing Research Reviews | Calorie restriction in humans: an update
See also: Caloric restriction in humans reveals immunometabolic regulators of health span
We could devote a whole article (or a whole book, really) to this, but the super-short version is that it lowers the metabolic “tax” on the body and allows the body to function better for longer.
CR may help us to live longer, but at the cost of enjoying it fully: True or False?
True or False, contingently, depending on what’s important to you. And that depends on psychology as much as physiology, but it’s worth noting that there is often a selection bias in the research papers; people ill-suited to CR drop out of the studies and are not counted in the final data.
Also, relevant for a lot of our readers, most (human-based) studies recruit people over 18 and under 60. So while it is reasonable to assume the same benefits will be carried over that age, there is not nearly as much data for it.
Studies into CR and Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) have been promising, and/but have caveats:
❝In non-obese adults, CR had some positive effects and no negative effects on HRQoL.❞
❝We do not know what degree of CR is needed to achieve improvements in HRQoL, but we do know it requires an extraordinary amount of support.
Therefore, the incentive to offer this intervention to a low-risk, normal or overweight individual is lacking and likely not sustainable in practice.❞
CR a dangerous fad that makes people weak, tired, sick, and unhealthy: True or False?
True if it is undertaken improperly, and/or without sufficient support. Many people will try CR and forget that the idea is to reduce metabolic load while still getting good nutrition, and focus solely on the calorie-counting.
So for example, if a person “saves” their calories for the day to have a night out in a bar where they drink their calories as alcohol, then this is going to be abysmal for their health.
That’s an extreme example, but lesser versions are seen a lot. If you save your calories for a pizza instead of a night of alcoholic drinks, then it’s not quite so woeful, but for example the nutrition-to-calorie ratio of pizza is typically not great. Multiply that by doing it as often as not, and yes, someone’s health is going to be in ruins quite soon.
Counting calories is irrelevant to good health; the body compensates: True or False?
True if by “good health” you mean weight loss—which is rarely, if ever, what we mean by “good health” here at 10almonds (unless we clarify such), but it’s a very common association and indeed, for some people it’s a health goal. You cannot sustainably and healthily lose weight by CR alone, especially if you’re not getting optimal nutrition.
Your body will notice that you are starving, and try to save you by storing as much fat as it can, amongst other measures that will similarly backfire (cortisol running high, energy running low, etc).
For short term weight loss though, yes, it’ll work. At a cost. That we don’t recommend.
❝By itself, decreasing calorie intake will have a limited short-term influence.❞
Source: Reducing Calorie Intake May Not Help You Lose Body Weight
See also…
❝Caloric restriction is a commonly recommended weight-loss method, yet it may result in short-term weight loss and subsequent weight regain, known as “weight cycling”, which has recently been shown to be associated with both poor sleep and worse cardiovascular health❞
Source: Dieting Behavior Characterized by Caloric Restriction
In summary…
Caloric restriction is a well-studied area of health science. We know:
- Practised well, it can extend not only lifespan, but also healthspan
- Practised well, it can improve mood, energy, sexual function, and the other things people fear losing
- Practised badly, it can be ruinous to the health—it is critical to practise caloric restriction with optimal nutrition.
- Practised badly, it can lead to unhealthy weight loss and weight regain
One final note…
If you’ve tried CR and hated it, and you practised it well (e.g., with optimal nutrition), then we recommend just not doing it.
You could also try intermittent fasting instead, for similar potential benefits. If that doesn’t work out either, then don’t do that either!
Sometimes, we’re just weird. It can often be because of a genetic or epigenetic quirk. There are usually workarounds, and/but not everything that’s right for most people will be right for all of us.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
5 dental TikTok trends you probably shouldn’t try at home
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
TikTok is full of videos that demonstrate DIY hacks, from up-cycling tricks to cooking tips. Meanwhile, a growing number of TikTok videos offer tips to help you save money and time at the dentist. But do they deliver?
Here are five popular dental TikTok trends and why you might treat them with caution.
1. Home-made whitening solutions
Many TikTok videos provide tips to whiten teeth. These include tutorials on making your own whitening toothpaste using ingredients such as hydrogen peroxide, a common household bleaching agent, and baking soda (sodium bicarbonate).
In this video, the influencer says:
And then you’re going to pour in your hydrogen peroxide. There’s really no measurement to this.
But hydrogen peroxide in high doses is poisonous if swallowed, and can burn your gums, mouth and throat, and corrode your teeth.
High doses of hydrogen peroxide may infiltrate holes or microscopic cracks in your teeth to inflame or damage the nerves and blood vessels in the teeth, which can cause pain and even nerve death. This is why dental practitioners are bound by rules when we offer whitening treatments.
Sodium bicarbonate and hydrogen peroxide are among the components in commercially available whitening toothpastes. While these commercial products may be effective at removing surface stains, their compositions are carefully curated to keep your smile safe.
2. Oil pulling
Oil pulling involves swishing one tablespoon of sesame or coconut oil in your mouth for up to 20 minutes at a time. It has roots in Ayurvedic medicine, a traditional medicine practice that originates from the Indian subcontinent.
While oil pulling should be followed by brushing and flossing, I’ve had patients who believe oil pulling is a replacement for these practices.
There has been some research on the potential of oil pulling to treat gum disease or other diseases in the mouth. But overall, evidence that supports the effectiveness of oil pulling is of low certainty.
For example, studies that test the effectiveness of oil pulling have been conducted on school-aged children and people with no dental problems, and often measure dental plaque growth over a few days to a couple of weeks.
Chlorhexidine is an ingredient found in some commercially available mouthwashes.
In one study, people who rinsed with chlorhexidine mouthwash (30 seconds twice daily) developed less plaque on their teeth compared to those who undertook oil pulling for eight to 10 minutes.Ultimately, it’s unlikely you will experience measurable gain to your oral health by adding oil pulling to your daily routine. If you’re time-poor, you’re better off focusing on brushing your teeth and gums well alongside flossing.
3. Using rubber bands to fix gaps
This TikTok influencer shows his followers he closed the gaps between his front teeth in a week using cheap clear rubber bands.
But this person may be one of the lucky few to successfully use bands to close a gap in his teeth without any mishaps. Front teeth are slippery and taper near the gums into cone-shaped roots. This can cause bands to slide and disappear into the gums to surround the tooth roots, which can cause infections and pain.
If this happens, you may require surgery that involves cutting your gums to remove the bands. If the bands have caused an infection, you may lose the affected teeth. So it’s best to leave this sort of work to a dental professional trained in orthodontics.
4. Filing or cutting teeth to shape them
My teeth hurt just watching this video.
Cutting or filing teeth unnecessarily can expose the second, more sensitive tooth layer, called dentine, or potentially, the nerve and blood vessels inside the tooth. People undergoing this sort of procedure could experience anything from sensitive teeth through to a severe toothache that requires root canal treatment or tooth removal.
You may notice dentist drills spray water when cutting to protect your teeth from extreme heat damage. The drill in this video is dry with no water used to cool the heat produced during cutting.
It may also not be sterile. We like to have everything clean and sterile to prevent contaminated instruments used on one patient from potentially spreading an infection to another person.
Importantly, once you cut or file your teeth away, it’s gone forever. Unlike bone, hair or nails, our teeth don’t have the capacity to regrow.
5. DIY fillings
Many people on TikTok demonstrate filling cavities (holes) or replacing gaps between teeth with a material made from heated moulded plastic beads. DIY fillings can cause a lot of issues – I’ve seen this in my clinic first hand.
While we may make it look simple in dental surgeries, the science behind filling materials and how we make them stick to teeth to fill cavities is sophisticated.
Filling a cavity with the kind of material made from these beads will be as effective as using sticky tape on sand. Not to mention the cavity will continue to grow bigger underneath the untreated “filled” teeth.
I know it’s easy to say “see a dentist about that cavity” or “go to an orthodontist to fix that gap in your teeth you don’t like”, but it can be expensive to actually do these things. However if you end up requiring treatment to fix the issues caused at home, it may end up costing you much more.
So what’s the take-home message? Stick with the funny cat and dog videos on TikTok – they’re safer for your smile.
Arosha Weerakoon, Senior Lecturer and General Dentist, School of Dentistry, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Does Someone Die From Dementia?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dementia is most often thought of in terms of the loss of certain cognitive faculties during the disease’s progress. So how does death occur?
A quiet departure
Notwithstanding it being a widely-feared disease (or set of diseases, since we’re using the umbrella term of dementia, and not the most well-known and common kind, Alzheimer’s), death from dementia is usually a peaceful one; any distressing confusions are usually in the past by this point.
Sometimes, it is not the dementia itself that directly causes death; rather, it leaves someone much more vulnerable to infections, with pneumonia being top of the list, and UTIs also ranking highly. And while a younger healthier person might drink some cranberry juice and shrug it off, for an older person with dementia, even a UTI can be much more serious. Pneumonia, of course, is well-known for often being the final straw.
Sometimes, it is the dementia that directly causes death; the disease causes a slow decline until the person stops eating and drinking. At this time, they will also tend to sleep more, and as mentioned, experience much less agitation and confusion than previously.
In terms of caregiving at this late stage, the hospice worker in the video recommends to do one’s best to keep the person clean and safe from falls or infections, check common pressure sore sites for redness, changing their position if necessary and using pillows to relieve any undue pressure.
For more on all of this, see:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
When Planning Is A Matter of Life & Death: Managing Your Mortality
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: